AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20241217
1. Byte Latent Transformer: Patches Scale Better Than Tokens
🔑 Keywords: Byte Latent Transformer, LLM architecture, inference efficiency, scaling, raw bytes
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Byte Latent Transformer (BLT), a byte-level LLM architecture that matches tokenization-based LLM performance with better inference efficiency and robustness.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Encoding bytes into dynamically sized patches that are segmented based on next byte entropy; conducting FLOP controlled scaling study with models up to 8B parameters.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BLT demonstrates feasibility in scaling models trained on raw bytes without fixed vocabulary, improving training and inference efficiency, with better performance in reasoning and long tail generalization compared to tokenization-based models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.09871

2. Evaluation Agent: Efficient and Promptable Evaluation Framework for Visual Generative Models
🔑 Keywords: visual generative models, Evaluation Agent, diffusion-based models, explainability, open-sourced
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address the inefficiencies and lack of user-tailored evaluation methods in assessing visual generative models by introducing the Evaluation Agent framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The Evaluation Agent utilizes human-like strategies to perform efficient, dynamic, multi-round evaluations using minimal samples per round, which provides detailed and user-specific analyses.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Evaluation Agent framework significantly reduces evaluation time to 10% of traditional methods while maintaining comparable results and is fully open-sourced to facilitate further research in visual generative model evaluation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.09645

3. RetroLLM: Empowering Large Language Models to Retrieve Fine-grained Evidence within Generation
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RetroLLM, Constrained Decoding
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the limitations of existing retrieval-augmented generation methods by integrating retrieval and generation into a unified framework called RetroLLM.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced hierarchical FM-Index constraints for identifying relevant documents and a forward-looking constrained decoding strategy to improve evidence accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RetroLLM demonstrates superior performance on both in-domain and out-of-domain tasks across five open-domain QA datasets, highlighting its effectiveness in enhancing evidence generation accuracy.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11919

4. BrushEdit: All-In-One Image Inpainting and Editing
🔑 Keywords: Image Editing, Diffusion Models, Inpainting, Multimodal Large Language Models
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address limitations of current image editing methods by proposing BrushEdit, an inpainting-based, instruction-guided approach that enhances user interaction and flexibility.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of an agent-cooperative framework integrating Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) and a dual-branch image inpainting model for editing category classification, main object identification, mask acquisition, and inpainting.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BrushEdit effectively combines MLLMs and inpainting models to achieve superior performance in image editing tasks, with proven results across seven evaluation metrics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.10316
5. ColorFlow: Retrieval-Augmented Image Sequence Colorization
🔑 Keywords: Image Colorization, Generative Models, Industrial Application, Diffusion Models, ColorFlow
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a robust and generalizable framework for automatic black-and-white image sequence colorization that maintains character and object identity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of ColorFlow, a three-stage diffusion-based framework with a Retrieval Augmented Colorization pipeline, utilizing a dual-branch design for color identity extraction and colorization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ColorFlow outperforms existing models across multiple metrics in sequential image colorization, offering significant potential benefits to the art industry and establishing a new standard.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11815
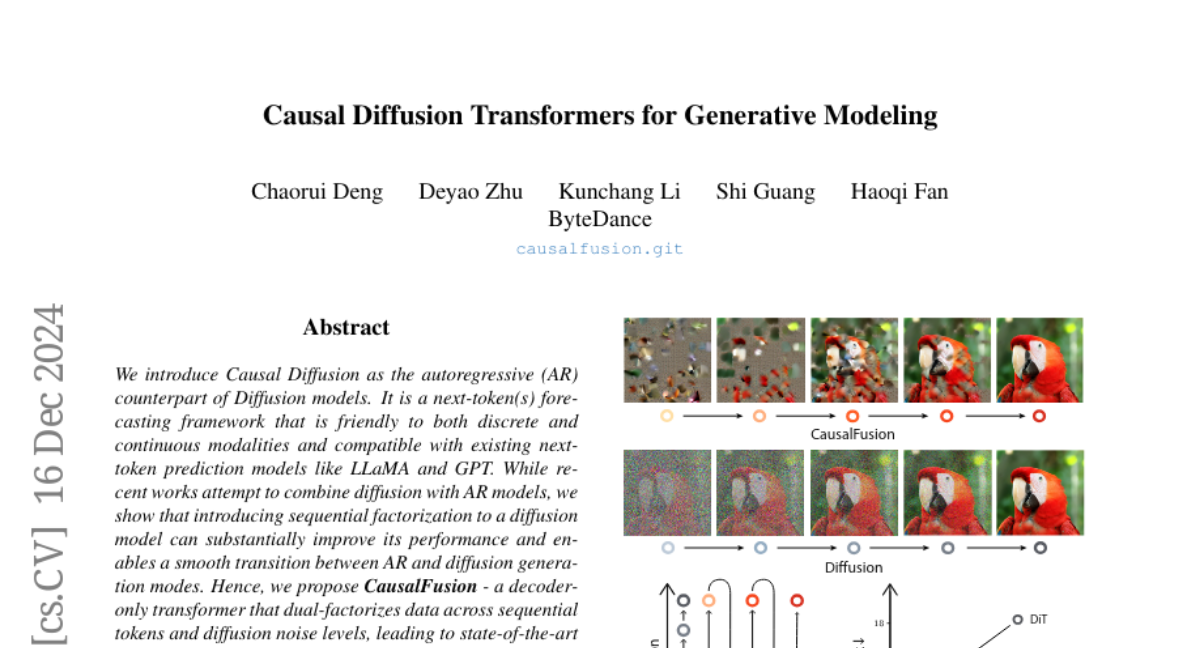
6. Causal Diffusion Transformers for Generative Modeling
🔑 Keywords: Causal Diffusion, Autoregressive, CausalFusion, Multimodal, Zero-shot
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Causal Diffusion as the autoregressive counterpart of diffusion models, enhancing performance in next-token prediction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposal of CausalFusion, a decoder-only transformer dual-factorizing data across sequential tokens and diffusion noise levels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved state-of-the-art results on the ImageNet generation benchmark, showcasing CausalFusion’s multimodal capabilities including zero-shot in-context image manipulations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.12095
7. Smaller Language Models Are Better Instruction Evolvers
🔑 Keywords: instruction tuning, large language models, smaller language models, instruction evolution, Instruction Complex-Aware IFD
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to investigate the potential of smaller language models (SLMs) in the context of instruction evolution, challenging the assumption that larger language models (LLMs) inherently perform better.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers conducted extensive experiments across three scenarios of instruction evolution to compare the performance of SLMs and LLMs.
– They introduced a new metric, Instruction Complex-Aware IFD (IC-IFD), to better evaluate the complexity and effectiveness of instruction data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Smaller language models (SLMs) can synthesize more effective and complex instructions than LLMs.
– SLMs demonstrate a broader output space, resulting in more diverse instruction variants.
– The current metrics do not accurately capture the impact of instructions, highlighting the need for the proposed IC-IFD metric.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11231

8. IDArb: Intrinsic Decomposition for Arbitrary Number of Input Views and Illuminations
🔑 Keywords: IDArb, intrinsic decomposition, multi-view consistency, diffusion-based model
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce IDArb, a diffusion-based model for intrinsic decomposition of images under varying illuminations, ensuring multi-view consistency in estimating surface normals and material properties.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ a novel cross-view, cross-domain attention module and an illumization-augmented, view-adaptive training strategy, supported by the new ARB-Objaverse dataset providing large-scale intrinsic data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– IDArb surpasses state-of-the-art methods both qualitatively and quantitatively and supports a range of downstream tasks like single-image relighting and 3D reconstruction, enhancing realistic 3D content creation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.12083
9. GaussianProperty: Integrating Physical Properties to 3D Gaussians with LMMs
🔑 Keywords: GaussianProperty, computer vision, robotics, physical properties
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to estimate physical properties from visual data to facilitate applications in augmented reality, physical simulation, and robotic grasping.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces GaussianProperty, a training-free framework that uses 3D Gaussians for material property representation, integrating segmentation from SAM and recognition from GPT-4V(ision).
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The methodology demonstrates effectiveness in applications such as physics-based dynamic simulation using the Material Point Method (MPM) and robotic grasping force prediction, validated through extensive experiments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11258

10. SPaR: Self-Play with Tree-Search Refinement to Improve Instruction-Following in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Instruction-following, Preference Learning, SPaR, LLaMA3-8B, Self-play
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve language models’ capability to follow instructions accurately by minimizing unnecessary variations in responses.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced SPaR, a self-play framework utilizing tree-search self-refinement to create valid preference pairs, and applied it over three iterations to a LLaMA3-8B model.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SPaR-enhanced models like LLaMA3-8B outperformed GPT-4-Turbo on the IFEval benchmark, demonstrating significant scalability and transferability without losing general capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11605

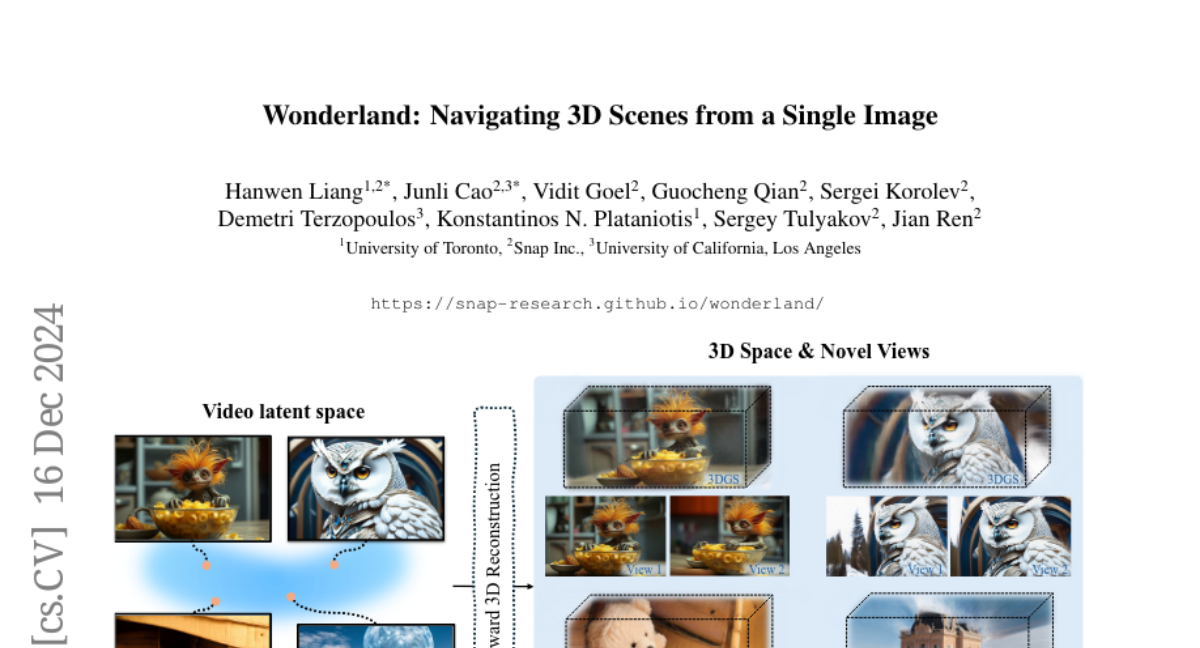
11. Wonderland: Navigating 3D Scenes from a Single Image
🔑 Keywords: 3D reconstruction, video diffusion model, Gaussian Splattings, single-view, high-quality
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to efficiently create high-quality, wide-scope 3D scenes from a single arbitrary image.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a novel pipeline using a large-scale reconstruction model and a video diffusion model to predict 3D Gaussian Splattings for scenes.
– Employs a progressive training strategy to generate compressed video latents, maintaining multi-view information and 3D consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates the model’s superiority over existing methods in single-view 3D scene generation, notably excelling with out-of-domain images.
– Pioneers building a 3D reconstruction model on the latent space of a diffusion model for efficient 3D scene generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.12091
12. SepLLM: Accelerate Large Language Models by Compressing One Segment into One Separator
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Inference Speed, SepLLM, KV Cache Reduction, Language Modeling
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the computational demands and inference speed challenges posed by Large Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging a new plug-and-play framework named SepLLM.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of SepLLM to accelerate inference through segment compression and elimination of redundant tokens.
– Implementation of efficient kernels for acceleration during training across different settings: training-free, training-from-scratch, and post-training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
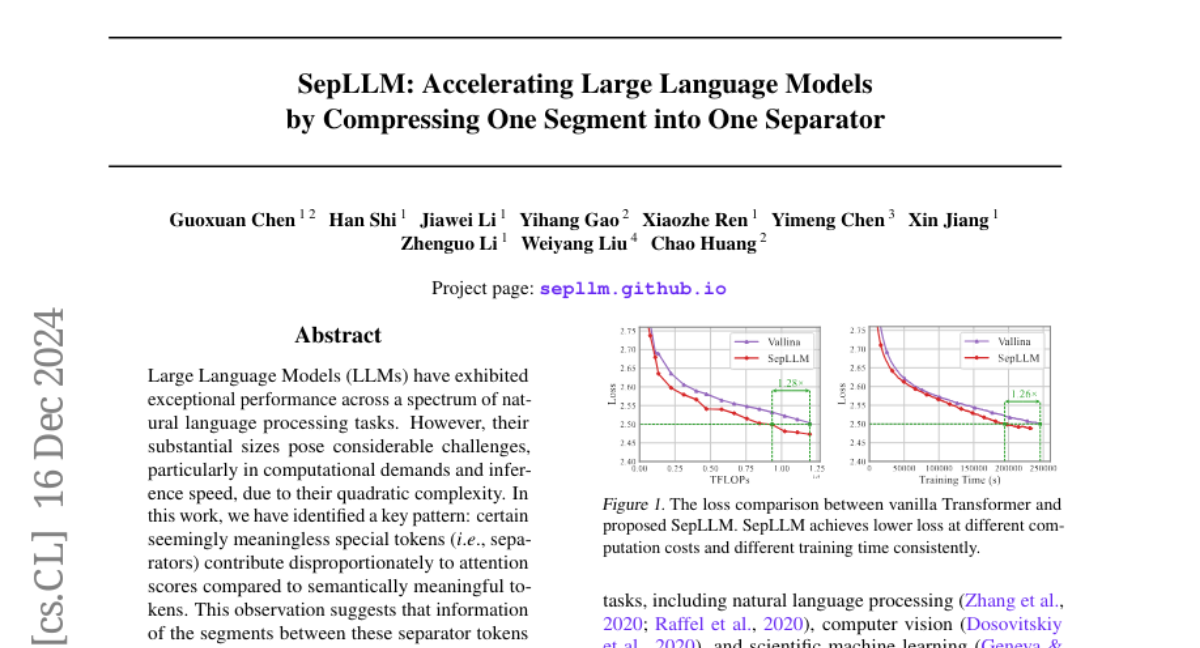
– SepLLM achieves significant reduction (over 50%) in KV cache on the GSM8K-CoT benchmark with the Llama-3-8B backbone while preserving performance.
– Demonstrates capability in processing sequences up to 4 million tokens effectively in streaming settings while maintaining language modeling performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.12094
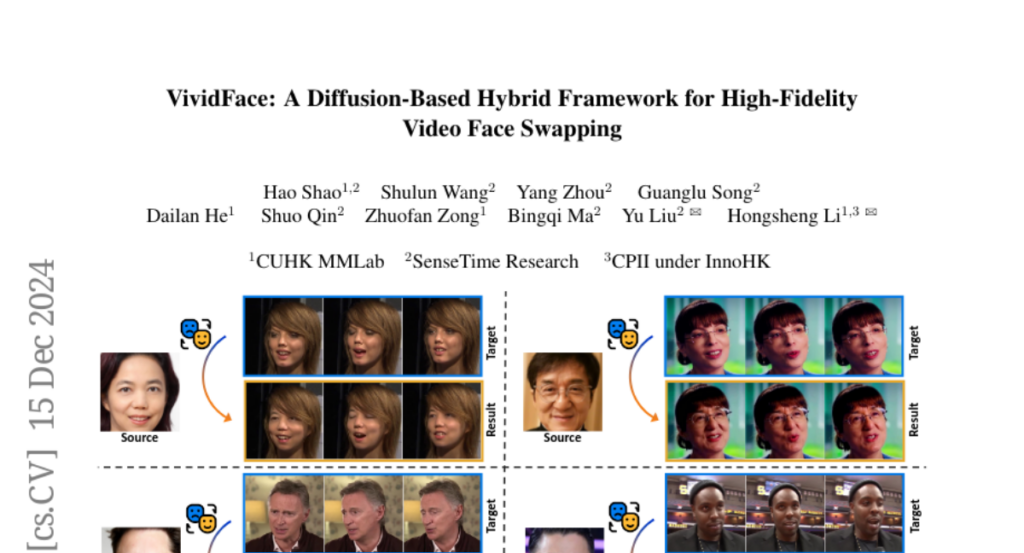
13. VividFace: A Diffusion-Based Hybrid Framework for High-Fidelity Video Face Swapping
🔑 Keywords: Video face swapping, Temporal consistency, Identity preservation, Diffusion-based framework, 3D reconstruction
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a novel diffusion-based framework for video face swapping that ensures temporal consistency and robust identity preservation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced an image-video hybrid training framework that uses static image data and temporal video sequences, alongside a diffusion model and VidFaceVAE.
– Constructed the Attribute-Identity Disentanglement Triplet (AIDT) Dataset to disentangle identity and pose features, incorporating occlusion augmentation.
– Integrated 3D reconstruction techniques as input conditioning to manage pose variations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
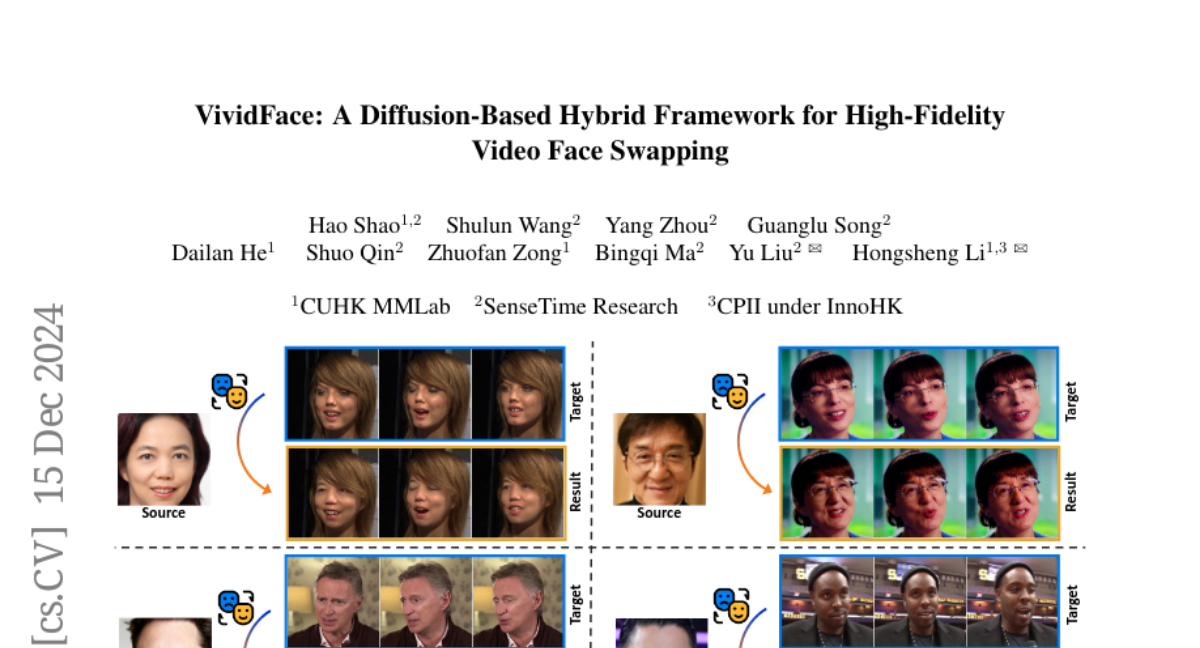
– The proposed framework achieves superior performance in identity preservation, temporal consistency, and visual quality over existing methods while reducing inference steps.
– Mitigates challenges such as temporal flickering, identity preservation, occlusion robustness, and pose variation handling in video face swapping.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11279
14. StrandHead: Text to Strand-Disentangled 3D Head Avatars Using Hair Geometric Priors
🔑 Keywords: StrandHead, 3D head avatar, text to 3D, generative diffusion models, Unreal Engine
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose a novel method named StrandHead for text to 3D head avatar generation with disentangled 3D hair strands.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a series of reliable priors on shape initialization, geometric primitives, and statistical haircut features with guidance from 2D generative diffusion models to generate realistic hair from text prompts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– StrandHead achieves state-of-the-art reality and diversity in generating 3D heads and hair, and the models can be used in applications like Unreal Engine for physical simulation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11586
15. Wonderful Matrices: Combining for a More Efficient and Effective Foundation Model Architecture
🔑 Keywords: Foundation Model, Sequence Transformation, State Transformation, Dynamic Mask Attention, Cross Domain Mixture of Experts
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the Foundation Model by combining sequence and state transformations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of rotary position embedding in the state space duality algorithm, introduction of dynamic mask attention, and design of cross domain mixture of experts for improved computational speed and efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed methods can outperform existing model architectures in perplexity reduction, accuracy in associative recall tasks, and computational speed in expert retrieval.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11834

16. TidyBot++: An Open-Source Holonomic Mobile Manipulator for Robot Learning
🔑 Keywords: Imitation Learning, Mobile Manipulation, Open-Source Design, Holonomic Base, Teleoperation Interface
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to introduce an open-source mobile manipulator design that is inexpensive, robust, and flexible, capable of supporting various robotic arms for household tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a holonomic base with powered casters to enhance maneuverability and eliminate kinematic constraints; employs a smartphone teleoperation interface for easy data collection in imitation learning applications.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research demonstrates that the collected data and resulting learned policies effectively perform a variety of common household mobile manipulation tasks successfully.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.10447
17. The Open Source Advantage in Large Language Models (LLMs)
🔑 Keywords: Large language models, Open-source models, Proprietary models, Ethical considerations, Transparency
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper explores the distinct differences and key innovations between closed-source and open-source large language models (LLMs), focusing on areas such as text generation, translation, and domain-specific reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study compares the approaches of closed-source models like GPT-4 with open-source models like LLaMA and BLOOM, examining their performance in linguistic diversity and domain-specific applications. It highlights techniques like Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and instruction-tuning datasets for enhancing open-source model capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study concludes that while closed-source models maintain superior performance through extensive resources, open-source initiatives promote democratization and accessibility. The tension between these paradigms reflects a broader debate on transparency and ethical AI development. Hybrid models that combine strengths from both approaches are predicted to influence future LLM innovation, emphasizing accessibility, technical performance, and ethical considerations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.12004

18. Emma-X: An Embodied Multimodal Action Model with Grounded Chain of Thought and Look-ahead Spatial Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Visual-Language-Action (VLA) models, spatial reasoning, robotic control
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the limitations of traditional reinforcement learning and Visual Language Models (VLMs) in robotic control by developing the Embodied Multimodal Action Model (Emma-X) to improve task generalization and spatial reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Construct a hierarchical dataset based on BridgeV2 with 60,000 robot manipulation trajectories.
– Implement a trajectory segmentation strategy based on gripper states and motion trajectories to enhance subtask grounding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Emma-X outperforms competitive baselines in real-world robotic tasks requiring advanced spatial reasoning and task planning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11974
19. MOVIS: Enhancing Multi-Object Novel View Synthesis for Indoor Scenes
🔑 Keywords: diffusion models, multi-object scenarios, cross-view consistency, novel view synthesis, structure-aware
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address limitations of pre-trained diffusion models in multi-object NVS scenarios, focusing on improving cross-view consistency and correct object placement.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Propose MOVIS, which incorporates structure-aware features, an auxiliary task for novel view mask prediction, and a structure-guided timestep sampling scheduler to enhance the view-conditioned diffusion model’s ability for multi-object NVS.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments show that MOVIS achieves strong generalization and consistent novel view synthesis, setting a foundation for future 3D-aware multi-object NVS tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11457

20. Whisper-GPT: A Hybrid Representation Audio Large Language Model
🔑 Keywords: WHISPER-GPT, generative audio, continuous audio representations, discrete tokens
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose WHISPER-GPT, a generative large language model for speech and music that integrates continuous audio representations with discrete tokens in a unified architecture.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Combines continuous audio representations like spectrograms with discrete audio tokens to retain comprehensive audio information and predict future tokens.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated improvements in perplexity and negative log-likelihood scores for next token prediction compared to traditional token-based LLMs for speech and music.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11449

21. DynamicScaler: Seamless and Scalable Video Generation for Panoramic Scenes
🔑 Keywords: immersive AR/VR applications, scene-level dynamic content synthesis, panoramic video
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the quality and scalability of scene-level and panoramic video generation for immersive AR/VR applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a DynamicScaler with an Offset Shifting Denoiser and Global Motion Guidance to enable scalable, coherent, and seamless panoramic scene synthesis.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated superior content and motion quality in panoramic video generation with a training-free, efficient, and scalable method that uses constant VRAM consumption.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11100
22. MaxInfoRL: Boosting exploration in reinforcement learning through information gain maximization
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, intrinsic rewards, exploration, MaxInfoRL, continuous state-action spaces
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce MaxInfoRL, a framework that effectively balances intrinsic and extrinsic exploration in reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Combines MaxInfoRL with Boltzmann exploration to guide exploration towards informative transitions and maximize intrinsic rewards.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves sublinear regret in multi-armed bandits and superior performance across complex exploration problems and visual control tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.12098

23. Just a Simple Transformation is Enough for Data Protection in Vertical Federated Learning
🔑 Keywords: Vertical Federated Learning, privacy protection, feature reconstruction attacks, MLP-based models
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to explore ways to protect input data during Vertical Federated Learning by assessing vulnerabilities to feature reconstruction attacks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research investigates the theoretical underpinnings of feature reconstruction attacks and assesses the effectiveness of different model architecture transformations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Key findings demonstrate that MLP-based models show resistance to state-of-the-art feature reconstruction attacks, thus enhancing data protection in VFL.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11689
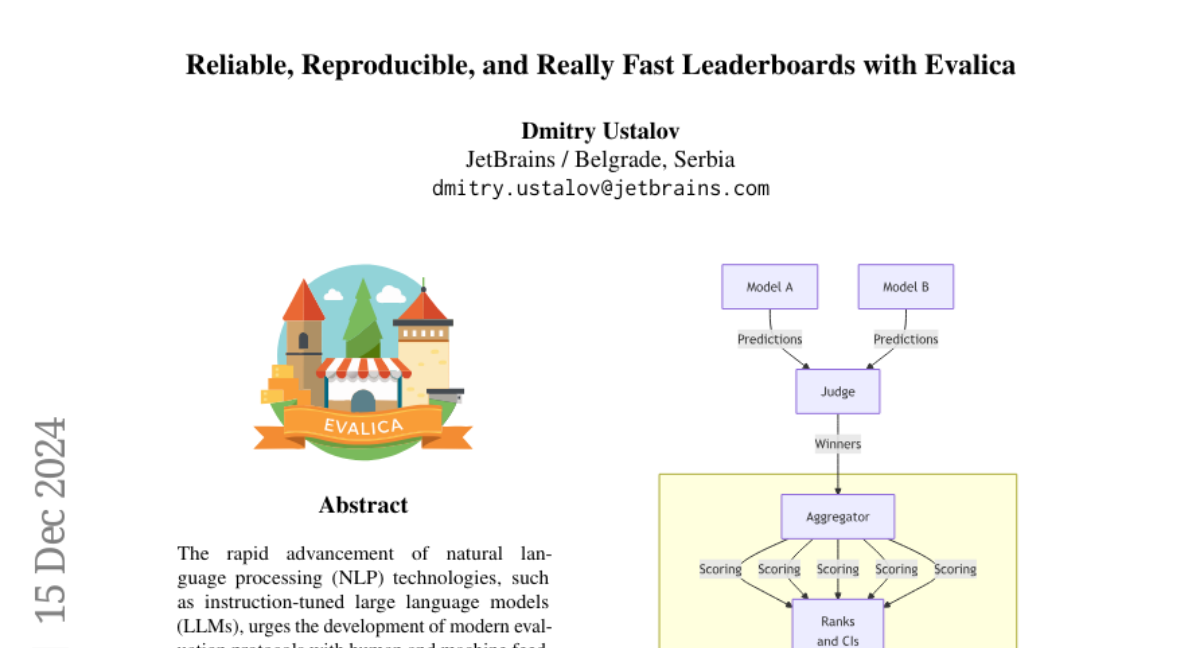
24. Reliable, Reproducible, and Really Fast Leaderboards with Evalica
🔑 Keywords: NLP, instruction-tuned, large language models, evaluation protocols, AI Systems and Tools
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop modern evaluation protocols for NLP technologies using Evalica, an open-source toolkit.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study presents the design of Evalica and evaluates its performance and usability through a web interface, command-line interface, and Python API.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Evalica facilitates the creation of reliable and reproducible model leaderboards for large language models, integrating human and machine feedback.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11314
25. RLDG: Robotic Generalist Policy Distillation via Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Robotic foundation models, Generalist policies, Reinforcement Learning Distilled Generalists, Precise manipulation tasks
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose a method called Reinforcement Learning Distilled Generalists (RLDG) that leverages reinforcement learning to generate high-quality training data for finetuning generalist policies in robotic systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized reinforcement learning to create training data.
– Conducted extensive real-world experiments focusing on tasks such as connector insertion and assembly.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The RLDG method significantly improves the performance of generalist policies, achieving up to a 40% higher success rate compared to those trained with human demonstrations.
– The performance gain is attributed to optimized action distributions and improved state coverage, suggesting that combining task-specific reinforcement learning with generalist policy distillation enhances robotic systems’ capabilities and efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.09858

26. SplineGS: Robust Motion-Adaptive Spline for Real-Time Dynamic 3D Gaussians from Monocular Video
🔑 Keywords: Dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting, Motion-Adaptive Spline, Novel View Synthesis, Monocular Videos
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose SplineGS, a method for high-quality reconstruction and fast rendering of dynamic scenes from in-the-wild monocular videos.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce Motion-Adaptive Spline (MAS) and Motion-Adaptive Control points Pruning (MACP) to model dynamic 3D Gaussian trajectories without needing multi-view cues.
– Employ a joint optimization strategy for camera parameter estimation and 3D Gaussian attributes to enhance robustness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SplineGS significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in novel view synthesis quality for dynamic scenes, achieving substantial speed improvements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.09982

27. GeoX: Geometric Problem Solving Through Unified Formalized Vision-Language Pre-training
🔑 Keywords: Multi-modal Large Language Models, Geometry Problem Solving, GeoX, diagram encoder, Generator-And-Sampler Transformer
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance automatic Geometry Problem Solving (GPS) by improving the geometric understanding and reasoning abilities of multi-modal models through GeoX.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced unimodal pre-training to develop a diagram encoder and symbol decoder specifically designed for geometric images and symbols.
– Proposed geometry-language alignment to bridge the modality gap and employed a Generator-And-Sampler Transformer (GS-Former) to improve query generation and representation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GeoX demonstrated superior performance compared to both generalist models and specialized geometric solvers across multiple geometric benchmarks like GeoQA and Geometry3K, illustrating its effectiveness in solving complex geometric tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11863

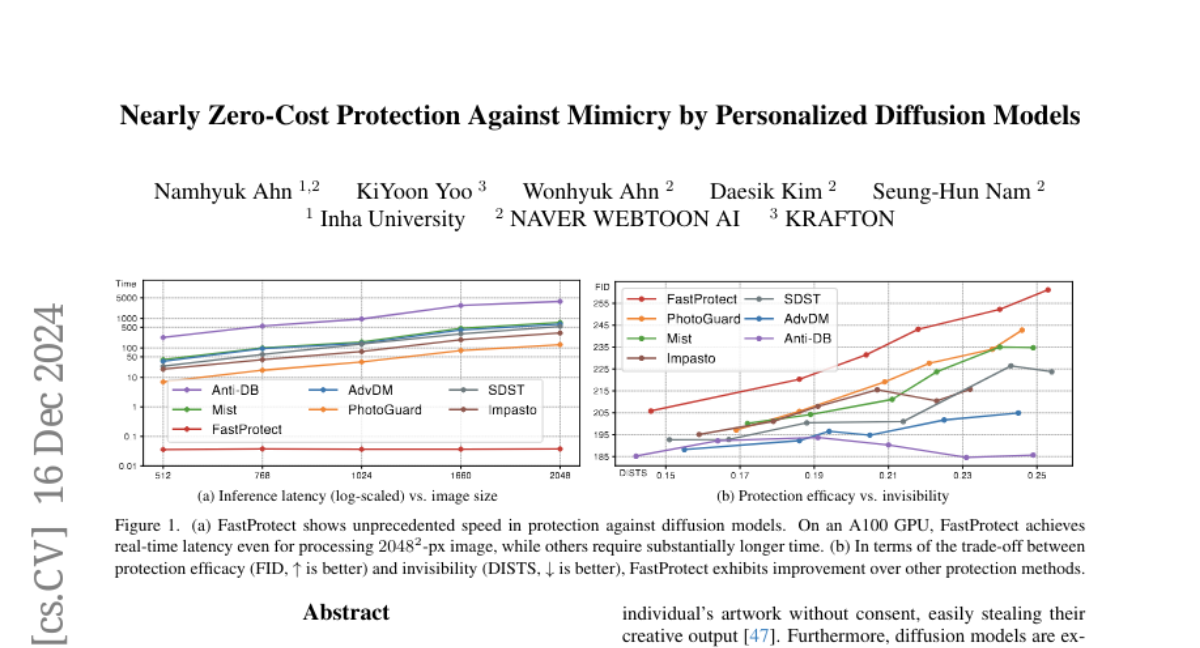
28. Nearly Zero-Cost Protection Against Mimicry by Personalized Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Models, Image Protection, Deepfakes, VAE Feature Spaces
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce a novel perturbation pre-training and mixture-of-perturbations approach to balance protection efficacy, invisibility, and latency in image protection methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a perturbation pre-training method to reduce latency.
– Implemented a mixture-of-perturbations approach and computed protection loss across multiple VAE feature spaces.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved comparable protection performance with improved invisibility and significantly reduced inference time.
– Made code and demo publicly available.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.11423