AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250116
1. Towards Best Practices for Open Datasets for LLM Training
🔑 Keywords: Copyright, Legal Challenges, AI Models, Transparency, Open Access
💡 Category: AI Ethics and Fairness
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the legal and ethical implications of training AI models without permission from copyright owners.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analysis of legal landscapes across different jurisdictions, including EU, Japan, and the US.
– Review of the challenges in creating AI models using open access and public domain data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– High-profile copyright lawsuits have emerged due to unauthorized data usage, impacting transparency and innovation.
– Building responsibly curated AI models requires collaboration across legal, technical, and policy fields.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.08365

2. MMDocIR: Benchmarking Multi-Modal Retrieval for Long Documents
🔑 Keywords: Multi-modal document retrieval, MMDocIR, visual retrievers, layout-level retrieval, VLM-text
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce MMDocIR benchmark for evaluating systems in multi-modal document retrieval, focusing on page-level and layout-level tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Collection of a robust dataset with annotated and bootstrapped labels to support training and evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Visual retrievers outperform text ones; MMDocIR train set benefits retrieval training; VLM-text usage improves text retrieval over OCR-text.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.08828

3. CityDreamer4D: Compositional Generative Model of Unbounded 4D Cities
🔑 Keywords: 4D cities, CityDreamer4D, neural fields, BEV representation, urban simulation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address the challenge of 4D city generation, focusing on developing a method to separate dynamic objects from static scenes and integrate different neural fields for realistic urban environment creation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of CityDreamer4D, a compositional generative model, utilizing Traffic Scenario Generator and Unbounded Layout Generator. These generators use customized generative hash grids and periodic positional embeddings for compact scene parameterization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CityDreamer4D demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in generating realistic 4D cities and supports various applications, including instance editing, city stylization, and urban simulation, backed by comprehensive datasets such as OSM, GoogleEarth, and CityTopia.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.08983

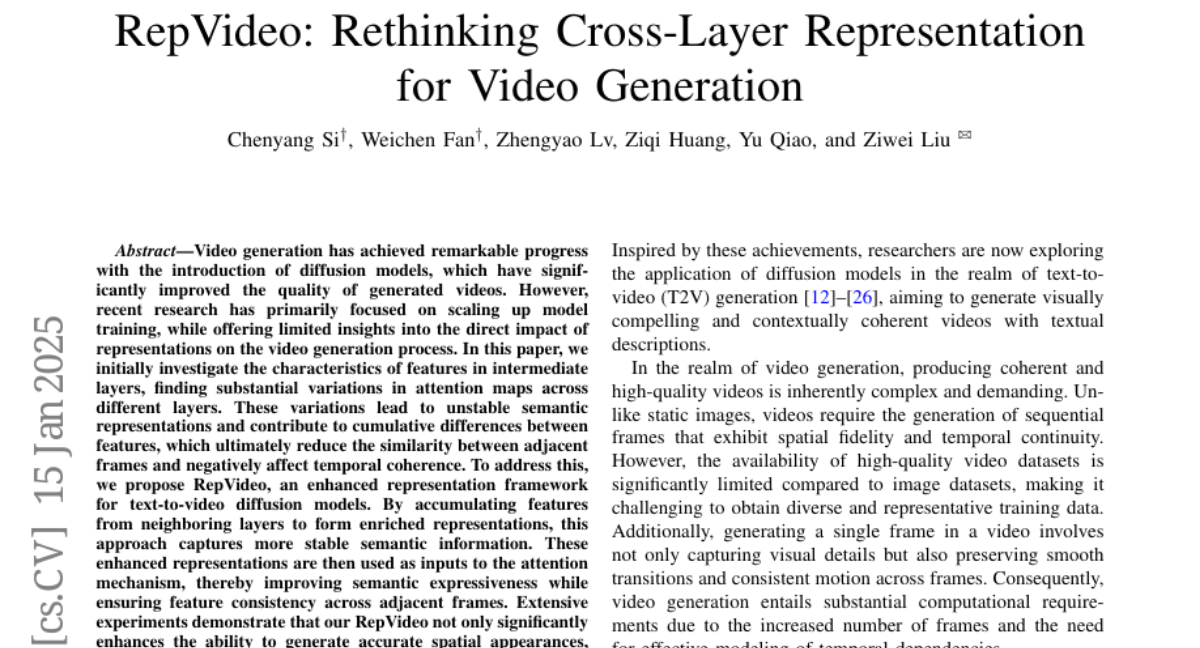
4. RepVideo: Rethinking Cross-Layer Representation for Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: video generation, diffusion models, semantic representations, temporal coherence, RepVideo
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate the impact of feature representations in diffusion models on video generation quality and temporal coherence.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analyze feature characteristics in intermediate layers and propose RepVideo for enhanced video generation by accumulating features to improve semantic expressiveness and feature consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RepVideo framework significantly improves the generation of accurate spatial appearances and temporal consistency in videos.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.08994
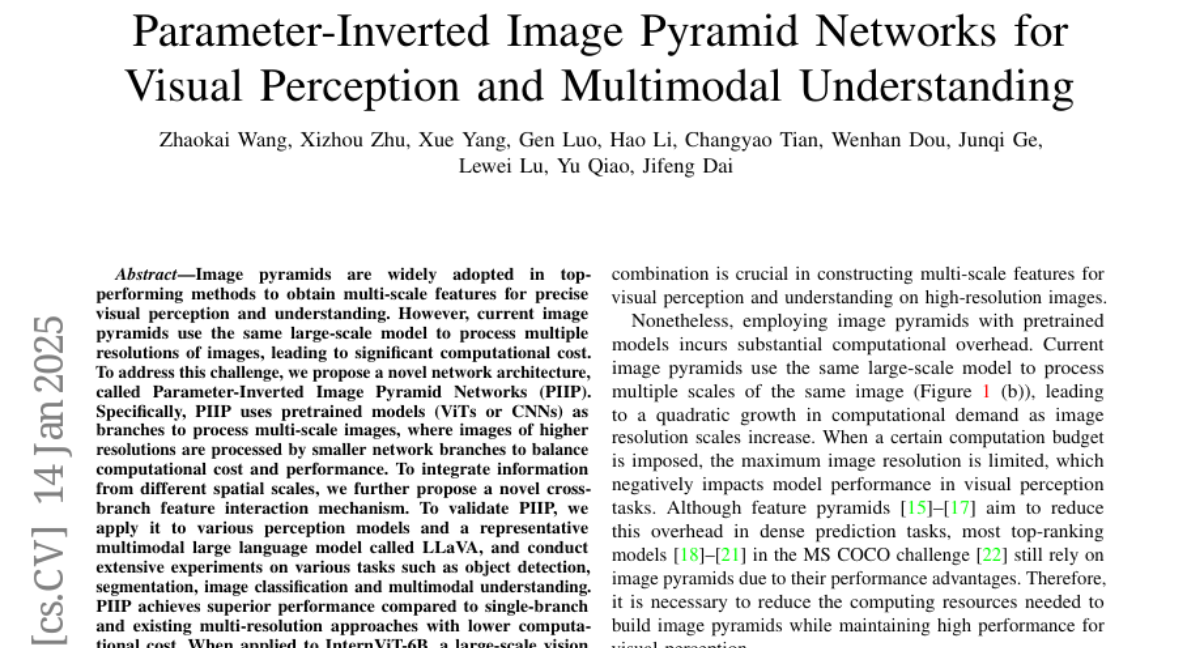
5. Parameter-Inverted Image Pyramid Networks for Visual Perception and Multimodal Understanding
🔑 Keywords: Image Pyramids, Parameter-Inverted Image Pyramid Networks, Computational Cost, Multi-Scale Features, Multimodal Understanding
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a novel network architecture called Parameter-Inverted Image Pyramid Networks (PIIP) to reduce computational cost while maintaining performance in visual perception tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of pretrained models (ViTs or CNNs) as branches for processing multi-scale images with a cross-branch feature interaction mechanism.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PIIP achieves superior performance over existing methods with reduced computational cost, showing improved results in object detection, segmentation, and multimodal understanding tasks.
– On tasks like object detection and segmentation, PIIP improves performance by 1%-2% while cutting computation by 40%-60%, achieving notable accuracy in various bench tests.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.07783
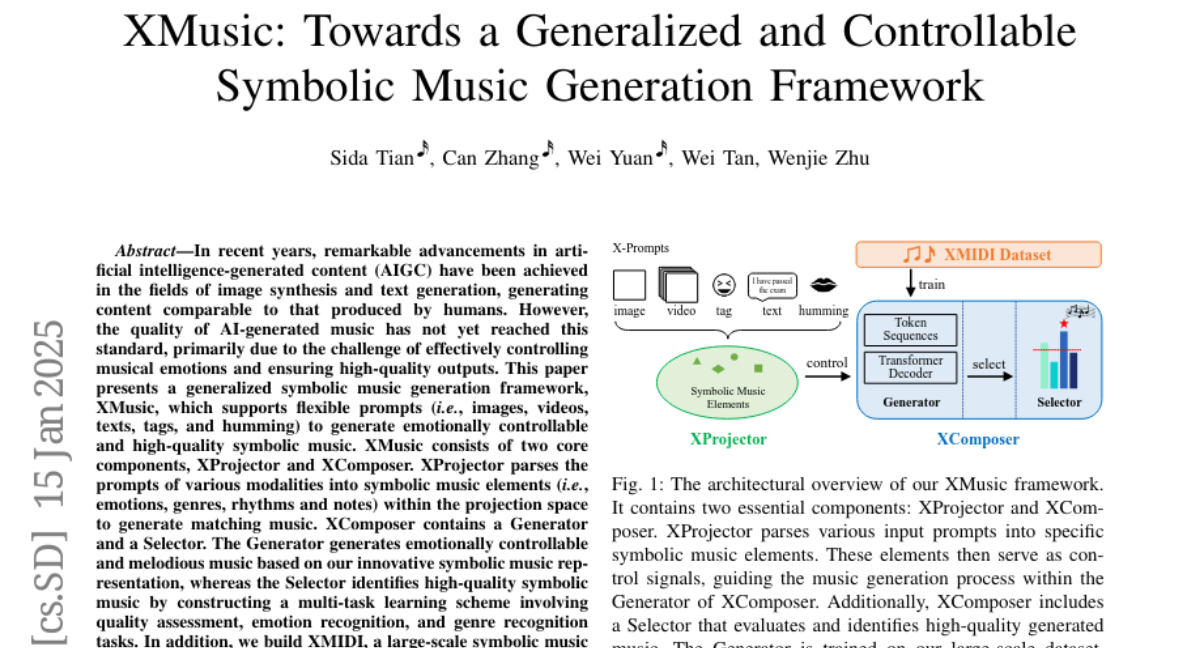
6. XMusic: Towards a Generalized and Controllable Symbolic Music Generation Framework
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated content, Emotionally controllable music, Symbolic music generation, Multi-task learning, XMIDI dataset
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve the quality of AI-generated music by developing a framework called XMusic that generates emotionally controllable and high-quality symbolic music.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The XMusic framework uses flexible prompts (images, videos, texts, tags, humming) and consists of two components, XProjector and XComposer, to translate prompts into music elements and generate music.
– XComposer uses a Generator for music creation and a Selector for high-quality music identification via a multi-task learning scheme.
– A large-scale XMIDI dataset with extensive emotion and genre annotations aids in training and evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– XMusic significantly outperforms existing methods, producing impressive music quality as evidenced by objective and subjective evaluations.
– XMusic was recognized as one of the nine Highlights of Collectibles at WAIC 2023.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.08809
7. Multimodal LLMs Can Reason about Aesthetics in Zero-Shot
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal LLMs, MM-StyleBench, art evaluation, hallucination, ArtCoT
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the reasoning ability of Multimodal LLMs in evaluating the aesthetics of artworks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Constructed MM-StyleBench dataset and developed a principled method for human preference modeling to analyze the correlation between MLLMs’ responses and human preference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified an inherent hallucination issue in MLLMs related to subjectivity and proposed ArtCoT, showing that art-specific task decomposition improves MLLMs’ aesthetic reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.09012

8. Ouroboros-Diffusion: Exploring Consistent Content Generation in Tuning-free Long Video Diffusion
🔑 Keywords: FIFO video diffusion, long video generation, Subject-Aware Cross-Frame Attention, Ouroboros-Diffusion, temporal consistency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to introduce Ouroboros-Diffusion, a new video denoising framework, enhancing structural and subject consistency for generating consistently coherent videos of arbitrary length.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a latent sampling technique at the queue tail for structural consistency and a Subject-Aware Cross-Frame Attention (SACFA) mechanism for visual coherence. Self-recurrent guidance is also introduced to leverage previous frames for improved denoising.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments on the VBench benchmark showcase Ouroboros-Diffusion’s superiority in subject consistency, motion smoothness, and temporal consistency when generating long videos.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.09019

9. Trusted Machine Learning Models Unlock Private Inference for Problems Currently Infeasible with Cryptography
🔑 Keywords: Trusted Capable Model Environments, Secure Computation, Privacy, Machine Learning Models
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to explore the use of capable machine learning models as trusted intermediaries to enable secure computations where traditional cryptographic solutions are infeasible.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces Trusted Capable Model Environments (TCMEs) as an alternative approach featuring input/output constraints, explicit information flow control, and stateless interactions to balance privacy and computational efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TCMEs can address privacy challenges and solve classic cryptographic problems, providing a new avenue for private inference. The paper also discusses current limitations and future implementation pathways.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.08970

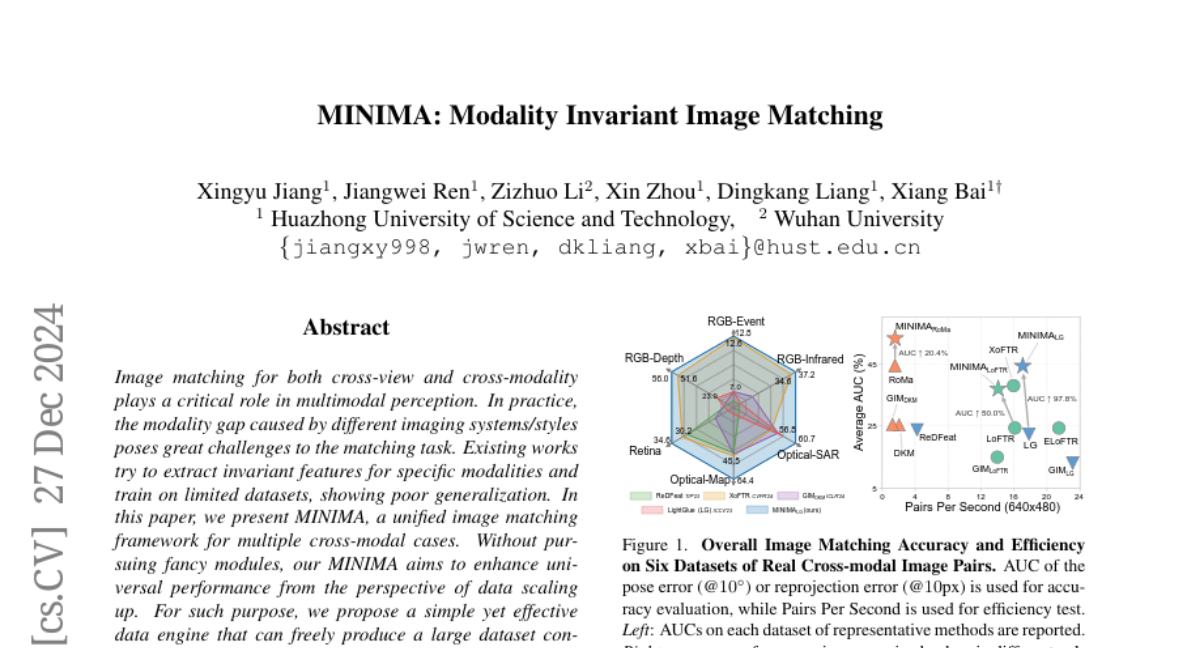
10. MINIMA: Modality Invariant Image Matching
🔑 Keywords: Image matching, Cross-modality, Multimodal perception, MINIMA, Generative models
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce MINIMA, a unified image matching framework designed for cross-modality scenarios to enhance performance by leveraging data scaling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a data engine to generate large datasets from RGB data using generative models, creating diverse multimodal datasets for better training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MINIMA significantly outperforms baseline methods in extensive experiments across 19 cross-modal cases, demonstrating improved generalization beyond modality-specific approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2412.19412
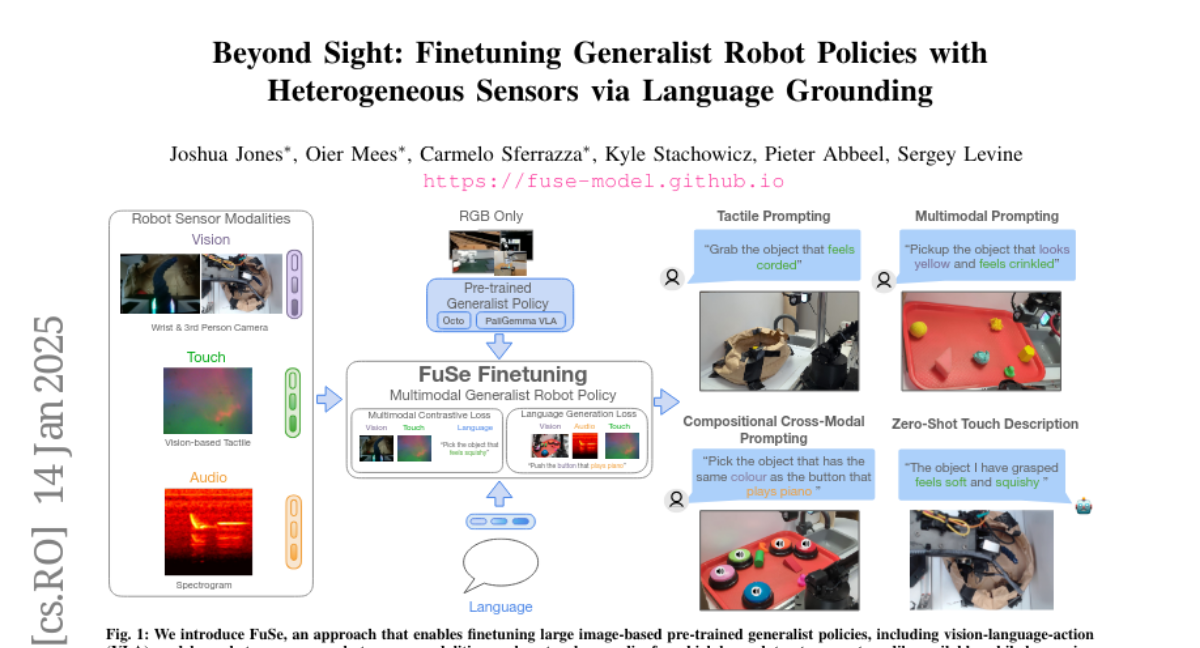
11. Beyond Sight: Finetuning Generalist Robot Policies with Heterogeneous Sensors via Language Grounding
🔑 Keywords: Multi-modal, FuSe, Visuomotor, Robotics
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose FuSe, a method for finetuning visuomotor generalist policies on various sensor modalities using natural language as a cross-modal grounding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed a multimodal contrastive loss along with sensory-grounded language generation loss to encode high-level semantics across vision, touch, and sound modalities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FuSe enhances success rates in robot manipulation tasks by over 20%, allowing for effective multi-modal interaction and reasoning in a zero-shot setting.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.04693