AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250918

1. Hala Technical Report: Building Arabic-Centric Instruction & Translation Models at Scale
🔑 Keywords: Arabic-centric, Hala, translate-and-tune pipeline, lightweight language model, NLP
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to develop Arabic-centric instruction and translation models that achieve state-of-the-art results using advanced methodologies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a translate-and-tune pipeline, compression to FP8, and slerp merging, alongside fine-tuning a lightweight language model on bilingual supervision.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Hala models, trained with varying parameters from 350M to 9B, deliver state-of-the-art performance on Arabic-centric benchmarks, publishing resources to further Arabic NLP research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.14008

2. SAIL-VL2 Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: SAIL-VL2, vision-language foundation model, data curation, progressive training, sparse MoE
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce SAIL-VL2, a vision-language foundation model, designed for comprehensive multimodal understanding and reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a large-scale data curation pipeline, a progressive training framework with a SAIL-ViT vision encoder, and efficient sparse MoE architectural designs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse benchmarks, demonstrating strong capabilities in both perception and reasoning, and ranks first on the OpenCompass leaderboard among open-source models under the 4B parameter scale.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.14033

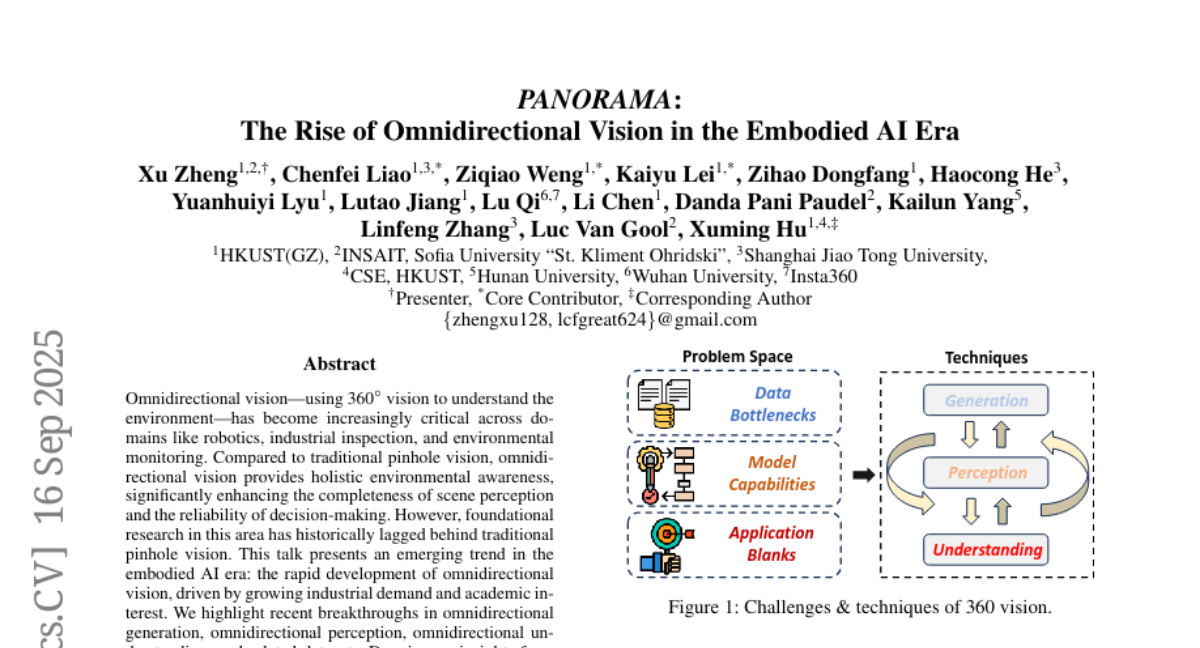
3. PANORAMA: The Rise of Omnidirectional Vision in the Embodied AI Era
🔑 Keywords: Omnidirectional vision, 360-degree vision, PANORAMA, Embodied AI
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose and study the implications of a new panoramic system architecture called PANORAMA in the field of omnidirectional vision within the embodied AI era.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Drawing insights from both academia and industry to highlight breakthroughs in omnidirectional generation, perception, and understanding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Omnidirectional vision enhances scene perception and decision-making compared to traditional vision systems.
– PANORAMA architecture offers an ideal design for future development, identifying emerging trends and open challenges at the intersection of panoramic vision and embodied AI.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.12989
4. GenExam: A Multidisciplinary Text-to-Image Exam
🔑 Keywords: GenExam, text-to-image, exam-style prompts, visual plausibility, general AGI
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce GenExam as the first benchmark for multidisciplinary text-to-image exams featuring exam-style prompts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement a benchmark with 1,000 samples across 10 subjects, equipped with ground-truth images and fine-grained scoring to evaluate semantic correctness and visual plausibility.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– State-of-the-art models, such as GPT-Image-1 and Gemini-2.5-Flash-Image, achieve less than 15% strict scores, indicating the benchmark’s challenge and providing insights into the path to general AGI.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.14232

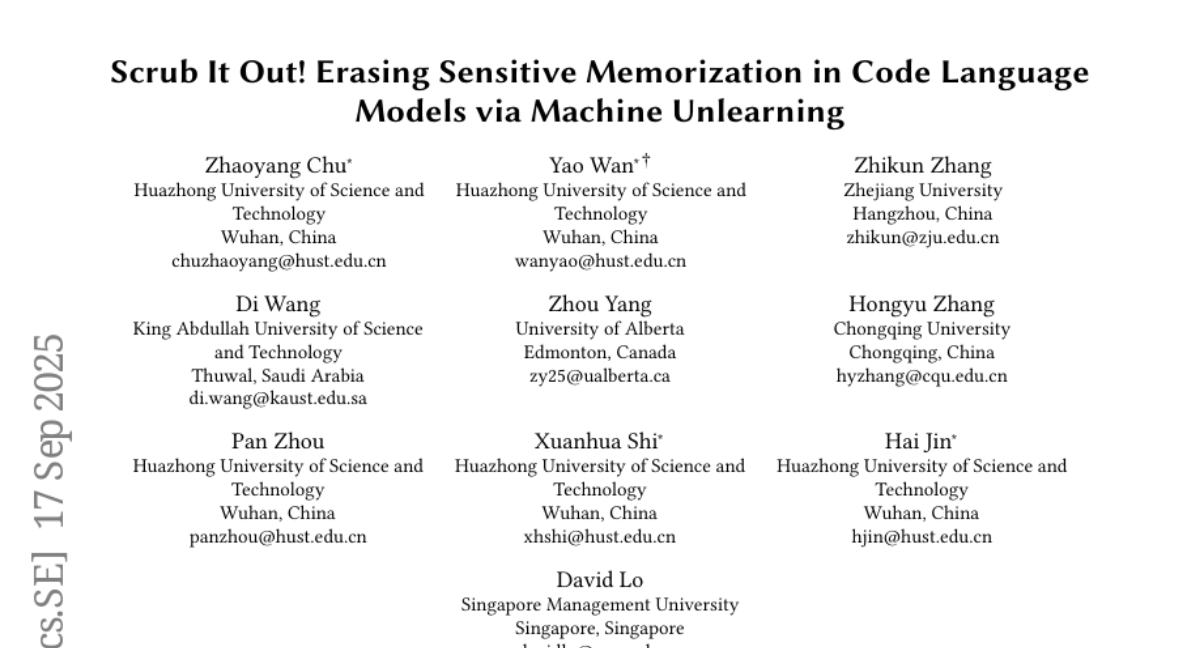
5. Scrub It Out! Erasing Sensitive Memorization in Code Language Models via Machine Unlearning
🔑 Keywords: CodeEraser, Code Language Models, Machine Unlearning, Sensitive Memorization
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the critical privacy vulnerability in Code Language Models by investigating techniques to erase sensitive memorized information without full retraining.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize machine unlearning techniques, including both vanilla and constraint-based gradient ascent methods, to target and remove sensitive memorized data efficiently.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Introduced CodeEraser, which effectively removes sensitive information from CLMs while maintaining code integrity and functionality, validated by experiments on CodeParrot, CodeGen-Mono, and Qwen2.5-Coder models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.13755
6. MedReseacher-R1: Expert-Level Medical Deep Researcher via A Knowledge-Informed Trajectory Synthesis Framework
🔑 Keywords: Medical Knowledge Graphs, Deep Research Agents, Multi-hop Question-answer Pairs, AI Native, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a medical deep research agent that excels in medical domain tasks and maintains competitive performance in general research.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a novel data synthesis framework with medical knowledge graphs to generate complex multi-hop question-answer pairs.
– Integrates a custom-built medical retrieval engine and employs a two-stage training paradigm incorporating supervised fine-tuning and online reinforcement learning with composite rewards.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The MedResearcher-R1-32B model sets new state-of-the-art results in medical benchmarks, outperforming larger proprietary systems in specialized domains through domain-specific innovations in architecture, tools, and training data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.14880

7. THOR: Tool-Integrated Hierarchical Optimization via RL for Mathematical Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: THOR, Large Language Models, Hierarchical Optimization, Reinforcement Learning, Tool-Integrated Reasoning
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to enhance mathematical reasoning and code generation through a framework that constructs high-quality datasets, optimizes reasoning paths, and corrects errors in inference using THOR, a tool-integrated hierarchical optimization framework via Reinforcement Learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introducing TIRGen: A multi-agent actor-critic-based pipeline for creating tool-integrated reasoning datasets.
– Implementing an RL strategy for fine-grained hierarchical optimization encompassing trajectory-level problem solving and step-level code generation.
– Incorporating a self-correction mechanism leveraging immediate tool feedback during inference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– THOR demonstrates strong generalization across diverse models, excelling in both reasoning and non-reasoning tasks.
– Achieves state-of-the-art performance on mathematical and code benchmarks, providing consistent improvements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.13761

8. AERIS: Argonne Earth Systems Model for Reliable and Skillful Predictions
🔑 Keywords: AERIS, Swin diffusion transformer, SWiPe, weather forecasting, scalable AI
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To scale diffusion-based methods for high-resolution weather forecasting using the AERIS model.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the Swin diffusion transformer with 1.3 to 80B parameters and the SWiPe technique for efficient window, sequence, and pipeline parallelism without added communication costs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AERIS achieves high performance, with up to 11.21 ExaFLOPS on the ERA5 dataset, outperforming existing models and demonstrating stability in long-term weather predictions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.13523

9. Improving Context Fidelity via Native Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: CARE, LLMs, in-context evidence, retrieval accuracy, answer generation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance large language models (LLMs) by integrating in-context evidence to improve retrieval accuracy and answer generation performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of CARE, a novel retrieval-augmented reasoning framework that leverages the model’s own retrieval capabilities to explicitly integrate in-context evidence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CARE significantly outperforms existing methods like supervised fine-tuning and traditional retrieval-augmented generation, making LLMs more accurate and efficient for knowledge-intensive tasks by integrating strategically retrieved in-context tokens.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.13683

10. Wan-Animate: Unified Character Animation and Replacement with Holistic Replication
🔑 Keywords: Wan-Animate, character animation, reference video, high-fidelity character videos, environmental integration
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Wan-Animate, a unified framework designed for character animation and replacement that achieves high-fidelity character videos with seamless environmental integration.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes spatially-aligned skeleton signals and implicit facial features extracted from source images to replicate body motion and expressions.
– Employs a modified input paradigm to differentiate reference conditions and generation regions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Wan-Animate demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in generating high-controllability and expressiveness in character videos and is committed to open-sourcing the model weights and source code.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.14055

11. MARS2 2025 Challenge on Multimodal Reasoning: Datasets, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Outlook
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Reasoning, Large Language Models (LLMs), MLLMs, Specialized Scenarios, Real-world Scenarios
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To advance multimodal reasoning with large language models by evaluating 40+ models across real-world and specialized scenarios in the MARS2 2025 Challenge.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized two tailored datasets, Lens and AdsQA, for general and domain-specific reasoning.
– Conducted evaluations in three competition tracks: Visual Grounding in Real-world Scenarios, Visual Question Answering with Spatial Awareness, and Visual Reasoning in Creative Advertisement Videos.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The challenge saw participation from 76 teams, resulting in over 40 valid submissions, and provided publicly available datasets, code sets, and rankings to promote further research in this area.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.14142

12. SteeringControl: Holistic Evaluation of Alignment Steering in LLMs
🔑 Keywords: SteeringControl, representation steering, bias, harmful generation, concept entanglement
💡 Category: AI Ethics and Fairness
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce SteeringControl as a benchmark to evaluate representation steering across core alignment objectives like bias, harmful generation, and hallucination, and their effects on secondary behaviors such as sycophancy and commonsense morality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a modular steering framework and collect a dataset of safety-relevant primary and secondary behaviors to evaluate five popular steering methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Strong steering performance depends on the combination of steering method, model, and targeted behavior. Poor combinations can result in severe concept entanglement.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.13450

13. Quantum Variational Activation Functions Empower Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
🔑 Keywords: Quantum Variational Activation Functions, Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks, Variational Quantum Circuits, Expressivity, Parameter Efficiency
💡 Category: Quantum Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance parameter efficiency and expressivity in quantum machine learning by introducing Quantum Variational Activation Functions (QVAFs) and quantum-inspired Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (QKANs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Unification of variational quantum circuits and learnable activation functions through single-qubit data re-uploading circuits, called DatA Re-Uploading ActivatioNs (DARUANs), and embedding them into KANs.
– Introduction of layer extension and hybrid QKANs as replacements for multi-layer perceptrons in feed-forward networks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Theoretical analysis and experiments demonstrate that QKANs improve parameter efficiency, expressivity, and generalization, offering scalability and feasibility for large-scale models in quantum machine learning.
– QKANs and DARUANs present promising advancements for quantum machine learning on both NISQ hardware and classical quantum simulators.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.14026

14. LLM-I: LLMs are Naturally Interleaved Multimodal Creators
🔑 Keywords: LLM-Interleaved, reinforcement learning, image-text generation, tool-use problem, state-of-the-art performance
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop a flexible and dynamic framework, LLM-Interleaved, to address limitations in current unified models for interleaved image-text generation by treating it as a tool-use problem.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing a central LLM to orchestrate a toolkit of specialized visual tools, including image search and diffusion-based generation, through a reinforcement learning framework with a hybrid reward system.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method, LLM-I, achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing methods across four benchmarks, and introduces a novel test-time scaling strategy to further enhance performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.13642

15. Synthesizing Behaviorally-Grounded Reasoning Chains: A Data-Generation Framework for Personal Finance LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Behavioral Finance, Qwen-3-8B, Personalized Financial Advice, Fine-Tuning, Cost Efficiency
💡 Category: AI in Finance
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a novel framework that integrates financial context and behavioral finance to enhance a Qwen-3-8B model for personalized financial advice.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Fine-tuned a Qwen-3-8B model on a newly created 19k sample reasoning dataset.
– Evaluated performance through a held-out test split and a blind LLM-jury study.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The 8B model achieved similar performance levels compared to larger models (14-32B) in terms of factual accuracy, fluency, and personalization, while reducing costs by 80%.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.14180

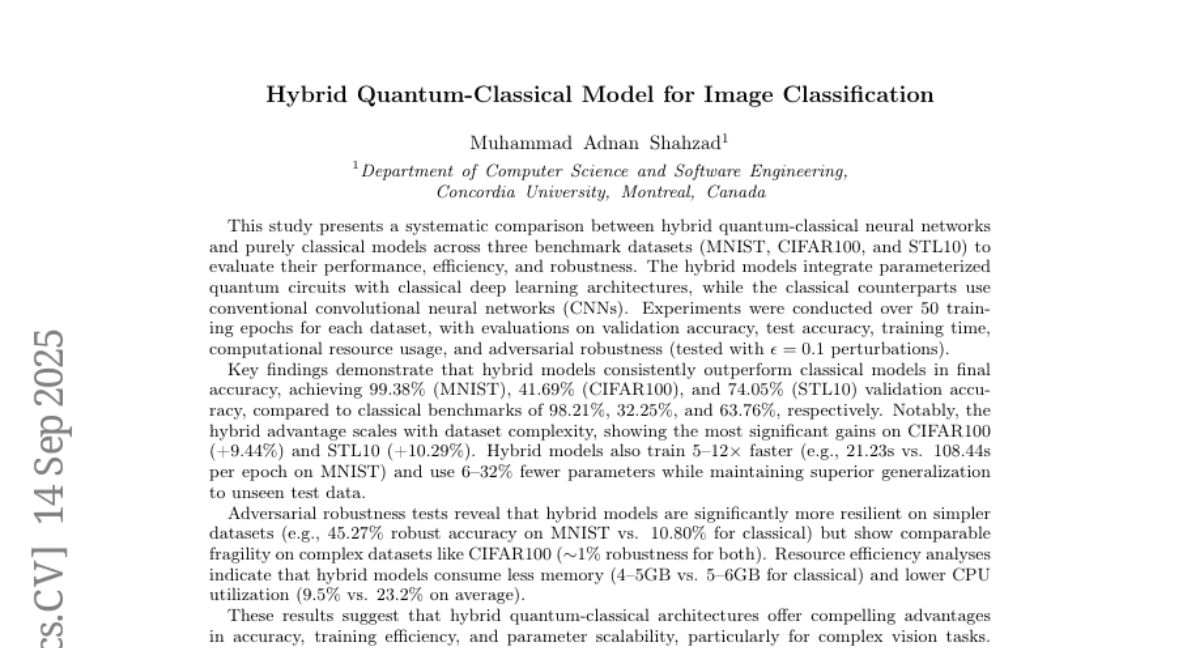
16. Hybrid Quantum-Classical Model for Image Classification
🔑 Keywords: Hybrid Quantum-Classical, Neural Networks, Parameterized Quantum Circuits, Classical Deep Learning Architectures, Adversarial Robustness
💡 Category: Quantum Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study systematically compares hybrid quantum-classical neural networks with classical models to evaluate performance, training efficiency, and robustness across various datasets.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Experiments were conducted on MNIST, CIFAR100, and STL10 datasets over 50 training epochs, measuring validation accuracy, test accuracy, training time, and computational resource usage.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Hybrid quantum-classical models outperform classical models in accuracy and training speed while using fewer parameters. Hybrids show significant gains on complex datasets and are more efficient in terms of resource usage.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.13353
17. Image Tokenizer Needs Post-Training
🔑 Keywords: Tokenizer Training, Latent Space, Generation Distribution, pFID, gFID
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve latent space construction and decoding in image generative models for enhanced image quality and robustness.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposed a novel tokenizer training scheme with main and post-training phases to address distribution discrepancies.
– Introduced a latent perturbation strategy and a plug-and-play tokenizer training approach.
– Developed a new tokenizer evaluation metric, pFID, to correlate tokenizer performance with generation quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The novel training scheme significantly enhances the robustness and quality of image generation by tokenizers.
– Notable improvements were observed in gFID scores with the proposed method.
– The effectiveness of the post-training strategy was validated on various tokenizer and generator models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.12474

18.
