AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251013
1. D2E: Scaling Vision-Action Pretraining on Desktop Data for Transfer to Embodied AI
🔑 Keywords: Embodied AI, Desktop environments, Sensorimotor interactions, OWA Toolkit, VAPT
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to demonstrate that desktop interactions, especially from gaming environments, can effectively pretrain embodied AI for physical manipulation and navigation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed the D2E framework involving components like the OWA Toolkit for data standardization, Generalist-IDM for zero-shot generalization, and VAPT for transferring pretrained representations to physical tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study validates desktop pretraining as a practical paradigm for robotics with high success rates, achieving 96.6% on LIBERO manipulation tasks and 83.3% on CANVAS navigation benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.05684
2. Thinking with Camera: A Unified Multimodal Model for Camera-Centric Understanding and Generation
🔑 Keywords: Puffin, Multimodal Model, Camera-Centric, Spatial Generation, Vision-Language
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance camera-centric spatial understanding and generation by integrating language regression and diffusion-based generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a new paradigm by treating camera parameters as language.
– Trained on a large-scale dataset, Puffin-4M, comprising 4 million vision-language-camera triplets.
– Employs both global camera parameters and pixel-wise camera maps for flexible spatial generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Puffin outperforms specialized models in camera-centric generation and understanding.
– Demonstrates generalization across diverse tasks, including spatial imagination and photography guidance.
– Plans to release the code, models, dataset pipeline, and benchmark to further research in multimodal spatial intelligence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.08673

3. TAG:Tangential Amplifying Guidance for Hallucination-Resistant Diffusion Sampling
🔑 Keywords: Tangential Amplifying Guidance, diffusion models, semantic inconsistencies, trajectory signals, plug-and-play
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Tangential Amplifying Guidance (TAG) to improve the quality of samples in diffusion models without modifying the model architecture.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize TAG to directly amplify tangential components of estimated scores through trajectory signals, using intermediate samples as a projection basis and leveraging a first-order Taylor expansion.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TAG enhances sampling fidelity and reduces semantic inconsistencies without additional computational overhead, offering a new architecture-agnostic approach to diffusion guidance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.04533

4. AutoPR: Let’s Automate Your Academic Promotion!
🔑 Keywords: Multi-agent framework, Automatic Promotion (AutoPR), PRBench, PRAgent, Engagement
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces Automatic Promotion (AutoPR) as a novel task to convert research papers into engaging public content, enhancing visibility and citations while reducing human effort.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the PRBench benchmark to assess systems based on fidelity, engagement, and alignment.
– Development of PRAgent, a multi-agent framework for automating the AutoPR process, involving content extraction, collaborative synthesis, and platform-specific adaptation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PRAgent significantly outperforms direct LLM pipelines, showing improvements in audience engagement metrics, including a 604% increase in total watch time, 438% rise in likes, and at least a 2.9x boost in overall engagement.
– Platform modeling and targeted promotion are major contributors to these improvements.
– AutoPR is established as a scalable and impactful research problem with potential for automated scholarly communication.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09558

5. Multimodal Prompt Optimization: Why Not Leverage Multiple Modalities for MLLMs
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Prompt Optimization, Large Language Models, Multimodal Expansions, Bayesian-based Selection Strategy, Performance Improvement
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce multimodal prompt optimization to fully exploit the potential of multimodal Large Language Models beyond text-only methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Propose Multimodal Prompt Optimizer (MPO), a framework that performs joint optimization of multimodal prompts using alignment-preserving updates and Bayesian-based selection strategy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MPO outperforms existing text-only optimization methods across various modalities, establishing multimodal prompt optimization as essential for enhancing the capabilities of multimodal Large Language Models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09201

6. Webscale-RL: Automated Data Pipeline for Scaling RL Data to Pretraining Levels
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, Webscale-RL pipeline, question-answer pairs
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the limitations in existing RL datasets by introducing the Webscale-RL pipeline, converting large-scale pre-training documents into diverse question-answer pairs for RL.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of the Webscale-RL pipeline: A scalable data engine producing a new dataset with 1.2 million examples across more than 9 domains.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model trained on the Webscale-RL dataset surpasses continual pre-training and data refinement baselines, achieving comparable performance with fewer computational resources.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.06499
7. StreamingVLM: Real-Time Understanding for Infinite Video Streams
🔑 Keywords: StreamingVLM, real-time vision-language model, supervised fine-tuning, AI-generated summary, real-time performance
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce StreamingVLM, a model crafted for real-time and stable comprehension of infinite video streams with minimal latency and memory usage.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implements a compact KV cache to process video streams efficiently, using a supervised fine-tuning strategy for full attention on overlapped video chunks without needing extensive context during training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– StreamingVLM demonstrates superior real-time performance up to 8 FPS on a single NVIDIA H100, achieving a 66.18% win rate against GPT-4O mini and improving performance on video datasets like LongVideoBench and OVOBench Realtime.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09608

8. R-Horizon: How Far Can Your Large Reasoning Model Really Go in Breadth and Depth?
🔑 Keywords: R-HORIZON, Long-Horizon Reasoning, Large Reasoning Models, Query Composition, Reinforcement Learning with Verified Rewards
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the limitations of existing benchmarks in evaluating Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) on complex, long-horizon tasks, by introducing R-HORIZON, a new method to enhance long-horizon reasoning capability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces R-HORIZON using query composition to create a benchmark for complex multi-step reasoning tasks that span long reasoning horizons and evaluates LRMs based on this benchmark.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– R-HORIZON identifies performance degradation in state-of-the-art LRMs on long-horizon tasks, yet improves performance and accuracy in reasoning tasks when used for Reinforcement Learning with Verified Rewards, demonstrating a scalable and low-cost approach to enhance and evaluate LRMs’ long-horizon reasoning capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.08189

9. BigCodeArena: Unveiling More Reliable Human Preferences in Code Generation via Execution
🔑 Keywords: BigCodeArena, LLM-generated code, human evaluation, code generation, AutoCodeArena
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal of this research is to explore human evaluation of LLMs in code generation tasks, facilitating real-time execution and interaction with code.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed BigCodeArena, a platform for executing and interacting with LLM-generated code, collecting over 14,000 conversation sessions across 10 languages.
– Curated benchmarks, BigCodeReward and AutoCodeArena, to evaluate LLM’s code understanding and generation capabilities systematically.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The analysis demonstrated LLMs excel in evaluating coding preferences when execution results are available.
– Proprietary LLMs like GPT-5 and Claude models have shown superior performance in recent code generation efforts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.08697

10. BEAR: Benchmarking and Enhancing Multimodal Language Models for Atomic Embodied Capabilities
🔑 Keywords: BEAR, Multimodal Large Language Models, Embodied Capabilities, BEAR-Agent, GPT-5
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to create a comprehensive benchmark named BEAR to evaluate the embodied capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– BEAR is developed as a fine-grained benchmark comprising 4,469 interleaved image-video-text entries across 14 domains in 6 categories, providing tasks from low-level pointing to high-level planning. The BEAR-Agent integrates pretrained vision models to enhance MLLM performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BEAR’s evaluation reveals persistent limitations in MLLMs across embodied capabilities. The introduction of BEAR-Agent significantly improves performance with a 9.12% absolute gain and a relative improvement of 17.5% on GPT-5, suggesting enhanced embodied capabilities benefit tasks in simulated environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.08759

11. SpaceVista: All-Scale Visual Spatial Reasoning from mm to km
🔑 Keywords: spatial reasoning, scale-aware experts, progressive rewards, large datasets
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to advance all-scale spatial reasoning across diverse scenarios by addressing challenges such as reliance on indoor 3D scans and absence of effective all-scale scene modeling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a holistic solution integrating structured spatial reasoning knowledge, scale-aware modeling, and progressive training.
– Curates the SpaceVista-1M dataset with over 38K video scenes and approximately 1M spatial QA pairs.
– Develops SpaceVista-7B, a spatial reasoning model that leverages scale-aware experts and progressive rewards.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates competitive performance with strong generalization across all scales and scenarios through extensive evaluations across 5 benchmarks.
– Plans to release the dataset, model, and benchmark for public access.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09606

12. Don’t Waste Mistakes: Leveraging Negative RL-Groups via Confidence Reweighting
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Verifiable Rewards, LENS, GRPO, Confidence-Weighted Penalty
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the efficiency and performance of Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) by modifying Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with a focus on leveraging negative groups using Likelihood Estimation with Negative Samples (LENS).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a modified GRPO approach that uses LENS, which assigns confidence-dependent rewards to incorrect responses, transforming previously wasted negative samples into valuable gradient updates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed LENS modified GRPO variant consistently outperformed the baseline on the MATH benchmark, particularly on more challenging tasks, demonstrating a practical method to enhance RLVR by making negative groups informative.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.08696

13. KORMo: Korean Open Reasoning Model for Everyone
🔑 Keywords: Synthetic Data, Korean LLM, Pretraining, Bilingual Instruction Tuning, Fully Open Models
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate the construction of a fully open bilingual large language model for Korean using synthetic data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of KORMo-10B, a model trained from a Korean-English corpus with a significant portion of synthetic Korean data.
– Systematic experimentation to assess the impact of synthetic data on large-scale pretraining and model stability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Synthetic data can sustain long-horizon pretraining without causing model instability.
– Bilingual instruction tuning facilitates near-native reasoning and discourse coherence in Korean.
– Establishes a reproducible framework for developing synthetic data-driven models in low-resource settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09426

14. DISCO: Diversifying Sample Condensation for Efficient Model Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: Model Disagreements, DISCO, Performance Prediction, State-of-the-art Results
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the prohibitively high cost of evaluating modern machine learning models and enhance accessibility and innovation by optimizing sample selection for performance prediction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce DISCO (Diversifying Sample Condensation), which selects samples with the greatest model disagreements, using greedy, sample-wise statistics rather than complex clustering.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DISCO achieves state-of-the-art results across various benchmarks such as MMLU, Hellaswag, Winogrande, and ARC, with reduced computational cost and theoretical grounding in information theory for optimal sample selection.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.07959

15. ARES: Multimodal Adaptive Reasoning via Difficulty-Aware Token-Level Entropy Shaping
🔑 Keywords: Adaptive Reasoning, Multimodal Reasoning Models, High Window-Entropy, ARES Framework, AI-generated Summary
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop ARES, a unified open-source framework for adaptive reasoning that dynamically allocates exploration effort based on task difficulty to improve performance and efficiency in reasoning models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a two-stage training pipeline, including Adaptive Cold-Start for initial difficulty awareness and Adaptive Entropy Policy Optimization, which uses high window-entropy tokens and hierarchical entropy rewards for exploration management.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ARES achieves superior performance and reasoning efficiency across various benchmarks, effectively balancing exploration on simple and challenging tasks while reducing inference costs compared to commercial systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.08457
16. Bridging Reasoning to Learning: Unmasking Illusions using Complexity Out of Distribution Generalization
🔑 Keywords: Complexity OoD, Reasoning Ability, System2, Generalization, Operationalization
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To define and measure reasoning ability in AI models using the Complexity Out of Distribution (Complexity OoD) framework, which focuses on test instances exhibiting higher solution complexity than training examples.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Formalize complexity using Kolmogorov complexity and operational proxies.
– Translate Complexity OoD into practical recommendations, including benchmark design and inductive biases.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Complexity OoD presents a unified approach for learning and reasoning, necessitating new architectures and training regimes that allocate computation resources based on complexity rather than data scaling alone.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.06274

17. Progressive Gaussian Transformer with Anisotropy-aware Sampling for Open Vocabulary Occupancy Prediction
🔑 Keywords: 3D occupancy prediction, Progressive Gaussian Transformer Framework, anisotropy-aware sampling, feed-forward strategy, state-of-the-art performance
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to enhance 3D occupancy prediction by addressing the trade-off between sparse and dense scene representations, allowing for effective open-vocabulary 3D scene modeling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a Progressive Gaussian Transformer Framework with progressive online densification and an anisotropy-aware sampling strategy, integrating spatio-temporal fusion to improve feature aggregation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PG-Occ significantly improves upon previous methods, achieving a 14.3% relative mIoU improvement, and will release code and pretrained models for broader adoption in the field.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.04759

18. Which Heads Matter for Reasoning? RL-Guided KV Cache Compression
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, KV Cache, Reasoning Quality, Attention Heads
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a reinforcement learning-based framework, called RLKV, that identifies and prioritizes critical attention heads for efficient KV cache compression in large language models while maintaining reasoning quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a reinforcement learning strategy to optimize the relationship between attention heads’ cache usage and reasoning quality, efficiently allocating full KV cache to important heads and compressed cache to others for effective inference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The RLKV framework enables improved KV compression by concentrating only on essential attention heads, achieving a 20-50% reduction in cache with nearly lossless performance compared to uncompressed models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.08525

19. MRMR: A Realistic and Expert-Level Multidisciplinary Benchmark for Reasoning-Intensive Multimodal Retrieval
🔑 Keywords: MRMR, multimodal retrieval, reasoning-intensive, contradiction retrieval, image-text interleaved
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to introduce MRMR, a benchmark designed for expert-level multidisciplinary multimodal retrieval, focusing on reasoning-intensive tasks and contradiction retrieval within diverse domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MRMR incorporates 1,502 queries across 23 domains, using human expert-verified documents, evaluates 4 categories of multimodal retrieval systems, and tests 14 frontier models to assess model performance across various tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MRMR demonstrates the need for improved multimodal models, highlighting that current models, such as Qwen3-Embedding, lead in performance yet still show potential for growth, particularly in reasoning-intensive tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09510

20. StatEval: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Large Language Models in Statistics
🔑 Keywords: Statistical reasoning, Large Language Models, Benchmarking, Evaluation framework, Human-in-the-loop validation
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– StatEval aims to fill the benchmarking gap in statistical reasoning by providing a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a multi-agent pipeline with human-in-the-loop validation to extract and evaluate statistical problems, ensuring academic rigor and quality control.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results indicate significant limitations in current LLMs, with closed-source models achieving low scores on research-level statistical problems, highlighting the challenges of statistical reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09517
21. Parallel Test-Time Scaling for Latent Reasoning Models
🔑 Keywords: Parallel test-time scaling, Latent reasoning, Monte Carlo Dropout, Latent Reward Model, Continuous vector spaces
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective was to enable parallel test-time scaling for latent reasoning models by introducing probabilistic sampling mechanisms and aggregation strategies in continuous space.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed two uncertainty-inspired sampling strategies: Monte Carlo Dropout and Additive Gaussian Noise.
– Designed a Latent Reward Model (LatentRM) trained with a step-wise contrastive objective for effective trajectory selection.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that both sampling strategies scale effectively with computational resources and exhibit distinct exploration dynamics.
– LatentRM facilitates effective trajectory selection, opening new directions for scalable inference in continuous spaces.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.07745

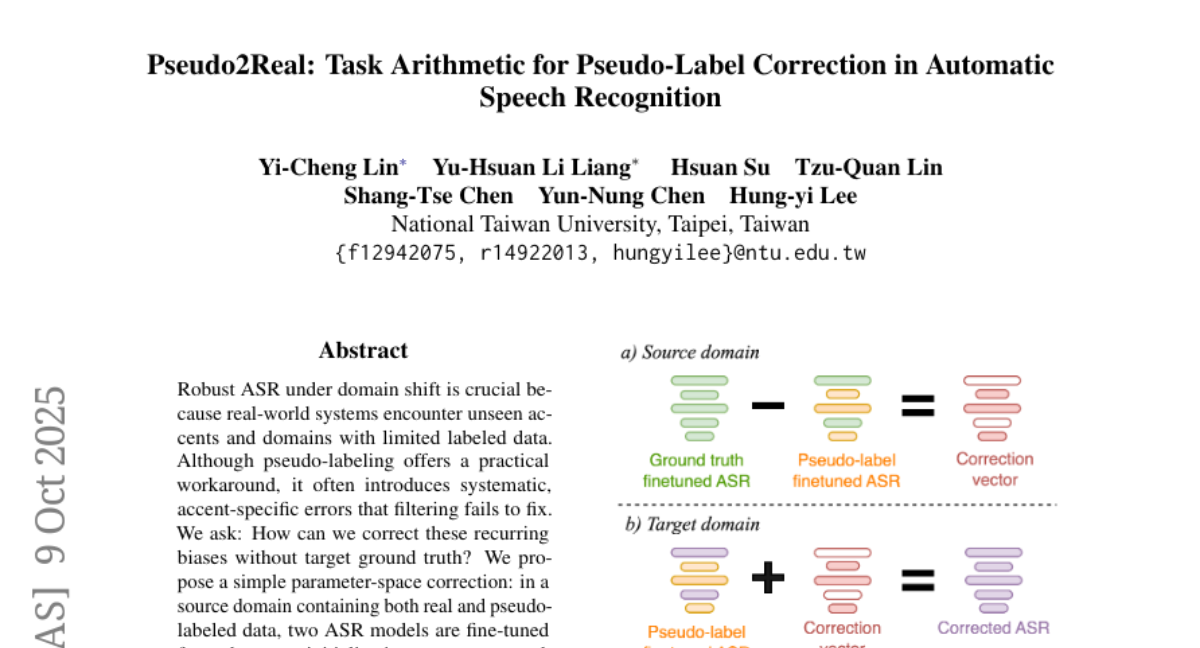
22. Pseudo2Real: Task Arithmetic for Pseudo-Label Correction in Automatic Speech Recognition
🔑 Keywords: ASR, domain shift, pseudo-labeling, correction vector, Word Error Rate (WER)
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim of the research is to reduce the Word Error Rate in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems by correcting pseudo-label biases without using target ground truth, particularly in scenarios involving domain shifts with limited labeled data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study involves a parameter-space correction approach where two ASR models are fine-tuned: one on actual ground-truth labels and the other on pseudo-labels. The difference in their weights is used to form a correction vector, which is then applied to enhance recognition in pseudo-labeled target models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The implementation of the correction vector in pseudo-labeled target models significantly improved recognition capabilities, achieving up to a 35% relative decrease in Word Error Rate across ten African accents using the Whisper tiny model on the AfriSpeech-200 dataset.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.08047
23. PhysToolBench: Benchmarking Physical Tool Understanding for MLLMs
🔑 Keywords: MLLMs, Tool Understanding, PhysToolBench, Vision-Language-Action
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to evaluate the comprehension of physical tools by Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) through a newly introduced benchmark called PhysToolBench.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a Visual Question Answering (VQA) dataset with over 1,000 image-text pairs, assessing models across three levels: Tool Recognition, Tool Understanding, and Tool Creation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Findings reveal significant deficiencies in tool understanding among 32 evaluated MLLMs, and the paper proposes preliminary solutions while offering public access to the code and dataset.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09507

24. TC-LoRA: Temporally Modulated Conditional LoRA for Adaptive Diffusion Control
🔑 Keywords: TC-LoRA, diffusion models, hypernetwork, generative fidelity, spatial conditions
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce TC-LoRA to enable dynamic, context-aware control by conditioning model weights directly for improved generative fidelity and spatial adherence.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a hypernetwork to dynamically generate LoRA adapters, tailoring weight modifications for the frozen backbone at each diffusion step.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Dynamic, parametric control via TC-LoRA significantly enhances generative quality compared to traditional static, activation-based methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09561
25. Dyna-Mind: Learning to Simulate from Experience for Better AI Agents
🔑 Keywords: Dyna-Mind, Reasoning, Simulation, AI Agents, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to enhance AI agents’ reasoning and planning abilities through a novel two-stage training framework named Dyna-Mind, enabling better performance in long-horizon interactive environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce a two-stage framework: Dyna-Mind, consisting of Reasoning with Simulations (ReSim) for generating structured reasoning traces and Dyna-GRPO, an online reinforcement learning method, for improving decision-making using real rollout feedback.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments on synthetic and realistic benchmarks demonstrated that ReSim effectively incorporates simulation abilities into AI agents, and Dyna-GRPO further enhances policy learning for planning-intensive tasks, underscoring simulation’s role in bolstering AI agents’ effectiveness in complex environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09577

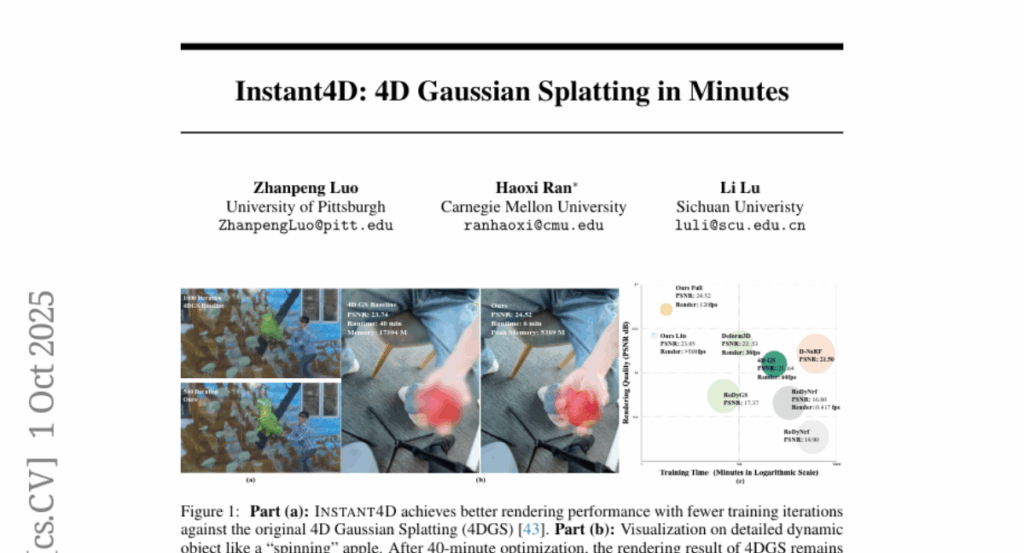
26. Instant4D: 4D Gaussian Splatting in Minutes
🔑 Keywords: Instant4D, deep visual SLAM, 4D Gaussian representation, AI-generated summary, dynamic view synthesis
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address the challenges in reconstructing scenes from uncalibrated, casual video sequences by introducing Instant4D, which utilizes a native 4D representation for efficient processing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves geometric recovery through deep visual SLAM and grid pruning to optimize scene representation, significantly reducing the model size and maintaining geometric integrity.
– A streamlined 4D Gaussian representation is used to handle temporal dynamics, achieving notable speed-up in processing and training times.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Instant4D is capable of reconstructing a single video within 10 minutes and demonstrates generalizability when applied to in-the-wild videos, maintaining competitive performance against benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.01119

27. LightReasoner: Can Small Language Models Teach Large Language Models Reasoning?
🔑 Keywords: LightReasoner, large language models, small language models, behavioral divergence, fine-tuning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore whether smaller language models can teach larger language models to improve reasoning accuracy and efficiency by identifying high-value reasoning moments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a novel framework, LightReasoner, which operates in two stages: sampling critical reasoning moments and fine-tuning the expert model with supervision examples derived from expert-amateur contrasts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LightReasoner enhances the reasoning capabilities of large language models, improving accuracy by up to 28.1% and substantially reducing resource consumption without ground-truth labels.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.07962

28. ReviewerToo: Should AI Join The Program Committee? A Look At The Future of Peer Review
🔑 Keywords: AI-assisted peer review, ReviewerToo, systematic assessments, accuracy, hybrid peer-review systems
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce ReviewerToo, a modular framework to enhance peer review by integrating AI to support systematic and consistent assessments alongside human judgment.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted experiments on 1,963 ICLR 2025 paper submissions with the gpt-oss-120b model and compared AI-assisted reviews to human reviewer performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ReviewerToo demonstrated 81.8% accuracy in categorizing papers, close to human reviewers at 83.9%.
– AI reviewers excel in tasks like fact-checking and literature coverage but struggle with methodological novelty and theoretical assessment.
– Guidelines were proposed for incorporating AI in peer-review processes to improve consistency, coverage, and fairness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.08867

29. Adaptive Attacks on Trusted Monitors Subvert AI Control Protocols
🔑 Keywords: AI control protocols, adaptive attacks, prompt injections, LLM monitors
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to investigate the vulnerabilities of AI control protocols when subjected to adaptive attacks using prompt injections, identifying weaknesses in current security mechanisms reliant on LLM monitors.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers explore adaptive attacks by leveraging an untrusted model familiar with both the protocol and monitor model, implementing a simple adaptive attack vector through publicly known or zero-shot prompt injections.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– It was discovered that adaptive attacks consistently evade diverse LLM monitors, completing malicious tasks, and revealing significant blind spots in current AI control protocols. These findings emphasize the need to incorporate adaptive attack evaluations into the development of future AI control mechanisms.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09462

30. A Goal Without a Plan Is Just a Wish: Efficient and Effective Global Planner Training for Long-Horizon Agent Tasks
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, EAGLET, Long-Horizon Tasks, Global Planner, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance the planning abilities of LLM-based agents in long-horizon tasks through a novel plan-and-execute framework with EAGLET, achieving state-of-the-art performance with reduced training costs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a two-step training process for a plug-and-play global planner using homologous consensus filtering and fine-tuning, followed by a reinforcement learning stage with an executor capability gain reward.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed planner with EAGLET significantly outperforms existing methods in long-horizon tasks, achieving new state-of-the-art performance while reducing training costs by 8x compared to RL-based baselines without requiring manual effort or additional training data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.05608

31. Understanding DeepResearch via Reports
🔑 Keywords: DeepResearch, LLM-as-a-Judge, research reports, expert concordance, standardized benchmark
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce DeepResearch-ReportEval, a framework for evaluating DeepResearch systems by measuring quality, redundancy, and factuality through research reports.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize an innovative LLM-as-a-Judge methodology to systematically assess systems, achieving expert concordance.
– Provide a standardized benchmark with 100 curated queries across 12 real-world categories.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Evaluates four leading commercial systems, highlighting distinct design philosophies and performance trade-offs.
– Establishes foundational insights for the evolution of DeepResearch systems from information assistants to intelligent research partners.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.07861

32. Mind-Paced Speaking: A Dual-Brain Approach to Real-Time Reasoning in Spoken Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Mind-Paced Speaking, real-time reasoning, dual-brain approach, Formulation Brain, Articulation Brain
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a brain-inspired framework, Mind-Paced Speaking (MPS), that enables high-fidelity reasoning and fluent speech generation in real-time by segmenting the process into distinct components for reasoning and speech.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The implementation of a dual-brain approach with a “Formulation Brain” for high-level reasoning and an “Articulation Brain” for speech generation, reducing mode-switching and preserving the reasoning process integrity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MPS significantly improves on current think-while-speaking methods, offering comparable reasoning accuracy to pre-computed models with much lower latency. It achieved 92.8% accuracy on math reasoning tasks and a score of 82.5 on speech conversation tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.09592
