AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251208

1. TwinFlow: Realizing One-step Generation on Large Models with Self-adversarial Flows
🔑 Keywords: TwinFlow, inference efficiency, generative models, text-to-image tasks
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop TwinFlow, a 1-step generative model framework to enhance inference efficiency without relying on fixed pretrained teacher models or standard adversarial networks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves creating a simple yet effective framework for training 1-step generative models, bypassing the need for adversarial networks and fixed pretrained teacher models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TwinFlow achieves high performance on text-to-image tasks with a GenEval score of 0.83 in 1-NFE, outperforming strong baselines. It demonstrates scalability and efficiency by reducing computational costs by 100 times and maintaining quality on benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05150

2. EditThinker: Unlocking Iterative Reasoning for Any Image Editor
🔑 Keywords: Deliberative Editing, Think-while-Edit cycle, Instruction-following capability, Reinforcement Learning, Image Editing
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve instruction-following in image editing through a deliberative editing framework that incorporates a reasoning engine for iterative critique and refinement.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a single MLLM called EditThinker to simulate a human cognitive process with a Think-while-Edit cycle, critiquing results, refining instructions, and repeating until satisfactory.
– Employ reinforcement learning to align the reasoning process with editing for better instruction adherence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach significantly enhances the instruction-following capability of image editing models, as demonstrated by extensive experiments on four benchmarks.
– Data construction framework, datasets, and models will be released for community benefit.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05965

3. From Imitation to Discrimination: Toward A Generalized Curriculum Advantage Mechanism Enhancing Cross-Domain Reasoning Tasks
🔑 Keywords: Curriculum Advantage Policy Optimization, Reinforcement Learning, Advantage Signals, Generalization, Mathematical Reasoning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to enhance the reasoning capabilities and generalization of large language models through a novel approach called Curriculum Advantage Policy Optimization (CAPO).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a curriculum mechanism based on advantage signals, utilizing positive-only signals initially to strengthen foundations, followed by negative signals to improve discriminative capabilities. CAPO is compatible with optimization methods like GRPO, PPO, RLOO, and Reinforce++.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CAPO consistently achieves significant improvements in mathematical reasoning tasks and generalizes effectively to complex scenarios, including multimodal GUI reasoning, establishing itself as a robust optimization framework.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02580

4. EMMA: Efficient Multimodal Understanding, Generation, and Editing with a Unified Architecture
🔑 Keywords: EMMA, multi-modal understanding, autoencoder, mixture-of-experts, AI-generated
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study proposes EMMA, an efficient and unified architecture for tasks involving multi-modal understanding, generation, and editing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The implementation of a 32x compression ratio autoencoder to optimize token generation.
– Use of channel-wise concatenation to streamline visual tokens in unified architectures.
– Integration of a shared-and-decoupled network for task-specific improvements.
– Adoption of a mixture-of-experts mechanism to enhance perceptual capabilities with minimal parameter increases.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EMMA-4B significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches like BAGEL-7B in efficiency and performance, showing competitive results against recent multimodal experts Qwen3-VL and Qwen-Image.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04810

5. PaCo-RL: Advancing Reinforcement Learning for Consistent Image Generation with Pairwise Reward Modeling
🔑 Keywords: PaCo-RL, Reinforcement Learning, Consistent Image Generation, PaCo-Reward, PaCo-GRPO
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance consistent image generation by developing PaCo-RL, a framework that combines reinforcement learning with a specialized consistency reward model and an efficient optimization strategy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces PaCo-Reward, which evaluates pairwise image consistency using a generative, autoregressive scoring mechanism within the framework.
– Utilizes PaCo-GRPO leveraging a novel resolution-decoupled optimization strategy and a log-tamed multi-reward aggregation for improved RL efficiency and stability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PaCo-RL demonstrates improved alignment with human perceptions of visual consistency and achieves state-of-the-art performance in consistent image generation, offering a scalable and practical solution.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04784

6. Entropy Ratio Clipping as a Soft Global Constraint for Stable Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Entropy Ratio Clipping, Reinforcement Learning, Distribution Shift, Policy Entropy, PPO-Clip
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research proposes the Entropy Ratio Clipping (ERC) mechanism to stabilize policy updates by addressing global distributional shifts in reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study uses entropy ratio between current and previous policies as a global metric to quantify policy exploration changes, and integrates this ERC mechanism into DAPO and GPPO algorithms.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ERC effectively stabilizes policy updates and consistently improves performance across various benchmarks compared to existing methods like PPO-Clip.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05591

7. SCAIL: Towards Studio-Grade Character Animation via In-Context Learning of 3D-Consistent Pose Representations
🔑 Keywords: SCAIL, 3D pose representation, diffusion-transformer architecture, full-context pose injection, studio-grade animation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance character animation quality to meet studio-grade standards through the development of the SCAIL framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a novel 3D pose representation and a diffusion-transformer architecture with full-context pose injection to enable effective spatio-temporal reasoning over full motion sequences.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SCAIL framework achieves state-of-the-art performance, advancing character animation toward studio-grade reliability and realism, with experiments confirming its effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05905
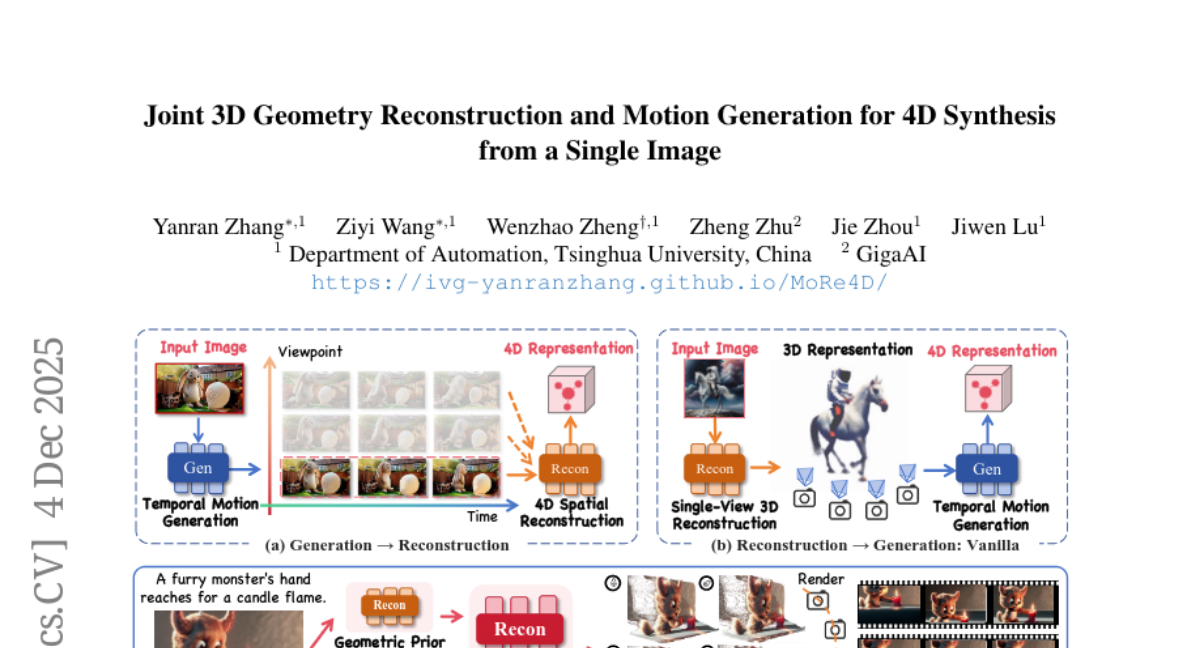
8. Joint 3D Geometry Reconstruction and Motion Generation for 4D Synthesis from a Single Image
🔑 Keywords: MoRe4D, diffusion-based trajectory generator, 4D Scene Trajectory Generator, depth-guided motion normalization, multi-view consistency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to generate high-quality 4D scenes with dynamic details and multi-view consistency from a single image using an integrated approach of motion and geometry.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces a large-scale dataset named TrajScene-60K and develops a diffusion-based 4D Scene Trajectory Generator to produce geometrically consistent and motion-plausible trajectories, alongside employing depth-guided motion normalization for effective integration.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed MoRe4D framework successfully creates high-quality 4D scenes from a single image with significant multi-view consistency and dynamic details.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05044
9. COOPER: A Unified Model for Cooperative Perception and Reasoning in Spatial Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Large Language Models, Spatial Reasoning, Depth, Segmentation, Auxiliary Modalities
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study investigates whether a unified MLLM can develop an intrinsic ability to enhance spatial perception and achieve stronger spatial intelligence through adaptive interleaved reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers propose COOPER, a unified MLLM that leverages depth and segmentation as auxiliary modalities. The model is trained in two stages to acquire auxiliary modality generation and adaptive, interleaved reasoning capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– COOPER achieves an average 6.91% improvement in spatial reasoning while maintaining general performance. A variant trained only for auxiliary modality generation shows a 7.92% gain in distance and size estimation, suggesting that learning to generate auxiliary modalities helps internalize spatial knowledge and strengthen spatial understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04563

10. RealGen: Photorealistic Text-to-Image Generation via Detector-Guided Rewards
🔑 Keywords: RealGen, photorealistic image generation, LLM, diffusion model, Detector Reward
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance photorealistic text-to-image generation by addressing the limitations of existing models with a new framework, RealGen.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– RealGen employs a Large Language Model (LLM) for prompt optimization and a diffusion model for image generation, incorporating a Detector Reward mechanism to improve realism and detail.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RealGen outperforms current models in terms of realism, detail, and aesthetics, with an automated evaluation using RealBench for more accurate assessment aligned with real user experience.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00473

11. ReVSeg: Incentivizing the Reasoning Chain for Video Segmentation with Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: ReVSeg, video object segmentation, pretrained vision language models, reinforcement learning, reasoning trajectories
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce ReVSeg, a reasoning-centric video object segmentation framework, to improve performance and interpretability using pretrained vision language models and reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– ReVSeg performs reasoning through sequential decisions using three explicit operations: semantics interpretation, temporal evidence selection, and spatial grounding.
– Utilizes reinforcement learning to optimize the decision-making process.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved state-of-the-art performance on standard benchmarks with interpretable reasoning outcomes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02835

12. SpaceControl: Introducing Test-Time Spatial Control to 3D Generative Modeling
🔑 Keywords: SpaceControl, 3D generation, geometric fidelity, interactive user interface, geometric inputs
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to provide explicit spatial control of 3D generation using various geometric inputs without additional training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a training-free test-time method that seamlessly integrates with modern pre-trained generative models and accommodates a range of geometric inputs from primitives to detailed meshes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SpaceControl demonstrates superior geometric faithfulness and high visual quality compared to existing methods and allows for practical deployment in creative workflows via an interactive user interface.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05343
13. World Models That Know When They Don’t Know: Controllable Video Generation with Calibrated Uncertainty
🔑 Keywords: Uncertainty Quantification, Controllable Video Models, Out-of-Distribution Detection, Generative Video Models, AI-generated Summary
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to address hallucination issues in controllable video models by introducing C3, an uncertainty quantification (UQ) method that provides dense confidence estimation and out-of-distribution detection.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a novel framework using strictly proper scoring rules for correctness and calibration.
– Estimated uncertainty in latent space to avoid instability and high training costs typical of pixel-space approaches.
– Mapped dense latent-space uncertainty to interpretable pixel-level uncertainty for intuitive visualization with high-resolution heatmaps.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method provides calibrated uncertainty estimates for the training distribution and enhances out-of-distribution detection capabilities.
– Extensive experiments on large-scale robot learning datasets and real-world evaluations validate the method’s effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05927
14. Self-Improving VLM Judges Without Human Annotations
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Model, self-training, AI-generated, Multimodal RewardBench, reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a self-training framework for a Vision-Language Model (VLM) judge without relying on human preference annotations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize an iterative three-stage process involving the generation of diverse multimodal instruction-response pairs, reasoning traces, and subsequent training on these traces and correct answers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework significantly improves the accuracy of a Llama-3.2-11B multimodal judge on VL-RewardBench, outperforming larger models and demonstrating strong capabilities in areas such as reasoning and hallucination management.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05145

15. M3DR: Towards Universal Multilingual Multimodal Document Retrieval
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Document Retrieval, Contrastive Training, Cross-lingual Alignment, AI-generated
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop M3DR, a framework that enables robust cross-lingual and cross-modal document retrieval, effective across diverse languages and cultural contexts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of synthetic multilingual document data and contrastive training for learning unified representations that generalize across vision-language architectures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– M3DR demonstrates consistent performance across 22 diverse languages, achieving state-of-the-art performance in cross-lingual retrieval with significant improvements compared to existing methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03514

16. AI & Human Co-Improvement for Safer Co-Superintelligence
🔑 Keywords: Collaborative Co-improvement, Human-AI Interaction, Safer AI Research, Co-superintelligence
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to maximize collaborative co-improvement between humans and AI systems to achieve safer and accelerated AI research and development.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Emphasis on improving AI systems’ ability to work alongside human researchers, covering processes from ideation to experimentation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Focusing on human research improvement within the collaborative loop will expedite the development of safer superintelligence through symbiotic relationships between humans and AI.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05356

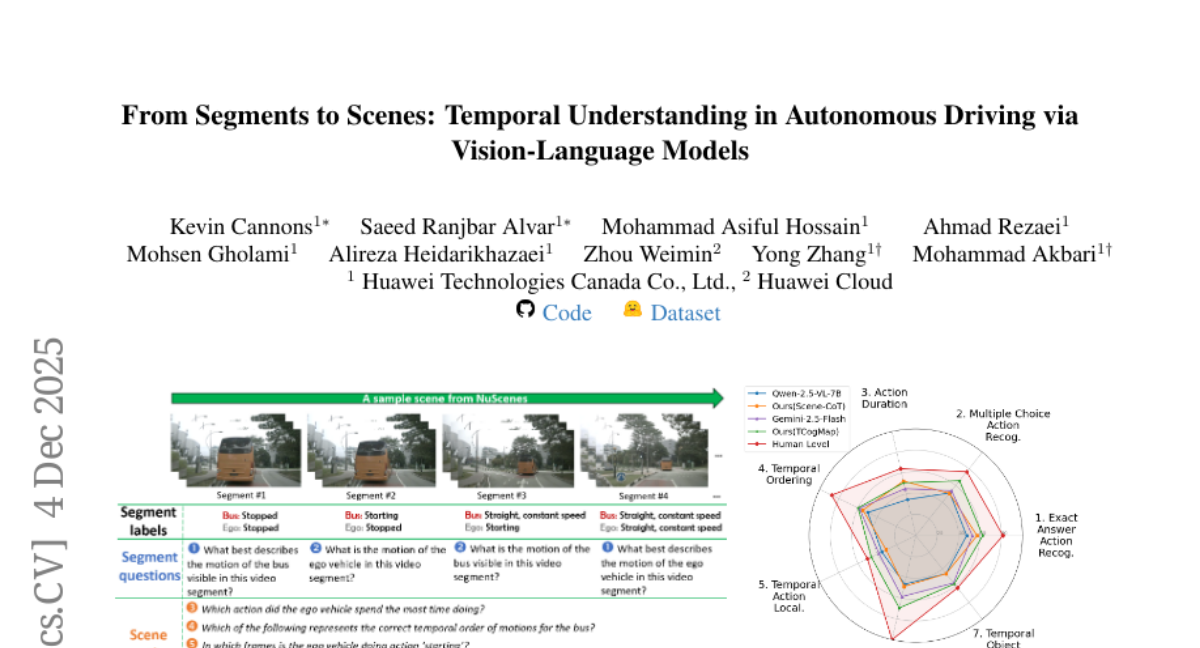
17. From Segments to Scenes: Temporal Understanding in Autonomous Driving via Vision-Language Model
🔑 Keywords: Temporary understanding, Vision-Language Models, TAD benchmark, Chain-of-Thought, ego-centric temporal cognitive map
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate and improve the temporal understanding of Vision-Language Models on ego-centric autonomous driving footage using a newly introduced TAD benchmark.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing nearly 6,000 QA pairs and 7 human-designed tasks, the research evaluates VLMs through the TAD benchmark, including 9 different models, and proposes training-free solutions like Scene-CoT and TCogMap.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current SoTA models show substandard performance, and the integration of Scene-CoT and TCogMap improves accuracy on the TAD benchmark by up to 17.72%, aiming to stimulate future research in this area.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05277
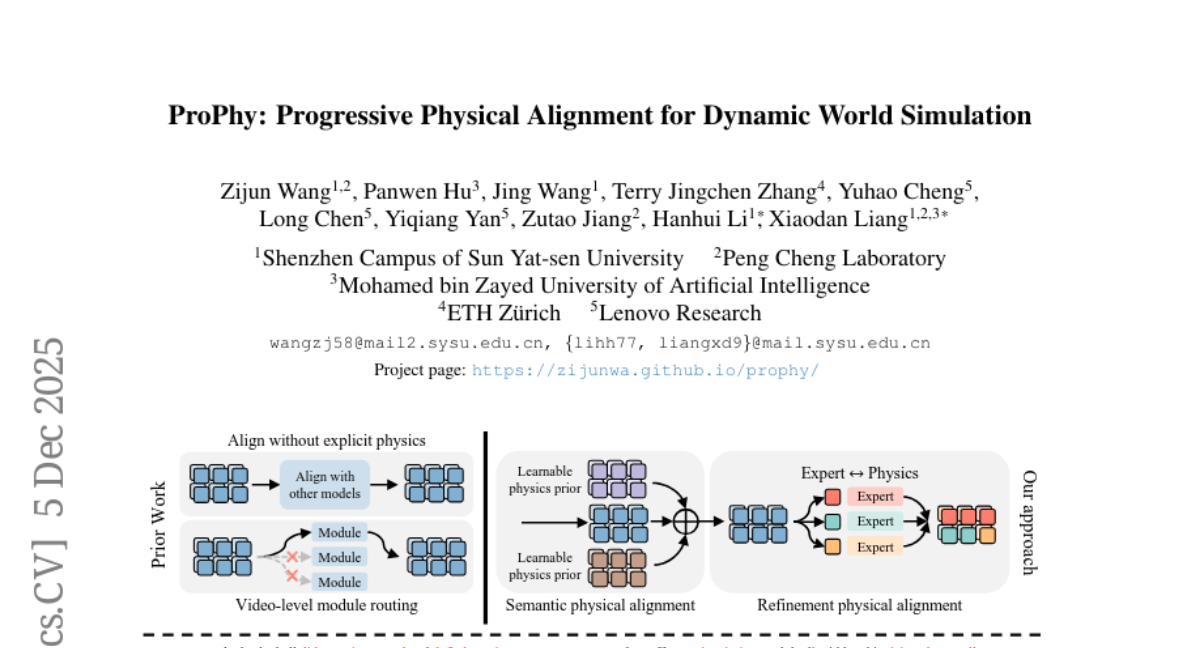
18. ProPhy: Progressive Physical Alignment for Dynamic World Simulation
🔑 Keywords: ProPhy, Video Generation, Physics-aware, Anisotropic Generation, Vision-language Models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve physical consistency and realism in AI-generated video content by addressing current models’ limitations in handling complex dynamics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of ProPhy, a two-stage framework with Semantic and Refinement Experts, enabling physics-aware conditioning and anisotropic generation using a Mixture-of-Physics-Experts mechanism.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ProPhy enhances the representation of dynamic physical phenomena, resulting in more realistic and physically coherent video generation compared to existing state-of-the-art methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05564
19. Colon-X: Advancing Intelligent Colonoscopy from Multimodal Understanding to Clinical Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Colon-X, multimodal intelligence, clinical reasoning, ColonVQA, ColonR1
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to advance multimodal intelligence in colonoscopy, particularly in moving from multimodal understanding to clinical reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Construction of ColonVQA, a large multimodal dataset, and assessment of 22 multimodal large language models to examine their reliability under human-induced perturbations.
– Development of ColonReason, a clinically grounded reasoning dataset, and ColonR1, which incorporates task-adaptive rewarding and gradient-stable optimization techniques.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ColonR1 outperformed traditional methods in data-scarce conditions with a 56.61% overall accuracy, surpassing supervised fine-tuning by 25.22%, and established a new reasoning-enabled baseline for multimodal colonoscopy analysis.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03667

20. TimesNet-Gen: Deep Learning-based Site Specific Strong Motion Generation
🔑 Keywords: TimesNet-Gen, latent bottleneck, site-specific, strong ground motion, conditional VAE
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve site-specific strong ground motion synthesis using a time-domain conditional generator named TimesNet-Gen, which factors in local site conditions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method introduced is a station-specific latent bottleneck within TimesNet-Gen, using HVSR curves and fundamental site-frequency distributions for evaluation against real records.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TimesNet-Gen shows strong alignment with site-specific data, outperforming a spectrogram-based conditional VAE baseline in synthesizing strong motion specific to individual stations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04694
21. SQ-format: A Unified Sparse-Quantized Hardware-friendly Data Format for LLMs
🔑 Keywords: SQ-format, Post-training Quantization, Large Language Models, Sparse Matrix, AI Accelerators
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the balance between accuracy and efficiency in post-training quantization of large language models through the proposed Sparse-Quantized Format (SQ-format).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a unified data format (SQ-format) leveraging sparse and low-precision matrix multiplications to potentially enhance hardware support and GPU compatibility.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SQ-format offers a Pareto improvement between performance and throughput, showing state-of-the-art PTQ performance. It paves the way for designing next-generation AI accelerators and enhances the capabilities for activations with outlier inequality status.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05409

22. From FLOPs to Footprints: The Resource Cost of Artificial Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: Material Footprint, Nvidia A100 GPU, Environmental Impact, GPT-4, Resource Efficiency
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To quantify the material footprint of AI training with a focus on the Nvidia A100 GPU and examine the environmental impact of training models like GPT-4, advocating for resource-efficient strategies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy was used to analyze the elemental composition of the Nvidia A100 GPU, alongside scenario-based analyses to evaluate the computational requirements of AI models at varying efficiency regimes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AI hardware is primarily composed of heavy metals, with copper, iron, tin, silicon, and nickel dominating the composition.
– Incremental performance gains in AI (e.g., from GPT-3.5 to GPT-4) result in high material costs.
– Combined software and hardware optimization strategies can significantly reduce material demands, emphasizing the importance of aligning AI advancements with resource efficiency and environmental responsibility.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04142

23. Taxonomy-Adaptive Moderation Model with Robust Guardrails for Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Roblox Guard 1.0, Instruction Fine-Tuning, LLM, Safety Taxonomies, Out-of-Domain Safety Benchmarks
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Roblox Guard 1.0, a state-of-the-art LLM designed for enhancing safety through comprehensive input-output moderation using a pipeline of LLMs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ instruction fine-tuning on the Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct backbone, utilizing synthetic and open-source safety datasets, enhanced with chain-of-thought rationales and input inversion to boost contextual understanding and decision making.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Roblox Guard 1.0 shows strong performance on out-of-domain safety benchmarks and demonstrates improved safety handling across unseen safety taxonomies. Additionally, RobloxGuard-Eval, a new benchmark, is released to assess LLM guardrails and moderation frameworks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05339
24. Active Video Perception: Iterative Evidence Seeking for Agentic Long Video Understanding
🔑 Keywords: Active Video Perception, Long video understanding, agentic pipelines, query-agnostic captioner
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve long video understanding by developing an Active Video Perception (AVP) framework, which iteratively selects and evaluates query-relevant video evidence to enhance accuracy and reduce computational cost.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces an interactive plan-observe-reflect process using MLLM agents, where a planner targets video interactions, an observer extracts time-stamped evidence, and a reflector evaluates the evidence’s sufficiency for answering the query.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AVP significantly enhances performance in long video understanding, achieving 5.7% higher accuracy than the best existing agentic methods, while also reducing inference time to 18.4% and input tokens to 12.4%.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05774

25.
