AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251201
1. Z-Image: An Efficient Image Generation Foundation Model with Single-Stream Diffusion Transformer
🔑 Keywords: Z-Image, Scalable Single-Stream Diffusion Transformer, photorealistic image generation, bilingual text rendering, consumer-grade hardware
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to develop Z-Image, an efficient 6B-parameter generative model that challenges the prevalent “scale-at-all-costs” approach, achieving competitive performance with reduced computational burden.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research utilized a Scalable Single-Stream Diffusion Transformer architecture followed by a few-step distillation scheme with reward post-training. This approach supports sub-second inference latency and compatibility with consumer-grade hardware.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Z-Image achieves performance that compares favorably with leading models in the field, particularly excelling in photorealistic image generation and bilingual text rendering, while requiring significantly lesser computational resources. The public release aims to foster the development of cost-effective yet state-of-the-art generative models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22699

2. REASONEDIT: Towards Reasoning-Enhanced Image Editing Models
🔑 Keywords: Image Editing, Multimodal Large Language Model, Diffusion Decoder, Reasoning Mechanisms
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the performance of image editing models by integrating reasoning mechanisms that improve instruction understanding and result correction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Exploration of two reasoning mechanisms, thinking and reflection, within a framework enabling a thinking-editing-reflection loop that leverages world knowledge to interpret instructions and review editing results.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Significant performance gains were achieved with the reasoning approach, showing improvements in ImgEdit (+4.3%), GEdit (+4.7%), and Kris (+8.2%) when initializing from Step1X-Edit, and outperforming previous methods on GEdit and Kris when integrated with Qwen-Image-Edit.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22625

3. AnyTalker: Scaling Multi-Person Talking Video Generation with Interactivity Refinement
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Diffusion Transformer, identity-aware attention, multi-stream processing, dataset
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop AnyTalker, a framework for generating high-quality multi-person talking videos with scalable identity awareness and interactivity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Extend Diffusion Transformer with an identity-aware attention mechanism.
– Train using single-person videos and minimal real multi-person clips to refine interactivity and speaking patterns.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AnyTalker achieves superior lip synchronization, visual quality, and natural interactivity, efficiently balancing data cost and identity scalability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.23475

4. Vision Bridge Transformer at Scale
🔑 Keywords: Vision Bridge Transformer (ViBT), Brownian Bridge Models, data-to-data translation, Transformer architecture, variance-stabilized velocity-matching objective
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Vision Bridge Transformer (ViBT) as an efficient model for data translation in image and video editing tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ a large-scale Transformer architecture with models scaled to 20B and 1.3B parameters.
– Utilize a variance-stabilized velocity-matching objective for robust training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The large-scale Bridge Models achieve robust performance in instruction-based image editing and complex video translation, demonstrating the power of this new data-to-data translation paradigm.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.23199
5. Architecture Decoupling Is Not All You Need For Unified Multimodal Model
🔑 Keywords: Attention Interaction Alignment, Multimodal Models, Cross-Modal Attention, Image Generation, Understanding
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study explores improving cross-modal attention in unified multimodal models for image generation and understanding without resorting to model decoupling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analysis of cross-modal attention behaviors and the proposal of Attention Interaction Alignment (AIA) loss to maintain task-specific multimodal interaction patterns.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AIA loss enhances cross-modal attention patterns and boosts both generation and understanding performances in unified multimodal models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22663

6. DeepSeekMath-V2: Towards Self-Verifiable Mathematical Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Large language models, mathematical reasoning, Self-verification, Theorem proving, Reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve mathematical reasoning by validating comprehensive and rigorous step-by-step derivations in theorem proving using large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Training a large language model-based verifier for theorem proving, and utilizing it as a reward model to train a proof generator, with self-verification as a key component.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model, DeepSeekMath-V2, demonstrates strong theorem-proving capabilities, achieving high scores in international competitions, indicating enhanced mathematical reasoning by self-verification methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22570

7. DiP: Taming Diffusion Models in Pixel Space
🔑 Keywords: DiP, Diffusion Transformer, Patch Detailer Head, computational efficiency, image generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce DiP, a pixel space diffusion framework, to balance high-quality image generation and computational efficiency without using VAEs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– DiP employs a Diffusion Transformer for global structure, and a Patch Detailer Head for restoring fine-grained local details, operating efficiently at high resolutions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DiP offers up to 10 times faster inference than previous methods with minimal increase in parameters, achieving a 1.79 FID score on ImageNet at 256×256 resolution.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18822

8. DualVLA: Building a Generalizable Embodied Agent via Partial Decoupling of Reasoning and Action
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action, DualVLA, dual-layer data pruning, action degeneration, dual-teacher adaptive distillation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance action performance while preserving reasoning capabilities in Vision-Language-Action models through a novel approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a dual-layer data pruning method to remove redundant embodied reasoning that may negatively affect action learning.
– Development of a dual-teacher adaptive distillation strategy to assign different supervision signals to distinct data domains, maintaining reasoning ability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DualVLA achieves a strong balance between precise action execution and multimodal understanding, with high success rates in multimodal benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22134

9. Adversarial Flow Models
🔑 Keywords: Adversarial flow models, Generative models, Adversarial training, FID, End-to-end training
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to present adversarial flow models that integrate adversarial and flow-based generative models for enhanced stability and efficiency in image generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model supports one-step or multi-step generation using an adversarial objective and focuses on a deterministic noise-to-data mapping similar to optimal transport, reducing training complexities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach stabilizes adversarial training, saves model capacity, and achieves superior FID scores on ImageNet-256px, demonstrating significant performance improvements over consistency-based methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22475

10. Every Token Counts: Generalizing 16M Ultra-Long Context in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Hierarchical Sparse Attention, Transformers, ultra-long context modeling, MoE model
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To tackle the challenge of ultra-long context modeling by integrating Hierarchical Sparse Attention (HSA) into Transformers for efficient handling and high accuracy on in-context retrieval tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of the HSA-UltraLong model, an 8B-parameter MoE model trained on over 8 trillion tokens, evaluated on tasks with varying context lengths.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model performs as well as full-attention baselines on in-domain lengths and achieves over 90% accuracy on most in-context retrieval tasks with contexts up to 16 million tokens, providing a strong foundation for future work in ultra-long context modeling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.23319

11. Decoupled DMD: CFG Augmentation as the Spear, Distribution Matching as the Shield
🔑 Keywords: CFG Augmentation, Distribution Matching Distillation, Text-to-Image Generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to decompose the training objective of Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD) in text-to-image generation to understand the primary driver of few-step distillation, challenging conventional beliefs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers conducted a rigorous decomposition of the DMD training objective to isolate effects of CFG Augmentation and Distribution Matching terms and tested alternative stabilizers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study found that CFG Augmentation, rather than Distribution Matching, is the primary driver of efficient few-step distillation in complex tasks such as text-to-image generation.
– Distribution Matching acts as a regularizer, not a unique component, as simpler constraints can achieve stabilization, motivating a more systematic analysis and modification of the distillation process.
– The findings are empirically validated by the adoption of the proposed method in the Z-Image project, enhancing image generation models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22677

12. Nemotron-Flash: Towards Latency-Optimal Hybrid Small Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Small Language Models, Real-Device Latency, Depth-Width Ratios, Efficient Attention Alternatives, AI Native
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to identify architectural factors and operators to optimize small language models (SLMs) for real-device latency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Investigated latency-optimal depth-width ratios and explored efficient attention alternatives.
– Developed an evolutionary search framework to discover optimal operator combinations for hybrid SLMs.
– Enhanced SLM training with a weight normalization technique for more effective weight updates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Nemotron-Flash family of hybrid SLMs advances the accuracy-efficiency frontier, achieving significant improvements in accuracy, latency, and throughput compared to existing models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18890

13. RefineBench: Evaluating Refinement Capability of Language Models via Checklists
🔑 Keywords: RefineBench, self-refinement, guided refinement, Natural Language Processing, reasoning models
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to evaluate language models’ ability to self-refine and improve their responses through self-reflection and guided refinement in various challenging tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced RefineBench, a benchmark with 1,000 problems across 11 domains paired with a checklist-based evaluation framework.
– Evaluated two modes of refinement: guided refinement with natural language feedback and self-refinement without guidance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Frontier language models demonstrate limited success in self-refinement, achieving modest scores.
– Guided refinement allows models to achieve near-perfect refinement, suggesting a need for significant improvements in self-refinement capabilities.
– RefineBench serves as a valuable testbed for tracking progress in this field.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22173

14. Captain Safari: A World Engine
🔑 Keywords: pose-conditioned world engine, dynamic local memory, video generation, OpenSafari, human study
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a pose-conditioned world engine, Captain Safari, that generates high-quality, long, 3D-consistent videos with precise camera maneuvers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a dynamic local memory and retriever to fetch pose-aligned world tokens that aid in maintaining stable 3D structures during video generation along specified trajectories.
– Introduces OpenSafari, an FPV dataset, for evaluating video quality, 3D consistency, and trajectory accuracy through a multi-stage validation pipeline.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Captain Safari surpasses existing methods in video quality, 3D consistency, and trajectory following, reducing MEt3R and improving AUC@30, and achieving lower FVD.
– In a human study, 67.6% of participants preferred results generated by Captain Safari over other models, demonstrating its effectiveness in controllable video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22815
15. World in a Frame: Understanding Culture Mixing as a New Challenge for Vision-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Culture Mixing, Large Vision-Language Models, Visual Question Answering, Supervised Fine-tuning, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study investigates the challenges LVLMs face in preserving cultural identities in culture mixing scenarios and how they perceive mixed cultural elements.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Construction of a benchmark named “CultureMix” with 23k human-verified culture mixing images across four subtasks to evaluate LVLMs.
– Evaluation of 10 LVLMs to assess their performance and identify failures in preserving cultural identity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LVLMs struggle with maintaining cultural identities and demonstrate strong reliance on backgrounds, decreasing accuracy when cultural backgrounds are included.
– Supervised fine-tuning with a diverse cultural dataset enhances model consistency and reduces background sensitivity.
– It is essential to focus on culture mixing scenarios for developing reliable LVLMs for diverse real-world environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22787

16. OralGPT-Omni: A Versatile Dental Multimodal Large Language Model
🔑 Keywords: OralGPT-Omni, TRACE-CoT, Dental Image Analysis, Multimodal Large Language Models, Intelligent Dentistry
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop OralGPT-Omni, a dental-specialized multimodal large language model, to enhance dental image analysis with a focus on trustworthiness and comprehensive analysis across various imaging modalities and clinical tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce TRACE-CoT, a clinically grounded chain-of-thought dataset, combined with a four-stage training paradigm to strengthen the model’s reasoning capabilities.
– Present MMOral-Uni, a unified multimodal benchmark for evaluating dental image analysis.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OralGPT-Omni significantly outperforms GPT-5 on dental image analysis benchmarks, achieving higher scores and promoting future advances in intelligent dentistry.
– Public availability of the code, benchmark, and models to foster further research and development in the field.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22055

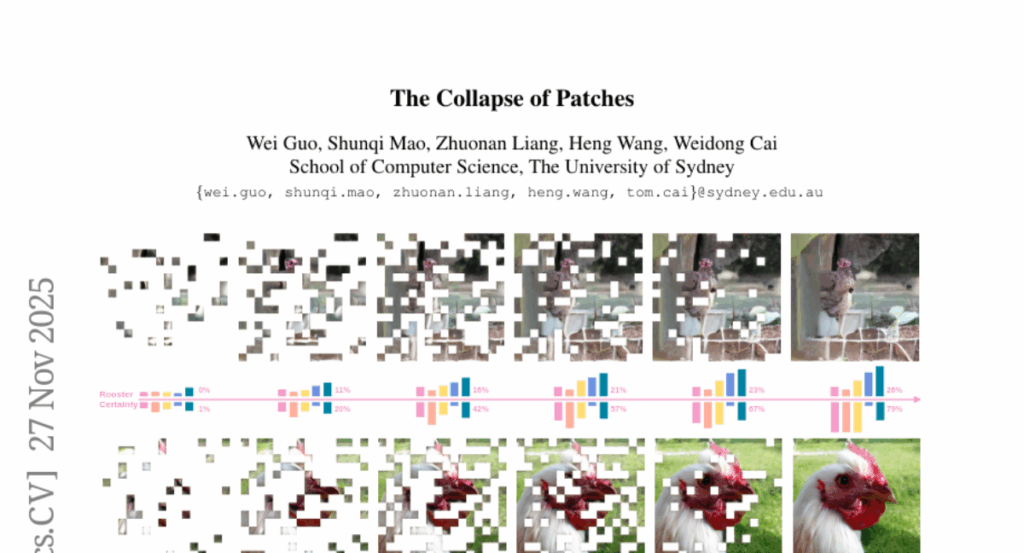
17. The Collapse of Patches
🔑 Keywords: Patch Collapse, Vision Efficiency, Masked Image Modeling, Autoencoder, Vision Transformers
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the concept of patch collapse in image modeling to improve vision efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A new autoencoder is designed to identify and select specific image patches to reconstruct target patches, using PageRank score to determine optimal patch order for image realization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study shows that autoregressive image generation benefits from respecting the patch order discovered, and Vision Transformers achieve high accuracy by being exposed to a select 22% of high-rank patches, thus promoting a novel perspective in image modeling for efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22281

18. CaptionQA: Is Your Caption as Useful as the Image Itself?
🔑 Keywords: CaptionQA, utility-based benchmark, downstream tasks, LLM, multimodal systems
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to evaluate the effectiveness of model-generated captions in supporting downstream tasks, assessing if they can effectively substitute for images in real-world applications using the CaptionQA benchmark.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– CaptionQA evaluates caption utility by creating a domain-dependent benchmark across four domains: Natural, Document, E-commerce, and Embodied AI, with finely detailed taxonomies. The benchmark involves 33,027 multiple-choice questions that require visual information, which are answered by a LLM using captions alone.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study reveals significant gaps between an image and its caption utility in supporting downstream tasks. State-of-the-art MLLMs show up to a 32% decrease in performance when relying solely on captions compared to traditional image-QA benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.21025

19. Focused Chain-of-Thought: Efficient LLM Reasoning via Structured Input Information
🔑 Keywords: F-CoT, cognitive psychology, chain-of-thought, token reduction, attention
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce an input-centric approach, F-CoT, inspired by cognitive psychology, for reducing token usage in large language models without compromising accuracy on arithmetic problems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A training-free method that separates information extraction from reasoning by organizing essential information into a structured context to guide reasoning, avoiding attention to irrelevant details.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– F-CoT significantly reduces token usage by 2-3 times while maintaining accuracy comparable to standard zero-shot chain-of-thought, demonstrating the effectiveness of structured input for efficient reasoning in large language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22176

20. SO-Bench: A Structural Output Evaluation of Multimodal LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal large language models, schema-grounded information extraction, reasoning over visual inputs, SO-Bench, structured generation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Evaluate schema-grounded information extraction and reasoning over visual inputs in multimodal large language models using the SO-Bench benchmark.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a benchmark, SO-Bench, covering four visual domains with 6.5K diverse JSON schemas and 1.8K curated image-schema pairs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified persistent gaps in predicting accurate, schema-compliant outputs, indicating a need for enhanced multimodal structured reasoning.
– Conducted training experiments to improve model’s structured output capability, with plans to make the benchmark available to the community.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.21750

21. Test-time scaling of diffusions with flow maps
🔑 Keywords: Flow Map Trajectory Tilting (FMTT), Diffusion Models, Flow Map, Reward Function, Image Editing
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance diffusion models at test-time through the utilization of Flow Map Trajectory Tilting (FMTT) for better alignment with user-specified rewards, facilitating more effective sampling and image editing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a novel algorithm, FMTT, leveraging flow maps to optimize reward ascent, contrasting with standard methods using reward gradients.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The FMTT algorithm demonstrates improved efficacy in sampling and engagement with complex reward functions, allowing for innovative forms of image editing, particularly when integrated with vision language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22688

22. YOLO Meets Mixture-of-Experts: Adaptive Expert Routing for Robust Object Detection
🔑 Keywords: Mixture-of-Experts, adaptive routing, YOLOv9-T, mean Average Precision, Average Recall
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve object detection by introducing a Mixture-of-Experts framework that utilizes adaptive routing among multiple YOLOv9-T experts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method incorporates adaptive routing for dynamic feature specialization, leveraging multiple YOLOv9-T experts to enhance detection performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework achieves higher mean Average Precision (mAP) and Average Recall (AR) compared to using a single YOLOv9-T model.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.13344

23. OmniRefiner: Reinforcement-Guided Local Diffusion Refinement
🔑 Keywords: Reference-guided image generation, diffusion models, reinforcement learning, fine-grained detail preservation, pixel-level consistency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance detail preservation and consistency in reference-guided image generation using a detail-aware refinement framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implements a single-image diffusion editor fine-tuned for coherent refinement and uses reinforcement learning to optimize detail accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates improved reference alignment and detail preservation, providing visually coherent edits that outperform other models on complex restoration benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19990

24. Layer-Aware Video Composition via Split-then-Merge
🔑 Keywords: Split-then-Merge, generative video composition, dynamic foreground, background layers, transformation-aware training
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Split-then-Merge (StM), a framework designed to enhance control in generative video composition and tackle data scarcity issues.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The StM framework splits a large corpus of unlabeled videos into dynamic foreground and background layers, employing a novel transformation-aware training pipeline with multi-layer fusion and augmentation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– StM achieves superior results compared to state-of-the-art methods through quantitative and qualitative evaluations, maintaining foreground fidelity during blending and learning compositional dynamics crucial for realistic video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20809
25. From Pixels to Feelings: Aligning MLLMs with Human Cognitive Perception of Images
🔑 Keywords: image cognitive properties, Multimodal Large Language Models, human perception, post-training phase, cognitive alignment
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce CogIP-Bench, a benchmark for evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models on subjective image cognitive properties.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluated current models on their alignment with human perception using CogIP-Bench and demonstrated the effectiveness of a post-training phase in bridging the gap.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Findings reveal current models are poorly aligned with human perception, but post-training improves this alignment, enhancing MLLMs’ capabilities in creative tasks and image generation processes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22805

26. Fast3Dcache: Training-free 3D Geometry Synthesis Acceleration
🔑 Keywords: 3D diffusion models, geometry-aware caching, Predictive Caching Scheduler Constraint, Spatiotemporal Stability Criterion
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to accelerate 3D diffusion model inference while maintaining geometric fidelity using a geometry-aware caching framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a Predictive Caching Scheduler Constraint to dynamically manage cache quotas based on voxel stabilization patterns.
– Utilizes a Spatiotemporal Stability Criterion to select stable features for reuse, improving efficiency in 3D synthesis.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Fast3Dcache significantly speeds up inference, achieving up to a 27.12% speed-up and a 54.8% reduction in FLOPs with minimal geometric quality degradation measured by Chamfer Distance (2.48%) and F-Score (1.95%).
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22533

27. Recognition of Abnormal Events in Surveillance Videos using Weakly Supervised Dual-Encoder Models
🔑 Keywords: Dual-backbone framework, Convolutional representations, Transformer representations, Top-k pooling, UCF-Crime
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to tackle the detection of rare and diverse anomalies in surveillance videos with only video-level supervision.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– It employs a dual-backbone framework that integrates convolutional and transformer representations with top-k pooling.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method achieves 90.7% area under the curve (AUC) on the UCF-Crime dataset, demonstrating its effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.13276

28. Find the Leak, Fix the Split: Cluster-Based Method to Prevent Leakage in Video-Derived Datasets
🔑 Keywords: cluster-based frame selection, information leakage, video-derived frames datasets, balanced dataset partitions
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose a strategy to mitigate information leakage in video-derived frames datasets by using a cluster-based frame selection approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Grouping visually similar frames before splitting into training, validation, and test sets to create more representative and reliable dataset partitions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method results in more balanced and reliable dataset partitions, reducing information leakage in the datasets derived from video frames.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.13944

29. MRI Super-Resolution with Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Survey
🔑 Keywords: MRI, Super-Resolution, Deep Learning, Computational Imaging, Inverse Problem
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To survey deep learning-based super-resolution techniques in MRI, addressing challenges and providing resources for generating high-resolution images from low-resolution scans.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Review of recent advances in MRI SR techniques focusing on deep learning approaches, examining from computer vision, computational imaging, inverse problems, and MR physics perspectives.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– A systematic taxonomy for categorizing MRI SR methods is proposed, highlighting both established and emerging techniques and addressing unique clinical and research challenges and open issues.
– Essential resources, tools, and tutorials are provided for the community on GitHub.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.16854

30. Xmodel-2.5: 1.3B Data-Efficient Reasoning SLM
🔑 Keywords: Xmodel-2.5, maximal-update parameterization, edge deployment, FP8-mixed-precision training, Muon
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Xmodel-2.5, a small language model with 1.3 billion parameters designed for enhanced performance and efficiency, particularly suitable for edge deployments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of maximal-update parameterization allowing hyper-parameters from a smaller model to transfer to the full model.
– Adoption of a 1.4T-token Warmup–Stable–Decay curriculum with a switch from AdamW to Muon during the decay phase to enhance reasoning performance.
– Use of FP8-mixed-precision training to balance accuracy and computation throughput.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The combination of early AdamW stability and late Muon sharpening improves downstream task performance by 4.58% on a 13-task reasoning average.
– Release of all checkpoints, recipes, and code under the Apache-2.0 license, which supports reproducibility and further development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19496

31. FedRE: A Representation Entanglement Framework for Model-Heterogeneous Federated Learning
🔑 Keywords: Federated Learning, Model-Heterogeneous Environments, Entangled Representation, Privacy, Communication Overhead
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance performance, privacy, and reduce communication overhead in model-heterogeneous environments through Federated Representation Entanglement (FedRE).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Use entangled representations and labels, with normalized random weights, to aggregate client data and mitigate global classifier overconfidence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FedRE achieves a balance among performance, privacy protection, and reduced communication overhead, demonstrating effectiveness in federated learning settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22265

32.
