AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251216

1. ReFusion: A Diffusion Large Language Model with Parallel Autoregressive Decoding
🔑 Keywords: ReFusion, masked diffusion model, parallel decoding, slot-based design, autoregressive models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce ReFusion, a novel masked diffusion model aimed at improving performance and efficiency through slot-based parallel decoding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes an iterative “plan-and-infill” decoding process, coupling diffusion-based planning with autoregressive infilling at a slot level.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ReFusion surpasses prior masked diffusion models with a 34% performance gain and an average 18x speedup, while closing the performance gap with autoregressive models with a 2.33x speedup.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13586

2. Towards Scalable Pre-training of Visual Tokenizers for Generation
🔑 Keywords: Visual Tokenizer Pre-training, Generative Performance, Latent Space, Image-Text Contrastive, Self-Supervised
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve generative performance by addressing the pre-training scaling problem and optimizing image-text contrastive, self-supervised, and reconstruction losses in visual tokenizers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a unified visual tokenizer pre-training framework (VTP) that simultaneously optimizes image-text contrastive, self-supervised, and reconstruction losses to improve scaling properties and generative performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The VTP framework enhances zero-shot accuracy, speeds up convergence, and results in significant improvements in generative performance with increased compute power. It achieves a 65.8% FID improvement in downstream generation compared to conventional autoencoders.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13687
3. Memory in the Age of AI Agents
🔑 Keywords: Agent Memory, Memory Automation, Reinforcement Learning Integration, Multimodal Memory
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To provide an updated overview and classification of current agent memory research, distinguishing between formats, functions, and dynamics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study offers a unified examination of agent memory, focusing on its forms, functions, and dynamics, and provides a taxonomy of agent memory systems.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The paper highlights the need for clear definitions and classifications in agent memory research and outlines emerging research areas, including integration with reinforcement learning and trustworthiness issues.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13564

4. QwenLong-L1.5: Post-Training Recipe for Long-Context Reasoning and Memory Management
🔑 Keywords: QwenLong-L1.5, Long-Context Reasoning, Data Synthesis, AI Native, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces QwenLong-L1.5, a model designed to enhance long-context reasoning capabilities through systematic post-training innovations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a Long-Context Data Synthesis pipeline to generate challenging reasoning tasks.
– Application of Stabilized Reinforcement Learning via task-balanced sampling and Adaptive Entropy-Controlled Policy Optimization.
– Development of a Memory-Augmented Architecture to handle ultra-long contexts exceeding 4 million tokens.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– QwenLong-L1.5 achieves performance comparable to advanced models like GPT-5, excelling in long-context reasoning benchmarks and surpassing its baseline by 9.90 points.
– The model’s framework shows a significant gain of 9.48 points on ultra-long tasks, and its long-context reasoning ability enhances performance in general domains such as scientific reasoning and extended dialogue.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12967

5. LongVie 2: Multimodal Controllable Ultra-Long Video World Model
🔑 Keywords: LongVie 2, video world models, autoregressive framework, controllability, temporal consistency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance video world models by developing an end-to-end autoregressive framework, LongVie 2, that improves controllability, visual quality, and temporal consistency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a progressive training approach in three stages: Multi-modal guidance, Degradation-aware training, and History-context guidance to enhance control, maintain visual quality, and ensure temporal consistency.
– Introduces LongVGenBench, a benchmark with 100 high-resolution videos for comprehensive evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LongVie 2 delivers state-of-the-art performance in video generation, achieving long-range controllability, temporal coherence, and visual fidelity, supporting video generation lasting up to five minutes, contributing significantly to unified video world modeling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13604

6. Finch: Benchmarking Finance & Accounting across Spreadsheet-Centric Enterprise Workflows
🔑 Keywords: AI agents, enterprise finance, AI-generated summary, GPT 5.1, expert annotation
💡 Category: AI in Finance
🌟 Research Objective:
– Finch is introduced as a benchmark specifically designed for evaluating AI agents in complex, real-world workflows within finance and accounting using genuine data from Enron and other financial institutions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The benchmark is established by deriving workflows with the assistance of LLM (Large Language Models) and expert verification from real-world email threads and spreadsheet version histories, further complemented by meticulous expert annotations. This resulted in 172 composite workflows entailing 384 tasks across 1,710 spreadsheets and other multimodal artifacts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Evaluations conducted with leading AI systems like GPT 5.1, Claude Sonnet 4.5, among others, reveal the challenging nature of real-world enterprise workflows. Specifically, GPT 5.1 Pro took 48 hours to achieve only a 38.4% pass rate, highlighting the difficulty AI systems face in navigating these complex tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13168

7. NL2Repo-Bench: Towards Long-Horizon Repository Generation Evaluation of Coding Agents
🔑 Keywords: coding agents, autonomous software development, long-horizon repository generation, installable Python library, test pass rates
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate the long-horizon capabilities of coding agents in generating complete Python libraries from natural-language requirements.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of NL2Repo Bench, a benchmark designed to test the ability of coding agents to autonomously generate full software systems, involving tasks such as planning, architecture design, dependency management, and multi-module logic implementation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Long-horizon repository generation is still unsolved with leading agents achieving below 40% average test pass rates. Agents face challenges such as premature termination, loss of global coherence, fragile cross-file dependencies, and inadequate planning, emphasizing the central bottleneck in long-horizon reasoning for future autonomous coding agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12730

8. Error-Free Linear Attention is a Free Lunch: Exact Solution from Continuous-Time Dynamics
🔑 Keywords: Error-Free Linear Attention, Linear-time attention, DeltaNet, Language modeling perplexity, Softmax attention
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces Error-Free Linear Attention (EFLA), which aims to address the quadratic cost bottleneck in long-context language models by providing a stable, parallelizable, and theoretically sound solution that outperforms existing models like DeltaNet.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– EFLA is formulated as a continuous-time dynamical system with a focus on leveraging the rank-1 structure of the dynamics matrix. This approach allows the derivation of an exact closed-form solution corresponding to the infinite-order Runge-Kutta method, ensuring error-free accumulation and preserving linear-time complexity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results indicate that EFLA achieves robust performance in noisy environments, showing lower language modeling perplexity and superior benchmark performance compared to DeltaNet, without introducing additional parameters, paving the way for high-fidelity and scalable linear-time attention models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12602

9. KlingAvatar 2.0 Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: KlingAvatar 2.0, spatio-temporal cascade, multimodal instruction alignment, high-resolution, Co-Reasoning Director
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To overcome the inefficiencies in generating long-duration high-resolution videos by using a novel spatio-temporal cascade framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a spatio-temporal cascade framework that upscales both spatial resolution and temporal dimension, aided by the Co-Reasoning Director and Negative Director for better multimodal instruction alignment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– KlingAvatar 2.0 effectively addresses challenges in video generation, achieving better visual clarity, realistic rendering, strong identity preservation, and coherent multimodal instruction following.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13313

10. MentraSuite: Post-Training Large Language Models for Mental Health Reasoning and Assessment
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Mental health disorders, Large language models (LLMs), MentraSuite, Mental-health reasoning
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces MentraSuite, a unified framework designed to enhance reliable mental health reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes Mindora, a post-trained model optimized through a hybrid SFT-RL framework with an inconsistency-detection reward.
– Implements MentraBench, a benchmark evaluating task performance and reasoning quality across five core reasoning aspects.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Mindora demonstrates high performance on MentraBench, achieving outstanding consistency and reliability in complex mental-health scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.09636

11. Openpi Comet: Competition Solution For 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge
🔑 Keywords: 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge, long-horizon tasks, simulated environments, mobile manipulation, embodied AI
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to deliver a solution for the 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge focused on solving everyday household tasks through pre-training and post-training techniques.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ systematic training techniques and data analysis, including pre-training, post-training, and careful ablations to enhance the performance of physical agents in simulated environments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Proposed solution achieved a close 2nd place in the challenge and significantly outperformed other submissions, providing practical lessons and design recommendations for adapting foundation models to embodied AI applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10071
12. Spatial-Aware VLA Pretraining through Visual-Physical Alignment from Human Videos
🔑 Keywords: Spatial-Aware VLA Pretraining, 3D spatial understanding, Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, dual-encoder architecture, 3D visual encoder
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose a Spatial-Aware VLA Pretraining paradigm to improve 3D spatial understanding in robots by aligning 2D visual inputs with 3D actions through a dual-encoder architecture.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Leverage large-scale human demonstration videos to extract 3D visual and action annotations for supervision, using a dual-encoder architecture incorporating a 3D visual encoder.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VIPA-VLA, the proposed model, shows significantly improved grounding between 2D vision and 3D action, leading to more robust and generalizable robotic policies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13080

13. WebOperator: Action-Aware Tree Search for Autonomous Agents in Web Environment
🔑 Keywords: WebOperator, Tree-search framework, backtracking mechanism, strategic exploration, safety considerations
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance web-based agents by introducing WebOperator, a tree-search framework that provides reliable backtracking and strategic exploration to address the limitations of handling irreversible actions and partial observability in web environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a best-first search strategy that prioritizes actions based on reward estimates and safety considerations, along with a robust backtracking mechanism to verify the feasibility of paths and minimize unintended side effects.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– WebOperator demonstrates effectiveness on WebArena and WebVoyager, achieving a state-of-the-art 54.6% success rate with gpt-4o, highlighting the benefits of integrating strategic foresight with safe execution.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12692

14. V-REX: Benchmarking Exploratory Visual Reasoning via Chain-of-Questions
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Models, Visual Reasoning, Multi-step Exploration, Chain-of-Questions, AI Native
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate vision-language models’ ability for multi-step reasoning and exploration using the V-REX evaluation suite.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of an evaluation framework called V-REX, which utilizes a Chain-of-Questions approach to test models on planning and following tasks through curated exploratory questions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study identifies distinct trends in models’ planning and following capabilities, highlights substantial differences and room for improvement in multi-step exploratory reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11995
15. DrivePI: Spatial-aware 4D MLLM for Unified Autonomous Driving Understanding, Perception, Prediction and Planning
🔑 Keywords: DrivePI, 3D perception, AI-generated summary, vision-action models
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to introduce DrivePI, a spatial-aware 4D multi-modal large language model, designed to enhance 3D perception, prediction, and planning in autonomous driving by integrating point clouds, images, and language instructions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method proposed employs a unified Vision-Language-Action (VLA) framework compatible with vision-action (VA) models, performing spatial understanding, 3D perception, prediction, and planning through end-to-end optimization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DrivePI outperforms existing VLA and specialized VA models, achieving higher mean accuracy and lower collision rates in autonomous driving tasks, showcasing its effectiveness with a 0.5B Qwen2.5 model as the backbone.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12799
16. Toward Ambulatory Vision: Learning Visually-Grounded Active View Selection
🔑 Keywords: Vision Language Models, Visual Question Answering, VG-AVS, Synthetic Dataset, RL-based Policy Optimization
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance performance and generalization in Visual Question Answering (VQA) by fine-tuning Vision Language Models (VLMs) for selecting informative viewpoints through the VG-AVS task.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A synthetic dataset with paired query-target views is created, followed by fine-tuning of pretrained VLMs through supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning-based policy optimization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The VG-AVS framework improves viewpoint-based question answering performance and enhances the accuracy of existing scene-exploration-based embodied question-answering systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13250

17. VLSA: Vision-Language-Action Models with Plug-and-Play Safety Constraint Layer
🔑 Keywords: AEGIS, Vision-Language-Action, control barrier functions, safety-critical benchmark, obstacle avoidance rate
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introducing AEGIS, a Vision-Language-Safe Action architecture, to enhance safety and performance in robotic manipulation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of AEGIS with existing Vision-Language-Action models using a plug-and-play safety constraint layer formed by control barrier functions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AEGIS improves obstacle avoidance rate by 59.16% and increases task execution success rate by 17.25%, demonstrated through a comprehensive safety-critical benchmark named SafeLIBERO.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11891

18. Aesthetic Alignment Risks Assimilation: How Image Generation and Reward Models Reinforce Beauty Bias and Ideological “Censorship”
🔑 Keywords: AI-Generated Summary, Aesthetic Preference, Reward Models, User Autonomy, Image-to-Image Editing
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the bias in state-of-the-art image generation and reward models that leads to a preference for conventional aesthetics over user-requested anti-aesthetic outputs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Constructed a wide-spectrum aesthetics dataset to evaluate the performance of image generation and reward models. Included tests using image-to-image editing and comparisons against real abstract artworks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Found a systemic bias in current models, which consistently default to conventional aesthetics and inadequately respond to prompts for anti-aesthetic images, prioritizing developer-centered values and compromising user autonomy and aesthetic diversity.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11883
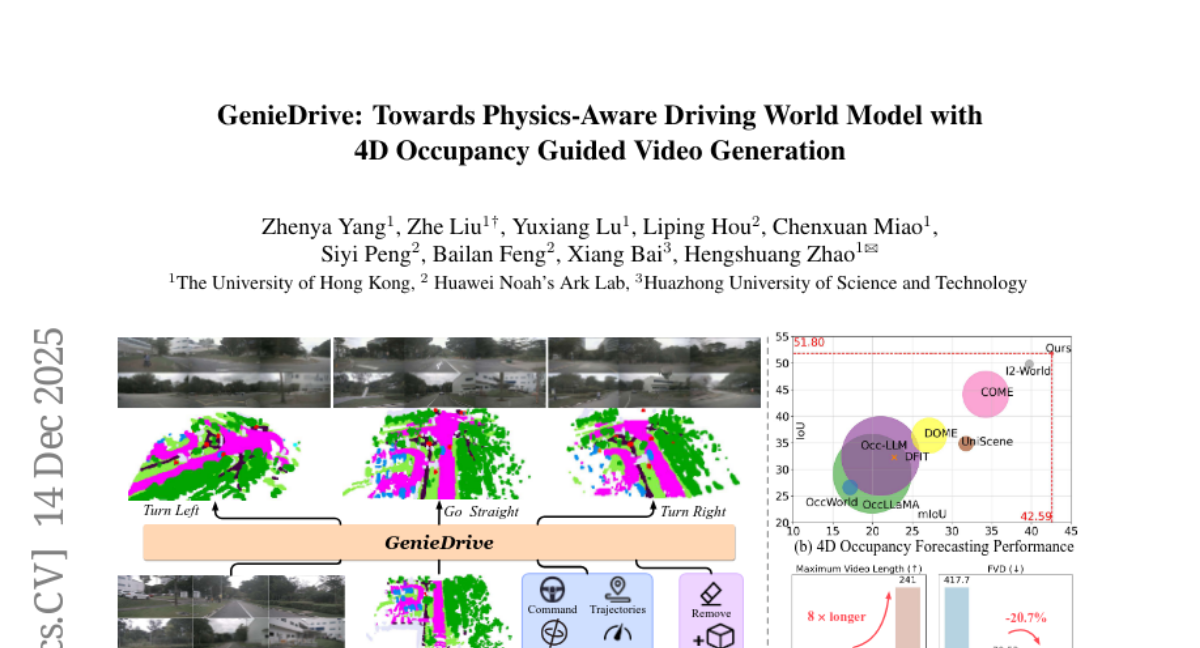
19. GenieDrive: Towards Physics-Aware Driving World Model with 4D Occupancy Guided Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: GenieDrive, 4D occupancy, physics-aware, VAE, Mutual Control Attention
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose GenieDrive, a framework for improving accuracy and quality in physics-aware driving video generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a 4D occupancy-based approach with VAE to compress high-resolution data into latent tri-plane representation.
– Introduce Mutual Control Attention (MCA) for effective modeling of control influence on occupancy evolution.
– Implement Normalized Multi-View Attention for enhanced multi-view video quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GenieDrive achieves a 7.2% improvement in forecasting mIoU at 41 FPS with only 3.47 M parameters.
– Video quality is significantly improved with a 20.7% reduction in FVD, enabling controllable, multi-view consistent and physics-aware video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12751
20. Image Diffusion Preview with Consistency Solver
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Preview, ConsistencySolver, low-step image generation, Reinforcement Learning, FID scores
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Diffusion Preview to enhance quality and consistency in low-step image generation, improving interactive user experiences.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize ConsistencySolver, a high-order trainable solver derived from general linear multistep methods and optimized using Reinforcement Learning, to improve quality and consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ConsistencySolver significantly improves generation quality and consistency with fewer steps, reduces user interaction time by nearly 50%, and maintains high-quality outputs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13592

21. CAPTAIN: Semantic Feature Injection for Memorization Mitigation in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: CAPTAIN, Diffusion Models, Memorization Mitigation, Latent Features, Denoising
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop CAPTAIN, a training-free framework that mitigates memorization in diffusion models by modifying latent features during the denoising process, ensuring prompt fidelity and visual quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes frequency-based noise initialization to reduce memorized patterns and identifies optimal denoising timesteps for feature injection.
– Injects semantically aligned features from non-memorized reference images into localized latent regions to suppress memorization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CAPTAIN significantly reduces memorization compared to CFG-based baselines while maintaining strong prompt alignment and visual quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10655
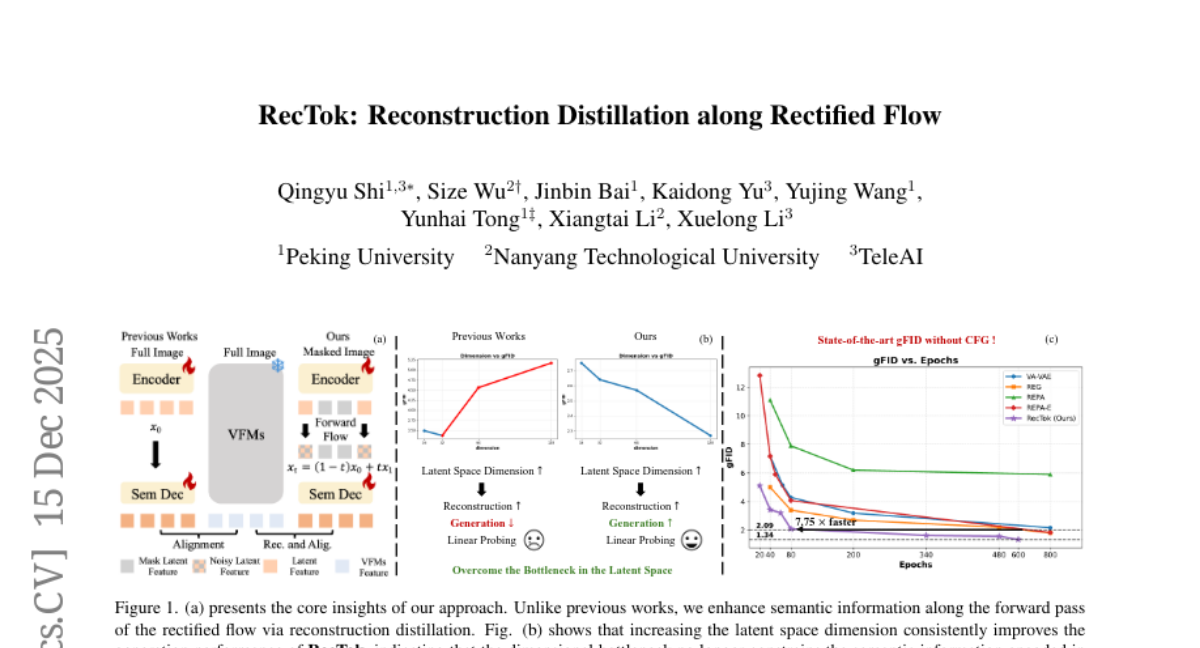
22. RecTok: Reconstruction Distillation along Rectified Flow
🔑 Keywords: RecTok, Visual Tokenizers, Diffusion Models, Latent Space, Generation Quality
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve diffusion models by enhancing forward flow semantics and reconstruction, focusing on overcoming limitations of high-dimensional visual tokenizers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposed two key innovations: flow semantic distillation and reconstruction–alignment distillation, distilling semantic information into forward flow trajectories and enhancing these through masked feature reconstruction loss.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RecTok achieves state-of-the-art results on gFID-50K, with superior image reconstruction and generation quality, maintaining a semantically rich latent space while consistently improving with increased latent dimensionality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13421
23. Towards Interactive Intelligence for Digital Humans
🔑 Keywords: Interactive Intelligence, Mio framework, AI-generated summary, cognitive reasoning, real-time multimodal embodiment
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the concept of Interactive Intelligence to enhance digital humans with personality, adaptive interactions, and self-evolution.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of the Mio framework, composed of five modules: Thinker, Talker, Face Animator, Body Animator, and Renderer, for integrating cognitive reasoning with real-time multimodal embodiment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework demonstrates superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods, achieving more intelligent interaction and surpassing current benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13674
24. Inferring Compositional 4D Scenes without Ever Seeing One
🔑 Keywords: COM4D, 4D reconstruction, spatio-temporal configuration, AI-generated, temporal attention
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To predict the structure and spatio-temporal configuration of 4D/3D objects from 2D video without using 4D compositional training data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a method called COM4D that employs spatial and temporal attentions during training on 2D video input, independent learning of attentions, and an attention mixing mechanism for inference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– COM4D achieves state-of-the-art results in 4D object and composed 3D reconstruction, reconstructing complete 4D scenes with multiple interacting objects from monocular videos without relying on 4D compositional training data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05272

25. START: Spatial and Textual Learning for Chart Understanding
🔑 Keywords: START, Multi-modal Large Language Models, Chart understanding, chart-element grounding, chart-to-code generation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance multimodal large language models by integrating spatial and textual learning for improved chart understanding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced chart-element grounding and chart-to-code generation to improve model understanding.
– Developed the START-Dataset using a novel data-generation pipeline to translate real chart images into executable chart code.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The START model delivers consistent improvements over base models and surpasses previous state-of-the-art methods in chart understanding benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07186

26. What matters for Representation Alignment: Global Information or Spatial Structure?
🔑 Keywords: Representation alignment, pretrained vision encoders, diffusion models, spatial structure, iREPA
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Determine whether global semantic information or spatial structure is more crucial for generative performance in diffusion models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted a large-scale empirical analysis of 27 different vision encoders and various model scales.
– Introduced modifications like replacing the MLP projection layer with a convolution layer and adding a spatial normalization layer in REPA.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Found spatial structure, rather than global semantic performance, drives generation performance.
– The iREPA method improves convergence speed across various vision encoders and training variants.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10794

27. Flowception: Temporally Expansive Flow Matching for Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: Flowception, non-autoregressive, video generation, discrete frame insertions, continuous denoising
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Flowception, a non-autoregressive video generation framework designed to improve efficiency and performance by interleaving discrete frame insertions with continuous denoising.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a probability path that combines discrete frame insertions and continuous frame denoising, reducing training FLOPs and being adaptable to local attention variants.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Flowception reduces error accumulation compared to autoregressive methods, decreases computational costs, and shows improved FVD and VBench metrics, facilitating tasks like image-to-video generation and video interpolation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11438

28. Few-Step Distillation for Text-to-Image Generation: A Practical Guide
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion distillation, text-to-image generation, unified framework, input scaling, diffusion generators
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To systematically adapt and evaluate diffusion distillation techniques in text-to-image (T2I) generation using a leading T2I model, FLUX.1-lite.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed diffusion distillation, integrating state-of-the-art techniques into a unified framework to handle free-form language prompts rather than discrete class labels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Developed practical guidelines for successful implementation, identifying key challenges, and providing an open-source solution, laying the foundation for efficient diffusion generators in real-world applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13006

29. Directional Textual Inversion for Personalized Text-to-Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: Directional Textual Inversion, Textual Inversion, prompt conditioning, Riemannian SGD, hyperspherical parameterization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve text-to-image personalization and enhance prompt conditioning through Directional Textual Inversion (DTI).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Constraints learned tokens to unit magnitude.
– Optimization of direction on the unit hypersphere using Riemannian SGD.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DTI enhances text fidelity over traditional Textual Inversion while retaining subject similarity.
– Enables smooth, semantically coherent interpolation between learned concepts, suggesting a robust and scalable approach for prompt-faithful personalization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13672

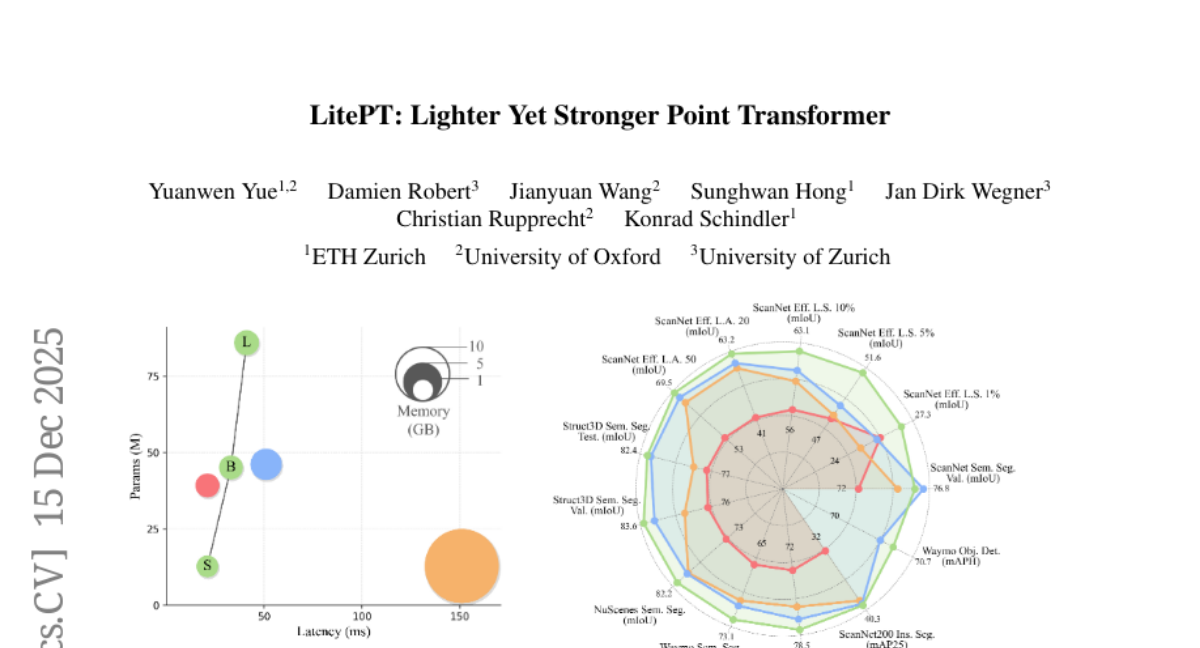
30. LitePT: Lighter Yet Stronger Point Transformer
🔑 Keywords: LitePT, 3D point cloud networks, convolutional layers, attention blocks, PointROPE
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve 3D point cloud processing by developing a new model, LitePT, which utilizes convolutions and attention blocks efficiently across different network layers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– LitePT adopts convolutions in early stages for low-level geometry extraction and attention in deeper layers for high-level semantics.
– Introduces PointROPE for 3D positional encoding, a training-free method to maintain spatial layout information while reducing redundant convolutional layers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LitePT is highly efficient, having 3.6 times fewer parameters, running 2 times faster, and using 2 times less memory compared to the state-of-the-art, yet matching or outperforming in performance.
– Code and models for LitePT are made publicly available for further research and application.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13689
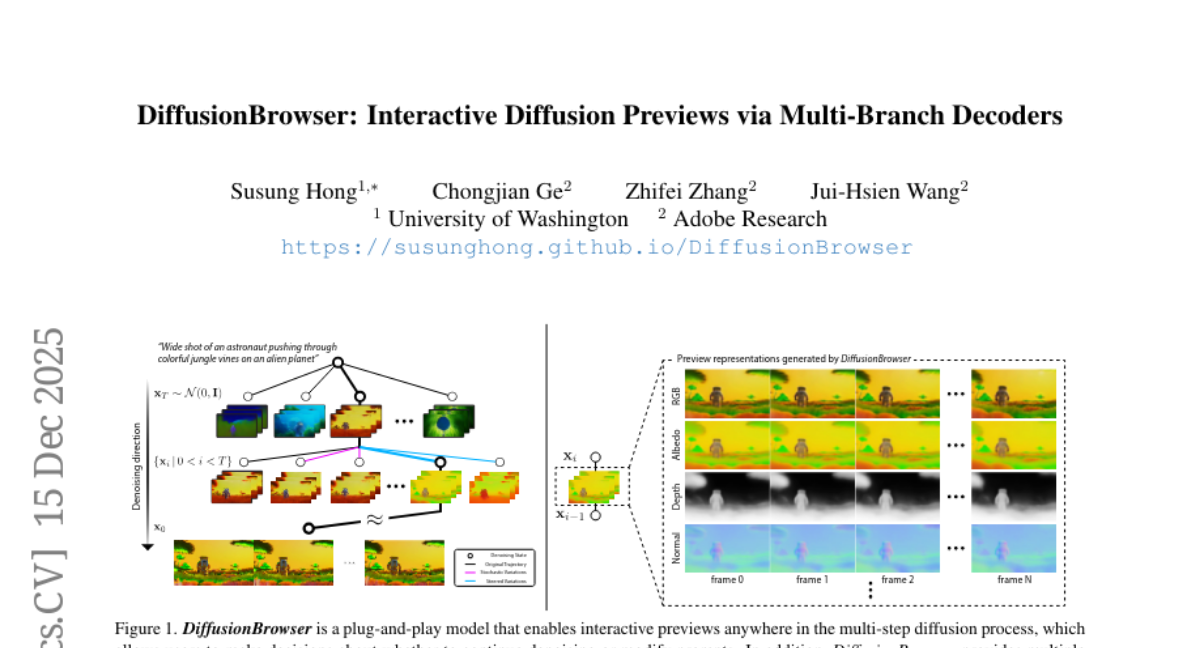
31. DiffusionBrowser: Interactive Diffusion Previews via Multi-Branch Decoders
🔑 Keywords: DiffusionBrowser, video diffusion models, generative video synthesis, lightweight decoder, control capability
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce DiffusionBrowser to enhance user interaction during video synthesis by allowing real-time previews and control.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a model-agnostic lightweight decoder framework to generate multi-modal preview representations at more than 4 times real-time speed.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Provides the ability to guide video generation interactively with stochasticity reinjection and modal steering, revealing details of the otherwise opaque denoising process.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13690
32. Towards Visual Re-Identification of Fish using Fine-Grained Classification for Electronic Monitoring in Fisheries
🔑 Keywords: Fish Re-identification, Electronic Monitoring Systems, AI-generated summary, Vision Transformer, Swin-T architecture
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop an optimized deep learning pipeline using the AutoFish dataset and Swin-T architecture to enhance fish re-identification metrics in Electronic Monitoring systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized hard triplet mining combined with a custom image transformation pipeline, including dataset-specific normalization, to improve key Re-ID metrics.
– Compared performance of the Vision Transformer-based Swin-T against the Convolutional Neural Network-based ResNet-50 architecture.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Swin-T architecture significantly outperforms the ResNet-50, achieving 41.65% mAP@k and 90.43% Rank-1 accuracy.
– Main challenge identified is intra-species errors, where viewpoint inconsistency is more detrimental than partial occlusion.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08400

33. Learning Robot Manipulation from Audio World Models
🔑 Keywords: generative latent flow matching model, AI-generated summary, multimodal reasoning, temporal evolution, rhythmic patterns
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop a generative latent flow matching model to predict future audio for robotic manipulation tasks, enhancing performance by capturing intrinsic rhythmic patterns.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a generative latent flow matching model to forecast future audio observations, facilitating long-term policy reasoning when integrated into robotic systems.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed model demonstrates superior capabilities compared to methods lacking future lookahead, emphasizing the importance of accurate future audio state predictions for successful robot action learning in tasks requiring perception of real-world audio or music signals.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08405
34. FoundationMotion: Auto-Labeling and Reasoning about Spatial Movement in Videos
🔑 Keywords: FoundationMotion, motion understanding, motion datasets, Large Language Models, data curation pipeline
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the limitations of existing motion datasets by creating a scalable automated pipeline, FoundationMotion, for constructing large-scale and fine-grained motion datasets to enhance motion understanding and spatial reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes object detection to track objects in videos, followed by trajectory extraction and the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate captions and question-answer pairs, effectively automating the dataset creation process.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Models fine-tuned with datasets from FoundationMotion significantly improve in motion understanding, outperforming strong closed-source and open-source baseline models, demonstrating the pipeline’s effectiveness in enhancing model capabilities without performance trade-offs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10927
35. Rethinking Expert Trajectory Utilization in LLM Post-training
🔑 Keywords: Sequential SFT-then-RL, Supervised Fine-Tuning, Reinforcement Learning, Plasticity-Ceiling Framework, Expert Trajectories
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to identify the optimal pipeline for integrating expert trajectories in AI systems, particularly focusing on the Sequential SFT-then-RL approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs the Plasticity-Ceiling Framework to theoretically ground the performance metrics and conducts extensive benchmarking to establish the effectiveness of the Sequential SFT-then-RL pipeline.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Sequential SFT-then-RL pipeline is found to be superior due to its ability to overcome stability challenges in synchronized approaches.
– Transitioning to RL during the SFT Stable or Mild Overfitting Sub-phase enhances the overall performance ceiling.
– The data scale significantly impacts post-training potential, and trajectory difficulty serves as a multiplier.
– Minimum SFT Validation Loss is a strong indicator for selecting expert trajectories that optimize the final performance outcomes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11470

36. AutoMV: An Automatic Multi-Agent System for Music Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: AutoMV, multi-agent system, music-to-video generation, benchmark, professional music videos
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop AutoMV, a multi-agent system for generating coherent full-length music videos directly from songs, improving upon previous methods and closing the gap to professional music videos.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– AutoMV employs a multi-agent system consisting of various agents including music processing tools, a screenwriter agent, a director agent, and a verifier agent, to collaboratively produce cohesive music videos. It also proposes a comprehensive benchmark with four high-level categories and twelve fine-grained criteria to assess music-to-video generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AutoMV significantly outperforms existing methods across all benchmark categories, demonstrating enhanced capability in aligning video content with the musical structure and providing a more coherent video narrative comparable to professional music videos. Additionally, while using large multimodal models as automatic MV judges shows potential, there remains a noticeable gap compared to human experts, suggesting future research directions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12196
37. State over Tokens: Characterizing the Role of Reasoning Tokens
🔑 Keywords: State over Tokens, Large Language Models, reasoning tokens, computational state, generation cycles
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the State over Tokens (SoT) framework to reinterpret reasoning tokens in LLMs as computational states, highlighting the necessity for new research focus.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Reframing reasoning tokens not as linguistic narratives, but as externalized computational states to explore their role in driving correct reasoning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– To genuinely understand LLM reasoning processes, it is crucial to decode reasoning tokens as states rather than interpreting them as textual narratives.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12777

38. FIN-bench-v2: A Unified and Robust Benchmark Suite for Evaluating Finnish Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: FIN-bench-v2, large language models, HuggingFace Datasets, instruction-tuned models, evaluation criteria
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce FIN-bench-v2 as a unified benchmark suite for evaluating Finnish large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Consolidate Finnish versions of widely used benchmarks and incorporate diverse datasets.
– Employ HuggingFace Datasets for prompt formulations and include human annotation for machine-translated resources.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Successfully retained robust tasks using specific criteria applied to pretrained decoder-only models.
– Evaluated larger instruction-tuned models to analyze performance across tasks and prompts.
– Made all datasets and configurations publicly available for community use and further research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13330

39. KD-OCT: Efficient Knowledge Distillation for Clinical-Grade Retinal OCT Classification
🔑 Keywords: Knowledge Distillation, ConvNeXtV2-Large, EfficientNet-B2, AMD, Optical Coherence Tomography
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop a novel knowledge distillation framework for compressing a high-performance ConvNeXtV2-Large model into an EfficientNet-B2 model for real-time AMD and CNV classification in clinical settings.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The proposed KD-OCT framework involves real-time distillation with a combined loss strategy, utilizing advanced augmentations, stochastic weight averaging, and focal loss to ensure efficient model compression and maintain diagnostic performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– KD-OCT achieves a balance between efficiency and accuracy, performing near-teacher level diagnosis while significantly reducing model size and inference time, facilitating edge deployment for AMD screening.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.09069

40. CoRe3D: Collaborative Reasoning as a Foundation for 3D Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: 3D understanding, CoRe3D, reasoning framework, multimodal models, spatially grounded reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce CoRe3D, a unified 3D understanding and generation framework using spatially grounded reasoning to align language intent with 3D content.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement a reasoning framework operating over semantic and spatial abstractions, decomposing 3D latent space into localized regions for structured spatial reasoning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CoRe3D enhances model reliability and performance by tightly coupling semantic inference with spatial reasoning, ensuring strong local consistency and alignment with linguistic descriptions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12768

41.
