AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250925

1. Video models are zero-shot learners and reasoners
🔑 Keywords: Veo 3, Zero-shot capabilities, Generative models, Unified vision foundation models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the zero-shot capabilities of the generative video model Veo 3 and its potential trajectory towards becoming a unified, generalist vision foundation model.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing large, generative models trained on web-scale data to demonstrate Veo 3’s ability to perform a variety of tasks it wasn’t explicitly trained for, such as object segmentation, edge detection, and image editing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Veo 3 exhibits zero-shot capabilities across diverse visual tasks, indicating a potential future as a generalist vision foundation model, akin to the development of general-purpose language understanding in Large Language Models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.20328

2. SIM-CoT: Supervised Implicit Chain-of-Thought
🔑 Keywords: SIM-CoT, Implicit Chain-of-Thought, step-level supervision, auxiliary decoder, token efficiency
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address latent instability in implicit Chain-of-Thought methods by introducing step-level supervision and enhancing performance and efficiency in Large Language Models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of SIM-CoT, a plug-and-play training module with step-level supervision using an auxiliary decoder that aligns implicit tokens with explicit reasoning steps during training but is removed during inference for efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SIM-CoT enhances accuracy and stability in both in-domain and out-of-domain tasks of implicit CoT methods, significantly improving performance over established baselines such as Coconut and CODI while also providing better token efficiency and interpretability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.20317

3. EmbeddingGemma: Powerful and Lightweight Text Representations
🔑 Keywords: EmbeddingGemma, state-of-the-art, encoder-decoder initialization, geometric embedding distillation, low-latency
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce EmbeddingGemma, a lightweight text embedding model that achieves high performance with fewer parameters.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes encoder-decoder initialization, geometric embedding distillation, and spread-out regularization to enhance the model’s robustness and expressiveness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EmbeddingGemma outperforms larger models with fewer parameters, offers a strong performance-to-cost ratio, and is well-suited for low-latency applications. It is released to the community to encourage further research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.20354

4. Advancing Speech Understanding in Speech-Aware Language Models with GRPO
🔑 Keywords: Group Relative Policy Optimization, Speech-Aware Large Language Models, BLEU, Spoken Question Answering, Automatic Speech Translation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a GRPO-based method to train SALLMs for open-format speech understanding tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize GRPO with BLEU as the reward signal to optimize SALLMs’ performance on tasks like Spoken Question Answering and Automatic Speech Translation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method outperforms standard SFT on various key metrics and shows potential for incorporating off-policy samples for further improvement.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.16990

5. EditVerse: Unifying Image and Video Editing and Generation with In-Context Learning
🔑 Keywords: Self-attention, AI-generated, Cross-modal knowledge transfer, In-context learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce EditVerse, a unified framework for both image and video generation and editing within a single model.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Leveraging self-attention to handle text, image, and video as a unified token sequence, along with a scalable data pipeline curating 232K video editing samples.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EditVerse surpasses existing models with state-of-the-art performance, demonstrating advanced editing and generation capabilities across different modalities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.20360

6. LLMs4All: A Review on Large Language Models for Research and Applications in Academic Disciplines
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, AI Native, Generative AI, Real-world Applications
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to provide an overview of state-of-the-art Large Language Models and their integration across various academic disciplines, highlighting their influence and potential in reshaping research and practice.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study offers a comprehensive review of how Large Language Models are applied in fields like arts, economics, business, science, and engineering, and discusses their limitations and future challenges.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Large Language Models have demonstrated significant performance in language tasks, positing broad impacts across disciplines but also presenting challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for future advancements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19580

7. Lavida-O: Elastic Large Masked Diffusion Models for Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation
🔑 Keywords: Lavida-O, Masked Diffusion Model, Multimodal Understanding, High-Resolution Synthesis, Elastic Mixture-of-Transformers
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce Lavida-O, a unified Masked Diffusion Model for enhanced multimodal understanding and generation tasks, outperforming existing models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a novel Elastic Mixture-of-Transformers architecture with lightweight and larger branches for generation and understanding, incorporating token compression, universal text conditioning, and stratified sampling.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Lavida-O achieves state-of-the-art performance in object grounding, image editing, and text-to-image generation, surpassing existing autoregressive and continuous diffusion models in efficiency and quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19244
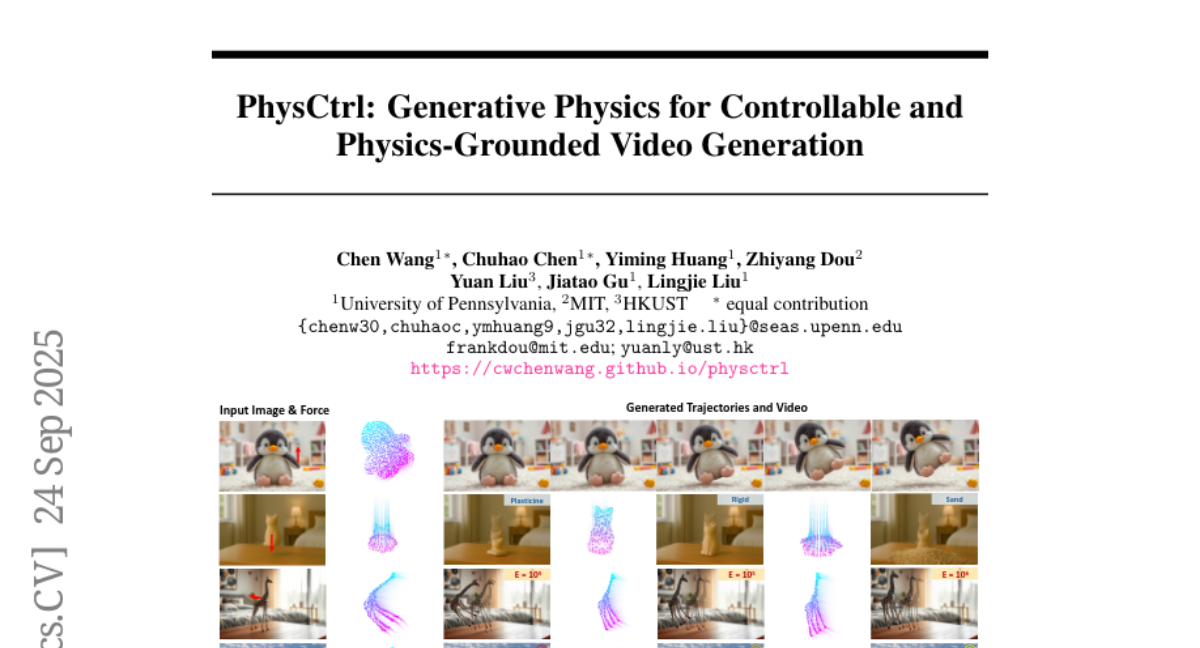
8. PhysCtrl: Generative Physics for Controllable and Physics-Grounded Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: PhysCtrl, diffusion model, spatiotemporal attention, physical plausibility, generative physics network
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce PhysCtrl, a framework designed for generating realistic and controllable videos from images through physics-grounded techniques enhanced by spatiotemporal attention and physics-based constraints.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a generative physics network to learn the distribution of physical dynamics across four types of materials using a diffusion model conditioned on physics parameters and applied forces.
– Enhanced the diffusion model with a spatiotemporal attention block and trained on a large-scale dataset of 550K animations from physics simulators to ensure physical plausibility.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PhysCtrl effectively generates realistic, physics-grounded motion trajectories, producing high-fidelity, controllable videos that surpass existing methods in visual quality and physical plausibility.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.20358
9. SimpleFold: Folding Proteins is Simpler than You Think
🔑 Keywords: SimpleFold, Protein folding, Transformer blocks, Flow-matching, Generative Models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a new protein folding model, SimpleFold, which leverages flow-matching and general-purpose transformer blocks to enhance efficiency and performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a generative flow-matching objective with adaptive layers and a structural term; trained a 3B parameter model using approximately 9M distilled protein structures and PDB data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SimpleFold achieves competitive performance on standard benchmarks and excels in ensemble predictions, demonstrating efficiency on consumer-level hardware and proposing an alternative to complex architectural designs in protein folding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.18480

10. Logics-Parsing Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: LVLM, end-to-end paradigms, reinforcement learning, layout analysis, reading order inference
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the study was to enhance document parsing capabilities by designing Logics-Parsing, an end-to-end LVLM-based model augmented with reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model utilizes reward mechanisms to improve layout analysis and reading order inference and includes supervised fine-tuning with various data types such as chemical formulas and handwritten Chinese characters.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments on LogicsParsingBench demonstrated the model’s state-of-the-art performance in handling diverse document analysis scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19760

11. ATLAS: Benchmarking and Adapting LLMs for Global Trade via Harmonized Tariff Code Classification
🔑 Keywords: HTS code classification, Atlas model, LLaMA-3.3-70B, data privacy, community benchmark
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to improve the accuracy and cost-effectiveness of HTS code classification, a crucial element in global trade that has been largely overlooked by the machine learning community.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A fine-tuned Atlas model (LLaMA-3.3-70B) is introduced and compared against existing models such as GPT-5-Thinking and Gemini-2.5-Pro-Thinking, using a newly released benchmark derived from the U.S. Customs Rulings Online Search System (CROSS).
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The LLaMA-3.3-70B model achieves notable improvements in classification accuracy with 40% correct 10-digit and 57.5% correct 6-digit classifications, outperforming other models by significant margins. Additionally, it offers cost advantages and ensures data privacy, inviting further research in areas like retrieval, reasoning, and alignment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.18400

12. On the Use of Agentic Coding: An Empirical Study of Pull Requests on GitHub
🔑 Keywords: AI agents, GitHub pull requests, Claude Code, software development, AI Native
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To empirically study the practical usefulness and acceptance rates of AI-generated pull requests in real-world open-source projects.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analysis of 567 GitHub pull requests generated by Claude Code across 157 diverse open-source projects to evaluate their acceptance rates and the extent of human modification required.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– 83.8% of agent-assisted pull requests are accepted and merged, with 54.9% merged without further modification, indicating high acceptance. However, 45.1% required human revisions for bug fixes, documentation, and project-specific standards, suggesting that human oversight enhances the effectiveness of AI-assisted development tools.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.14745

13. kh2d-solver: A Python Library for Idealized Two-Dimensional Incompressible Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability
🔑 Keywords: Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities, NumPy, SciPy, Fast Sine Transform, subgrid-scale representation
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To simulate two-dimensional incompressible Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities in stratified shear flows using an open-source Python library.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Uses a fractional-step projection method with spectral Poisson solution via Fast Sine Transform to achieve second-order spatial accuracy.
– Implements the solution using NumPy, SciPy, and Numba JIT compilation for efficient computation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Double shear layers achieve significantly higher mixing rates than forced turbulence, suggesting a need for refining subgrid-scale representation in climate models.
– Highlights that mixing efficiency in stratified flows depends more on instability generation pathways rather than intensity measures.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.16080

14.
