AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250625
1. AnimaX: Animating the Inanimate in 3D with Joint Video-Pose Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: AnimaX, video diffusion models, skeleton-based animation, multi-view pose sequences, inverse kinematics
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal of AnimaX is to bridge the motion priors from video diffusion models with controllable structures in skeleton-based 3D animation, allowing for diverse articulated meshes with arbitrary skeletons.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– AnimaX employs a joint video-pose diffusion approach with shared positional encodings and modality-aware embeddings to achieve spatial-temporal alignment, facilitating the conversion of multi-view 2D pose maps into 3D joint positions using inverse kinematics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AnimaX demonstrates state-of-the-art results on VBench for generalization, motion fidelity, and efficiency, providing a scalable solution for category-agnostic 3D animation using a curated dataset of 160,000 rigged sequences.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19851
2. Matrix-Game: Interactive World Foundation Model
🔑 Keywords: Matrix-Game, interactive world foundation model, large-scale unlabeled pretraining, action-labeled training, controllable image-to-world generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Matrix-Game, a model for controllable game world generation using Minecraft videos.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Uses a two-stage training pipeline: large-scale unlabeled pretraining and action-labeled training.
– Developed a comprehensive Minecraft dataset, enabling controllable image-to-world generation with over 17 billion parameters.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Matrix-Game outperforms previous Minecraft world models in visual quality, controllability, and physical consistency.
– The model and benchmark will be open-sourced to support future research on interactive image-to-world generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.18701
3. Skywork-SWE: Unveiling Data Scaling Laws for Software Engineering in LLMs
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, SWE datasets, Skywork-SWE model, data scaling, test-time scaling techniques
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the performance of large language models (LLMs) on software engineering (SWE) tasks by developing an automated data-curation pipeline that increases dataset volume and diversity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– An incremental, automated data-curation pipeline was proposed, generating a dataset of 10,169 Python task instances from GitHub. This dataset includes runtime-environment images for automated unit-test validation, facilitating the training of the Skywork-SWE model.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study uncovered a data scaling phenomenon, where the model’s performance in software engineering capabilities continued to improve as data size increased, without saturation. The Skywork-SWE model achieved state-of-the-art performance on the SWE-bench Verified benchmark, with and without test-time scaling techniques, and results were further enhanced by test-time scaling techniques.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19290

4. GRPO-CARE: Consistency-Aware Reinforcement Learning for Multimodal Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: GRPO-CARE, SEED-Bench-R1, Multimodal LLMs, Reinforcement Learning, Video Understanding
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces GRPO-CARE, aiming to optimize consistency and correctness in multimodal large language models (MLLMs), improving both performance and logical coherence.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– This study proposes a new benchmark called SEED-Bench-R1 for evaluating MLLMs using complex real-world video scenarios. GRPO-CARE is evaluated with a two-tiered reward system to ensure both answer correctness and reasoning coherence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GRPO-CARE outperforms standard GRPO by achieving significant improvements in performance and logical consistency on SEED-Bench-R1, with 6.7% gain on the hardest level and 24.5% improvement in consistency, highlighting strong transferability across video understanding benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.16141

5. ScaleCap: Inference-Time Scalable Image Captioning via Dual-Modality Debiasing
🔑 Keywords: ScaleCap, Image Captioning, Multimodal Bias, Linguistic Bias, LVLMs
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces ScaleCap, a strategy aimed at improving image captioning by addressing multimodal and linguistic biases to enhance accuracy, balance, and informativeness.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– ScaleCap employs heuristic question answering and contrastive sentence rating to iteratively enrich and calibrate captions, tackling biases by progressively injecting relevant information and eliminating hallucinations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ScaleCap was validated through extensive modality alignment experiments, demonstrating its effectiveness. It consistently improves LVLM pretraining performance across 11 benchmarks and excels in additional tasks like VQA and semantic coverage assessment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19848
6. JarvisArt: Liberating Human Artistic Creativity via an Intelligent Photo Retouching Agent
🔑 Keywords: JarvisArt, MLLM, AI-generated, Chain-of-Thought supervised fine-tuning, Group Relative Policy Optimization
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce JarvisArt, an MLLM-driven agent, to improve photo retouching by understanding user intent and coordinating multiple Lightroom tools.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a two-stage training process combining Chain-of-Thought supervised fine-tuning and Group Relative Policy Optimization for enhanced decision-making and tool proficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– JarvisArt outperforms GPT-4o by 60% on novel benchmarks like MMArt-Bench in photo retouching tasks, demonstrating superior generalization and control.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.17612

7. SWE-SQL: Illuminating LLM Pathways to Solve User SQL Issues in Real-World Applications
🔑 Keywords: SQL Debugging, Open-Source Models, BIRD-CRITIC, Six-Gym, f-Plan Boosting
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance the performance of open-source models in debugging SQL issues using the newly introduced benchmark and training environments, BIRD-CRITIC and Six-Gym.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers developed BIRD-CRITIC, comprising PostgreSQL and multi-dialect SQL tasks, for rigorous evaluation and proposed Six-Gym leveraging SQL-Rewind for dataset generation and f-Plan Boosting for improving training trajectories.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Bird-Fixer, an open-source agent based on Qwen-2.5-Coder-14B, demonstrates notable performance, exceeding proprietary models and achieving a success rate of 38.11% and 29.65% on BIRD-CRITIC-PG and BIRD-CRITIC-Multi, respectively, indicating progress towards democratizing SQL-debugging capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.18951

8. Can Large Language Models Capture Human Annotator Disagreements?
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, Human Annotation Variation, Disagreement Prediction, RLVR-style
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to predict human annotation disagreements without access to repeated human labels.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Extensive evaluation of LLMs in modeling annotation disagreements and the effect of RLVR-style reasoning on this task.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LLMs struggle to predict annotation disagreements, which are often ignored by majority label-based evaluations.
– RLVR-style reasoning decreases LLM performance in disagreement prediction, highlighting the need for improving LLMs in this area.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19467

9. Guidance in the Frequency Domain Enables High-Fidelity Sampling at Low CFG Scales
🔑 Keywords: Frequency-decoupled guidance, Classifier-free guidance, Diffusion models, Frequency domain, Image quality
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve image quality and diversity in diffusion models by separately controlling low- and high-frequency guidance components.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of frequency-decoupled guidance (FDG), which breaks down classifier-free guidance into low- and high-frequency components, applying separate strengths to each.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FDG enhances sample fidelity and diversity, improving FID scores and recall compared to standard classifier-free guidance, and is proposed as a plug-and-play alternative.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19713
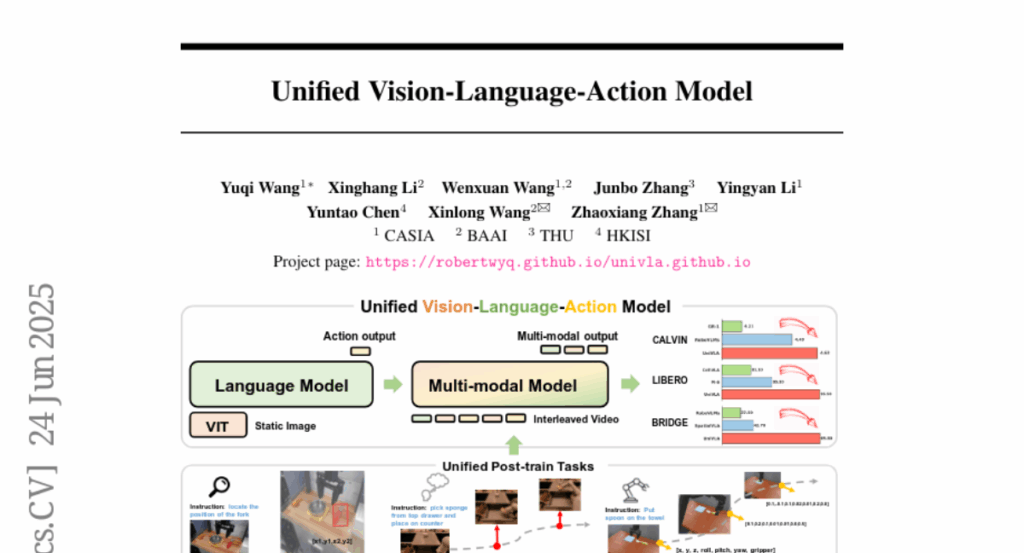
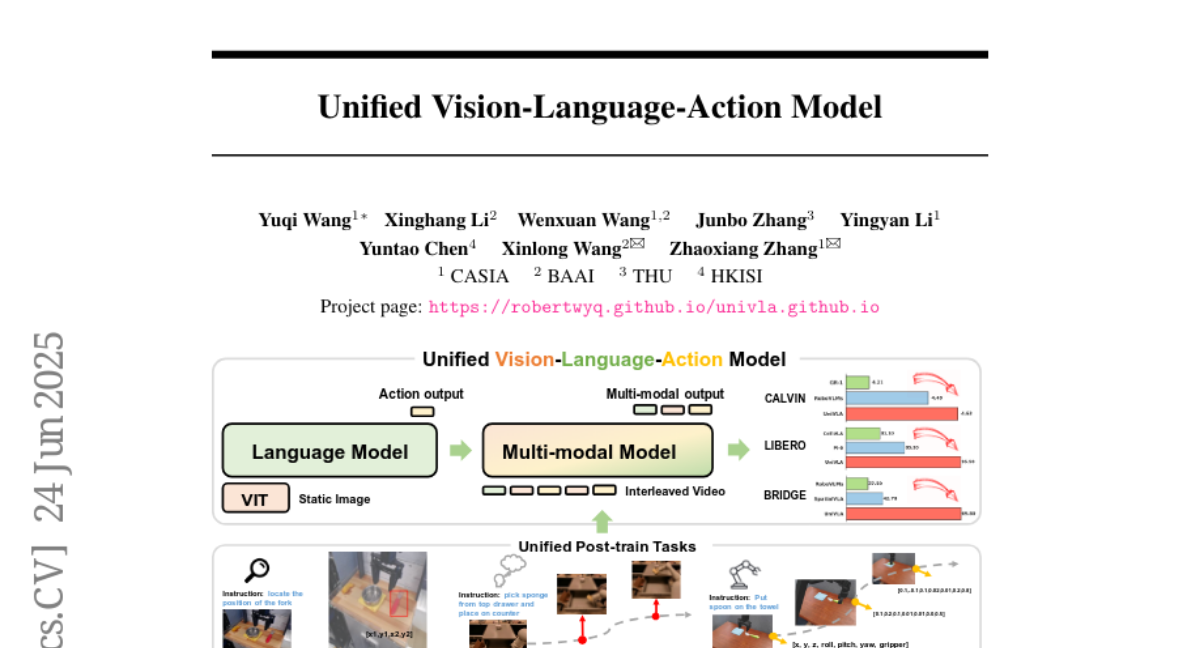
10. Unified Vision-Language-Action Model
🔑 Keywords: UniVLA, Multimodal Tasks Learning, World Modeling, Causal Dynamics
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a unified multimodal VLA model, UniVLA, which processes vision, language, and action as token sequences for improved policy learning in robotic manipulation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize an autoregressive approach to model vision, language, and action as token sequences.
– Incorporate world modeling to capture causal dynamics from large-scale video data, enabling effective transfer to long-horizon tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UniVLA sets a new state-of-the-art across multiple benchmarks, achieving a 95.5% success rate on the LIBERO benchmark.
– Demonstrates broad applicability on both simulation and real-world contexts, including robotic manipulation and autonomous driving.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19850
11. Chain-of-Experts: Unlocking the Communication Power of Mixture-of-Experts Models
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-Experts, Mixture-of-Experts, sequential expert communication, iterative routing, expert specialization
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose a new Mixture-of-Experts architecture called Chain-of-Experts (CoE) that improves performance and memory efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces sequential expert communication within each layer, dynamically routing tokens through a chain of experts using a dedicated router for each iteration.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CoE improves model performance, demonstrated by reduced validation loss on math reasoning tasks, and offers an additional scaling axis that reduces memory usage while enhancing expert specialization through iterative routing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.18945

12. Lost in the Mix: Evaluating LLM Understanding of Code-Switched Text
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, code-switching, comprehension, fine-tuning, embedding
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper investigates how Large Language Models (LLMs) process and reason about mixed-language text, specifically under code-switching conditions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A systematic evaluation involving generating code-switching variants of established reasoning and comprehension benchmarks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Embedding English into other languages can enhance LLM comprehension.
– Prompting shows mixed results, while fine-tuning offers a stable approach to mitigate degradation when processing code-switched inputs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.14012

13. USAD: Universal Speech and Audio Representation via Distillation
🔑 Keywords: Universal Speech and Audio Distillation, Self-supervised learning, audio representation, layer-to-layer distillation, single encoder
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a unified approach called Universal Speech and Audio Distillation (USAD) for audio representation learning that integrates diverse audio types into a single model.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes efficient layer-to-layer distillation from domain-specific SSL models to train a student on a comprehensive audio dataset.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– USAD achieves competitive performance across various benchmarks, demonstrating near state-of-the-art results on tasks like speech processing, audio tagging, and sound classification using a single encoder.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.18843

14. SRFT: A Single-Stage Method with Supervised and Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Supervised Reinforcement Fine-Tuning, Large Language Models, Entropy-aware weighting, Supervised Fine-Tuning, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to optimize language models using the integration of Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning through a method called Supervised Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (SRFT).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research utilizes an entropy-aware weighting mechanism that combines Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning in a single-stage optimization process for language models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Supervised Reinforcement Fine-Tuning method achieves a significant improvement in accuracy, outperforming zero-RL methods by 9.0% on mathematical reasoning benchmarks and by 10.9% on out-of-distribution benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19767

15. SimpleGVR: A Simple Baseline for Latent-Cascaded Video Super-Resolution
🔑 Keywords: cascaded video super-resolution, degradation strategies, timestep sampling, noise augmentation, sparse local attention
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the study is to enhance high-resolution video generation through the development of design principles for cascaded video super-resolution models. This includes the introduction of degradation strategies, timestep sampling, noise augmentation, and advanced temporal attention mechanisms.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research utilizes a decoupled two-stage approach for video generation, where a lightweight cascaded VSR model is employed for high-resolution synthesis. The authors also propose specific degradation strategies, analyze timestep sampling and noise augmentation on low-resolution inputs, and introduce interleaving temporal unit with sparse local attention to optimize computational efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study establishes a simple yet effective baseline for cascaded video super-resolution models, with extensive experiments and ablation studies demonstrating the superiority and efficiency of the proposed framework. It provides practical insights into improving future video generation systems through architectural and training innovations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19838

16. Why Do Open-Source LLMs Struggle with Data Analysis? A Systematic Empirical Study
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Data Analysis, Strategic Planning, Interaction Design, Data Quality
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance the data analysis capabilities of open-source large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluation of models across data understanding, code generation, and strategic planning using a curated seed dataset of diverse scenarios.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Strategic planning quality is key to model performance.
– Interaction design and task complexity significantly influence reasoning capabilities.
– Data quality impacts performance more than diversity.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19794

17. KnowRL: Exploring Knowledgeable Reinforcement Learning for Factuality
🔑 Keywords: KnowRL, Large Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, hallucination, factuality reward
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to reduce hallucinations in slow-thinking Large Language Models (LLMs) by incorporating factuality rewards into the reinforcement learning training process.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– KnowRL, a knowledge-enhanced reinforcement learning approach, is proposed, which integrates a factuality reward based on knowledge verification to guide models in fact-based slow thinking.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– KnowRL successfully mitigates hallucinations in slow-thinking models while maintaining their strong reasoning capabilities, as demonstrated through experimental results on various hallucination and reasoning evaluation datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19807

18. Scaling Speculative Decoding with Lookahead Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Lookahead Reasoning, Speculative Decoding, Step-level Parallelism, AI-generated summary, Token-level SD
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal of this research is to improve the speed of speculative decoding by introducing step-level parallelism through Lookahead Reasoning, while maintaining the quality of answers produced by the models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study incorporates a lightweight draft model to propose future steps, uses a target model to expand these proposals in one batched pass, and employs a verifier to maintain semantically correct steps, leveraging two layers of parallelism to enhance speed.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Lookahead Reasoning significantly increases the speedup of speculative decoding, lifting the peak from 1.4x to 2.1x across various benchmarks like GSM8K and AIME, with improved scalability under additional GPU throughput, while preserving answer quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19830

19. Improving Progressive Generation with Decomposable Flow Matching
🔑 Keywords: Visual Generation, Flow Matching, Multi-Scale Representation, DFM Framework, Video Quality
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance visual generation and video quality using the Decomposable Flow Matching (DFM) framework without complex multi-stage architectures.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of Flow Matching independently at multiple scales within a user-defined multi-scale representation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DFM improves visual quality in images and videos, achieving substantial improvements in FDD scores on datasets like Imagenet-1k compared to existing frameworks. It also shows faster convergence in finetuning large models while maintaining simplicity and minimal modifications to training pipelines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19839

20. Intelligent Operation and Maintenance and Prediction Model Optimization for Improving Wind Power Generation Efficiency
🔑 Keywords: Predictive Maintenance, Intelligent O&M, Digital Twins, AI Refinement
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– This study aims to explore the effectiveness of predictive maintenance models and optimize intelligent Operation and Maintenance (O&M) systems to enhance wind power generation efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted structured interviews with five experienced wind farm engineers and maintenance managers, employing thematic analysis to derive key insights.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Predictive maintenance models are effective in reducing turbine downtime by identifying major faults but struggle with smaller failures due to challenges like false positives and sensor malfunctions. Advanced technologies are enhancing maintenance practices but need improvements, especially in AI refinement and real-time data integration, to fully optimize wind turbine performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.16095
21. Mem4Nav: Boosting Vision-and-Language Navigation in Urban Environments with a Hierarchical Spatial-Cognition Long-Short Memory System
🔑 Keywords: Vision-and-Language Navigation, hierarchical spatial-cognition, reversible Transformer, dual-memory modules, semantic topology graph
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) by integrating a hierarchical spatial-cognition system with dual-memory modules to improve task completion, speed, and detour detection.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Mem4Nav system employs a sparse octree for fine-grained voxel indexing and a semantic topology graph for landmark connectivity. These are embedded into trainable memory tokens using a reversible Transformer.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Mem4Nav achieves significant improvements in task completion, SPD reduction, and nDTW across various VLN backbones, confirming the effectiveness of the hierarchical map and dual memory modules.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19433

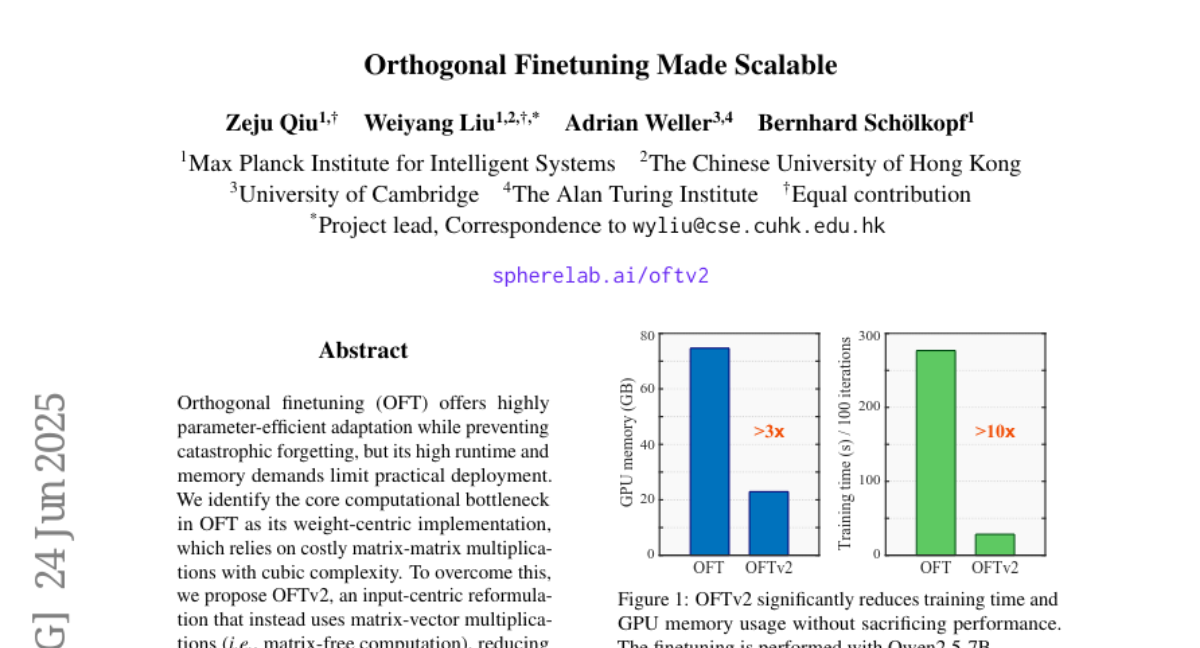
22. Orthogonal Finetuning Made Scalable
🔑 Keywords: Orthogonal Fine-tuning, Matrix-Free Computation, Cayley-Neumann Parameterization, Catastrophic Forgetting, GPU Memory Usage
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to optimize orthogonal fine-tuning (OFT) by reducing computational costs and enhancing performance through the development of OFTv2.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Shift from matrix-matrix multiplications to matrix-vector multiplications to reduce computational complexity.
– Introduce the Cayley-Neumann parameterization for efficient orthogonal parameterization and improved matrix inversion approximation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OFTv2 achieves up to 10x faster training and 3x lower GPU memory usage without compromising performance.
– Extends capability to fine-tune quantized foundation models, outperforming existing methods like QLoRA in several metrics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.19847
23.
