AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250214

1. InfiniteHiP: Extending Language Model Context Up to 3 Million Tokens on a Single GPU
🔑 Keywords: Long Context, LLM Inference, Token Pruning, RoPE Adjustment, GPU Memory
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enable efficient and practical utilization of long contexts in large language models by overcoming slow inference speeds and high memory costs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces InfiniteHiP, an LLM inference framework that accelerates processing using a hierarchical token pruning algorithm and employs RoPE adjustment methods to support longer sequences.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– InfiniteHiP processes up to 3 million tokens on a single 48GB GPU, achieving an 18.95x speedup in attention decoding without additional training, demonstrating effectiveness through implementation in SGLang framework.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.08910

2. Skrr: Skip and Re-use Text Encoder Layers for Memory Efficient Text-to-Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: Text-to-Image Diffusion, Text Encoders, Memory Efficiency, Transformer Blocks, Skrr
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to enhance memory efficiency in text encoders used in Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models without degrading the image quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced the Skrr pruning strategy designed specifically for T2I tasks, exploiting redundancy by selectively skipping or reusing layers in transformer blocks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Skrr successfully maintains image quality while achieving state-of-the-art memory efficiency. It performs well on several evaluation metrics, such as FID, CLIP, DreamSim, and GenEval scores, and outperforms existing blockwise pruning methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.08690

3. SelfCite: Self-Supervised Alignment for Context Attribution in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: SelfCite, LLMs, citations, preference optimization, LongBench-Cite
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a novel self-supervised approach, SelfCite, for generating high-quality, sentence-level citations in LLM-generated responses.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a reward signal from the LLM itself through context ablation, guiding a best-of-N sampling strategy and preference optimization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SelfCite significantly improves citation quality, increasing citation F1 scores by up to 5.3 points on the LongBench-Cite benchmark across multiple long-form question answering tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09604

4. An Open Recipe: Adapting Language-Specific LLMs to a Reasoning Model in One Day via Model Merging
🔑 Keywords: Data Selection, Model Merging, Thai LLM, DeepSeek R1, Low-resource Languages
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance reasoning capabilities of language-specific LLMs like Thai LLM while maintaining their linguistic abilities using methodologies derived from DeepSeek R1.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementing data selection and model merging techniques with a focus on low-resource languages, utilizing publicly available datasets and a $120 computational budget.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– It is possible to enhance language-specific LLMs to reach advanced reasoning levels akin to DeepSeek R1 without loss of performance in target language tasks, even with limited resources.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09056

5. Can this Model Also Recognize Dogs? Zero-Shot Model Search from Weights
🔑 Keywords: ProbeLog, classification models, zero-shot retrieval, collaborative filtering
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Present ProbeLog, a method for retrieving classification models without model metadata or training data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Computes descriptors for each model’s output dimension using probes.
– Supports logit-based and zero-shot, text-based retrieval.
– Utilizes collaborative filtering to reduce encoding costs by 3x.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates high retrieval accuracy in various search tasks.
– Scalable to full-size repositories.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09619

6. EmbodiedBench: Comprehensive Benchmarking Multi-modal Large Language Models for Vision-Driven Embodied Agents
🔑 Keywords: Multi-modal Large Language Models, Embodied Agents, EmbodiedBench, Vision-driven
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to bridge the gap in the comprehensive evaluation framework for MLLM-based embodied agents by introducing EmbodiedBench, a benchmark to evaluate these agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed EmbodiedBench featuring 1,128 testing tasks across different environments, focusing on tasks from high-level semantic to low-level atomic actions.
– Evaluated 13 proprietary and open-source MLLMs using this benchmark.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MLLMs show proficiency at high-level tasks but face challenges with low-level manipulation tasks, with GPT-4o scoring an average of 28.9%.
– EmbodiedBench not only identifies existing challenges but also provides insights for advancing MLLM-based embodied agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09560

7. Exploring the Potential of Encoder-free Architectures in 3D LMMs
🔑 Keywords: Encoder-free architectures, 3D understanding, Large Multimodal Models, Semantic Encoding, Hierarchical Geometry Aggregation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the effectiveness of encoder-free architectures in the 3D understanding domain, and how they can handle challenges faced by encoder-based 3D Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), such as adapting to varying point cloud resolutions and meeting the semantic needs of Large Language Models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of the LLM-embedded Semantic Encoding strategy during pre-training to explore effects of various point cloud self-supervised losses.
– The use of Hierarchical Geometry Aggregation in the instruction tuning stage to incorporate inductive bias into the LLM early layers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The development of ENEL, the first Encoder-free 3D LMM, which achieves competitive performance on classification, captioning, and visual question answering tasks. The results highlight the promise of encoder-free architectures as capable replacements in 3D understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09620

8. CoSER: Coordinating LLM-Based Persona Simulation of Established Roles
🔑 Keywords: Role-playing language agents, Large language models, Character simulation, CoSER dataset, LLaMA-3.1 models
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve role-playing language agents by presenting CoSER, a comprehensive dataset and evaluation protocol for simulating established characters effectively using large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of CoSER dataset covering dialogues and diverse data types for character simulation.
– Introduction of given-circumstance acting methodology for training and evaluating LLMs.
– Creation of CoSER 8B and CoSER 70B models based on LLaMA-3.1 for advanced role-playing capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The CoSER dataset effectively aids in the training and evaluation of RPLAs.
– CoSER 70B model demonstrates state-of-the-art performance, surpassing or matching existing benchmarks like GPT-4o.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09082

9. TripoSG: High-Fidelity 3D Shape Synthesis using Large-Scale Rectified Flow Models
🔑 Keywords: generative AI, 3D shape generation, high-fidelity 3D meshes, data processing pipeline, TripoSG
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance 3D shape generation with improved output quality, generalization capability, and fidelity to input images through the development of TripoSG.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a large-scale rectified flow transformer trained on high-quality data.
– Developed a hybrid supervised training strategy incorporating SDF, normal, and eikonal losses for 3D VAE.
– Established a data processing pipeline to produce 2 million high-quality 3D samples.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Validated the effectiveness of each component in TripoSG for state-of-the-art performance.
– Achieved enhanced detail and high-fidelity 3D shapes, demonstrating improved versatility and generalization capabilities.
– Plan to make the model publicly available to advance the field of 3D generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.06608

10. The Stochastic Parrot on LLM’s Shoulder: A Summative Assessment of Physical Concept Understanding
🔑 Keywords: Stochastic Parrot, LLMs, Physical Concept Understanding
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate whether LLMs truly understand the concepts they articulate, through a task named PhysiCo focused on physical concept understanding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a grid-format input to present varying levels of understanding, from core phenomena to analogous patterns, minimizing memorization by abstractly describing physical phenomena.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LLMs, including state-of-the-art models like GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0, perform significantly worse than humans, showcasing a 40% lag.
– These models exhibit the Stochastic Parrot phenomenon, struggling with abstract grid tasks despite recognizing and describing concepts well in natural language.
– The grid-format task challenges LLMs due to intrinsic difficulties, with minimal performance improvement from in-context learning and fine-tuning on similar data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.08946

11. Logical Reasoning in Large Language Models: A Survey
🔑 Keywords: Logical Reasoning, Large Language Models, AI Systems, Deductive Reasoning, Neuro-Symbolic Approaches
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To synthesize recent advancements in logical reasoning within large language models (LLMs) and assess their reasoning capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analyzing reasoning paradigms such as deductive, inductive, abductive, and analogical reasoning, and evaluating strategies like data-centric tuning and neuro-symbolic approaches.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current LLMs show remarkable reasoning capabilities, but further exploration is needed to enhance logical reasoning in AI systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09100

12. MME-CoT: Benchmarking Chain-of-Thought in Large Multimodal Models for Reasoning Quality, Robustness, and Efficiency
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-Thought, Large Language Models, Multimodal Models, MME-CoT, reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate the Chain-of-Thought reasoning performance of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) across six domains using the MME-CoT benchmark.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a comprehensive evaluation suite with three novel metrics to assess reasoning quality, robustness, and efficiency, supported by curated high-quality data and a unique evaluation strategy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Models with reflection mechanisms demonstrate superior CoT quality, with Kimi k1.5 leading.
– CoT prompting may degrade performance in perception-heavy tasks due to overthinking.
– Despite high CoT quality, LMMs with reflection show inefficiency in normal response and self-correction phases.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09621

13. Typhoon T1: An Open Thai Reasoning Model
🔑 Keywords: Reasoning Model, Large Language Models, Low-Resource Language, Supervised Fine-Tuning, Thai
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop Typhoon T1, an open Thai reasoning model that enhances performance on complex tasks through a long chain of thought process, particularly for languages with limited resources.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes supervised fine-tuning with open datasets to build the model more cost-effectively, focusing on synthetic data generation, training, and sharing of dataset and model weights.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study provides insights into creating a reasoning model that generalizes across domains and generates reasoning traces in low-resource languages, using Thai as an example, setting a foundation for future research in the field.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09042

14. CoT-Valve: Length-Compressible Chain-of-Thought Tuning
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-Thought, CoT-Valve, reasoning chains, compressibility, task difficulty
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to dynamically control the length of reasoning paths using a single model, thus reducing inference overhead based on task difficulty.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduced CoT-Valve, a tuning and inference strategy for generating various reasoning chain lengths. This included a direction in parameter space for controlling CoT length and constructing datasets with chains of varied lengths for enhancement strategies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CoT-Valve allows for effective control and compression of reasoning chains. It outperforms prompt-based control methods and achieves significant reductions in chain lengths with minimal performance drop in the tested models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09601

15. SQuARE: Sequential Question Answering Reasoning Engine for Enhanced Chain-of-Thought in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, SQuARE, CoT frameworks, reasoning tasks, self-interrogation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce SQuARE, a novel prompting technique aimed at enhancing reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models through a self-interrogation approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized Sequential Question Answering Reasoning Engine (SQuARE) on Llama 3 and GPT-4o models across various question-answering datasets to evaluate its efficacy compared to traditional CoT prompts and rephrase-and-respond methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SQuARE significantly improves reasoning performance over traditional methods by decomposing queries and generating auxiliary questions for comprehensive exploration.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09390

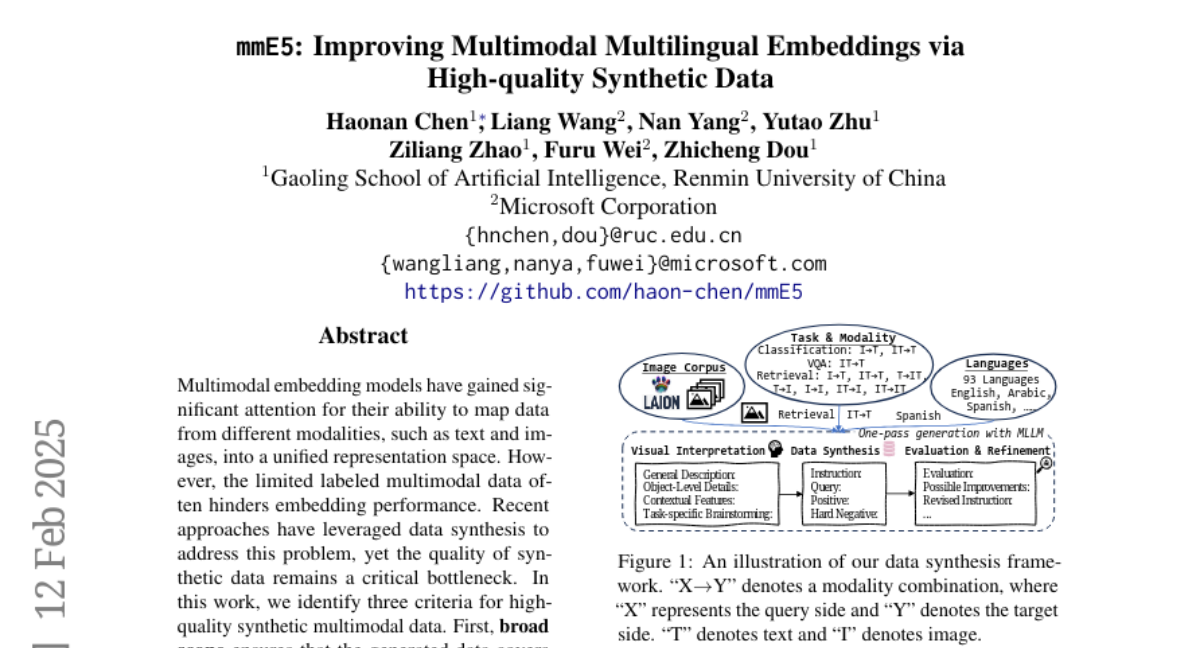
16. mmE5: Improving Multimodal Multilingual Embeddings via High-quality Synthetic Data
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal embedding, synthetic data, cross-modal alignment, fidelity, multilingual performance
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the performance of multimodal embedding models by synthesizing high-quality multimodal data that can be applied to various scenarios.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Identifying criteria for effective synthetic data: broad scope, robust cross-modal alignment, and high fidelity.
– Synthesizing datasets using a multimodal large language model with real-world images and accurate texts, ensuring quality through self-evaluation and refinement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The mmE5 model, trained on these high-quality synthetic datasets, achieves state-of-the-art performance on the MMEB Benchmark and exceptional multilingual performance on the XTD benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.08468
17. VFX Creator: Animated Visual Effect Generation with Controllable Diffusion Transformer
🔑 Keywords: Generative Artificial Intelligence, Controllable VFX Generation, Video Diffusion Transformer, Temporal Control
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study focuses on developing a novel paradigm for animated VFX generation using image animation through textual descriptions and static reference images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers created Open-VFX, a diverse VFX video dataset, and VFX Creator, a framework utilizing a Video Diffusion Transformer with spatial and temporal LoRA adapters for minimal training and precise control over effects.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed system demonstrates superior performance in generating realistic and dynamic effects with state-of-the-art spatial and temporal controllability, making advanced VFX accessible to a broader audience.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.05979

18. Mathematical Reasoning in Large Language Models: Assessing Logical and Arithmetic Errors across Wide Numerical Ranges
🔑 Keywords: Mathematical reasoning, Large Language Models, GSM-Ranges, Evaluation methods, Logical errors
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the limitations of evaluating mathematical reasoning in Large Language Models by introducing GSM-Ranges, a dataset generator to assess robustness across varying numerical scales and proposing a novel grading methodology for precise error evaluation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Creation of GSM-Ranges, a dataset generator, from GSM8K to systematically perturb numerical values, along with a new grading methodology distinguishing logical from non-logical errors.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Models exhibit significant weaknesses in reasoning with out-of-distribution numerical values, with logical errors increasing as numerical complexity rises, despite high accuracy in standalone arithmetic.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.08680

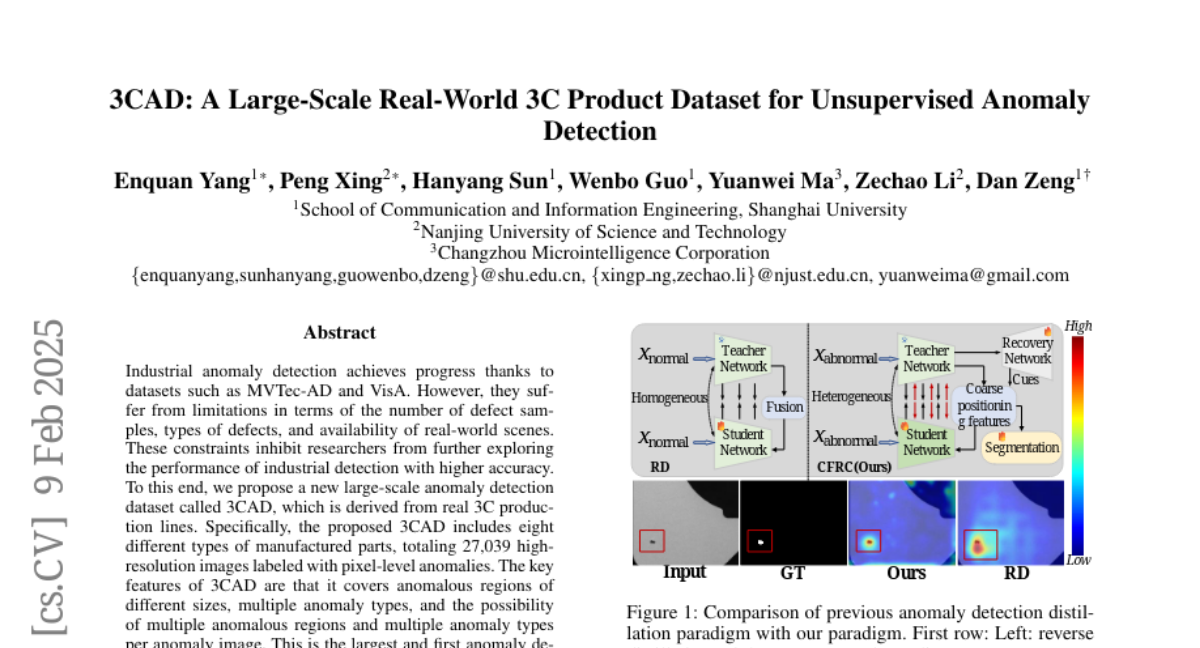
19. 3CAD: A Large-Scale Real-World 3C Product Dataset for Unsupervised Anomaly
🔑 Keywords: Anomaly Detection, 3CAD, Industrial, Unsupervised, Coarse-to-Fine
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to overcome the limitations of existing industrial anomaly detection datasets by proposing 3CAD, which is derived from real 3C production lines and provides a large-scale dataset with diverse defect types and pixel-level annotations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a new unsupervised anomaly detection framework called Coarse-to-Fine detection paradigm with Recovery Guidance (CFRG), utilizing a heterogeneous distillation model for coarse localization and a segmentation model for fine localization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The results of the CFRG framework on 3CAD demonstrate strong competitiveness, establishing a challenging benchmark to advance the field of anomaly detection. The dataset and methodologies are made available for community use and development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.05761
20. DexTrack: Towards Generalizable Neural Tracking Control for Dexterous Manipulation from Human References
🔑 Keywords: Neural Tracking Controller, Dexterous Manipulation, Reinforcement Learning, Imitation Learning, Homotopy Optimization
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a generalizable neural tracking controller for dexterous manipulation guided by human references.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Curating large-scale successful robot tracking demonstrations to train the neural controller.
– Utilizing reinforcement learning and imitation learning in synergy.
– Implementing a homotopy optimization method to enhance the diversity and quality of tracking demonstrations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method improves success rates by over 10% compared to existing baselines in both simulated and real-world environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2502.09614