AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251105
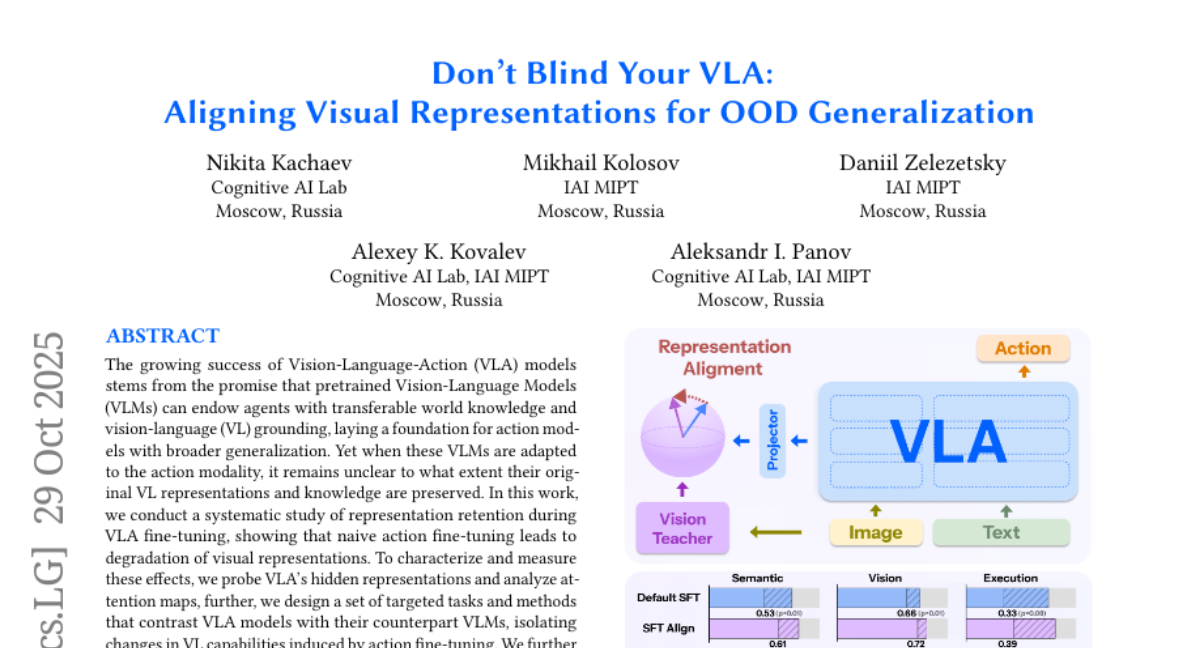
1. Don’t Blind Your VLA: Aligning Visual Representations for OOD Generalization
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action models, Vision-Language Models, VL representations, action fine-tuning, visual representations
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To study the effects of naive action fine-tuning on visual representation degradation in Vision-Language-Action models and explore mitigation strategies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study involves probing hidden representations, analyzing attention maps, designing targeted tasks, and comparing VLA models with their VLM counterparts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Naive action fine-tuning degrades visual representations, but targeted strategies can mitigate degradation and improve generalization to out-of-distribution scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.25616
2. VCode: a Multimodal Coding Benchmark with SVG as Symbolic Visual Representation
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, VCode, SVG, multimodal understanding, VCoder
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a benchmark (VCode) for generating SVG code from images to enhance visual-centric coding by preserving symbolic meaning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed CodeVQA, a novel evaluation protocol, to assess symbolic fidelity through question-answering over rendered SVGs.
– Proposed VCoder, an agentic framework, to refine SVG generation by augmenting VLMs through Thinking with Revision and Acting with Visual Tools.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified a gap in performance between language-centric and visual-centric coding.
– Demonstrated that VCoder improves SVG generation fidelity, evidenced by a 12.3-point performance gain over top benchmarks.
– Highlighted the promise of symbolic visual representation through human and VLM studies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02778

3. When Visualizing is the First Step to Reasoning: MIRA, a Benchmark for Visual Chain-of-Thought
🔑 Keywords: MIRA, intermediate visual images, multimodal problems, Visual-CoT
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces MIRA, a benchmark designed to assess model performance in scenarios requiring the generation and use of intermediate visual images to enhance reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MIRA focuses on challenging tasks that involve complex structures and spatial relationships, requiring models to generate sketches, structural diagrams, or path drawings to guide reasoning.
– The benchmark includes 546 multimodal problems and implements a unified evaluation protocol with three levels of input, including Visual-CoT.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results indicate that models relying solely on textual prompts perform poorly compared to when intermediate visual cues are provided, resulting in a 33.7% performance improvement on average.
– The study highlights the critical role of imagined visual information in achieving successful reasoning on the MIRA benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02779

4. When Modalities Conflict: How Unimodal Reasoning Uncertainty Governs Preference Dynamics in MLLMs
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal large language models, Modality following, Relative reasoning uncertainty, Inherent modality preference, Entropy
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to decompose modality following in multimodal large language models into relative reasoning uncertainty and inherent modality preference to better resolve conflicts in information.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a new framework to separate modality following into two fundamental factors and validated it using a controllable dataset varying the reasoning difficulty of visual and textual inputs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Discovered that the probability of following a modality decreases as its relative uncertainty increases, with a balance point indicating a model’s inherent preference. This measure characterizes modality bias more accurately and explains the internal oscillation mechanism across layers.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02243

5. The Collaboration Gap
🔑 Keywords: agent-based systems, collaboration gap, collaborative maze-solving benchmark, training strategies, relay inference
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate collaboration capabilities of agent-based systems and explore methods to bridge the identified collaboration gap.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposed a collaborative maze-solving benchmark to test and isolate collaborative capabilities of 32 open- and closed-source models in solo, homogeneous, and heterogeneous pairings.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Models that excel individually often struggle in collaborative settings, indicating a significant collaboration gap. A “relay inference” approach where a stronger agent begins tasks can improve outcomes. This advocates for collaboration-aware evaluation, specialized training strategies, and effective interaction design for both AI-AI and human-AI collaboration contexts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02687

6. Brain-IT: Image Reconstruction from fMRI via Brain-Interaction Transformer
🔑 Keywords: Brain Interaction Transformer, fMRI, Image Reconstruction, Diffusion Model, Brain Voxels
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To reconstruct images from fMRI data with high fidelity using the Brain Interaction Transformer (BIT).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The use of a Brain Interaction Transformer to facilitate interactions between clusters of brain voxels and predict complementary image features to guide the reconstruction process.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method achieves highly faithful image reconstructions, surpassing current state-of-the-art approaches, and works effectively with limited training data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.25976

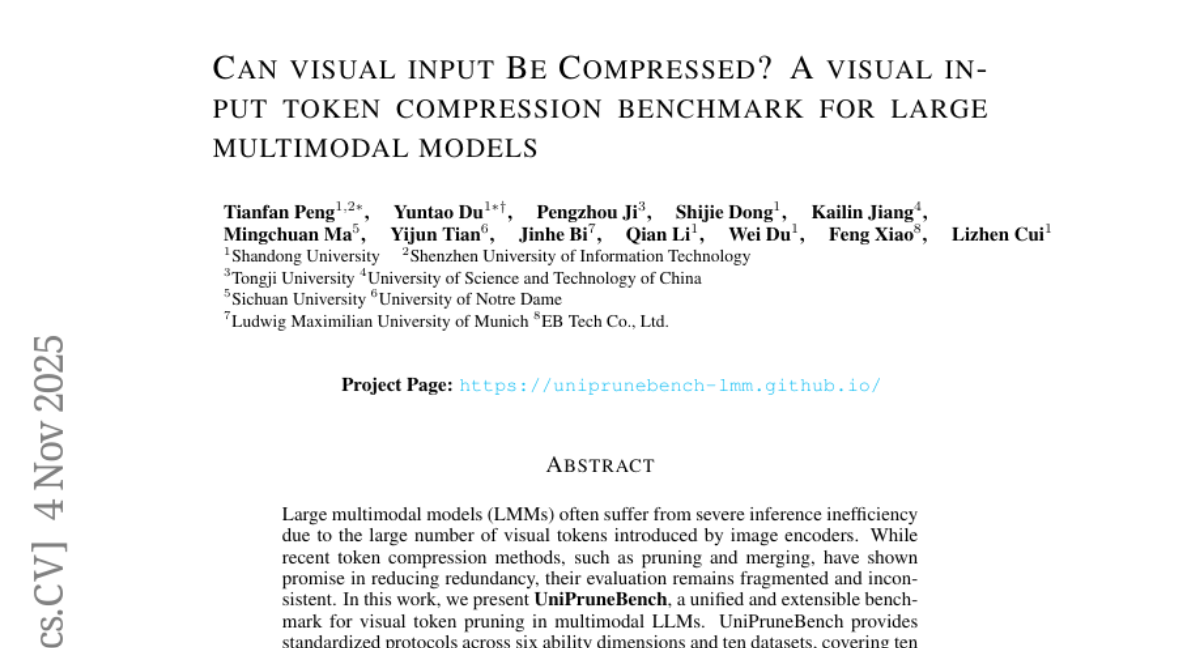
7. Can Visual Input Be Compressed? A Visual Token Compression Benchmark for Large Multimodal Models
🔑 Keywords: UniPruneBench, visual token pruning, multimodal LLMs, pruning sensitivity, compression algorithms
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce UniPruneBench as a unified benchmark for evaluating visual token pruning in multimodal LLMs, promoting standardized assessment across various tasks and models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize six ability dimensions and ten datasets, covering ten representative compression algorithms and three families of LMMs, to provide a comprehensive evaluation framework.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Random pruning serves as a surprisingly strong baseline, with no single method consistently outperforming others; pruning sensitivity varies across tasks, particularly impacting OCR; the pruning ratio is identified as a dominant factor affecting performance degradation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02650
8. Shorter but not Worse: Frugal Reasoning via Easy Samples as Length Regularizers in Math RLVR
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Large language models, step-by-step reasoning, RLVR, emergent brevity
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to reduce verbosity in large language models (LLMs) by modifying RLVR pipelines, avoiding explicit length penalization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Retaining and up-weighting moderately easy problems in RLVR is proposed to implicitly regulate output length, using Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507 for experimental validation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach leads to emergent brevity, solving complex problems without increasing output length, demonstrating nearly half-length solutions while maintaining baseline accuracy.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.01937

9. LTD-Bench: Evaluating Large Language Models by Letting Them Draw
🔑 Keywords: LTD-Bench, large language models, spatial reasoning, visual outputs, diagnostic analysis
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate the spatial reasoning capabilities of large language models by requiring them to generate visual outputs, addressing the gap between numerical scores and practical performance in understanding spatial concepts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of LTD-Bench, a benchmark that assesses models through tasks generating drawings via dot matrices or executable code, and testing spatial imagination and perception across varying difficulty levels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Discovered significant deficiencies in language-spatial mapping in large language models, revealing a fundamental limitation that questions their capacity as world models and emphasizes the need for improved evaluation approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02347

10. CodeClash: Benchmarking Goal-Oriented Software Engineering
🔑 Keywords: CodeClash, language models, codebase, strategic reasoning, autonomous development
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Evaluate language models’ ability to iteratively develop code for open-ended objectives through competitive tournaments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducting 1680 tournaments consisting of 25,200 rounds across six arenas to assess eight language models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Despite diverse development styles, language models exhibit fundamental limitations in strategic reasoning and long-term codebase maintenance compared to expert human programmers.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.00839

11. iFlyBot-VLA Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: iFlyBot-VLA, Vision-Language-Action (VLA), latent action model, dual-level action representation, 3D perceptual and reasoning
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the iFlyBot-VLA, a large-scale Vision-Language-Action model aimed at enhancing 3D perceptual and reasoning capabilities for manipulation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a latent action model thoroughly trained on human and robotic manipulation videos.
– Implements a dual-level action representation framework to simultaneously supervise both Vision-Language Model (VLM) and action expert training.
– Employs a mixed training strategy combining robot trajectory data with general and spatial QA datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The experimental results on the LIBERO Franka benchmark demonstrate the superiority of the framework, with competitive success rates in diverse manipulation tasks.
– Plans to open-source part of their constructed dataset to support future research in the community.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.01914

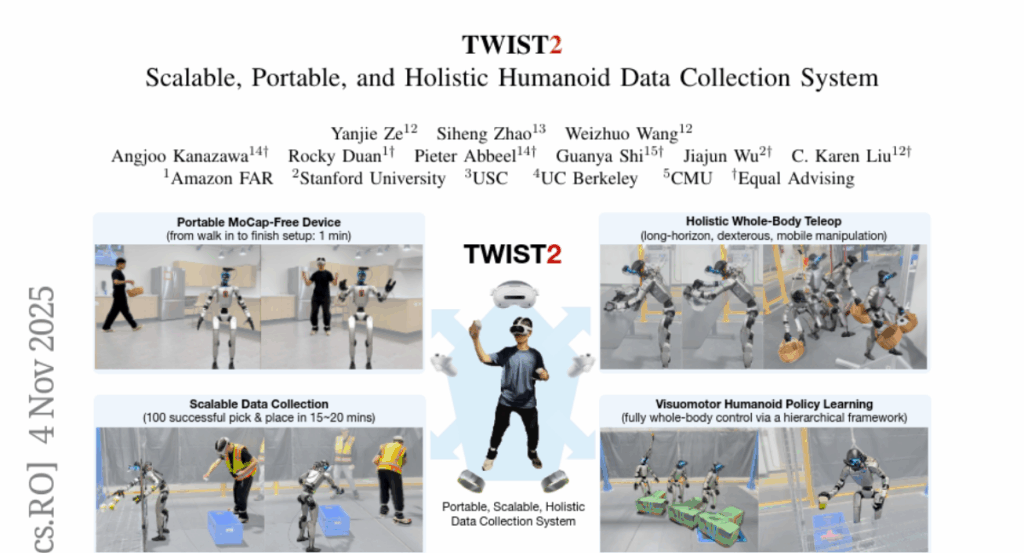
12. TWIST2: Scalable, Portable, and Holistic Humanoid Data Collection System
🔑 Keywords: Mocap-free, Humanoid Robotics, Egocentric Vision, Hierarchical Visuomotor Policy
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to introduce TWIST2, a portable, mocap-free system for humanoid teleoperation and data collection, which aims to enhance scalability and preserve full whole-body control.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The system utilizes PICO4U VR for real-time whole-body motion capture of human operators and employs a custom 2-DoF robot neck for egocentric vision, enabling comprehensive human-to-humanoid control.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The TWIST2 system allows the collection of 100 demonstrations in 15 minutes with a nearly 100% success rate, demonstrating effective whole-body dexterous manipulation and dynamic tasks. The entire system and dataset are open-sourced for further research and development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02832

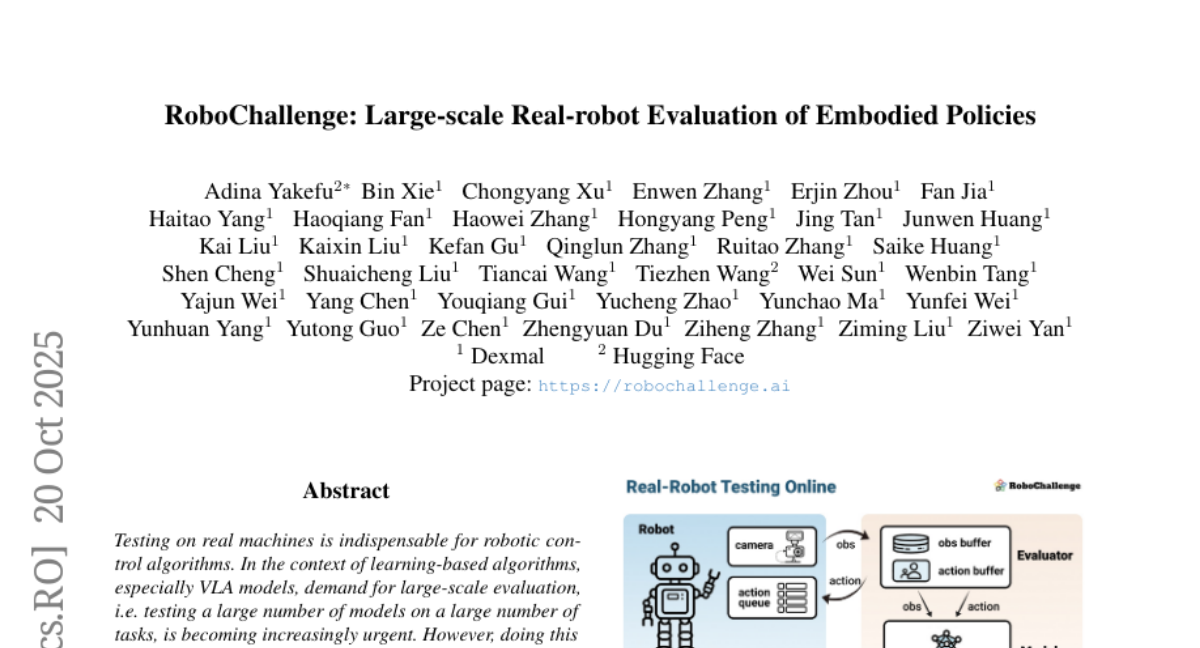
13. RoboChallenge: Large-scale Real-robot Evaluation of Embodied Policies
🔑 Keywords: RoboChallenge, VLA models, robotic control algorithms, scalability, reproducibility
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop RoboChallenge, an online evaluation system for testing robotic control algorithms, with a focus on scalability and reproducibility.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A methodology for constructing the RoboChallenge system and surveying state-of-the-art VLA models using an initial benchmark called Table30.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Highlighted the necessity of large-scale evaluation for learning-based robotic control algorithms and provided a potential solution through RoboChallenge.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.17950
14. ChartM^3: A Multi-Stage Code-Driven Pipeline for Constructing Multi-Dimensional and Multi-Step Visual Reasoning Data in Chart Comprehension
🔑 Keywords: Retrieval-Augmented Generation, Chain-of-Thought, Visual Reasoning, Supervised Fine-tuning, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance reasoning capabilities in complex chart understanding tasks using an automated multi-stage code-driven pipeline.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The pipeline integrates Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) strategies to generate diverse visual reasoning datasets systematically.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments using supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning demonstrate that the constructed dataset significantly improves reasoning capabilities and cross-domain generalization performance, enabling smaller models to achieve comparable results to larger ones in complex chart comprehension.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02415

15. BRAINS: A Retrieval-Augmented System for Alzheimer’s Detection and Monitoring
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Alzheimer’s disease, Cognitive assessments, Case retrieval, AI in Healthcare
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the challenge of early and accurate Alzheimer’s disease detection, especially in resource-limited regions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop BRAINS, a system using Large Language Models with a dual-module architecture (cognitive diagnostic and case retrieval modules) to enhance Alzheimer’s detection and monitoring.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BRAINS proves effective in classifying disease severity and early signs of cognitive decline and holds potential as an assistive tool for scalable and explainable Alzheimer’s detection.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02490
16. D2D: Detector-to-Differentiable Critic for Improved Numeracy in Text-to-Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: D2D, Text-to-image diffusion models, Non-differentiable, Semantic alignment, Image quality
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Transform non-differentiable detection models into differentiable critics to improve object counting accuracy in text-to-image diffusion models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed the Detector-to-Differentiable (D2D) framework with custom activation functions to convert detector logits into soft binary indicators for optimizing noise prior in pre-trained T2I models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated significant improvements in object counting accuracy across several benchmarks with minimal impact on image quality and computational overhead.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.19278

17. RiddleBench: A New Generative Reasoning Benchmark for LLMs
🔑 Keywords: RiddleBench, Large Language Models, multifaceted reasoning, hallucination cascades, self-confirmation bias
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to reveal fundamental weaknesses in state-of-the-art language models, particularly in their multifaceted reasoning abilities and susceptibility to errors like hallucination cascades and poor self-correction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced RiddleBench, a benchmark of 1,737 challenging puzzles designed to assess core reasoning capabilities such as logical deduction, spatial awareness, and constraint satisfaction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Top proprietary models demonstrate a significant shortfall in reasoning, achieving just over 60% accuracy on RiddleBench. They exhibit flaws, including a pronounced self-confirmation bias, and performance decreases with changes in constraints or addition of irrelevant information, underscoring the need for more robust language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2510.24932

18. Reg-DPO: SFT-Regularized Direct Preference Optimization with GT-Pair for Improving Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: GT-Pair, Reg-DPO, video generation quality, Direct Preference Optimization, memory optimization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance video generation quality by addressing challenges related to data construction, training stability, and memory consumption.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces GT-Pair to automatically create high-quality preference pairs using real videos as positives and model-generated videos as negatives.
– Develops Reg-DPO that integrates SFT loss as a regularization term to enhance training stability and generation fidelity.
– Combines FSDP framework with multiple memory optimization techniques to improve training capacity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method consistently outperforms existing approaches in I2V and T2V tasks across multiple datasets, delivering superior video generation quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.01450

19. TabDSR: Decompose, Sanitize, and Reason for Complex Numerical Reasoning in Tabular Data
🔑 Keywords: Query decomposition, Table sanitization, Program-of-thoughts reasoning, Numerical reasoning, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve large language models’ performance on complex tabular numerical reasoning tasks using a new framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a framework combining query decomposition, table sanitization, and program-of-thoughts reasoning. Evaluated using a new dataset, CalTab151.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– \method framework consistently outperforms existing methods, showing significant accuracy improvements on benchmarks. It integrates seamlessly with mainstream LLMs, enhancing performance in complex numerical reasoning tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02219

20. AyurParam: A State-of-the-Art Bilingual Language Model for Ayurveda
🔑 Keywords: AyurParam-2.9B, Ayurveda, Domain-specialized, Bilingual language model, Fine-tuned
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce AyurParam-2.9B, a domain-specialized bilingual language model fine-tuned for Ayurveda, and evaluate its performance against other models in its size class.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model is fine-tuned from Param-1-2.9B using an expertly curated Ayurveda dataset, which includes classical texts and clinical guidance in both English and Hindi, ensuring factual precision and clarity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AyurParam-2.9B outperforms all open-source instruction-tuned models in its size class and showcases competitive or superior performance compared to larger models, emphasizing the importance of domain adaptation and high-quality supervision in AI for specialized medical knowledge.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02374

21. VidEmo: Affective-Tree Reasoning for Emotion-Centric Video Foundation Models
🔑 Keywords: Emotion Understanding, VideoLLMs, Video Emotion Foundation Models, Affective Cues, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop an affective cues-guided reasoning framework for improved emotion understanding from videos, focusing on dynamic and cues-dependent properties of emotions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework introduces video emotion foundation models (VidEmo) that employ a two-stage tuning process: curriculum emotion learning and affective-tree reinforcement learning. Additionally, it utilizes a fine-grained dataset, Emo-CFG, which consists of 2.1M instruction-based samples.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach achieves competitive performance, setting a new milestone across 15 face perception tasks, offering significant advancements in emotion reasoning and understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02712

22. Discriminately Treating Motion Components Evolves Joint Depth and Ego-Motion Learning
🔑 Keywords: Unsupervised learning, Depth, Ego-motion, Geometric constraints, 3D perception
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the performance and robustness of unsupervised learning in depth and ego-motion estimation by leveraging geometric constraints.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a discriminative approach to motion components using geometric regularities from optical flows and alignments of optical axes and imaging planes between consecutive video frames.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed DiMoDE framework outperforms existing methods on multiple public and newly collected diverse datasets, especially under challenging conditions, offering a more robust joint learning process for depth and ego-motion estimation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.01502

23. LiveSecBench: A Dynamic and Culturally-Relevant AI Safety Benchmark for LLMs in Chinese Context
🔑 Keywords: LiveSecBench, Chinese-language LLM, AI safety, Ethics, Privacy
💡 Category: AI Ethics and Fairness
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce LiveSecBench, a dynamic safety benchmark for Chinese-language LLMs, evaluating them on legality, ethics, factuality, privacy, adversarial robustness, and reasoning safety.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Continuous updates and evaluation of 18 LLMs across six critical dimensions based on Chinese legal and social frameworks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LiveSecBench provides an evolving landscape of AI safety measures with plans to incorporate new safety dimensions such as Text-to-Image Generation Safety and Agentic Safety.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.02366

24.
