AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251120

1. Kandinsky 5.0: A Family of Foundation Models for Image and Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: Kandinsky 5.0, Generative Models, Foundation Models, High-Resolution Image, AI-generated videos
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce Kandinsky 5.0, a set of state-of-the-art models designed for high-resolution image and short video generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of varied parameter models including Kandinsky 5.0 Image Lite, Video Lite, and Video Pro.
– Implementation of a comprehensive data curation lifecycle and multi-stage training pipeline with techniques such as self-supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning-based post-training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Kandinsky 5.0 demonstrates superior generation quality and performance, confirmed by human evaluation.
– The framework is open-source, seeking to enhance the accessibility and development of high-quality generative models within the research community.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.14993

2. Reasoning via Video: The First Evaluation of Video Models’ Reasoning Abilities through Maze-Solving Tasks
🔑 Keywords: VR-Bench, Video Models, Spatial Reasoning, Maze-solving, SFT
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate video models’ spatial reasoning capabilities through maze-solving tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of VR-Bench, a benchmark consisting of 7,920 procedurally generated videos across five maze types designed for spatial planning and multi-step reasoning evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Video Models excel in spatial perception and reasoning, outperform VLMs, and benefit from diverse sampling during inference which improves reasoning reliability by 10-20%.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.15065

3. What Does It Take to Be a Good AI Research Agent? Studying the Role of Ideation Diversity
🔑 Keywords: Ideation diversity, AI research agents, MLE-bench, agent trajectories, agent scaffolds
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To examine the role of ideation diversity in the performance of AI research agents on the MLE-bench benchmark across various models and agent scaffolds.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analyzed agent trajectories on the MLE-bench benchmark.
– Conducted a controlled experiment to modify ideation diversity levels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Higher ideation diversity correlates with stronger performance in AI research agents.
– The findings hold across various agent performance metrics beyond the standard medal-based scoring.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.15593

4. VisPlay: Self-Evolving Vision-Language Models from Images
🔑 Keywords: VisPlay, Vision-Language Models, self-evolving RL framework, Reinforcement Learning, visual reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in reasoning, generalization, and response quality through a self-evolving Reinforcement Learning framework using unlabeled image data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces VisPlay, which leverages two interacting roles: an Image-Conditioned Questioner and a Multimodal Reasoner. These roles are trained together using Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to maintain a balance between question complexity and response quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VisPlay demonstrated consistent improvements in visual reasoning and compositional generalization, as well as reduction in hallucination, across various benchmarks, establishing a path for scalable self-evolving multimodal intelligence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.15661

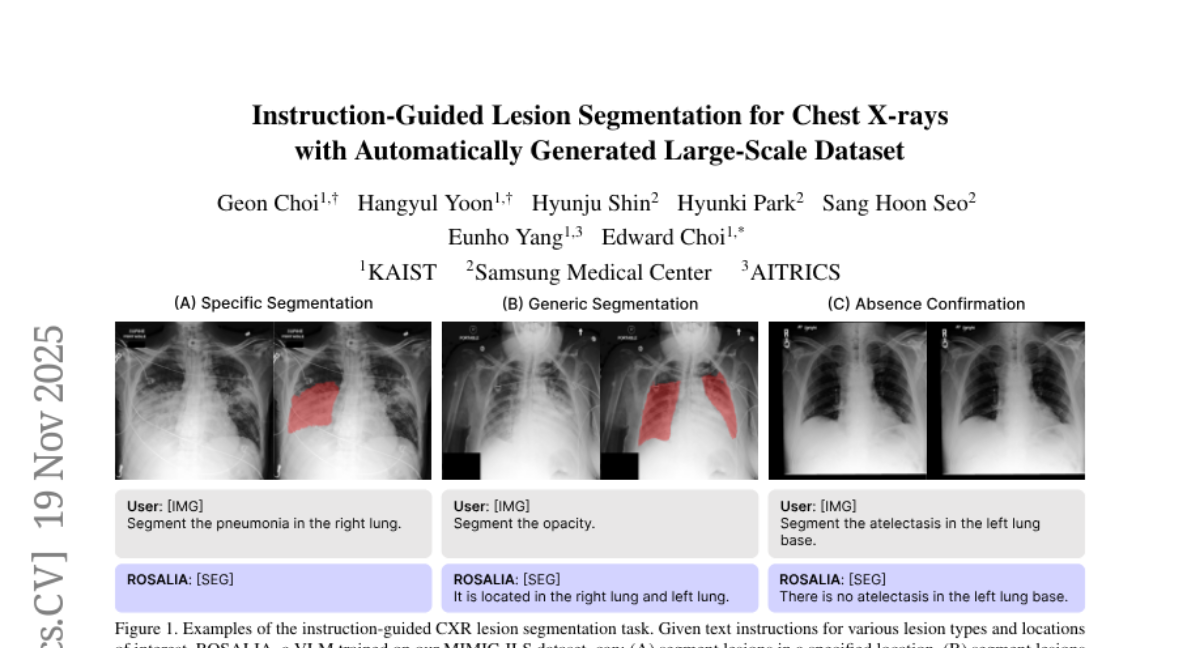
5. Instruction-Guided Lesion Segmentation for Chest X-rays with Automatically Generated Large-Scale Dataset
🔑 Keywords: Instruction-guided Lesion Segmentation, Vision-Language Model, AI in Healthcare, Pixel-level CXR Lesion Grounding
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces instruction-guided lesion segmentation (ILS) to facilitate diverse lesion segmentation in chest X-rays using simple instructions to overcome existing limitations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of MIMIC-ILS, a large-scale instruction-answer dataset, using an automated multimodal pipeline to generate annotations from chest X-ray images.
– Introduction of ROSALIA, a vision-language model fine-tuned on MIMIC-ILS to segment lesions and provide textual explanations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model achieved high segmentation and textual accuracy, demonstrating the pipeline’s effectiveness and establishing MIMIC-ILS as a foundational resource for pixel-level CXR lesion grounding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.15186
6. ARC-Chapter: Structuring Hour-Long Videos into Navigable Chapters and Hierarchical Summaries
🔑 Keywords: Video Chaptering, Bilingual Dataset, GRACE, Transferability, F1 score
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop ARC-Chapter, a large-scale video chaptering model, to enhance performance and transferability in structuring long video content through extensive training data and a new evaluation metric.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A bilingual English-Chinese chapter dataset was curated with multi-level annotations, integrating ASR transcripts, scene texts, and visual captions to support the training process.
– Introduction of a new evaluation metric, GRACE, that includes many-to-one segment overlaps and semantic similarity for better reflecting real-world application needs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ARC-Chapter significantly surpasses previous models by 14.0% in F1 score and 11.3% in SODA score, setting a new state-of-the-art.
– The model demonstrates excellent transferability, improving performance on downstream tasks like dense video captioning on the YouCook2 dataset.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.14349

7. MHR: Momentum Human Rig
🔑 Keywords: parametric human body model, ATLAS, AR/VR, graphics pipelines, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce MHR, a parametric human body model that integrates the skeleton/shape paradigm of ATLAS with a modern rig and pose corrective system for expressive and anatomically plausible human animation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Combines the decoupled skeleton/shape paradigm with a flexible rig and pose corrections influenced by the Momentum library, supporting non-linear pose correctives.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Successfully enables robust integration of human animation in AR/VR and graphics applications by providing expressive and anatomically plausible animations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.15586

8. FreeAskWorld: An Interactive and Closed-Loop Simulator for Human-Centric Embodied AI
🔑 Keywords: Embodied AI, Simulation Framework, Large Language Models, Human-Agent Interaction, Vision-and-Language Navigation
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop FreeAskWorld, a simulation framework that enhances high-level behavior planning and human-centered social interactions in embodied AI systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) for behavior planning and interaction.
– Extension of the Vision-and-Language Navigation task to include interactive navigational guidance.
– Establishment of a benchmark dataset with diverse tasks and environments for AI training and evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FreeAskWorld improves the performance of fine-tuned models in semantic understanding and interaction.
– The framework highlights the potential of socially grounded simulation in advancing embodied AI towards complex planning and more natural interactions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.13524

9. Mixture of States: Routing Token-Level Dynamics for Multimodal Generation
🔑 Keywords: MoS, multimodal diffusion models, token-wise router, state-of-the-art, compute-efficient paradigm
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce MoS, a new fusion paradigm for multimodal diffusion models, to improve text-to-image generation and editing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement a learnable, token-wise router for modality interaction, utilizing a sparsely selected top-k hidden states strategy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MoS achieves state-of-the-art results with minimal parameters and computational overhead, matching or surpassing larger models in efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.12207

10. Aligning Generative Music AI with Human Preferences: Methods and Challenges
🔑 Keywords: preference alignment, MusicRL, DiffRhythm+, AI-generated music, temporal coherence
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the gap between computational optimization and human musical appreciation by systematically applying preference alignment techniques to music generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement preference alignment techniques including large-scale preference learning from MusicRL and diffusion-based preference optimization in DiffRhythm+ to tackle challenges like temporal coherence and harmonic consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Highlight the potential of preference-aligned music generation to enable transformative applications in interactive composition tools and personalized music services, emphasizing the need for interdisciplinary research combining machine learning and music theory.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.15038

11. Medal S: Spatio-Textual Prompt Model for Medical Segmentation
🔑 Keywords: Medal S, medical segmentation, spatial prompts, textual prompts, multi-class segmentation
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of this research is to develop Medal S, a medical segmentation foundation model that integrates spatial and textual prompts for high-accuracy multi-class segmentation across various imaging modalities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Medal S utilizes a framework supporting native-resolution spatial and textual prompts, ensuring channel-wise alignment between volumetric prompts and text embeddings. It incorporates a lightweight 3D convolutional module for precise voxel-space refinement and employs dynamic resampling, optimized text preprocessing, and a two-stage inference strategy to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Medal S demonstrates superior performance in multi-class medical segmentation tasks, significantly reducing inference time and improving memory efficiency, precision, and inference speed compared to sequential prompt-based approaches, as evidenced by outperforming the SAT model on several evaluation metrics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.13001
12.
