AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250429

1. CipherBank: Exploring the Boundary of LLM Reasoning Capabilities through Cryptography Challenges
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Cryptographic Reasoning, AI Native
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
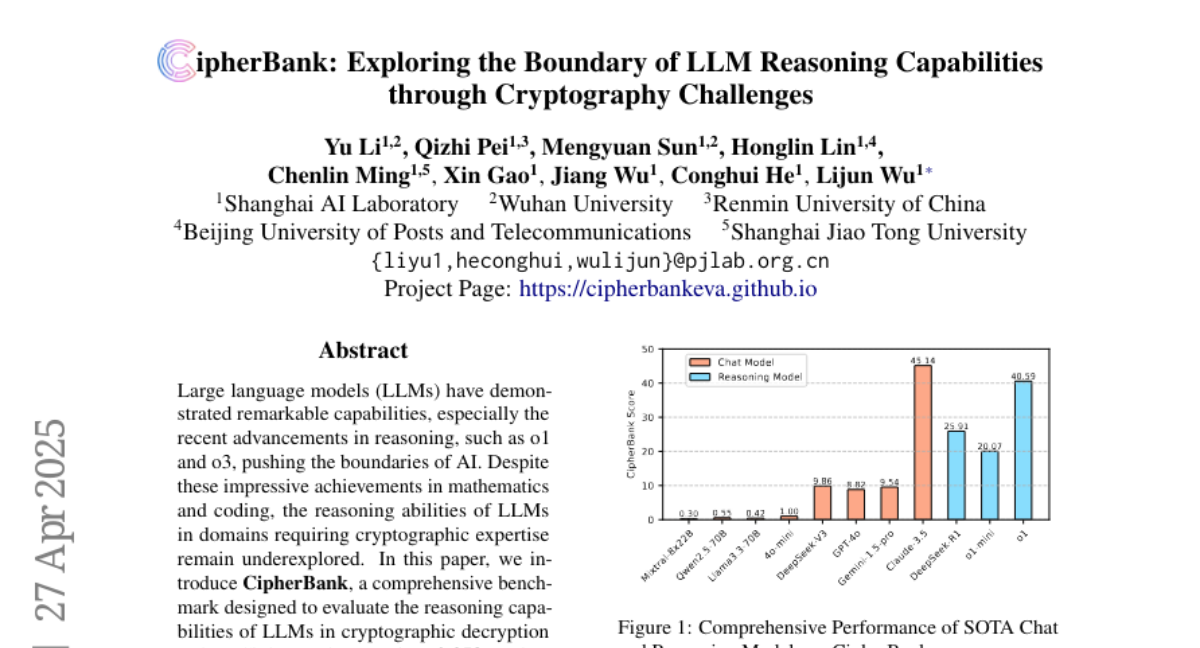
– The paper introduces CipherBank, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in cryptographic decryption tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– CipherBank contains 2,358 problems, 262 unique plaintexts across 5 domains and 14 subdomains, focusing on privacy-sensitive real-world scenarios.
– It incorporates 3 major encryption categories with 9 algorithms, evaluating state-of-the-art LLMs like GPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Significant gaps are found in the reasoning abilities of general-purpose chat LLMs and reasoning-focused LLMs in cryptographic tasks.
– The paper highlights challenges and potential improvement areas for LLMs in understanding and manipulating encrypted data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.19093
2. LLM-Powered GUI Agents in Phone Automation: Surveying Progress and Prospects
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models (LLMs), Phone Automation, Multimodal Perception, Reinforcement Learning, User-Centric Adaptation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to review the evolution of LLM-driven phone GUI agents, focusing on how these models transform automation by addressing challenges like limited generality and weak intent comprehension.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper presents a taxonomy of agent frameworks and modeling approaches, including single-agent and multi-agent systems, as well as prompt engineering and training-based strategies. It also explores task-specific architectures and methodologies like supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning strategies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The review highlights remaining challenges, such as dataset diversity and security concerns, and suggests that the paper serves as a comprehensive reference for utilizing LLMs to design scalable, user-friendly phone GUI agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.19838

3. SPC: Evolving Self-Play Critic via Adversarial Games for LLM Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Self-Play Critic, Chain-of-Thought, Adversarial Self-Play, Reinforcement Learning, Step-Level Annotation
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the step-by-step reliability of large language model reasoning by eliminating the need for manual step-level annotation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introducing Self-Play Critic (SPC) where two fine-tuned models, a “sneaky generator” and a “critic,” engage in adversarial self-play games to assess and improve reasoning steps using reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SPC enhances error detection capabilities, achieving improved accuracy on reasoning benchmarks and enhances mathematical reasoning performance in diverse LLMs, outperforming state-of-the-art models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.19162

4. MMInference: Accelerating Pre-filling for Long-Context VLMs via Modality-Aware Permutation Sparse Attention
🔑 Keywords: Vision Language Models, Multi-Modal, Sparse Attention, Long-Context
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the challenge of quadratic attention complexity in Vision Language Models by introducing a method to accelerate the prefilling stage for long-context inputs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce MMInference, a dynamic sparse attention method utilizing a unique Grid pattern, optimized GPU kernels, and permutation-based techniques to efficiently manage sparse distributions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MMInference significantly accelerates the prefilling stage by up to 8.3 times at 1M tokens without sacrificing accuracy, seamlessly integrating into existing VLM pipelines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.16083

5. Benchmarking Multimodal Mathematical Reasoning with Explicit Visual Dependency
🔑 Keywords: Large Vision-Language Models, VCBENCH, Multimodal Reasoning, Visual-Mathematical Integration
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to identify a gap in current benchmarks concerning the evaluation of elementary-level mathematical problems requiring integration of visual and linguistic information.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of VCBENCH, a benchmark designed for assessing multimodal mathematical reasoning with explicit visual dependencies, comprising 1,720 problems across six cognitive domains with 6,697 images.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Evaluation of 26 state-of-the-art LVLMs reveals substantial performance disparities with accuracies below 50%, highlighting challenges in visual-mathematical integration and suggesting areas for future advancements in LVLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.18589

6. RepText: Rendering Visual Text via Replicating
🔑 Keywords: Text-to-image generation, Typographic elements, Multilingual visual text, ControlNet
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance text-to-image generation models to accurately render multilingual visual text in user-specified fonts without understanding the text.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a language-agnostic approach from ControlNet incorporating glyph and positioning. It employs a text perceptual loss alongside diffusion loss, and uses noisy glyph latent with region masks to ensure accurate rendering.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The RepText model effectively improves accuracy in rendering non-Latin alphabets and outperforms open-source methods while matching closed-source models. Despite its effectiveness, the study also delves into the approach’s limitations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.19724

7. ChiseLLM: Unleashing the Power of Reasoning LLMs for Chisel Agile Hardware Development
🔑 Keywords: Domain-Specific Architecture, Agile Hardware Development Methodology, Large Language Models, Chisel, Syntax Correctness
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve code generation for Domain-Specific Architecture using Agile Hardware Development Methodology with a focus on enhancing syntax correctness and design variability in Chisel code through model adaptation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study involves constructing high-quality datasets, applying prompt-guided reasoning trace synthesis, and employing domain-adapted model training to guide models in structured thinking patterns for Chisel code generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The ChiseLLM-7B and ChiseLLM-32B models achieved significant improvements, with syntax correctness enhanced by 18.85% and 26.32% over base models, and design variability increased by 47.58% compared to baseline reasoning models. The datasets and models are publicly available, providing effective resources for future research in HCL-Based AHDM.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.19144

8. ICL CIPHERS: Quantifying “Learning” in In-Context Learning via Substitution Ciphers
🔑 Keywords: In-Context Learning, Task Retrieval, Task Learning, Substitution Ciphers, Language Model
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to explore the dual modes of In-Context Learning (ICL), focusing on task retrieval and task learning through a novel class of task reformulations called ICL CIPHERS.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs substitution ciphers from classic cryptography, substituting a subset of tokens in inputs with irrelevant tokens while maintaining a bijective, reversible pattern.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The findings reveal that Large Language Models (LLMs) perform better at solving tasks with bijective mappings compared to non-bijective baselines, showcasing their capability to decipher latent ciphers across various datasets and models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.19395

9. TrustGeoGen: Scalable and Formal-Verified Data Engine for Trustworthy Multi-modal Geometric Problem Solving
🔑 Keywords: Geometric Problem Solving, Multimodal Information, Benchmark, Formal Verification
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop a scalable data engine called TrustGeoGen that integrates multimodal information and ensures logical coherence for generating geometric problem-solving benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Synthesis of geometric data through multimodal-aligned generation, formal verification for rule compliance, a bootstrapping mechanism for complexity escalation, and GeoExplore series algorithms for producing multi-solution variants.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TrustGeoGen generates a GeoTrust-200K dataset with high modality integrity. Models show a stringent 49.17% accuracy on the GeoTrust-test, and improved OOD generalization on GeoQA compared to traditional pseudo-labeled models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.15780

10. Versatile Framework for Song Generation with Prompt-based Control
🔑 Keywords: Song Generation, Multi-task, VersBand, VocalBand, AccompBand
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to produce controllable high-quality songs through the VersBand framework, addressing challenges in generating aligned vocals and accompaniments with prompt-based control.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a multi-model system with VocalBand for vocal generation using a flow-matching method, AccompBand for accompaniment using a flow-based transformer model, and LyricBand and MelodyBand for song components.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VersBand outperforms baseline models in multiple song generation tasks, demonstrating superior performance in both objective and subjective measures.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.19062

11. Mem0: Building Production-Ready AI Agents with Scalable Long-Term Memory
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Context Windows, Memory-Centric Architecture, Graph-Based Memory Representations, Long-Term Conversational Coherence
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Mem0, a scalable architecture to enhance memory mechanisms in Large Language Models (LLMs) for maintaining consistency over extended multi-session dialogues.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed Mem0 with dynamic extraction, consolidation, and retrieval of salient information and further enhanced with graph-based memory representations. Evaluated against six baseline categories on the LOCOMO benchmark.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Mem0 and its enhanced version outperform other memory systems across various question categories, achieving notable improvements in accuracy and computational efficiency, significantly reducing latency and token costs while enhancing conversational coherence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.19413

12. Group Downsampling with Equivariant Anti-aliasing
🔑 Keywords: Downsampling layers, CNN architectures, G-CNNs, Anti-aliasing
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to generalize uniform downsampling layers for group equivariant architectures like G-CNNs by targeting the downsampling of signals on general finite groups with anti-aliasing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– An algorithm is presented to form a suitable choice of subgroup given a finite group and downsampling rate.
– The study explores the concept of bandlimited-ness and proposes a method for anti-aliasing within G-equivariant networks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed downsampling operation enhances accuracy, better preserves equivariance, and reduces model size in image classification tasks through its integration in G-equivariant networks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.17258

13. Clinical knowledge in LLMs does not translate to human interactions
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, medical advice, user interactions, GPT-4o, healthcare
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To test if large language models (LLMs) can assist the public in identifying medical conditions and choosing a course of action in medical scenarios.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted a controlled study with 1,298 participants, comparing assistance from LLMs (GPT-4o, Llama 3, Command R+) to a control source.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LLMs performed well in identifying conditions but failed to enhance users’ performance in practical scenarios due to user interaction challenges.
– Standard medical benchmarks do not predict user interaction failures, suggesting a need for systematic human user testing before deploying LLMs in healthcare.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.18919

14. NORA: A Small Open-Sourced Generalist Vision Language Action Model for Embodied Tasks
🔑 Keywords: Visual-Language-Action (VLA) models, Zero-shot scenarios, NORA, Computational overhead, Real-time robotic autonomy
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the limitations in existing VLA models by proposing a novel method, NORA, that reduces computational overhead while maintaining high task performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– NORA is based on the Qwen-2.5-VL-3B multimodal model which enhances visual reasoning and action grounding. It is trained on 970k real-world robot demonstrations with the FAST+ tokenizer for efficient action sequence generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– NORA outperforms existing large-scale VLA models by achieving better task performance with significantly reduced computational overhead, making it suitable for real-time robotic environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.19854
