AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20241230

1. HuatuoGPT-o1, Towards Medical Complex Reasoning with LLMs
🔑 Keywords: OpenAI o1, Reasoning, Medical Domain, Reinforcement Learning, HuatuoGPT-o1
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to explore reasoning capabilities in medical domains by creating verifiable medical problems and using a medical verifier for correctness checks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs a two-stage approach: guiding complex reasoning with a medical verifier for fine-tuning LLMs and enhancing reasoning through reinforcement learning with verifier-based rewards.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The introduction of HuatuoGPT-o1 demonstrates enhanced complex reasoning, outperforming existing baselines in medical problem-solving, and highlighting the potential for reinforcement learning to contribute significantly to reasoning improvement.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.18925

2. 1.58-bit FLUX
🔑 Keywords: 1.58-bit FLUX, quantization, text-to-image generation, computational efficiency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Present 1.58-bit FLUX, a quantization approach for the FLUX.1-dev model to maintain generation quality with reduced complexity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized 1.58-bit weights with a custom kernel, leveraging self-supervision from FLUX.1-dev without image data access.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– 1.58-bit FLUX achieves significant storage reduction and enhanced computational efficiency while maintaining performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.18653

3. Next Token Prediction Towards Multimodal Intelligence: A Comprehensive Survey
🔑 Keywords: Next Token Prediction, Large Language Models, Multimodal Learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a comprehensive taxonomy unifying understanding and generation within multimodal learning through Next Token Prediction (NTP).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Survey covering five key aspects: Multimodal tokenization, MMNTP model architectures, unified task representation, datasets & evaluation, and open challenges.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Aims to aid researchers in exploring multimodal intelligence, with an associated GitHub repository for the latest papers and resources.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.18619

4. Orient Anything: Learning Robust Object Orientation Estimation from Rendering 3D Models
🔑 Keywords: Object Orientation, 3D World, Zero-Shot Ability, Synthetic-to-Real Transfer, Spatial Concepts
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Orient Anything, a foundational model for estimating object orientation from single and free-view images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a pipeline to annotate 3D objects, produce 2M labeled images, and use probability distributions to model 3D orientation.
– Implement strategies for improved synthetic-to-real transfer.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art accuracy in orientation estimation for both rendered and real images, and demonstrates strong zero-shot capabilities across different scenarios.
– Enhances applications such as complex spatial concept comprehension and 3D object pose adjustment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.18605

5. Task Preference Optimization: Improving Multimodal Large Language Models with Vision Task Alignment
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Large Language Models, Task Preference Optimization, Visual Tasks, Multi-Task Co-Training, Zero-Shot Capabilities
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance multimodal large language models (MLLMs) with fine-grained understanding of visuals and improved performance on specific visual tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposed Task Preference Optimization (TPO), using learnable task tokens to connect multiple task-specific heads with MLLMs and employing rich visual labels during training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TPO significantly improves MLLM’s multimodal and task-specific capabilities, showing a 14.6% performance increase over baseline models and demonstrating robust zero-shot capabilities across tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.19326

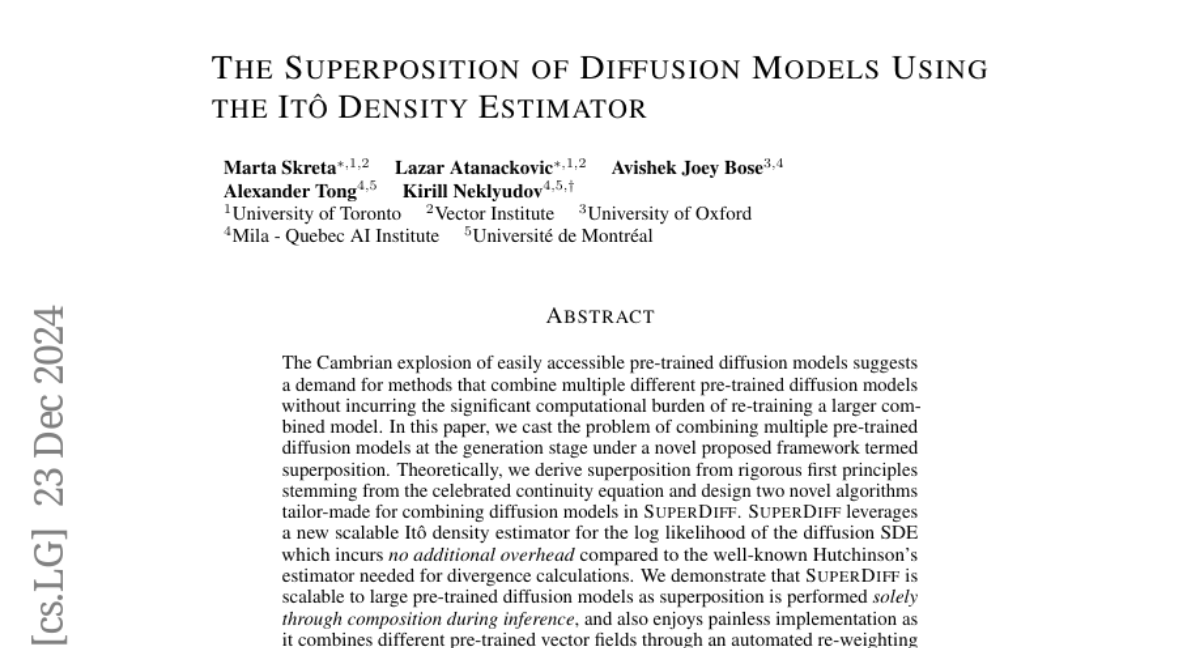
6. The Superposition of Diffusion Models Using the Itô Density Estimator
🔑 Keywords: Superposition, SuperDiff, Diffusion Models, CIFAR-10, Stable Diffusion
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a novel framework, termed superposition, for efficiently combining multiple pre-trained diffusion models without re-training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of two novel algorithms within SuperDiff using a scalable Itô density estimator for the log likelihood of the diffusion SDE.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SuperDiff allows for scalable and efficient combination of diffusion models, enhancing image generation diversity and quality in various applications such as CIFAR-10 and Stable Diffusion.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.17762
7. From Elements to Design: A Layered Approach for Automatic Graphic Design Composition
🔑 Keywords: LaDeCo, Large Multimodal Models, design composition, generative models
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce a novel approach, called LaDeCo, for automatic design composition using multimodal graphic elements, addressing limitations in current generative models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of the layered design principle in Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) to perform layer planning and layer-wise element composition.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LaDeCo effectively decomposes complex tasks into manageable steps, demonstrating its effectiveness in design composition and outperforming specialized models in certain subtasks without task-specific training.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.19712

8. VideoMaker: Zero-shot Customized Video Generation with the Inherent Force of Video Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: Zero-shot customized video generation, Video Diffusion Model, feature extraction, feature injection
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance zero-shot customized video generation using the inherent capabilities of the Video Diffusion Model (VDM) without additional reference feature models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introducing a framework that directly utilizes VDM for reference feature extraction and a novel bidirectional interaction method for feature injection via spatial self-attention.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that VDM can effectively maintain subject fidelity and diversity in generated videos through its intrinsic processes, validated by experiments on customized human and object video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.19645

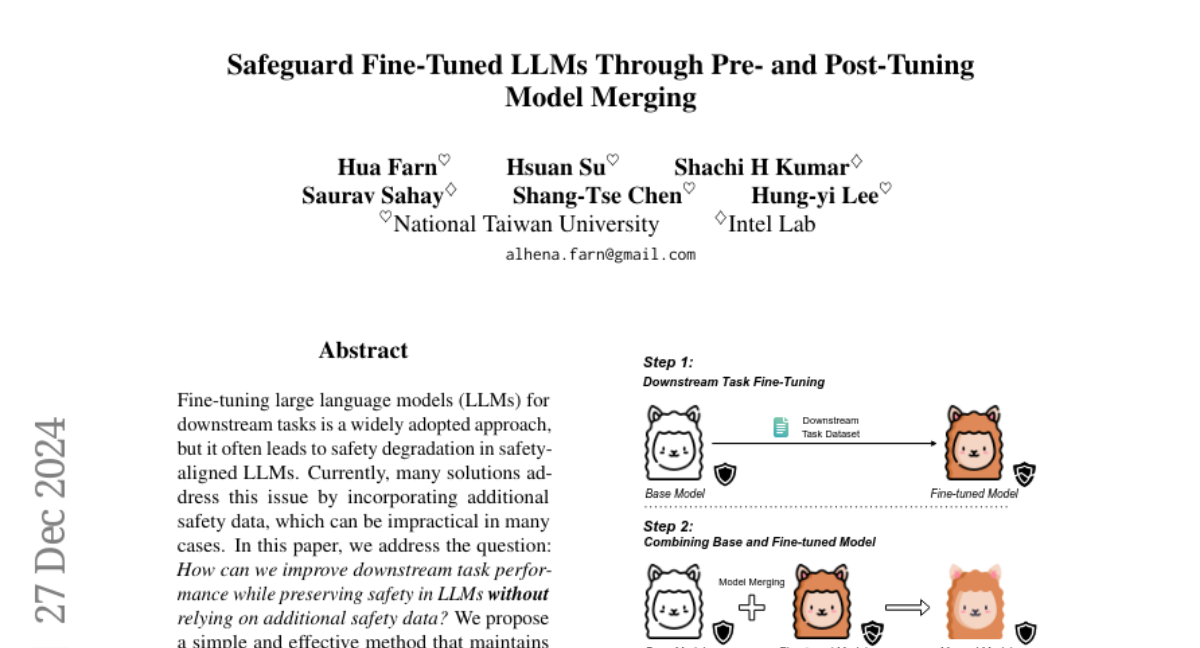
9. Safeguard Fine-Tuned LLMs Through Pre- and Post-Tuning Model Merging
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Safety Degradation, Downstream Task, Fine-tuning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve downstream task performance of safety-aligned LLMs without relying on additional safety data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposed merging the weights of pre- and post-fine-tuned safety-aligned language models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach effectively mitigates safety degradation while enhancing downstream performance, providing a practical solution for adapting safety-aligned LLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.19512
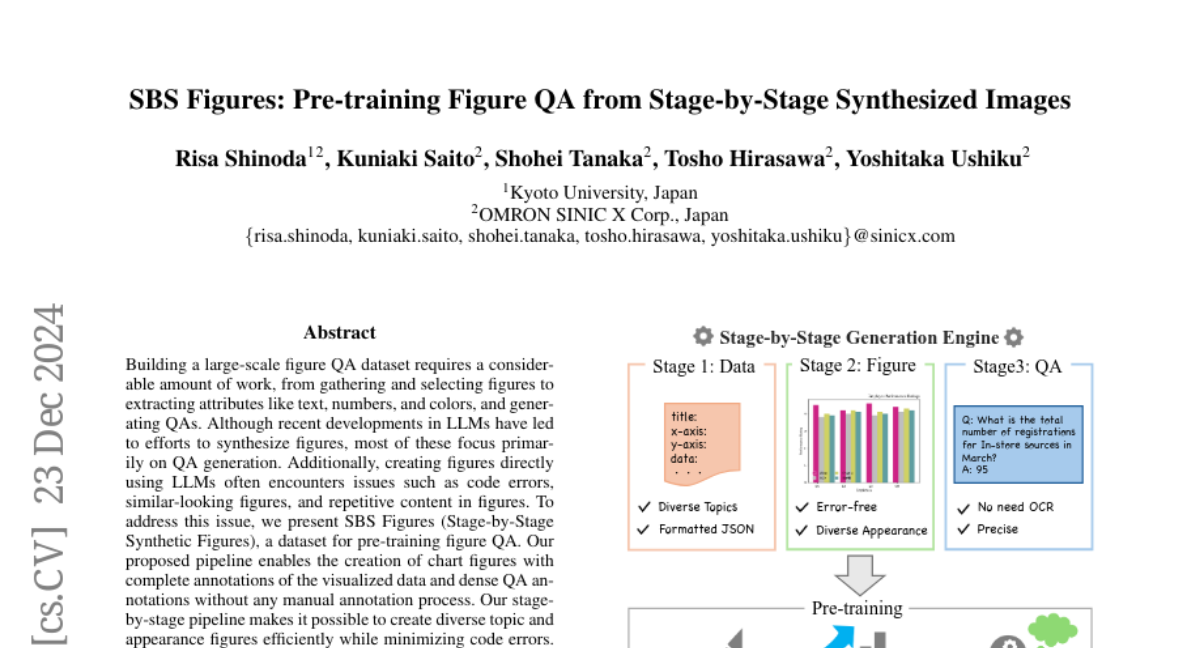
10. SBS Figures: Pre-training Figure QA from Stage-by-Stage Synthesized Images
🔑 Keywords: Large-Scale Figure QA, LLMs, Pre-training, SBSFigures
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To create a large-scale figure QA dataset called SBSFigures for pre-training figure QA without manual annotations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a stage-by-stage pipeline to synthesize chart figures with full annotations, minimizing code errors and enhancing diversity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SBSFigures dataset enables efficient pre-training, providing robust training data even with limited real-world chart data, starting from pre-trained weights.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.17606
11. CypherBench: Towards Precise Retrieval over Full-scale Modern Knowledge Graphs in the LLM Era
🔑 Keywords: Graph Data Retrieval, RDF Knowledge Graphs, LLM Efficiency, Cypher, CypherBench
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve retrieval from graph data for Large Language Models, addressing inefficiencies in existing modern RDF knowledge graphs like Wikidata.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Propose property graph views queried by LLMs using Cypher.
– Develop an RDF-to-property graph conversion engine.
– Introduce CypherBench, a benchmark with 11 multi-domain property graphs and more than 10,000 questions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Modern RDF knowledge graphs are less efficient for LLMs due to schema size, resource identifiers, and normalization issues.
– Property graph views can significantly enhance LLMs’ ability to query encyclopedic knowledge graphs effectively.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.18702
