AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251204

1. Qwen3-VL Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Qwen3-VL, vision-language model, interleaved contexts, enhanced interleaved-MRoPE, DeepStack integration
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Qwen3-VL as the most capable model in the Qwen series, aiming to achieve superior performance across a range of multimodal benchmarks by supporting interleaved contexts up to 256K tokens.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs both dense and mixture-of-experts model variants to accommodate diverse latency-quality trade-offs, integrating advanced multimodal reasoning, enhanced spatial-temporal modeling, and explicit textual timestamp alignment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Qwen3-VL demonstrates markedly stronger text understanding and robust long-context comprehension, with superior performance under comparable token budgets and latency, serving as a foundational engine for image-grounded reasoning and multimodal code intelligence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.21631

2. Steering Vision-Language-Action Models as Anti-Exploration: A Test-Time Scaling Approach
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action, distribution shift, Test-Time-Scaling, pseudo-count estimator, offline reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance inference stability and success rates of Vision-Language-Action models by preventing distribution shifts in downstream tasks using a test-time-scaling framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a pseudo-count estimator within a Test-Time-Scaling framework as a high-fidelity verifier of action chunks to execute actions with maximum pseudo-count, preventing distribution shifts and preserving generalization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method significantly improves inference stability and success rates across various simulation benchmarks, demonstrating its computational efficiency and effectiveness in downstream-task adaptations for Vision-Language-Action models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02834

3. PretrainZero: Reinforcement Active Pretraining
🔑 Keywords: PretrainZero, reinforcement learning, active learning, self-supervised learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to propose PretrainZero, a reinforcement active learning framework to enhance general reasoning capabilities by pretraining large models on a corpus without verifiable labels.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing active pretraining to identify and learn from informative content.
– Employing self-supervised learning, pretraining reasoners on the Wikipedia corpus using reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PretrainZero significantly improves general reasoning abilities and benchmark performances, showing advancements in both reinforcement pretraining and post-training as versatile reasoning foundation models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03442

4. ViDiC: Video Difference Captioning
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Large Language Models, ViDiC, Video Difference Captioning, edit awareness, video understanding
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces the ViDiC task and the ViDiC-1K dataset aimed at evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models’ ability to describe differences between video pairs, focusing on motion continuity and event evolution.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A dual-checklist framework using the LLM-as-a-Judge protocol is proposed to measure the accuracy of similarity and difference separately. The dataset comprises 1,000 curated video pairs with over 4,000 annotated comparative checklist items across seven categories.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments on nineteen multimodal models highlight a significant performance gap in their ability to discern and describe differences between dynamic scenes, suggesting that ViDiC-1K serves as a challenging benchmark to advance comparative reasoning, edit awareness, and video understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03405

5. OneThinker: All-in-one Reasoning Model for Image and Video
🔑 Keywords: OneThinker, RL, Multimodal Large Language Models, Image and Video Reasoning, Zero-Shot Generalization
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose OneThinker, an all-in-one reasoning model that integrates image and video understanding across multiple visual tasks, aiming to overcome the limitations of separate task models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a comprehensive OneThinker-600k training corpus and CoT annotation to support cold start, along with EMA-GRPO for balanced optimization in multi-task RL scenarios.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OneThinker demonstrated strong performance across 31 benchmarks and 10 fundamental visual tasks, showcasing effective knowledge transfer and preliminary zero-shot generalization capabilities, pushing towards a unified multimodal reasoning generalist.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03043

6. SpaceTools: Tool-Augmented Spatial Reasoning via Double Interactive RL
🔑 Keywords: Double Interactive Reinforcement Learning, Vision Language Models, multi-tool coordination, spatial reasoning, real-world manipulation
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Double Interactive Reinforcement Learning (DIRL) to enhance Vision Language Models (VLMs) for precise spatial reasoning by coordinating multiple tools.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research utilizes a two-phase training framework: a teaching phase with demonstrations from specialists and a frontier model, followed by an exploration phase to refine multi-tool coordination through continued reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The DIRL approach significantly improves spatial reasoning performance, achieving state-of-the-art results on various benchmarks and effectively using a 7-DOF robot for real-world tasks, surpassing standard baseline methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04069

7. Rethinking Prompt Design for Inference-time Scaling in Text-to-Visual Generation
🔑 Keywords: Prompt Redesign, Text-to-Visual Generation, Element-level Factual Correction, Scaling Laws
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance alignment between user intent and generated visuals by adaptively revising prompts during inference.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce PRIS, a framework that revises prompts by identifying failure patterns in visuals and uses a verifier for element-level factual correction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Jointly scaling prompts and visuals improves the effectiveness, achieving a 15% gain on VBench 2.0 benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03534
8. RELIC: Interactive Video World Model with Long-Horizon Memory
🔑 Keywords: RELIC, interactive world modeling, long-horizon memory, video-diffusion, AI Native
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a unified framework, RELIC, for real-time, memory-aware exploration of scenes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of autoregressive video-diffusion distillation to integrate long-horizon memory, spatial consistency, and user control.
– Employment of a bidirectional teacher video model fine-tuned for long-duration sequences and transformed into a causal student generator.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RELIC demonstrates enhanced real-time generation capabilities with improved action following, stable long-horizon streaming, and robust spatial-memory retrieval.
– Establishes a strong foundation for the future of interactive world modeling by achieving 16 FPS with a 14B-parameter model trained on an Unreal Engine-rendered dataset.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04040
9. Thinking with Programming Vision: Towards a Unified View for Thinking with Images
🔑 Keywords: CodeVision, Multimodal Large Language Models, Supervised Fine-Tuning, Reinforcement Learning, Tool Composition
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the brittleness and performance degradation of state-of-the-art Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in handling visual inputs by proposing a flexible code-as-tool framework called CodeVision.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs a two-stage training methodology incorporating Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) on curated datasets and Reinforcement Learning (RL) with a novel reward function to enhance tool-based reasoning and strategic tool use.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CodeVision significantly improves performance and introduces capabilities like flexible tool composition, efficient execution, and robust error recovery, as demonstrated in experiments with Qwen2.5-VL and Qwen3-VL series.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03746

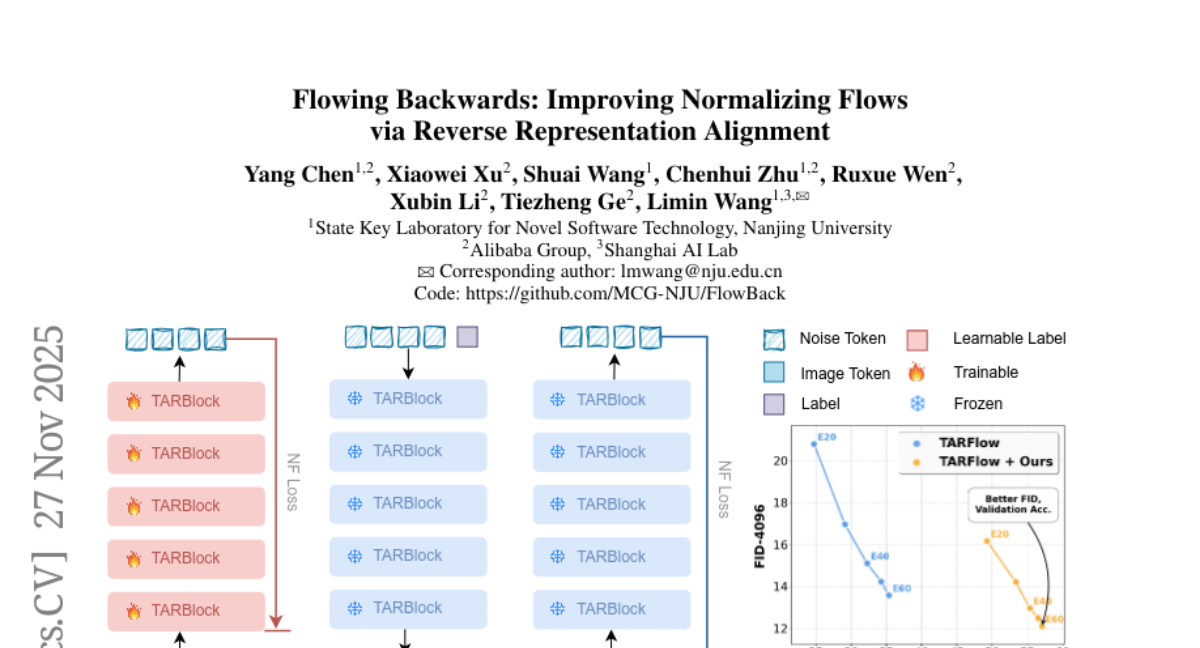
10. Flowing Backwards: Improving Normalizing Flows via Reverse Representation Alignment
🔑 Keywords: Normalizing Flows, generative models, invertible architecture, alignment strategy, vision foundation model
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance generative quality and classification accuracy of Normalizing Flows by introducing a novel alignment strategy and a test-time optimization algorithm.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of the invertibility feature of Normalizing Flows to align intermediate features with representations from a powerful vision foundation model.
– Introduction of a training-free, test-time optimization algorithm to improve classification accuracy and evaluate semantic knowledge.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach significantly accelerates the training process of Normalizing Flows, enhancing both generative quality and classification accuracy, achieving new state-of-the-art results on ImageNet.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22345
11. SR-GRPO: Stable Rank as an Intrinsic Geometric Reward for Large Language Model Alignment
🔑 Keywords: Stable Rank, LLM Alignment, Human Preferences, Reinforcement Learning, External Supervision
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to improve the alignment of Large Language Models (LLMs) with human preferences using an intrinsic quality signal called Stable Rank, which avoids the limitations of external supervision.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces Stable Rank, which measures effective dimensionality by computing the ratio of total variance to dominant-direction variance, capturing information distribution across representation dimensions. SR-GRPO, a policy optimization method leveraging Stable Rank as a reward signal, is proposed for reinforcement learning without external supervision.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study demonstrates that Stable Rank can enhance task accuracy and outperform existing methods in alignment tasks without external supervision. It shows potential for scalable alignment through extracting quality signals from internal model geometry.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02807

12. Economies of Open Intelligence: Tracing Power & Participation in the Model Ecosystem
🔑 Keywords: Open Model Economy, Multimodal Generation, Quantization, AI-generated Summary, Data Transparency
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To examine the shifts in the open model economy by analyzing the Hugging Face Model Hub data from June 2020 to August 2025.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analysis of 851,000 models, 200+ attributes per model, and 2.2 billion downloads to study concentration dynamics and model properties.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– A significant decline in US open-weight industry dominance with a rise in unaffiliated and Chinese developers.
– Notable increases in model size, multimodal generation, quantization, and mixture-of-experts architectures.
– Introduction of developer intermediaries adapting models for efficiency and artistic purposes.
– Release of a complete dataset with a dashboard for ongoing research and monitoring.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03073

13. AutoNeural: Co-Designing Vision-Language Models for NPU Inference
🔑 Keywords: NPU-native, Vision-Language Models, integer-only inference, MobileNetV5, State-Space Model
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the efficiency and performance mismatch of Vision-Language Models tailored for GPUs when deployed on NPUs, by proposing AutoNeural, a new NPU-native architecture.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Co-design of an NPU-native VLM architecture using integer-only inference, replacing the standard Vision Transformer encoder with a MobileNetV5-style backbone and integrating State-Space Model principles with Transformer layers to reduce quantization errors and latency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AutoNeural architecture delivers significant efficiency gains, achieving up to 7x reduction in quantization error, 14x reduction in end-to-end latency, 3x faster decoding speed, and 4x longer context windows compared to conventional baselines, validated through real-world automotive case studies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02924
14. CookAnything: A Framework for Flexible and Consistent Multi-Step Recipe Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: CookAnything, diffusion-based framework, Step-wise Regional Control, Flexible RoPE, Cross-Step Consistency Control
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a framework called CookAnything to generate coherent image sequences from cooking instructions, addressing the challenges in structured multi-step scenarios.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Step-wise Regional Control to align textual steps with image regions, Flexible RoPE for temporal coherence and spatial diversity, and Cross-Step Consistency Control for ingredient consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CookAnything outperforms existing methods in both training-based and training-free settings, supporting scalable, high-quality visual synthesis of complex multi-step instructions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03540
15. Jina-VLM: Small Multilingual Vision Language Model
🔑 Keywords: Jina-VLM, vision-language model, multilingual visual question answering, SigLIP2, Qwen3
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The introduction and development of Jina-VLM, a 2.4 billion parameter vision-language model designed to achieve top performance in multilingual visual question answering tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a SigLIP2 vision encoder combined with a Qwen3 language backbone, integrated via an attention-pooling connector to enable token-efficient processing of images at arbitrary resolutions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Jina-VLM surpasses comparable models across standard VQA benchmarks and multilingual evaluations, maintaining competitive performance in text-only scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04032

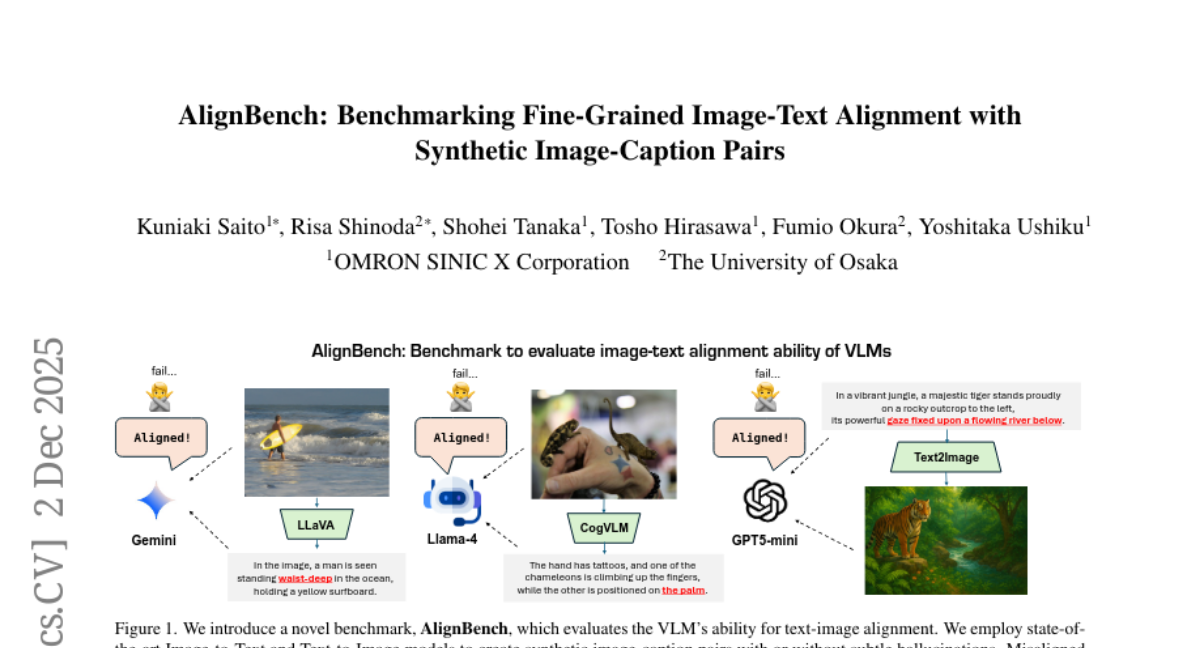
16. AlignBench: Benchmarking Fine-Grained Image-Text Alignment with Synthetic Image-Caption Pairs
🔑 Keywords: Image-Text Alignment, CLIP, Compositional Reasoning, AlignBench, Decoder-Based VLMs
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of AlignBench is to evaluate and provide insights into the alignment and compositional reasoning capabilities of image-text models through detailed captioning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing a benchmark that analyzes image-caption pairs generated by various image-to-text and text-to-image models, with annotations on correctness to assess alignment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CLIP-based models are found to be deficient in compositional reasoning.
– Detectors have a tendency to over-score early sequences in evaluations.
– There is a noted self-preference in models, favoring their own outputs, which adversely affects performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20515
17. UniQL: Unified Quantization and Low-rank Compression for Adaptive Edge LLMs
🔑 Keywords: UniQL, large language models, quantization, low-rank compression, memory reduction
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces UniQL, a unified framework aimed at enhancing the deployment of large language models on mobile devices by reducing memory usage and improving token throughput without sacrificing accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– UniQL implements post-training quantization and low-rank compression with configurable pruning rates. It incorporates structured weight-sorting, quantization-aware singular value decomposition, and state-aware weight sorting among others.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework achieves a memory reduction of 4x-5.7x and improves token throughput by 2.7x-3.4x while maintaining model accuracy within 5% of the original, even with significant pruning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03383

18. In-Context Representation Hijacking
🔑 Keywords: Doublespeak, in-context representation hijacking, large language models, safety alignment, internal representation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the Doublespeak attack, which manipulates in-context representations in large language models to bypass safety measures.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Use systematized substitution of harmful keywords with benign tokens in-context, analyzed with interpretability tools to trace semantic overwrites across model layers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Doublespeak demonstrates a new attack vector in latent space, achieving high success rates and revealing the insufficiency of current alignment strategies at the representation level.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03771

19. SkillFactory: Self-Distillation For Learning Cognitive Behaviors
🔑 Keywords: SkillFactory, cognitive skills, reinforcement learning, fine-tuning, AI Native
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop SkillFactory as a method for fine-tuning models to learn cognitive skills through supervised fine-tuning before reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces SkillFactory, which utilizes samples from the model itself, rearranged as training data, to enable learning of cognitive skills during a supervised fine-tuning stage prior to reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Starting models with SkillFactory’s supervised fine-tuning enables better generalization for tougher tasks post-reinforcement learning.
– Models successfully utilize cognitive skills after being enhanced by reinforcement learning.
– SkillFactory-based models show increased robustness compared to base models on out-of-domain tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04072

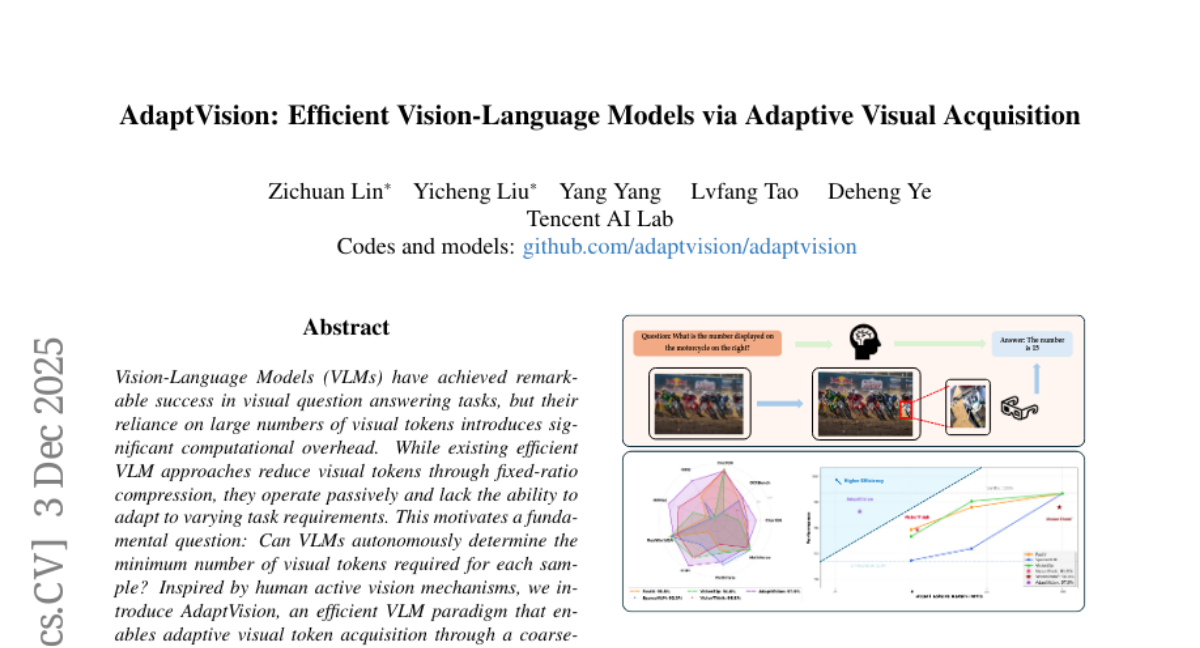
20. AdaptVision: Efficient Vision-Language Models via Adaptive Visual Acquisition
🔑 Keywords: AdaptVision, vision-language model, visual tokens, reinforcement learning, Decoupled Turn Policy Optimization
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop AdaptVision, a vision-language model that autonomously adjusts visual token usage to enhance accuracy and efficiency in visual question answering tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a reinforcement learning framework featuring Decoupled Turn Policy Optimization (DTPO) to balance tool learning and answer accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AdaptVision outperforms state-of-the-art efficient vision-language models by achieving superior performance with fewer visual tokens.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03794
21. BlurDM: A Blur Diffusion Model for Image Deblurring
🔑 Keywords: Blur Diffusion Model, image deblurring, dual diffusion, motion blur, latent space
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the Blur Diffusion Model (BlurDM) that integrates blur formation into diffusion processes to enhance image deblurring by simultaneously addressing noise and blur.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a dual-diffusion forward scheme where noise and blur are diffused onto a sharp image, employing dual denoising and deblurring during reverse generation.
– Operate BlurDM in latent space to form a flexible prior generation network for deblurring networks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BlurDM significantly improves existing deblurring methods across four benchmark datasets, demonstrating consistent enhancement and maximizing the use of the blur formation process within diffusion models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03979
22. Divide, then Ground: Adapting Frame Selection to Query Types for Long-Form Video Understanding
🔑 Keywords: Large Multimodal Models, long-form video understanding, query-aware frame selection, global query, localized query
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve long-form video understanding by introducing a framework that efficiently handles global and localized queries using Large Multimodal Models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Identified query typology to distinguish between global and localized queries.
– Proposed DIG, a training-free frame selection framework that adapts its strategy based on the query type, employing uniform sampling for global queries and query-aware selection for localized ones.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DIG consistently outperforms existing baselines in long-form video understanding and enhances Large Multimodal Model performance, even with increased input frame counts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04000

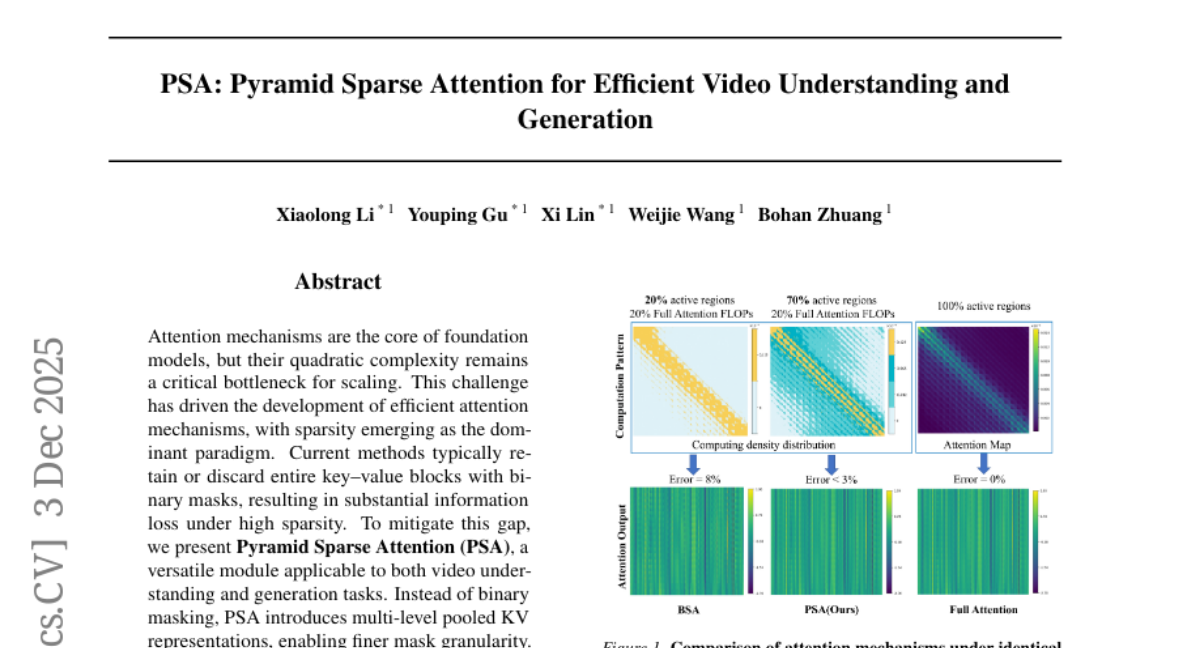
23. PSA: Pyramid Sparse Attention for Efficient Video Understanding and Generation
🔑 Keywords: Pyramid Sparse Attention, Sparse Attention, Video Understanding, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim is to enhance sparse attention mechanisms by introducing Pyramid Sparse Attention (PSA) for improved performance in video understanding and generation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– PSA employs multi-level pooled KV representations for finer mask granularity and incorporates a native, hardware-friendly kernel using a decoupled block-tile design for efficient execution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PSA effectively mitigates information loss while preserving computational efficiency, consistently outperforming or matching existing sparse attention baselines across various benchmarks with a superior efficiency-quality trade-off.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04025
24. Adversarial Confusion Attack: Disrupting Multimodal Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Adversarial Confusion Attack, Multimodal Large Language Models, Confidently Incorrect Outputs, Ensemble, Next-Token Entropy
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces the Adversarial Confusion Attack aimed at systematically disrupting multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to produce incoherent or confidently incorrect outputs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves using a small ensemble of open-source MLLMs and basic adversarial techniques (specifically PGD) to maximize next-token entropy, tested in both full-image and Adversarial CAPTCHA settings.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The attack effectively disrupts all models in the ensemble and transfers perturbations to both unseen open-source and proprietary models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20494

25. PosterCopilot: Toward Layout Reasoning and Controllable Editing for Professional Graphic Design
🔑 Keywords: PosterCopilot, LMMs, Geometric Reasoning, Iterative Editing, Generative Models
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Aim to improve professional graphic design by enhancing layout reasoning and controllable editing capabilities of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a three-stage training strategy including Perturbed Supervised Fine-Tuning, Reinforcement Learning for Visual-Reality Alignment, and Reinforcement Learning from Aesthetic Feedback. Developed a complete workflow for layer-controllable iterative editing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PosterCopilot produces geometrically accurate and aesthetically superior layouts, providing unprecedented controllability for professional iterative design.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04082

26.
