AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251215

1. EgoX: Egocentric Video Generation from a Single Exocentric Video
🔑 Keywords: Egocentric Videos, Video Diffusion Models, LoRA Adaptation, Unified Conditioning, Geometry-Guided Self-Attention
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to generate egocentric videos from exocentric inputs to enable immersive understanding while preserving content and ensuring geometric consistency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The EgoX framework employs large-scale video diffusion models with lightweight LoRA adaptation.
– A unified conditioning strategy combining exocentric and egocentric priors, along with geometry-guided self-attention, enhances spatial relevance and visual fidelity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EgoX achieves coherent and realistic egocentric video generation and demonstrates scalability and robustness across various scenarios, including unseen and in-the-wild videos.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08269
2. DentalGPT: Incentivizing Multimodal Complex Reasoning in Dentistry
🔑 Keywords: DentalGPT, multimodal large language models, domain knowledge injection, reinforcement learning, dental VQA
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address limitations in current multimodal large language models by developing DentalGPT, a specialized model for dentistry that enhances disease classification and dental visual question answering tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs high-quality domain knowledge injection and reinforcement learning. It involves constructing the largest annotated multimodal dataset to date for dentistry with over 120k dental images paired with detailed descriptions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The findings demonstrate that DentalGPT, despite having only 7B parameters, surpasses state-of-the-art models in dental disease classification and VQA tasks. This is due to high-quality dental data and staged adaptation enhancing the model’s capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11558
3. SVG-T2I: Scaling Up Text-to-Image Latent Diffusion Model Without Variational Autoencoder
🔑 Keywords: SVG-T2I, Visual Foundation Model, text-to-image synthesis, generative tasks, open-source
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to explore and scale the SVG framework for enabling high-quality text-to-image synthesis directly in the Visual Foundation Model (VFM) feature domain.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a text-to-image diffusion pipeline within the VFM representation space to validate generative capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SVG-T2I achieves competitive performance metrics, validating VFM’s representational power for generative tasks and is fully open-sourced to encourage further research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11749
4. V-RGBX: Video Editing with Accurate Controls over Intrinsic Properties
🔑 Keywords: V-RGBX, intrinsic-aware video editing, photorealistic video synthesis, video inverse rendering, keyframe-based video editing
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop an end-to-end framework, V-RGBX, for intrinsic-aware video editing capable of producing consistent and physically plausible video edits.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Combines video inverse rendering, photorealistic synthesis, and a keyframe-based editing approach using an interleaved conditioning mechanism.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– V-RGBX demonstrates effectiveness in creating temporally consistent and photorealistic videos, outperforming prior methods in object appearance editing and scene-level relighting tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11799
5. Sliding Window Attention Adaptation
🔑 Keywords: Sliding Window Attention Adaptation, Transformer-based Large Language Models, Long-Context Performance, Full Attention, Chain-of-Thought
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore how Full Attention-pretrained Transformer-based Large Language Models can be adapted to Sliding Window Attention (SWA) without requiring pretraining, and to recover long-context performance effectively.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study proposes a set of adaptation techniques named Sliding Window Attention Adaptation (SWAA), incorporating five methods including applying SWA only during prefilling, preserving sink tokens, interleaving Full Attention/SWA layers, using Chain-of-Thought, and fine-tuning to achieve effective adaptation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research concludes that SWA adaptation for LLMs is feasible, requires notable effort, and no single method is sufficient alone. Synergistic combinations of methods effectively recover original long-context performance, with performance-efficiency trade-offs analyzed and recommended for different scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10411

6. PersonaLive! Expressive Portrait Image Animation for Live Streaming
🔑 Keywords: PersonaLive, AI-generated summary, diffusion-based framework, real-time portrait animation, multi-stage training
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal of the study is to address generation latency and improve real-time performance in diffusion-based portrait animation models for live streaming scenarios.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a multi-stage training process using hybrid implicit signals, appearance distillation, and autoregressive micro-chunk streaming to enhance speed and efficiency in animation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PersonaLive achieves state-of-the-art performance with significant speed improvements, offering up to 7-22x faster processing than existing diffusion-based portrait animation models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11253
7. Exploring MLLM-Diffusion Information Transfer with MetaCanvas
🔑 Keywords: MetaCanvas, Multimodal Learning, Latent-space planners, Diffusion models, Image and video generation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce MetaCanvas as a framework that enhances precise and structured image and video generation using multimodal large language models (MLLMs) as latent-space planners.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of MetaCanvas on three different diffusion backbones.
– Evaluation across six tasks, including text-to-image generation, text/image-to-video generation, image/video editing, and in-context video generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MetaCanvas consistently outperforms global-conditioning methods, demonstrating the potential of employing MLLMs as latent-space planners to bridge the gap between multimodal understanding and generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11464
8. MeshSplatting: Differentiable Rendering with Opaque Meshes
🔑 Keywords: MeshSplatting, differentiable rendering, novel view synthesis, AR/VR, real-time 3D engines
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal of the research is to improve novel view synthesis quality and efficiency using MeshSplatting, a mesh-based reconstruction method that optimizes geometry and appearance through differentiable rendering.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves using MeshSplatting to enforce connectivity via restricted Delaunay triangulation and refine surface consistency, creating high-quality meshes that render efficiently in real-time 3D engines.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MeshSplatting enhances the quality and efficiency of mesh-based novel view synthesis, achieving a +0.69 dB boost in PSNR on Mip-NeRF360 compared to the state-of-the-art MiLo, while training twice as fast and requiring half the memory, effectively bridging neural rendering with interactive 3D graphics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06818

9. Structure From Tracking: Distilling Structure-Preserving Motion for Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: SAM2VideoX, Bidirectional Video Diffusion, Structure-Preserving Motion, Local Gram Flow loss, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance realistic motion generation in video models by integrating structure-preserving priors into a bidirectional diffusion model using novel feature fusion and local alignment techniques.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a new algorithm distilling motion priors from an autoregressive video tracking model into a bidirectional video diffusion model.
– Introduced a bidirectional feature fusion module and a Local Gram Flow loss to maintain motion fidelity and structure.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SAM2VideoX significantly improves results over existing baselines on VBench and in human studies, demonstrating gains in motion generation and fidelity.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11792
10. Fairy2i: Training Complex LLMs from Real LLMs with All Parameters in {pm 1, pm i}
🔑 Keywords: Fairy2i, quantization, complex-valued LLMs, pre-trained models, efficient inference
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study presents Fairy2i, a framework designed to transform pre-trained real-valued models into a complex form, facilitating efficient low-bit quantization while preserving model performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes mathematical equivalence between real and widely-linear complex maps to convert Transformers.
– Implements phase-aware quantization and recursive residual quantization to minimize quantization error and enhance inference efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Fairy2i achieves nearly comparable performance to full-precision models at 2-bit precision, significantly surpassing existing binary and ternary quantization techniques, enabling efficient inference on standard hardware.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02901

11. LEO-RobotAgent: A General-purpose Robotic Agent for Language-driven Embodied Operator
🔑 Keywords: LEO-RobotAgent, large language models, human-robot interaction, task planning, generalization
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces LEO-RobotAgent, a general-purpose language-driven framework aimed at enhancing human-robot interaction and task planning using large language models across various robot types and tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework employs a streamlined structure, which allows large language models to independently think, plan, and act. It includes a modular toolset for flexibility in tool usage and incorporates a mechanism for human-robot collaboration.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework is demonstrated to easily adapt to mainstream robot platforms, including UAVs, robotic arms, and wheeled robots, efficiently executing tasks of varying complexity. The authors provide a public code repository for further exploration and use.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10605
12. Task adaptation of Vision-Language-Action model: 1st Place Solution for the 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge
🔑 Keywords: correlated noise, flow matching, learnable mixed-layer attention, BEHAVIOR Challenge, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a vision-action policy to excel in the 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge by tackling complex household tasks using innovative methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced correlated noise for flow matching to enhance training efficiency and improve action sequence smoothness.
– Applied learnable mixed-layer attention and System 2 stage tracking for ambiguity resolution in decision-making processes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved 1st place in the 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge with a 26% q-score across 50 household tasks, demonstrating the efficacy of the proposed approach in simulation environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06951
13. Causal Judge Evaluation: Calibrated Surrogate Metrics for LLM Systems
🔑 Keywords: Causal Judge Evaluation, AI-generated summary, Calibration, Confidence Intervals, Pairwise Ranking Accuracy
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces the Causal Judge Evaluation (CJE) framework to improve model evaluation accuracy and efficiency by addressing calibration, weight stabilization, and uncertainty in confidence intervals.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– CJE employs three main components: (i) AutoCal-R for reward calibration using mean-preserving isotonic regression, (ii) SIMCal-W for weight stabilization through stacking of S-monotone candidates, and (iii) Oracle-Uncertainty Aware (OUA) inference to propagate calibration uncertainty.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CJE achieves 99% pairwise ranking accuracy at full sample size with significant cost reduction, and it demonstrates superior coverage performance in confidence intervals compared to traditional methods. Key findings include the limitations of existing estimators and the benefits of using OUA for improved coverage.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11150

14. CLINIC: Evaluating Multilingual Trustworthiness in Language Models for Healthcare
🔑 Keywords: trustworthiness, language models, healthcare, multilingual benchmark, AI Ethics and Fairness
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper presents CLINIC, a multilingual benchmark aimed at evaluating the trustworthiness of language models in the healthcare sector across five dimensions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– CLINIC benchmarks language models through 18 tasks across 15 languages, encompassing critical healthcare topics to assess truthfulness, fairness, safety, robustness, and privacy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The evaluation reveals that language models struggle with factual correctness and demonstrate bias, privacy issues, and vulnerabilities to adversarial attacks. CLINIC aims to improve the global applicability and safety of language models in multilingual healthcare settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11437

15. CheXmask-U: Quantifying uncertainty in landmark-based anatomical segmentation for X-ray images
🔑 Keywords: Uncertainty Estimation, Landmark-based Segmentation, Hybrid Neural Networks, AI in Healthcare, Out-of-Distribution Detection
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve reliability and robustness in clinical deployment of landmark-based segmentation on chest X-rays by leveraging uncertainty estimation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Combines hybrid neural network architectures, which integrate image convolutional encoders with graph-based generative decoders, to derive latent and predictive uncertainty measures.
– Utilizes controlled corruption experiments to validate the effectiveness of these measures against perturbations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates that both latent and predictive uncertainty measures can identify unreliable predictions, reflecting both global and local degradation.
– Establishes uncertainty estimation as a promising approach to enhance the robustness and safe deployment of anatomical segmentation methods, supported by the release of the CheXmask-U dataset.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10715

16. Scaling Behavior of Discrete Diffusion Language Models
🔑 Keywords: DLMs, Scaling Behavior, Uniform Diffusion, Masked Diffusion, Hyperparameters
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study explores the scaling behavior of discrete diffusion language models (DLMs) on different noise types to understand their efficiency compared to autoregressive language models (ALMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– By interpolating between masked and uniform diffusion, the researchers examine key hyperparameters such as batch size and learning rate to analyze the scaling behavior of DLMs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The results show that DLMs display a distinct scaling behavior highly dependent on noise type. Uniform diffusion, while requiring more parameters, is more data-efficient than masked diffusion in compute-efficient training, making it a potential candidate for data-bound settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10858

17. Interpretable Embeddings with Sparse Autoencoders: A Data Analysis Toolkit
🔑 Keywords: Sparse autoencoders, Interpretable concepts, SAE embeddings, Bias identification, Semantic differences
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop Sparse autoencoders to create interpretable and cost-effective embeddings for large-scale text analysis that surpass LLMs and dense embeddings in tasks such as dataset comparison and bias identification.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs Sparse Autoencoders to generate embeddings whose dimensions correlate with interpretable concepts, demonstrating their effectiveness through four data analysis tasks compared to LLMs and dense embeddings.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SAE embeddings provide more cost-effective and reliable insights, uncovering semantic differences and concept correlations within documents at 2-8x lower cost, while being more controllable and outperforming dense embeddings in property-based retrieval tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10092
18. Sharp Monocular View Synthesis in Less Than a Second
🔑 Keywords: SHARP, photorealistic view synthesis, 3D Gaussian representation, zero-shot generalization, neural network
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– SHARP aims to synthesize photorealistic views from a single image using a 3D Gaussian representation, setting new benchmarks in speed and quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a single feedforward pass through a neural network to regress the parameters of a 3D Gaussian representation, enabling rapid rendering on a standard GPU.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art results with robust zero-shot generalization, reducing LPIPS by 25-34% and DISTS by 21-43% compared to prior models, while significantly decreasing synthesis time.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10685

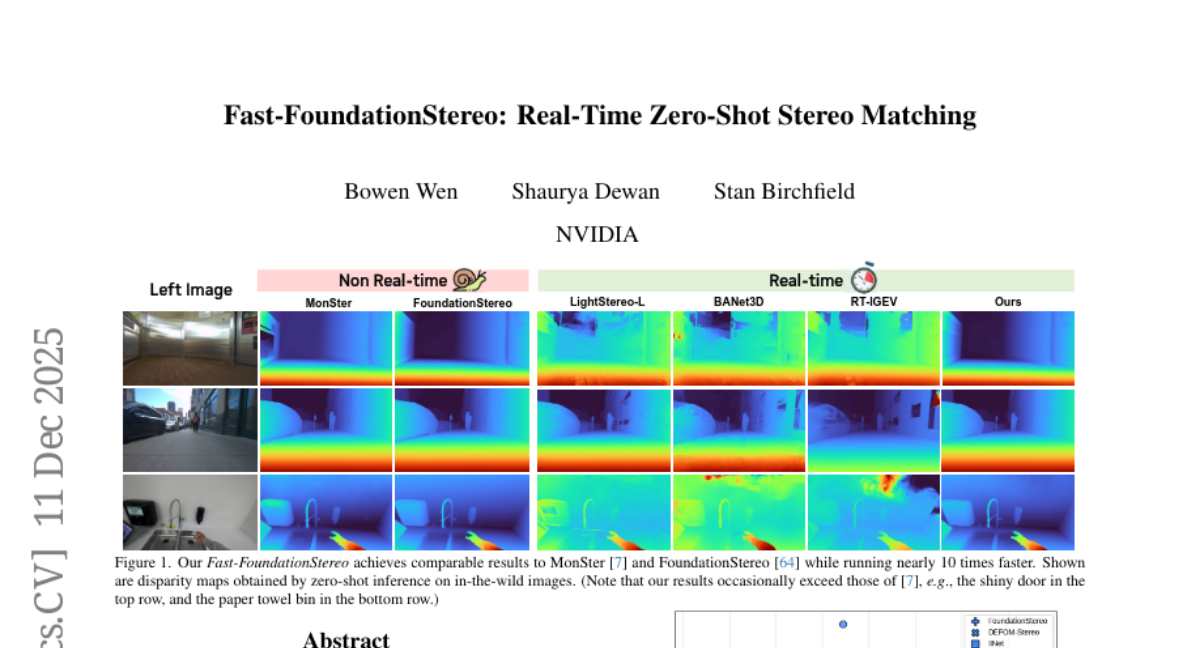
19. Fast-FoundationStereo: Real-Time Zero-Shot Stereo Matching
🔑 Keywords: Zero-Shot Generalization, Knowledge Distillation, Blockwise Neural Architecture Search, Structured Pruning
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop Fast-FoundationStereo, achieving real-time zero-shot stereo generalization with efficient architectures bridging robustness and speed gaps.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed a divide-and-conquer acceleration strategy combining knowledge distillation, blockwise neural architecture search, and structured pruning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Fast-FoundationStereo runs over 10x faster than existing models, matching zero-shot accuracy, and sets a new state-of-the-art performance in real-time methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11130
20. The N-Body Problem: Parallel Execution from Single-Person Egocentric Video
🔑 Keywords: N-Body Problem, Vision-Language Model (VLM), object conflicts, 3D environment, action coverage
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to explore how a model can learn to parallelize tasks from a single egocentric video, specifically addressing spatial and object conflicts to improve action coverage and reduce collisions by conceptualizing the N-Body Problem.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces a suite of metrics to assess task performance and feasibility, alongside a structured prompting strategy for Vision-Language Model (VLM) to effectively manage 3D environments, object usage, and temporal dependencies for parallel task execution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Results from 100 videos demonstrate a 45% increase in action coverage and a substantial decrease in collision, object, and causal conflict rates by up to 55%, highlighting the efficiency of the proposed methods over baseline models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11393
21. Particulate: Feed-Forward 3D Object Articulation
🔑 Keywords: Particulate, Transformer Network, Articulated 3D Structures, AI-generated 3D assets, Benchmark
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Particulate aims to infer articulated 3D structures from single static meshes using a transformer network.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a feed-forward approach with a Part Articulation Transformer that processes point clouds to predict 3D parts, kinematic structure, and motion constraints.
– Trained on diverse articulated 3D assets from public datasets and supports multi-joint articulation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Particulate significantly outperforms previous methods by delivering faster and more accurate articulated 3D models.
– Introduces a new benchmark for 3D articulation estimation, aligning evaluation with human preferences.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11798

22.
