AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250508

1. Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation Models: Advances, Challenges, and Opportunities
🔑 Keywords: multimodal understanding, image generation, autoregressive-based architectures, diffusion-based models, GPT-4o
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to explore and present a comprehensive overview of unification efforts between multimodal understanding and image generation domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A survey that categorizes existing unified models into diffusion-based, autoregressive-based, and hybrid approaches, analyzing their structural designs and innovations.
– Compilation of datasets and benchmarks specifically for unified models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current research in unification showcases significant architectural challenges but also promising advancements, with emphasis on tokenization strategy and cross-modal attention.
– The field is nascent, suggesting potential for rapid development and a need for regular updates to the survey.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.02567

2. ZeroSearch: Incentivize the Search Capability of LLMs without Searching
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Search Capabilities, ZeroSearch, API Costs
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the search capabilities of large language models (LLMs) without relying on live search engines or incurring high costs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced ZeroSearch, a framework that uses lightweight supervised fine-tuning to transform an LLM into a retrieval module. Utilized a curriculum-based rollout strategy during reinforcement learning to gradually enhance the model’s reasoning ability by presenting increasingly challenging retrieval scenarios.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ZeroSearch effectively boosts search capabilities of LLMs, with larger modules outperforming real search engines. It generalizes well to various model sizes and aligns with multiple RL algorithms.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.04588

3. Beyond Recognition: Evaluating Visual Perspective Taking in Vision Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Vision Language Models, visual tasks, spatial reasoning, visual perspective taking, geometric representations
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the ability of Vision Language Models (VLMs) in performing visual perspective taking using a set of novel visual tasks inspired by human tests.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of controlled scenes with a humanoid minifigure and object, varying spatial configurations to create 144 unique visual tasks, paired with 7 diagnostic questions assessing scene understanding, spatial reasoning, and perspective taking.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– State-of-the-art models excel in scene understanding but show significant performance decline in spatial reasoning and perspective taking, revealing a gap in deep spatial and perspective reasoning. There’s a need for explicit geometric representations and tailored training protocols in future VLM development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.03821

4. R&B: Domain Regrouping and Data Mixture Balancing for Efficient Foundation Model Training
🔑 Keywords: Data Mixing, Semantic Similarity, Domain Gradients, Gram Matrix
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve data mixing strategies by overcoming the limitations of predetermined data domains and computational scalability issues.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced R&B, a framework that rearranges (Regroup) training data based on semantic similarity and optimizes (Balance) data composition using a Gram matrix derived from domain gradients.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– R&B effectively enhances training efficiency and performance with minimal compute overhead, matching or surpassing state-of-the-art data mixing approaches across diverse datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.00358

5. HunyuanCustom: A Multimodal-Driven Architecture for Customized Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: multi-modal customized video generation, identity consistency, text-video alignment, HunyuanCustom, AudioNet
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a multi-modal video generation framework that improves identity consistency and supports various input modalities like image, audio, video, and text.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of HunyuanCustom framework leveraging a text-image fusion module and image ID enhancement for identity consistency.
– Use of modality-specific condition injection mechanisms, including AudioNet for audio-condition and a patchify-based network for video-condition generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HunyuanCustom outperforms existing models in ID consistency, realism, and text-video alignment, demonstrating robust performance in customized video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.04512

6. Benchmarking LLMs’ Swarm intelligence
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Multi-Agent Systems, swarm intelligence, coordination effectiveness, SwarmBench
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce SwarmBench to systematically evaluate swarm intelligence capabilities of LLMs in decentralized multi-agent systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Designed five foundational MAS coordination tasks within a configurable 2D grid environment, focusing on local sensory input and communication.
– Proposed metrics for coordination effectiveness and analyzed emergent group dynamics in a zero-shot setting.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Found significant performance variations across tasks highlighting challenges in local information constraints.
– Results indicated limitations in robust planning and strategy formation under uncertainty, emphasizing the importance of assessing LLMs in decentralized systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.04364

7. PrimitiveAnything: Human-Crafted 3D Primitive Assembly Generation with Auto-Regressive Transformer
🔑 Keywords: Primitive Assembly, Computer Vision, Shape Primitive Abstraction, Human Perception, Geometric Optimization
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To reformulate shape primitive abstraction as a primitive assembly generation task using a novel framework called PrimitiveAnything.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A shape-conditioned primitive transformer for auto-regressive generation and an ambiguity-free parameterization scheme to represent multiple types of primitives are introduced.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PrimitiveAnything can generate high-quality primitive assemblies that align with human perception while maintaining geometric fidelity across various shape categories.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.04622

8. Beyond Theorem Proving: Formulation, Framework and Benchmark for Formal Problem-Solving
🔑 Keywords: problem-solving, AI-based problem-solving agents, deterministic Markov decision process, formal theorem proving, human-alignment
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present a principled formulation of problem-solving as a deterministic Markov decision process and develop a novel framework, FPS, for process-verified problem-solving.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized formal theorem proving environments and developed D-FPS to separate solving and verification processes for better alignment with human reasoning.
– Constructed benchmarks like FormalMath500, MiniF2F-Solving, and PutnamBench-Solving; proposed RPE approach for evaluating correctness through formal verification.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Proven expressiveness, soundness, and completeness of the proposed frameworks.
– Evaluated performance on constructed benchmarks, achieving up to 27.47% solving rate with baseline models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.04528

9. OpenHelix: A Short Survey, Empirical Analysis, and Open-Source Dual-System VLA Model for Robotic Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: Dual-system VLA, embodied intelligence, open-source
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To summarize and compare the structural designs of existing dual-system Vision-Language-Action (VLA) architectures.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conduct systematic empirical evaluations on core design elements of existing dual-system architectures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Provides a low-cost open-source model for exploration, with ongoing updates and improvements available for further performance enhancements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.03912

10. OmniGIRL: A Multilingual and Multimodal Benchmark for GitHub Issue Resolution
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, OmniGIRL, Multi-Modal, Multilingual, Multi-Domain
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address limitations in existing GitHub issue resolution benchmarks by introducing OmniGIRL, which is multilingual, multimodal, and multi-domain.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– OmniGIRL benchmark consists of 959 task instances from repositories in Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, and Java across eight domains. It evaluates LLMs’ performance on GitHub issue resolution using both textual and image information.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current LLMs, including the best-performing models like GPT-4o and Claude-3.5-Sonnet, demonstrate limited capability on OmniGIRL, resolving only a small fraction of issues. The findings suggest that LLMs struggle particularly with issues requiring image understanding, highlighting areas for future improvement.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.04606

11. Knowledge Augmented Complex Problem Solving with Large Language Models: A Survey
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Chain-of-Thought reasoning, domain knowledge integration, result verification
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the capabilities and limitations of Large Language Models in complex problem-solving across various domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analysis of techniques like Chain-of-Thought reasoning, knowledge augmentation, and LLM-based and tool-based verification techniques.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The paper discusses the domain-specific challenges and fundamental limitations of current LLM solutions, highlighting future directions for LLMs in addressing complex problems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.03418

12. OSUniverse: Benchmark for Multimodal GUI-navigation AI Agents
🔑 Keywords: OSUniverse, GUI-navigation AI agents, SOTA, automated validation
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduction of OSUniverse as a benchmark for evaluating complex, multimodal desktop-oriented tasks for GUI-navigation AI agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Tasks are divided into increasing levels of complexity, with an automated validation mechanism ensuring accuracy with less than 2% error rate.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OSUniverse provides a robust framework for measuring the progress and capabilities of GUI-navigation AI agents, with current SOTA agents getting less than 50% success compared to perfect human performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.03570
13. OpenVision: A Fully-Open, Cost-Effective Family of Advanced Vision Encoders for Multimodal Learning
🔑 Keywords: OpenVision, vision encoder, multimodal framework, CLIP, multimodal models
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop fully-open, cost-effective vision encoders that match or surpass the performance of OpenAI’s CLIP in multimodal applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes existing training frameworks like CLIPS and datasets such as Recap-DataComp-1B, with the release of vision encoders ranging from 5.9M to 632.1M parameters.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OpenVision provides a flexible trade-off between capacity and efficiency, where larger models improve multimodal performance and smaller models facilitate edge-ready deployments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.04601

14. RAIL: Region-Aware Instructive Learning for Semi-Supervised Tooth Segmentation in CBCT
🔑 Keywords: Semi-supervised learning, 3D tooth segmentation, Region-Aware Instructive Learning (RAIL), pseudo-labels, intergroup knowledge transfer
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve 3D tooth segmentation from CBCT scans using a minimal labeled dataset by addressing challenges such as limited corrective supervision and unreliable pseudo-labels.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces RAIL, a semi-supervised framework with a dual-group dual-student structure and a shared teacher network, featuring mechanisms like Disagreement-Focused Supervision (DFS) and Confidence-Aware Learning (CAL) for enhanced learning and instruction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results demonstrate that RAIL outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in tooth segmentation under constraints of limited annotations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.03538

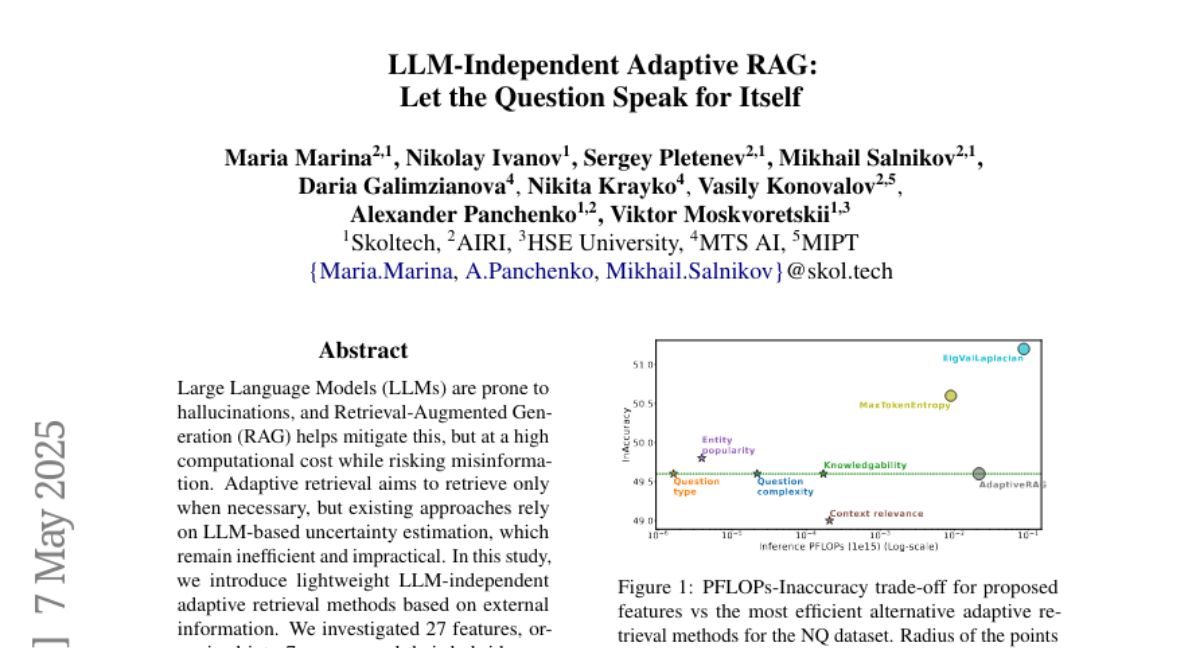
15. LLM-Independent Adaptive RAG: Let the Question Speak for Itself
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, adaptive retrieval, external information, QA performance
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces lightweight LLM-independent adaptive retrieval methods to mitigate hallucinations in large language models efficiently.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methodology involved investigating 27 features, creating hybrid combinations, and evaluating different methods on six QA datasets for performance and efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The findings highlight that the proposed methods match complex LLM-based approaches in performance while offering significant improvements in retrieval efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.04253
16. COSMOS: Predictable and Cost-Effective Adaptation of LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Large language models, Adaptation strategies, COSMOS framework, Prediction accuracy, Computational cost
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To accurately predict performance and cost of large language models’ adaptation strategies without extensive trials.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the COSMOS framework, featuring embedding-augmented lightweight proxy models and low-sample scaling laws for prediction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– COSMOS achieves high prediction accuracy and significantly reduces computational costs by an average of 92.72%, maintaining performance standards.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.01449

17. Uncertainty-Weighted Image-Event Multimodal Fusion for Video Anomaly Detection
🔑 Keywords: Image-Event Fusion, Video Anomaly Detection, event representations, Student’s-t likelihood, Kalman-style updates
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance video anomaly detection by incorporating Image-Event Fusion to synthesize and fuse event representations from RGB videos.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a Student’s-t likelihood for modeling sensor noise.
– Applies Kalman-style frame-wise updates for temporal balancing.
– Iteratively refines latent states to remove cross-modal noise.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed IEF-VAD framework sets a new state of the art in anomaly detection benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of synthetic event representations in improving motion cue detection without needing dedicated event sensors.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.02393

18. AutoLibra: Agent Metric Induction from Open-Ended Feedback
🔑 Keywords: AutoLibra, open-ended human feedback, fine-grained behaviors, agent evaluation, meta-metrics
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper proposes AutoLibra, a framework designed to improve the evaluation of agents by transforming open-ended human feedback into metrics for evaluating detailed behaviors in agent trajectories.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– AutoLibra grounds feedback to behaviors, clusters similar behaviors, and formulates concrete metrics for evaluating agents. It also introduces meta-metrics “coverage” and “redundancy” to align metrics with open feedback.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AutoLibra can induce more concrete evaluation metrics than existing benchmarks, leading to improved agent performance in text-based tasks by 20%, and aids in selecting high-quality fine-tuning data for web navigation agents, proving its effectiveness as a task-agnostic evaluation and improvement tool for language agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.02820

19. Cognitio Emergens: Agency, Dimensions, and Dynamics in Human-AI Knowledge Co-Creation
🔑 Keywords: Epistemic Partnerships, Human-AI Interaction, Knowledge Co-Creation, Epistemic Alienation
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to transform scientific knowledge creation by establishing co-evolutionary epistemic partnerships between humans and AI systems, moving beyond traditional tool-user dynamics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces the Cognitio Emergens framework, which addresses limitations in current models by integrating Agency Configurations, Epistemic Dimensions, and Partnership Dynamics to capture the emergence of scientific understanding through recursive human-AI interaction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– By reconceptualizing human-AI collaboration as co-evolutionary, the framework offers tools for cultivating partnerships that balance human involvement with AI advancements, preventing epistemic alienation and facilitating transformative scientific progress.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.03105

20.
