AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250623
1. Drag-and-Drop LLMs: Zero-Shot Prompt-to-Weights
🔑 Keywords: Drag-and-Drop LLMs, Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning, LoRA, prompt-conditioned parameter generation, cross-domain generalization
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Drag-and-Drop LLMs (DnD) that utilize prompt-conditioned parameter generation to eliminate per-task training and achieve cross-domain generalization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a lightweight text encoder and a cascaded hyper-convolutional decoder to transform condition embeddings into LoRA weight updates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DnD offers substantial efficiency gains with up to 12,000 times lower overhead compared to full fine-tuning and enhances performance by up to 30% over traditional LoRA across various benchmarks.
– Demonstrates robust cross-domain generalization without prior exposure to target data or labels.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.16406
2. Vision-Guided Chunking Is All You Need: Enhancing RAG with Multimodal Document Understanding
🔑 Keywords: Large Multimodal Models, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, document chunking, semantic coherence, structural integrity
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces a novel multimodal document chunking method using Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) to enhance Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) performance by accurately processing complex PDF documents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach processes documents in configurable page batches, maintaining semantic coherence and structural integrity, and preserving cross-batch context to handle multi-page tables and embedded visuals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– This vision-guided method demonstrates improved chunk quality and downstream RAG performance compared to traditional RAG systems, showing superior preservation of document structure and semantic coherence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.16035

3. PAROAttention: Pattern-Aware ReOrdering for Efficient Sparse and Quantized Attention in Visual Generation Models
🔑 Keywords: PAROAttention, visual attention patterns, sparsification, quantization, INT8/INT4
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to reduce memory and computational costs in visual generation without significant performance loss by reorganizing visual attention patterns.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a novel Pattern-Aware token ReOrdering (PARO) technique that unifies diverse attention patterns into a hardware-friendly block-wise pattern, thereby enhancing sparsification and quantization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed PAROAttention method achieves nearly lossless video and image generation, with end-to-end latency speedup by 1.9x to 2.7x at lower density and bitwidths (INT8/INT4), compared to full-precision baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.16054

4. VIKI-R: Coordinating Embodied Multi-Agent Cooperation via Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: VIKI-Bench, VIKI-R, Vision-Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, Multi-Agent Cooperation
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to evaluate and improve visual-driven cooperation among diverse embodied agents using VIKI-Bench, a hierarchical benchmark developed for embodied multi-agent cooperation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of VIKI-Bench, featuring structured levels of evaluation including agent activation, task planning, and trajectory perception. It incorporates diverse robot embodiments, multi-view visual observations, and structured supervision signals.
– Proposal of VIKI-R, a two-stage framework that fine-tunes pretrained vision-language models with Chain-of-Thought annotations and reinforcement learning under multi-level reward signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VIKI-R significantly outperforms baseline methods across all task levels, demonstrating the utility of VIKI-Bench in advancing multi-agent, visual-driven cooperation.
– Reinforcement learning facilitates the emergence of compositional cooperation patterns among heterogeneous agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.09049

5. Hunyuan-GameCraft: High-dynamic Interactive Game Video Generation with Hybrid History Condition
🔑 Keywords: High-dynamic interactive video generation, Shared camera representation space, Hybrid history-conditioned training, Model distillation, Real-time deployment
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Hunyuan-GameCraft, a framework to address limitations in dynamics, generality, efficiency, and consistency for video generation in game environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a unified input representation and hybrid history-conditioned training strategy to improve the video generation process.
– Implementation of model distillation to enhance inference efficiency and suitability for real-time deployment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Hunyuan-GameCraft substantially improves visual fidelity, realism, and action controllability, significantly outperforming existing models in interactive game video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.17201

6. Optimizing Multilingual Text-To-Speech with Accents & Emotions
🔑 Keywords: TTS architecture, accent accuracy, phoneme alignment, emotion recognition, code switching
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve accent accuracy and emotion recognition in Hindi and Indian English TTS systems by integrating phoneme alignment and culture-sensitive emotion embeddings.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces a novel TTS architecture by extending the Parler-TTS model, incorporating language-specific phoneme alignment, hybrid encoder-decoder architecture, and dynamic accent code switching with residual vector quantization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved a 23.7% improvement in accent accuracy and 85.3% emotion recognition accuracy, outperforming existing TTS models. The system effectively maintains emotional consistency and accent shifts, receiving a high mean opinion score of 4.2/5 for cultural correctness from users.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.16310

7. DreamCube: 3D Panorama Generation via Multi-plane Synchronization
🔑 Keywords: 3D panorama generation, 2D foundation models, DreamCube, multi-plane synchronization, RGB-D diffusion model
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to extend 2D foundation models to 3D panorama generation by introducing multi-plane synchronization and the DreamCube model for achieving diverse appearances and accurate geometry.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Application of multi-plane synchronization to operators from 2D foundation models, and the introduction of DreamCube, a multi-plane RGB-D diffusion model to enhance the effectiveness of existing methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study showcases the successful extension of 2D foundation models through multi-plane synchronization, displayed by the DreamCube model’s ability to produce diverse and accurate 3D panoramas while ensuring multi-view consistency and effectiveness in panoramic image generation and depth estimation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.17206

8. Hunyuan3D 2.5: Towards High-Fidelity 3D Assets Generation with Ultimate Details
🔑 Keywords: Hunyuan3D 2.5, LATTICE, 3D diffusion models, physical-based rendering, multi-view architecture
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To advance shape and texture generation using 3D diffusion models and improve upon the capabilities of Hunyuan3D 2.0 with more detailed and high-fidelity 3D assets.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developing a new shape foundation model named LATTICE, trained with a scaled high-quality dataset and incorporating a new multi-view architecture for physical-based rendering.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Hunyuan3D 2.5 exhibits significant improvements in both shape and end-to-end texture generation, outperforming prior methods with sharper, detailed 3D shapes and accurate image-3D integration.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.16504

9. Machine Mental Imagery: Empower Multimodal Reasoning with Latent Visual Tokens
🔑 Keywords: Vision-language models, Multimodal reasoning, Latent visual tokens, Reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance vision-language models (VLMs) by integrating latent visual tokens to improve multimodal reasoning without generating explicit images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a framework called Mirage, which augments VLM decoding with latent visual tokens and uses a combination of supervision through distillation and reinforcement learning to enhance multimodal reasoning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Mirage successfully strengthens multimodal reasoning capabilities in VLMs without the need for explicit image generation, as demonstrated by experiments on diverse benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.17218
10. InfiniPot-V: Memory-Constrained KV Cache Compression for Streaming Video Understanding
🔑 Keywords: Real-time generation, Temporal-axis Redundancy, Value-Norm ranking, Streaming video understanding, On-device streaming video assistants
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to develop a training-free, query-agnostic framework, InfiniPot-V, that compresses the key-value cache during video encoding to enforce a fixed memory cap for streaming video understanding, enhancing real-time performance and accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– InfiniPot-V employs a lightweight compression technique that removes redundant tokens using the Temporal-axis Redundancy metric and retains significant tokens through Value-Norm ranking without needing prior training or knowledge of the query.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– InfiniPot-V significantly reduces peak GPU memory usage by up to 94%, sustains real-time generation, and matches or even surpasses the accuracy of full-cache methods across multiple models and benchmarks, efficiently solving the key-value cache bottleneck for on-device streaming video assistants.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.15745
11. Hunyuan3D 2.1: From Images to High-Fidelity 3D Assets with Production-Ready PBR Material
🔑 Keywords: 3D AI-generated content, Hunyuan3D 2.1, 3D generative model, texture synthesis, data preparation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To provide a comprehensive guide for generating high-resolution and textured 3D models using Hunyuan3D 2.1, focusing on making the process accessible for non-experts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a step-by-step tutorial covering data preparation, model architecture, training strategies, evaluation metrics, and deployment using Hunyuan3D 2.1.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The tutorial equips users with the knowledge to finetune or develop robust 3D generative models applicable in gaming, virtual reality, and industrial design.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.15442

12. UniFork: Exploring Modality Alignment for Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation
🔑 Keywords: UniFork, Y-shaped architecture, Transformer backbones, modality alignment, task-specific branches
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the challenge of optimal architectural design for unified image understanding and generation models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– An analysis of modality alignment behaviors in both task-specific expert models and current unified models.
– Introduction and evaluation of a novel Y-shaped architecture named UniFork through extensive ablation experiments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UniFork effectively balances shared learning and task specialization.
– It consistently outperforms fully shared Transformer architectures and achieves competitive or superior performance compared to task-specific models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.17202
13. From Intention to Execution: Probing the Generalization Boundaries of Vision-Language-Action Models
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action models, generalization, motor execution, simulation-based tasks, perceptual understanding
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate the generalization and motor execution capabilities of Vision-Language-Action models using a unified benchmark suite.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a probing suite with 50 simulation-based tasks across 10 subcategories, designed to assess language instruction, vision, and object recognition.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Vision-Language Models endow VLAs with robust perceptual understanding and high-level planning but fall short in precise motor execution. Finetuning on action data can compromise the VLM’s generalist reasoning abilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.09930

14. Reranking-based Generation for Unbiased Perspective Summarization
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, perspective summarization, reranking-based methods, preference tuning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve the evaluation and generation of perspective summaries by LLMs in real-world applications, particularly in political settings.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Two main methodologies are employed: identifying reliable metrics for summarization quality and examining the effectiveness of LLM-based methods beyond zero-shot inference using reranking and preference tuning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study finds that language model-based metrics outperform traditional ones by providing more reliable evaluation results. Additionally, employing reranking and preference tuning enhances the quality of the summaries generated by LLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.15925

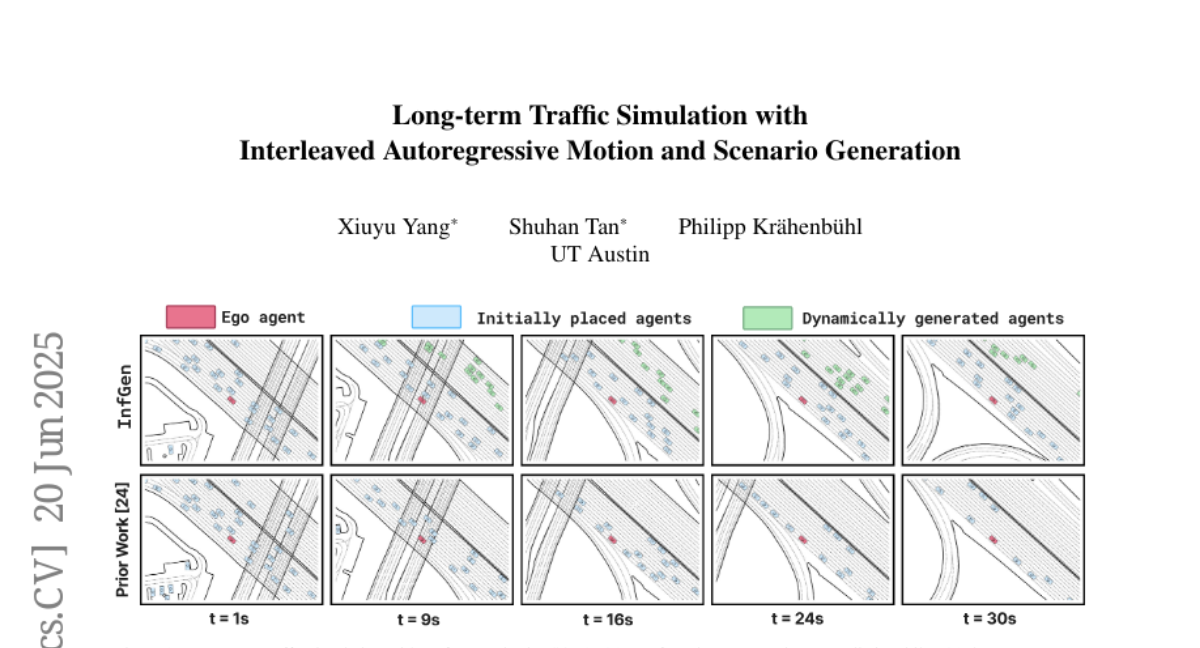
15. Long-term Traffic Simulation with Interleaved Autoregressive Motion and Scenario Generation
🔑 Keywords: InfGen, next-token prediction, closed-loop motion simulation, scene generation, long-term traffic simulation
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop a unified next-token prediction model, InfGen, that can facilitate stable long-term traffic simulation by integrating closed-loop motion simulation with scene generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– InfGen employs an automatic interchange between closed-loop motion simulation and scene generation to maintain a realistic traffic flow even as agents dynamically enter and exit the scene.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– InfGen demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in short-term traffic simulations of 9 seconds and significantly outperforms other methods in long-term traffic simulations of 30 seconds, providing a robust tool for reliable traffic modeling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.17213
16. MEXA: Towards General Multimodal Reasoning with Dynamic Multi-Expert Aggregation
🔑 Keywords: MEXA, Multimodal Reasoning, Large Reasoning Model, Expert Models
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce MEXA, a framework for modality- and task-aware aggregation of expert models for multimodal reasoning across various domains without training requirements.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MEXA dynamically selects expert models based on input modalities and task-specific reasoning needs, utilizing a Large Reasoning Model for output aggregation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MEXA delivers performance improvements on diverse benchmarks, demonstrating its effectiveness and broad applicability in multimodal reasoning tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.17113

17. Watermarking Autoregressive Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: Watermarking, Autoregressive Image Generation Models, Token Level, Reverse Cycle-Consistency, Synchronization Layer
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop the first watermarking approach for autoregressive image generation models at the token level to ensure reliable detection and provenance tracking.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Adaptation of language model watermarking techniques to image generation.
– Introduction of a custom tokenizer-detokenizer finetuning procedure to enhance reverse cycle-consistency.
– Implementation of a watermark synchronization layer to improve robustness against transformations and attacks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method enables reliable and robust watermark detection in autoregressive image generation models, demonstrated with theoretically grounded p-values.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.16349

18. Better Language Model Inversion by Compactly Representing Next-Token Distributions
🔑 Keywords: Prompt Inversion, Logprob Sequences, Language Model Inversion, Prompt Recovery, Next-Token Probabilities
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces a new method called Prompt Inversion from Logprob Sequences (PILS) aimed at recovering hidden prompts in language models by analyzing next-token probabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method leverages the insight that language model outputs exist in a low-dimensional subspace, allowing for efficient compression of next-token probability distributions which aids in prompt recovery.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PILS achieves significantly higher exact recovery rates than previous methods, with improvements between 2 to 3.5 times, and demonstrates robust generalization capabilities. Additionally, the method appears effective for recovering hidden system messages and highlights vulnerabilities in current model security concerning inversion attacks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.17090

19.
