AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250616
1. Effective Red-Teaming of Policy-Adherent Agents
🔑 Keywords: CRAFT, policy-adherent agents, adversarial users, policy-aware persuasive strategies, tau-break
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– To assess and improve the robustness of policy-adherent LLM-based agents in customer service against adversarial attacks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a multi-agent red-teaming system, CRAFT, employing policy-aware persuasive strategies.
– Introduction of tau-break, a new benchmark for evaluating robustness against manipulative user behavior.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Conventional defense strategies provide some protection but are insufficient, highlighting the need for stronger safeguards against adversarial attacks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.09600

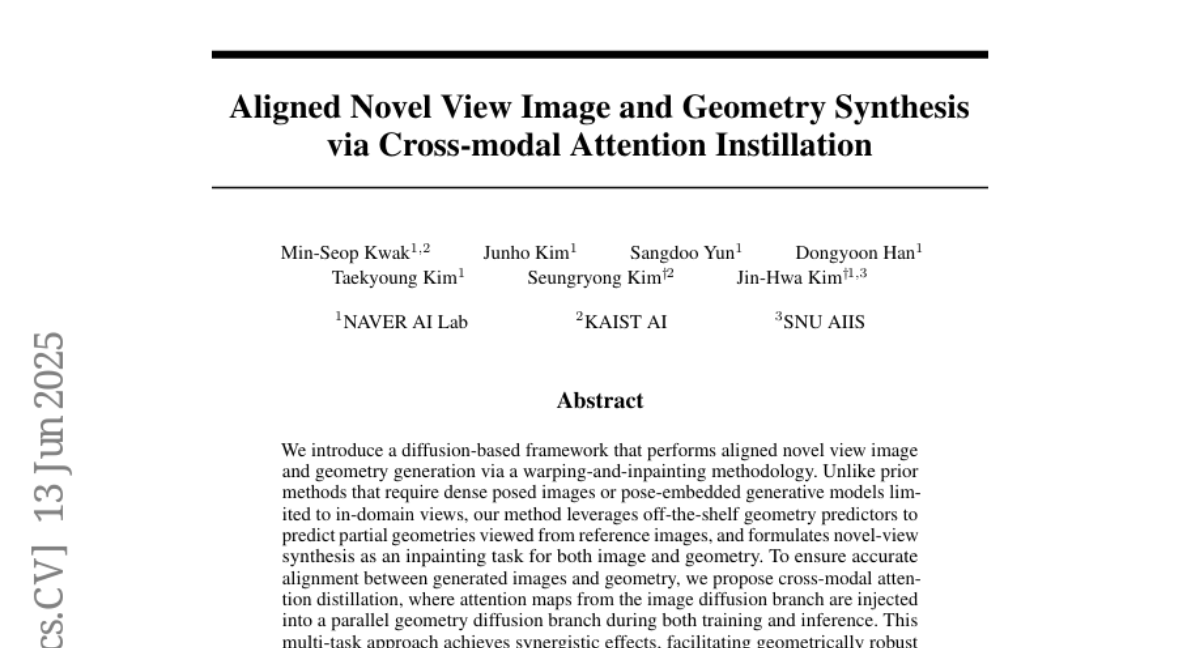
2. Aligned Novel View Image and Geometry Synthesis via Cross-modal Attention Instillation
🔑 Keywords: diffusion-based framework, novel-view synthesis, cross-modal attention distillation, multi-task approach, 3D completion
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The framework aims to generate aligned novel views of images and geometry using a unique combination of warping-and-inpainting techniques.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach leverages off-the-shelf geometry predictors and formulates synthesis as an inpainting task. Cross-modal attention distillation is used to ensure alignment between images and geometry, with a focus on a multi-task approach for robustness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method achieves high-fidelity image and geometry synthesis, particularly excelling in extrapolative view synthesis, and producing aligned colored point clouds for 3D completion across unseen scenes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11924
3. The Diffusion Duality
🔑 Keywords: Uniform-state discrete diffusion models, Gaussian diffusion, curriculum learning, Discrete Consistency Distillation, few-step generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance the speed and efficiency of Uniform-state discrete diffusion models for text generation by incorporating techniques from Gaussian diffusion.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors introduced a curriculum learning strategy driven by Gaussian processes to double the training speed and improve model performance.
– They adapted consistency distillation to a discrete setting through Discrete Consistency Distillation, enabling much faster few-step generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The models trained with curriculum learning show superior performance compared to autoregressive models in zero-shot perplexity on several benchmarks.
– The Discrete Consistency Distillation algorithm significantly accelerates sampling, opening up possibilities for rapid text generation in diffusion language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.10892
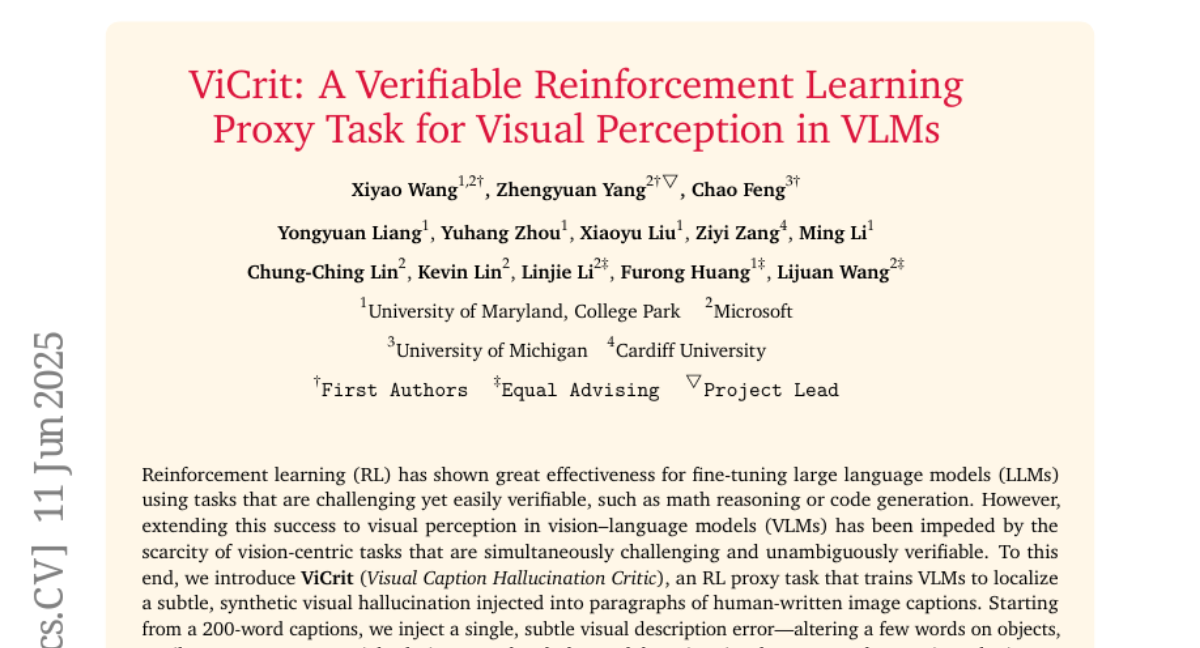
4. ViCrit: A Verifiable Reinforcement Learning Proxy Task for Visual Perception in VLMs
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Vision-Language Models, Visual Perception, ViCrit, Abstract Image Reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance visual perception in vision-language models (VLMs) by developing ViCrit, a task that trains models to detect subtle hallucinations in image captions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized Reinforcement Learning (RL) to create ViCrit, where models identify synthetic visual hallucinations in 200-word captions, allowing exact-match rewarding and transferability to diverse visual domains.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The ViCrit task results in substantial performance improvements across various VL benchmarks, showing potential in generalizing visual perception capabilities beyond memorization, with additional evaluation provided by the ViCrit-Bench diagnostic tool.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.10128
5. LiveCodeBench Pro: How Do Olympiad Medalists Judge LLMs in Competitive Programming?
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Competitive Programming, Algorithmic Reasoning, LiveCodeBench Pro
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the limitations of Large Language Models (LLMs) compared to human experts in competitive programming.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of LiveCodeBench Pro, a continuously updated benchmark consisting of problems from platforms like Codeforces, ICPC, and IOI, analyzed by Olympiad medalists.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LLMs excel in implementation-heavy tasks but struggle with nuanced algorithmic reasoning and complex case analysis, achieving limited success compared to human experts.
– The gap between LLM performance and human grandmaster levels is highlighted, emphasizing the need for improved reasoning in code-centric AI models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11928

6. Feedback Friction: LLMs Struggle to Fully Incorporate External Feedback
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, Feedback Friction, Generative Models, AI Native
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate how effectively LLMs can incorporate external feedback to improve their responses.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Designed controlled experimental environment with a feedback pipeline using near-complete ground-truth answers and various reasoning tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LLMs exhibit resistance to feedback even under optimal conditions, termed Feedback Friction.
– Sampling-based strategies show improvements, but challenges in achieving target performance persist.
– Several potential causes of Feedback Friction are explored, aiming to guide future research in self-improvement for LLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11930

7. SwS: Self-aware Weakness-driven Problem Synthesis in Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Verifiable Rewards, Self-aware, Weakness-driven, Problem Synthesis
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance large language model performance on reasoning tasks by employing a Self-aware Weakness-driven problem Synthesis framework that leverages model weaknesses.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of the Self-aware Weakness-driven problem Synthesis framework, identifying model deficiencies, and synthesizing new problems to address these weaknesses, enabling robust generalization in reinforcement learning training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework successfully improved model generalization without external knowledge distillation, leading to average performance gains of 10.0% and 7.7% on 7B and 32B models across mainstream reasoning benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.08989

8. DeepVideo-R1: Video Reinforcement Fine-Tuning via Difficulty-aware Regressive GRPO
🔑 Keywords: DeepVideo-R1, Reg-GRPO, Video Large Language Models, Video Reasoning, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance video reasoning performance using a novel approach called DeepVideo-R1 which integrates Reg-GRPO and difficulty-aware data augmentation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs a regression-based GRPO approach to reformulate the objective function, removing the need for safeguards.
– A difficulty-aware data augmentation strategy is used to dynamically enhance training samples to create a diverse and informative reward signal environment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed DeepVideo-R1 significantly improves video reasoning capabilities over various video reasoning benchmarks by employing direct policy guidance and optimizing model alignment with advantage values.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.07464

9. Beyond Homogeneous Attention: Memory-Efficient LLMs via Fourier-Approximated KV Cache
🔑 Keywords: FourierAttention, orthogonal Fourier bases, long-context accuracy, FlashFourierAttention
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance memory efficiency in Large Language Models using a training-free framework called FourierAttention.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Compressing long-context-insensitive transformer head dimensions with orthogonal Fourier bases to maintain accuracy without training.
– Designing a custom Triton kernel, FlashFourierAttention to optimize memory through efficient read-write operations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FourierAttention achieves the best long-context accuracy on benchmarks like LongBench and Needle-In-A-Haystack.
– Enables efficient deployment without compromising performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11886

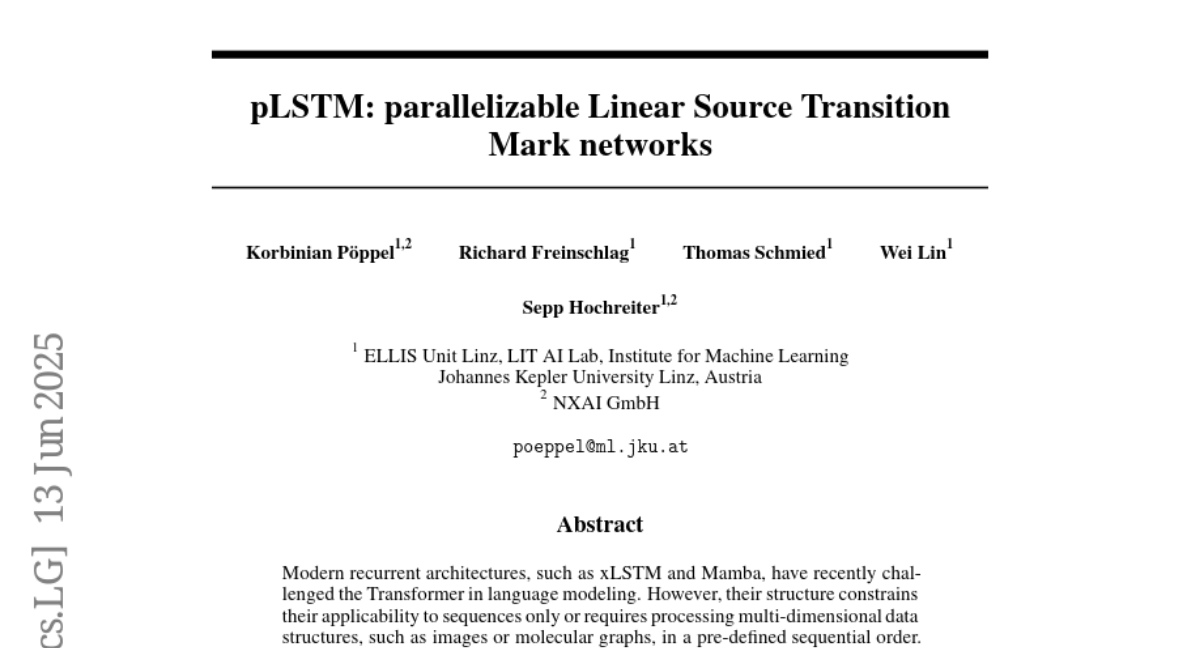
10. pLSTM: parallelizable Linear Source Transition Mark networks
🔑 Keywords: pLSTMs, DAGs, parallelization, long-range tasks, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aimed to extend multi-dimensionality to linear RNNs and introduce parallelizable Linear Source Transition Mark networks (pLSTMs) for improved performance on directed acyclic graphs (DAGs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors utilized Source, Transition, and Mark gates in pLSTMs, enabling parallelization with DAGs. For regular grids like images, efficient implementation was achieved using einsum operations, concatenations, and padding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– pLSTMs demonstrated strong performance on synthetic computer vision tasks by tackling long-range directional information, outpacing Transformers in extrapolation capabilities. They also performed well on molecular graph and computer vision benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11997
11. SkillBlender: Towards Versatile Humanoid Whole-Body Loco-Manipulation via Skill Blending
🔑 Keywords: SkillBlender, hierarchical reinforcement learning, task-agnostic primitive skills, loco-manipulation, reward engineering
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop a hierarchical reinforcement learning framework, SkillBlender, to solve diverse loco-manipulation tasks for humanoid robots using pretrained primitive skills.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework employs a novel approach by pretraining goal-conditioned, task-agnostic primitive skills and dynamically blending these skills with minimal task-specific reward engineering.
– A simulated benchmark, SkillBench, was introduced, encompassing various embodiments and tasks with scientific evaluation metrics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments demonstrate that SkillBlender significantly outperforms baseline models in accuracy and feasibility, with better regulation to avoid reward hacking.
– The framework and benchmark are open-sourced to facilitate further research in the community.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.09366

12. A High-Quality Dataset and Reliable Evaluation for Interleaved Image-Text Generation
🔑 Keywords: InterSyn, SEIR, SynJudge, multimodal understanding, image-text synergy
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve multimodal understanding and generation by introducing InterSyn, a large-scale dataset featuring tightly interleaved image-text outputs and enhanced quality refinement.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of the Self-Evaluation with Iterative Refinement (SEIR) method for constructing the InterSyn dataset.
– Introduction of SynJudge, an automatic evaluation tool to assess multimodal outputs on four dimensions, ensuring robust assessment capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SEIR method significantly enhances dataset quality, leading to better performance by LMMs across all evaluation metrics.
– InterSyn’s design and refinement make it an effective tool for advancing instruction-following capabilities in multimodal systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.09427

13. Detecting Harmful Memes with Decoupled Understanding and Guided CoT Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: U-CoT+, harmful meme detection, zero-shot CoT prompting, high-fidelity meme-to-text pipeline, small-scale LLMs
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop U-CoT+, a novel framework for detecting harmful memes with high flexibility and explainability using small-scale LLMs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementing a meme-to-text pipeline that converts visual memes into textual descriptions.
– Incorporating human-crafted guidelines for zero-shot CoT prompting to enhance flexibility and explainability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– U-CoT+ allows for resource-efficient detection of harmful memes and adapts to different harmfulness criteria across various platforms and regions.
– Extensive experiments confirm the efficacy of the framework using small-scale LLMs across seven benchmark datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.08477

14. Dense Retrievers Can Fail on Simple Queries: Revealing The Granularity Dilemma of Embeddings
🔑 Keywords: CapRetrieval, Text Encoders, Dense Retrieval, AI-generated summary, Granularity Dilemma
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce CapRetrieval dataset to assess text encoders’ ability to recognize fine-grained entities and events in dense retrieval tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conduct zero-shot evaluation and finetune text encoders using proposed data generation strategies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Text encoders often fail on fine-grained entity and event recognition, revealing a granularity dilemma, but improvements were noted after finetuning with proposed methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.08592

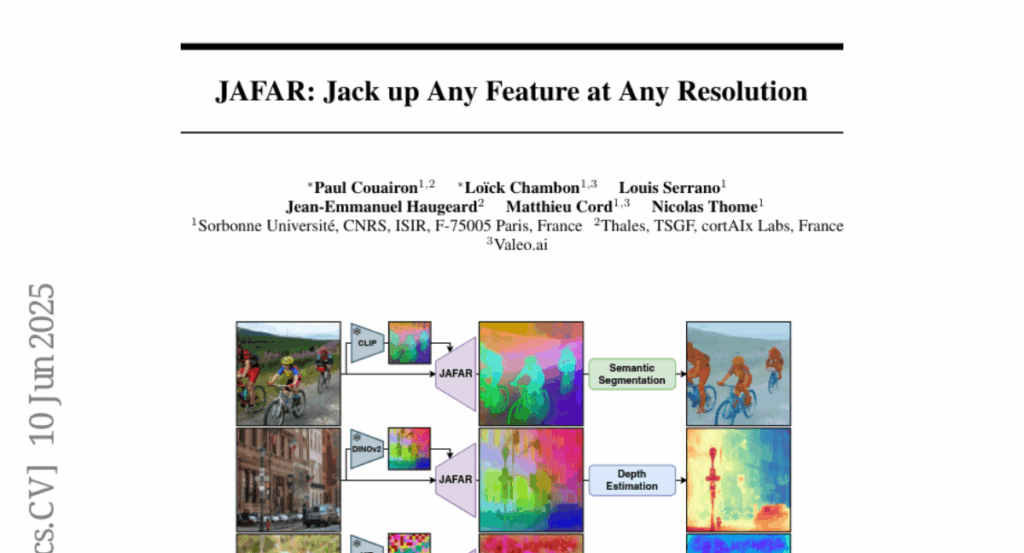
15. JAFAR: Jack up Any Feature at Any Resolution
🔑 Keywords: Foundation Vision Encoders, feature upsampling, attention-based module, Spatial Feature Transform, semantic alignment
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce JAFAR, a lightweight and flexible feature upsampler for enhancing the spatial resolution of visual features from Foundation Vision Encoders to any desired resolution.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ an attention-based module with Spatial Feature Transform modulation to align high-resolution queries with semantically enriched low-resolution keys without high-resolution supervision.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– JAFAR effectively recovers fine-grained spatial details and consistently outperforms existing feature upsampling methods across a variety of downstream tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11136

16. Learning a Continue-Thinking Token for Enhanced Test-Time Scaling
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Language Model, Continue-Thinking Token, Accuracy Improvement, Inference
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to explore the effectiveness of a dedicated continue-thinking token learned through reinforcement learning to improve language model accuracy during inference.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Incorporated a continue-thinking token into a distilled model version of DeepSeek-R1, trained its embedding with reinforcement learning while keeping the model weights frozen.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The learned continue-thinking token achieved higher accuracy compared to both the baseline model and a fixed-token approach with budget forcing, notably a 4.2% increase in accuracy on the GSM8K benchmark, outperforming a 1.3% improvement by the fixed-token method.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11274

17. Med-PRM: Medical Reasoning Models with Stepwise, Guideline-verified Process Rewards
🔑 Keywords: Med-PRM, Process Reward Modeling, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, Medical Knowledge Bases, AI in Healthcare
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance clinical decision making by verifying reasoning steps against medical knowledge databases, achieving improved accuracy in medical QA benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes process reward modeling framework combined with retrieval-augmented generation, verifying reasoning steps with evidence from clinical guidelines and literature.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art performance with up to 13.50% improvement in base models, demonstrating generality by integrating with models like Meerkat, achieving over 80% accuracy on MedQA.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11474

18. AbstentionBench: Reasoning LLMs Fail on Unanswerable Questions
🔑 Keywords: AbstentionBench, Large Language Models, uncertainty, reasoning fine-tuning, Abstention
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to evaluate the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to abstain from answering uncertain or unanswerable questions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of AbstentionBench, a benchmark evaluating abstention across 20 diverse datasets to analyze LLMs’ performance on questions with unknown answers, false premises, and subjective interpretations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Reasoning fine-tuning degrades the abstention capability of LLMs by an average of 24%, indicating it is an unresolved problem that scaling models does not address. A well-designed system prompt can improve practice results but does not solve the fundamental challenge of understanding uncertainty.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.09038

19. Prompt Candidates, then Distill: A Teacher-Student Framework for LLM-driven Data Annotation
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, candidate annotation paradigm, teacher-student framework, text classification
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a novel candidate annotation paradigm using a teacher-student framework to improve data quality for downstream applications by encouraging multiple label outputs from LLMs when uncertainty arises.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a teacher-student framework named CanDist to distill candidate annotations using a Small Language Model from the annotations generated by Large Language Models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method enhances data quality for downstream applications by providing superior theoretical guarantees and is validated through extensive experiments across six text classification tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03857

20. Infinity Instruct: Scaling Instruction Selection and Synthesis to Enhance Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Infinity-Instruct, instruction datasets, foundational instructions, chat instructions
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance both foundational and chat capabilities of Large Language Models using a newly curated and synthesized dataset called Infinity-Instruct.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a two-phase pipeline: Phase 1 involved curating 7.4M foundational instructions through hybrid data selection, and Phase 2 involved synthesizing 1.5M chat instructions using instruction selection, evolution, and diagnostic filtering.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Substantial performance gains were observed when fine-tuning open-source models, consistently surpassing official instruction-tuned counterparts. Notably, InfInstruct-LLaMA3.1-70B outperformed GPT-4-0314 by 8.6% on instruction following tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11116

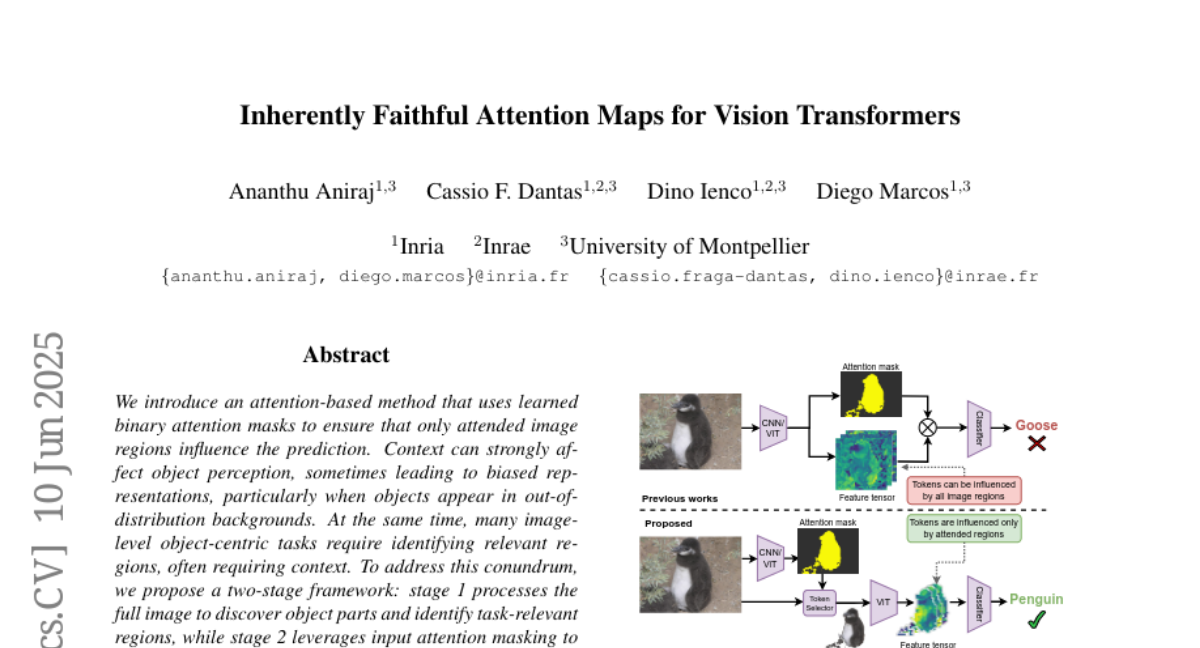
21. Inherently Faithful Attention Maps for Vision Transformers
🔑 Keywords: Attention-based method, Object perception, Task-relevant regions, Robustness, Spurious correlations
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve object perception robustness by focusing on relevant image regions using learned binary masks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a two-stage framework with attention-based method using learned binary attention masks, where Stage 1 identifies task-relevant regions, and Stage 2 restricts the receptive field to these regions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method significantly enhances robustness against spurious correlations and out-of-distribution backgrounds in various benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.08915
22. A Self-Refining Framework for Enhancing ASR Using TTS-Synthesized Data
🔑 Keywords: self-refining framework, ASR, pseudo-labels, TTS, synthesized speech, Whisper-large-v2, Twister, Mandarin, Mandarin-English code-switching
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance ASR performance using a self-refining framework with unlabeled datasets by integrating pseudo-labeling, TTS, and synthesized speech.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Use an existing ASR model to generate pseudo-labels on unannotated speech to train a TTS system. Then, bootstrap synthesized speech-text pairs into the ASR system.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework, demonstrated on Taiwanese Mandarin speech, significantly reduces error rates on Mandarin and Mandarin-English code-switching benchmarks, presenting a practical alternative to pseudo-labeling self-distillation approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11130

23. Reward Models Enable Scalable Code Verification by Trading Accuracy for Throughput
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Outcome Reward Model, Verification, Generate-Prune-Then-Rank
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Challenge the existing assumption that comprehensive verifiers should always be prioritized over Outcome Reward Models (ORMs) by exploring the tradeoff between speed and accuracy in coding tasks solved by Large Language Models (LLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Systematic exploration of the generate-prune-then-rank approach, which utilizes a faster, less accurate verifier to remove incorrect solutions before ranking, in contrast to using a full test suite.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The generate-prune-then-rank approach is significantly faster (11.65x) with minimal reduction in accuracy (only 8.33% less) than a full test suite, demonstrating its effectiveness in creating scalable and accurate program ranking systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.10056
24. LoRA-Edit: Controllable First-Frame-Guided Video Editing via Mask-Aware LoRA Fine-Tuning
🔑 Keywords: Video Editing, Diffusion Models, LoRA Tuning, Spatial Masks, Image-to-Video Models
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a mask-based LoRA tuning method to adapt pretrained Image-to-Video models for flexible and high-quality video editing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of spatial masks and reference images for context-specific adaptation without changing the model architecture.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method achieves superior video editing performance, preserving background regions while enabling controllable edits compared to state-of-the-art methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.10082
25. Mirage-1: Augmenting and Updating GUI Agent with Hierarchical Multimodal Skills
🔑 Keywords: Hierarchical Multimodal Skills, Skill-Augmented Monte Carlo Tree Search, long-horizon tasks, AI-generated summary, Mirage-1
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the performance of multimodal GUI agents in long-horizon tasks by addressing knowledge abstraction and bridging the domain gap between offline and online environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the Hierarchical Multimodal Skills (HMS) module to create a hierarchical knowledge structure through the abstraction of trajectories into execution, core, and meta-skills.
– Development of the Skill-Augmented Monte Carlo Tree Search (SA-MCTS) algorithm to efficiently utilize offline skills in online environments, reducing the action search space.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The newly proposed Mirage-1, a multimodal, cross-platform GUI agent, demonstrated superior performance, outperforming previous agents by up to 79% on various benchmarks such as AndroidWorld and AndroidLH.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.10387
26. Don’t Pay Attention
🔑 Keywords: Avey, Transformer, long-range dependencies, ranker, autoregressive neural processor
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose a new neural architecture, Avey, to improve processing of long-range dependencies in sequences compared to Transformer models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Avey uses a combination of a ranker and an autoregressive neural processor to identify and contextualize relevant tokens, allowing for effective processing of sequences beyond fixed context windows.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results show Avey’s superior performance over Transformers in handling long-range dependencies, with competitive results on short-range NLP tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11305

27. Configurable Preference Tuning with Rubric-Guided Synthetic Data
🔑 Keywords: Configurable Preference Tuning, language models, fine-grained control, human feedback, inference-time modulation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To challenge the static nature of embedded preferences in language models by introducing a dynamic framework, Configurable Preference Tuning (CPT).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing synthetically generated preference data from structured rubrics for system prompts, enabling models to dynamically adjust behavior based on human-interpretable directives.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CPT provides nuanced and context-dependent modulation of outputs at inference time without retraining, facilitating more precise control in AI alignment with human preferences.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.11702
28.
