AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251111

1. HaluMem: Evaluating Hallucinations in Memory Systems of Agents
🔑 Keywords: Memory Hallucination, HaluMem, LLMs, User-centric Datasets, Memory Reliability
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces HaluMem, an evaluation benchmark to identify and analyze memory hallucinations in AI systems across memory extraction, updating, and question answering stages.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– It employs large-scale human-AI interaction datasets, namely HaluMem-Medium and HaluMem-Long, featuring multi-turn dialogues to evaluate memory hallucination behaviors and context complexity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Empirical studies indicate that existing memory systems often generate and propagate hallucinations during the memory extraction and updating stages, impacting the question answering performance. The research emphasizes the need for interpretable and constrained memory operation mechanisms to enhance memory reliability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.03506

2. IterResearch: Rethinking Long-Horizon Agents via Markovian State Reconstruction
🔑 Keywords: IterResearch, Markov Decision Process, Efficiency-Aware Policy Optimization, reinforcement learning, long-horizon tasks
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces IterResearch, aimed at improving long-horizon reasoning in AI agents by reformulating it as a Markov Decision Process.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employs strategic workspace reconstruction and Efficiency-Aware Policy Optimization (EAPO) with geometric reward discounting and adaptive downsampling.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– IterResearch significantly outperforms existing agents, showcasing dramatic improvements in interaction scaling and serving as an effective prompting strategy for frontier models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07327

3. DRIVE: Data Curation Best Practices for Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Reward in Competitive Code Generation
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Competitive Programming, State-of-the-Art Performance, Group Relative Policy Optimization, Curriculum Design
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a two-stage reinforcement learning approach for state-of-the-art competitive-programming code generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a two-stage RL pipeline starting with supervised fine-tuning and followed by Group Relative Policy Optimization using testcase-driven rewards.
– It involves a hard-focus curriculum for refining the model’s performance on challenging problems.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in code generation tasks, comparable to prominent models like DeepSeek v3.1.
– The study provides best practices for data curation, entropy expansion, and curriculum design.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.06307

4. The Station: An Open-World Environment for AI-Driven Discovery
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, autonomous scientific discovery, emergent behavior, multi-agent environment, open-world environment
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce the STATION, an open-world multi-agent environment simulating a scientific ecosystem for autonomous scientific discovery.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Leveraging extended context windows, agents can independently read papers, form hypotheses, submit code, perform analyses, and publish results without centralized coordination.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AI agents in the STATION achieve state-of-the-art performance across various benchmarks, surpassing existing models like AlphaEvolve, and organically developing novel methods such as a new algorithm for scRNA-seq batch integration.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.06309

5. MVU-Eval: Towards Multi-Video Understanding Evaluation for Multimodal LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Large Language Models, Multi-Video Understanding, MVU-Eval, question-answer pairs, autonomous systems
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce MVU-Eval as a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate multi-video understanding in Multimodal Large Language Models, highlighting its necessity over existing single-video benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MVU-Eval assesses eight core competencies through 1,824 question-answer pairs across 4,959 videos from diverse domains, focusing on both fundamental perception and higher-order reasoning tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified significant performance discrepancies in state-of-the-art models for multi-video understanding, with MVU-Eval enabling more accurate evaluation and fostering future research improvements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07250

6. Routing Manifold Alignment Improves Generalization of Mixture-of-Experts LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Sparse Mixture-of-Experts, routing weights, task embedding, manifold regularization, RoMA
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to align routing weights with task embeddings in Sparse Mixture-of-Experts models to improve generalization and reduce performance gaps in large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method, named Routing Manifold Alignment (RoMA), introduces a manifold regularization term in the post-training objective, requiring lightweight finetuning of the routers while keeping other parameters frozen.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments showed substantial improvement when using RoMA, as it allows samples targeting similar tasks to share similar expert choices across layers, enhancing task understanding and solution generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07419

7. RedOne 2.0: Rethinking Domain-specific LLM Post-Training in Social Networking Services
🔑 Keywords: RedOne 2.0, Reinforcement Learning, Social Networking Services, Large Language Models, Data Efficiency
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce RedOne 2.0, a social networking service-oriented large language model (LLM), designed for rapid and stable adaptation in the context of social networking services.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a progressive, RL-prioritized post-training paradigm with a three-stage pipeline: Exploratory Learning on curated SNS corpora, Targeted Fine-Tuning with supervised fine-tuning, and Refinement Learning using reinforcement learning with SNS-centric signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RedOne 2.0 demonstrates superior data efficiency and stability with an average improvement of 2.41 over a 7B sub-optimal baseline, and an average performance lift of 8.74 from the base model, establishing a competitive and cost-effective baseline for domain-specific LLMs in social networking scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07070

8. SofT-GRPO: Surpassing Discrete-Token LLM Reinforcement Learning via Gumbel-Reparameterized Soft-Thinking Policy Optimization
🔑 Keywords: SofT-GRPO, Large Language Models, soft-thinking, Gumbel-Softmax, policy optimization
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance soft-thinking in Large Language Models (LLMs) by developing a novel policy optimization algorithm, SofT-GRPO, integrating Gumbel noise and the Gumbel-Softmax technique.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– SofT-GRPO algorithm is developed to reinforce the soft-thinking paradigm by injecting Gumbel noise, using the Gumbel-Softmax technique, and leveraging the reparameterization trick in policy gradient methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed SofT-GRPO slightly outperforms discrete-token GRPO in Pass@1 and shows significant improvement in Pass@32 across LLMs ranging from 1.5B to 7B parameters, demonstrating its effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.06411

9. Reasoning with Confidence: Efficient Verification of LLM Reasoning Steps via Uncertainty Heads
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, uncertainty quantification, transformer-based, reasoning verification, introspective LLMs
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve step-level reasoning verification within Large Language Models (LLMs) by using transformer-based uncertainty quantification heads to estimate uncertainty from internal states.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of transformer-based uncertainty quantification heads (UHeads) trained on frozen LLM internal states, generating target labels automatically via other LLMs or self-supervised approaches. UHeads are lightweight with less than 10M parameters.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UHeads demonstrate effectiveness across domains like mathematics, planning, and question answering, matching or surpassing the performance of significantly larger models while suggesting LLMs’ internal states encode reliable signals for reasoning verification, paving the way for scalable and generalizable introspective LLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.06209

10. Teaching Pretrained Language Models to Think Deeper with Retrofitted Recurrence
🔑 Keywords: Depth-recurrent language models, Recurrence, Effective depth, Computational cost
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To convert pretrained non-recurrent language models into depth-recurrent models to improve performance at a given compute budget.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing a curriculum of recurrences to increase the effective depth during training and reduce total computational cost.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Converting pretrained non-recurrent models to depth-recurrent models results in better performance under a fixed compute budget compared to simply post-training the original models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07384
11. Robot Learning from a Physical World Model
🔑 Keywords: PhysWorld, Video Generation, Physical World Modeling, Zero-shot Generalizable Robotic Manipulation
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce PhysWorld to enable robotic learning from video generation through physical world modeling without needing real robot data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize video generation and physical world reconstruction to generate task-conditioned videos and reconstruct the underlying physical world.
– Implement object-centric residual reinforcement learning to convert video motions into physically accurate robotic actions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PhysWorld significantly improves manipulation accuracy in diverse real-world tasks compared to previous approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07416
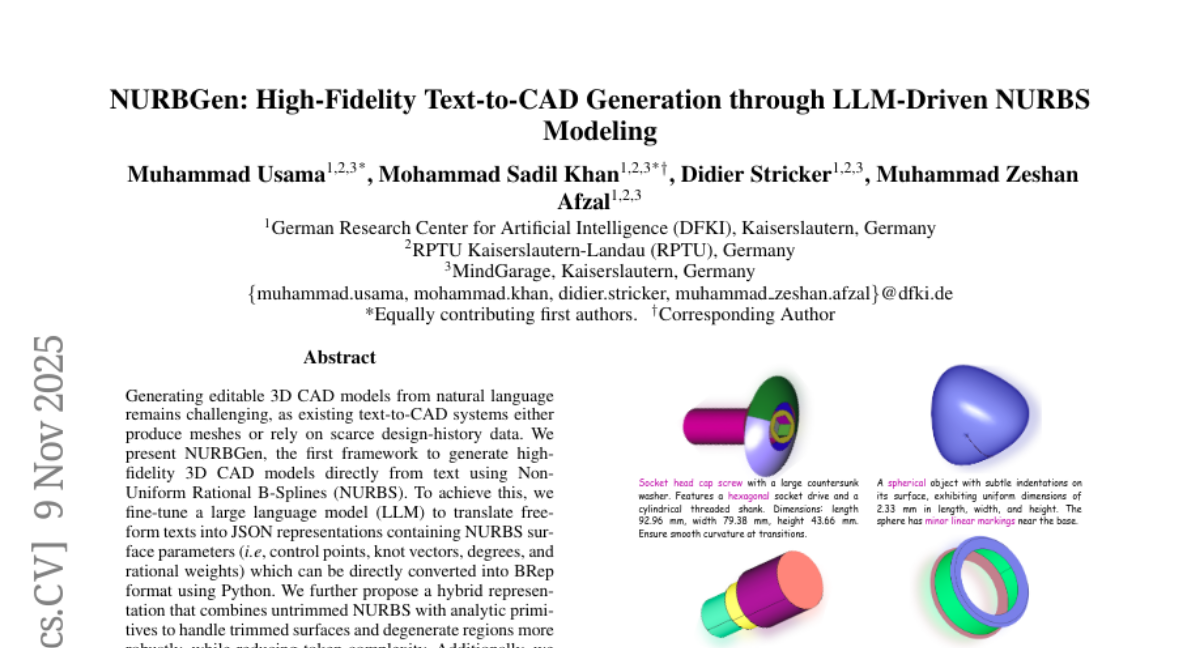
12. NURBGen: High-Fidelity Text-to-CAD Generation through LLM-Driven NURBS Modeling
🔑 Keywords: NURBS, 3D CAD Models, Large Language Model, BRep format, partABC
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces NURBGen, a novel framework designed to generate high-fidelity 3D CAD models from text using Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers fine-tuned a large language model to translate free-form texts into JSON representations with NURBS surface parameters, which are then converted into BRep format.
– They proposed a hybrid representation combining untrimmed NURBS and analytic primitives for robust handling of trimmed surfaces and degenerate regions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– NURBGen demonstrated superior performance in geometric fidelity and dimensional accuracy compared to prior methods, as validated by expert evaluations. The code and dataset are to be released publicly.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.06194
13. Ariadne: A Controllable Framework for Probing and Extending VLM Reasoning Boundaries
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, spatial reasoning, synthetic mazes, zero-shot generalization
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the extension of Vision-Language Models’ capabilities in visual-centric spatial reasoning through reinforcement learning post-training, specifically using synthetic mazes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of Ariadne, a framework employing synthetic mazes and Reinforcement Learning with Verified Rewards (RLVR), structured within a difficulty-aware curriculum to test and extend the capability of VLMs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Ariadne post-training significantly improves model performance, with VLMs achieving over 50% accuracy on previously unachievable tasks and demonstrating considerable zero-shot generalization improvements on real-world benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.00710

14. RLoop: An Self-Improving Framework for Reinforcement Learning with Iterative Policy Initialization
🔑 Keywords: RLoop, Reinforcement Learning, Rejection-sampling Fine-Tuning, Catastrophic Forgetting, Generalization
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address overfitting and improve generalization in Reinforcement Learning for Verifiable Rewards using a new framework called RLoop.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of RLoop framework based on iterative policy initialization and Rejection-sampling Fine-Tuning.
– Development of a virtuous cycle from exploration using RL, creation of an expert dataset from successful trajectories, and iterative policy refinement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RLoop significantly mitigates forgetting and enhances generalization, leading to a 9% increase in average accuracy and over a 15% improvement in pass@32 compared to vanilla RL.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.04285

15. Llama-Embed-Nemotron-8B: A Universal Text Embedding Model for Multilingual and Cross-Lingual Tasks
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, open-source, multilingual, ablation studies, text embedding
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a fully open-source text embedding model called llama-embed-nemotron-8b that achieves state-of-the-art performance in multilingual scenarios
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a novel data mix of 16.1 million query-document pairs, including public datasets and synthetically generated examples
– Conduct detailed ablation studies to analyze core design choices, such as contrastive loss implementations and synthetic data generation strategies
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The llama-embed-nemotron-8b model excels in multilingual embedding tasks and low-resource languages, serving as a universal text embedding solution with flexible user-defined instructions
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07025

16. MPJudge: Towards Perceptual Assessment of Music-Induced Paintings
🔑 Keywords: MPJudge, perceptual coherence, modulation-based fusion, Direct Preference Optimization, music-induced painting
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose a novel framework, MPJudge, for assessing music-induced paintings by evaluating the perceptual coherence between music and visual art.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of music features into a visual encoder using a modulation-based fusion mechanism.
– Utilization of the MPD dataset for training, with pairwise preference annotations to handle ambiguous cases.
– Application of Direct Preference Optimization to learn more effectively from ambiguous data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed MPJudge model outperforms existing emotion recognition models, offering more accurate identification of music-relevant regions in paintings, as demonstrated by extensive experiments and qualitative results.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07137

17. DigiData: Training and Evaluating General-Purpose Mobile Control Agents
🔑 Keywords: DigiData, DigiData-Bench, Mobile Control Agents, AI-Powered Evaluations, Dynamic Evaluation Protocols
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce DigiData, a diverse and high-quality dataset designed for training mobile control agents to achieve complex and human-relevant goals.
– To offer DigiData-Bench as a benchmark for evaluating mobile control agents on real-world complex tasks, enhancing agent performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The construction of DigiData through comprehensive exploration of app features for greater diversity and goal complexity.
– Proposal of dynamic evaluation protocols and AI-Powered Evaluations as rigorous alternatives to the step-accuracy metric for assessing mobile control agents.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The contributions aim to significantly advance the development of mobile control agents, paving the way for more intuitive and effective human-device interactions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07413

18. Diffusion-SDPO: Safeguarded Direct Preference Optimization for Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion-SDPO, text-to-image, preference optimization, loser gradient, alignment
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance the text-to-image generation quality by addressing issues in preference optimization using an adaptive scaling mechanism for the loser gradient.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a safeguarded update rule, named Diffusion-SDPO, which adaptively scales the loser gradient. A closed-form scaling coefficient is computed to ensure non-increasing error of the preferred output at each optimization step.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed Diffusion-SDPO method shows consistent improvements over baseline models in terms of automated preference, aesthetic, and prompt alignment metrics with marginal computational overhead.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.03317

19. Long Grounded Thoughts: Distilling Compositional Visual Reasoning Chains at Scale
🔑 Keywords: multimodal reasoning, reasoning data generation framework, synthetic vision-centric questions, cross-modality transfer, finetuning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a reasoning data generation framework with over 1M synthetic vision-centric questions, enhancing performance and enabling cross-modality transfer.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework involves a two-stage synthesis process utilizing VLMs and reasoning LLMs for generating reasoning traces, supporting offline and online RL.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Finetuning on the created data outperforms existing open-data benchmarks and strong closed-data models, proving the dataset’s transferability to text-only and audio reasoning tasks and effectiveness in cross-modality transfer.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.05705

20. 10 Open Challenges Steering the Future of Vision-Language-Action Models
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, Multimodality, Reasoning, Safety, Human Coordination
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to discuss the development and major milestones of Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, focusing on aspects such as multimodality, reasoning, and safety, while highlighting the trends in spatial understanding and human coordination.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study analyzes 10 principal milestones in the VLA model advancements, including multimodality, reasoning, and cross-robot action generalization, among others. It further explores emerging trends like spatial understanding and data synthesis.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– It emphasizes the importance of these milestones and trends to drive wider acceptance and practical implementations of VLA models, by drawing attention to promising research avenues.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.05936

21. SWE-fficiency: Can Language Models Optimize Real-World Repositories on Real Workloads?
🔑 Keywords: SWE-fficiency, performance optimization, software engineering, expert speedup
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces SWE-fficiency, a benchmark designed to evaluate performance optimization in large-scale software repositories by assessing how software agents address bottlenecks while maintaining program correctness.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methodology employs an automated pipeline that extracts performance-improving edits from GitHub pull requests. This involves keyword filtering, static analysis, coverage tooling, and execution validation to confirm expert speedup baselines and identify unit tests.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Empirical evaluation shows that state-of-the-art agents are significantly underperforming, achieving on average less than 0.15x the expert speedup. Agents particularly struggle with localizing optimization opportunities, reasoning about execution across functions, and maintaining correctness in the proposed edits.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.06090

22. Do LLMs Feel? Teaching Emotion Recognition with Prompts, Retrieval, and Curriculum Learning
🔑 Keywords: Emotion Recognition in Conversation, LLMs, Prompt engineering, Demonstration retrieval, Curriculum learning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance LLMs’ ability to perceive emotions in conversations using a novel ERC training framework called PRC-Emo.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of prompt engineering, demonstration retrieval, and curriculum learning to create emotion-sensitive prompts and a dedicated repository for ERC.
– Implementation of a curriculum learning strategy in the LoRA fine-tuning process to organize training samples in an easy-to-hard sequence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets IEMOCAP and MELD, highlighting the effectiveness and generalizability of the PRC-Emo framework in improving LLM-based emotional understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07061

23. RLVE: Scaling Up Reinforcement Learning for Language Models with Adaptive Verifiable Environments
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Adaptive Environments, Language Models, Verifiable Rewards, Environment Scaling
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance language model reasoning by using Reinforcement Learning with Adaptive Verifiable Environments (RLVE), which adjusts problem difficulty dynamically.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented RLVE-Gym, a suite of 400 verifiable environments, to procedurally generate problems and verify rewards algorithmically.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RLVE improves generalizable reasoning capabilities by yielding a 3.37% absolute improvement on benchmarks, outperforming traditional RL training with a more efficient compute utilization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07317

24. Generating an Image From 1,000 Words: Enhancing Text-to-Image With Structured Captions
🔑 Keywords: Text-to-image models, long structured captions, DimFusion, FIBO
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the precision and controllability of text-to-image models by training on long structured captions, achieving state-of-the-art prompt alignment.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of DimFusion, a fusion mechanism to integrate intermediate tokens from a lightweight LLM without increasing token length.
– Introduction of Text-as-a-Bottleneck Reconstruction (TaBR) evaluation protocol to effectively measure controllability and expressiveness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The trained model, FIBO, achieves state-of-the-art prompt alignment among open-source models, demonstrating improved control over visual factors and enhanced detail generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.06876

25. DIMO: Diverse 3D Motion Generation for Arbitrary Objects
🔑 Keywords: generative approach, video models, latent space, 3D motions, neural key point trajectories
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop DIMO, a generative approach that can generate diverse 3D motions for arbitrary objects from a single image.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing well-trained video models to extract motion patterns and embedding them into a shared low-dimensional latent space.
– Training a shared motion decoder to learn motion distribution represented by neural key point trajectories.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DIMO can instantly sample diverse 3D motions using a learned latent space, enabling applications such as 3D motion interpolation and language-guided motion generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.07409
