AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251222
1. Probing Scientific General Intelligence of LLMs with Scientist-Aligned Workflows
🔑 Keywords: Scientific General Intelligence, Practical Inquiry Model, SGI-Bench, Test-Time Reinforcement Learning, hypothesis novelty
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To establish a coherent framework for Scientific General Intelligence (SGI) and evaluate existing models’ capabilities using the SGI-Bench benchmark.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of the Practical Inquiry Model (PIM) grounded tasks and SGI-Bench comprising cross-disciplinary examples. Introduction of Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL) for optimizing retrieval-augmented novelty rewards.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified gaps in current AI models’ abilities across scientific tasks, particularly concerning feasibility, detail, and execution accuracy. Test-Time Reinforcement Learning enhances hypothesis novelty, laying the groundwork for better AI-driven scientific discovery.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16969

2. When Reasoning Meets Its Laws
🔑 Keywords: Large Reasoning Models, Laws of Reasoning, compute law, accuracy law, LoRe-Bench
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the Laws of Reasoning (LoRe) framework to define desired reasoning behaviors in Large Reasoning Models (LRMs), focusing on compute and accuracy laws.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposed compute law assuming linear scaling with question complexity and extended analysis with a supplementary accuracy law.
– Introduced LoRe-Bench as a benchmark to measure monotonicity and compositionality in reasoning models.
– Developed a finetuning approach to enforce compute-law compositionality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Evaluation reveals that most reasoning models show reasonable monotonicity but lack compositionality.
– Better compliance with compute laws correlates with improved reasoning performance, uncovering synergistic effects across properties and laws.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17901

3. Both Semantics and Reconstruction Matter: Making Representation Encoders Ready for Text-to-Image Generation and Editing
🔑 Keywords: Latent Diffusion Models, Variational Autoencoder, pixel-level reconstruction, semantic-pixel reconstruction objective
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a systematic framework to adapt understanding-oriented encoder features for generative tasks, aiming to improve image reconstruction and generation performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement a semantic-pixel reconstruction objective to regularize the latent space and ensure both semantic richness and compactness, optimizing for efficient image reconstruction and generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction and significant performance gains in Text-to-Image and image editing tasks, proving that representation encoders can serve as robust generative components.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17909

4. Are We on the Right Way to Assessing LLM-as-a-Judge?
🔑 Keywords: LLM-as-a-Judge, rational choice theory, local self-consistency, global logical consistency, situational preference
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Sage, a novel evaluation suite aiming to assess the quality and reliability of LLM-as-a-Judge without human annotation, using principles from rational choice theory.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors develop Sage by combining structured benchmark problems with real-world queries, creating a dataset of 650 questions to evaluate local self-consistency and global logical consistency of LLM judges.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Results reveal significant reliability issues in current LLM judges, including in leading models like Gemini-2.5-Pro and GPT-5, largely due to situational preference. The study highlights the potential enhancements possible through finetuning and panel-based judges, while casting doubt on the reliability of human annotation as a gold standard.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16041

5. GroundingME: Exposing the Visual Grounding Gap in MLLMs through Multi-Dimensional Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: Visual grounding, multimodal large language models, GroundingME, rejection accuracy, test-time scaling
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal of the research is to evaluate and improve the visual grounding capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) in a comprehensive manner, particularly through the introduction of the GroundingME benchmark.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs a new benchmark, GroundingME, which tests MLLMs across four dimensions: Discriminative, Spatial, Limited, and Rejection. Moreover, it evaluates 25 state-of-the-art models and introduces strategies such as test-time scaling and data-mixture training for potential improvements.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study reveals a significant gap in current MLLM capabilities, with top models achieving only 45.1% accuracy on complex grounding tasks and 0% on certain rejection tasks. Proposed strategies improved rejection accuracy to 27.9%, providing a roadmap to advance MLLMs towards human-level visual grounding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17495

6. An Anatomy of Vision-Language-Action Models: From Modules to Milestones and Challenges
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action models, Robotics, Embodied intelligence, Representation, Safety
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To provide a comprehensive overview of Vision-Language-Action models, highlighting the main challenges and opportunities in robotics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The survey is structured as a roadmap, beginning with fundamental modules of VLA models, exploring key milestones, and detailing five significant challenges.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The paper serves as both an introductory guide for newcomers and a strategic roadmap for seasoned researchers, with the aim of advancing learning and inspiring innovative ideas in embodied intelligence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11362

7. HERBench: A Benchmark for Multi-Evidence Integration in Video Question Answering
🔑 Keywords: HERBench, VideoQA, multi-evidence integration, Minimum Required Frame-Set, Video-LLMs
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces HERBench, a VideoQA benchmark designed to assess the integration of multiple, temporally separated visual cues in Video Large Language Models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study presents HERBench with 26K multiple-choice questions that require aggregating at least three distinct visual cues, and introduces the Minimum Required Frame-Set (MRFS) as a metric for measuring evidential demand.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Evaluations of 13 state-of-the-art Video-LLMs on HERBench show significant failures with accuracies only slightly above random chance, indicating critical retrieval and fusion deficits in current models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14870

8. SWE-Bench++: A Framework for the Scalable Generation of Software Engineering Benchmarks from Open-Source Repositories
🔑 Keywords: SWE-Bench++, GitHub pull requests, code generation models, benchmark, multilingual
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to introduce SWE-Bench++, an automated framework that generates repository-level coding tasks from live GitHub pull requests to evaluate and improve code generation models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– SWE-Bench++ employs a pipeline involving programmatic sourcing, environment synthesis, test oracle extraction, and quality assurance. It turns GitHub PRs into executable tasks and uses hint-guided trajectory synthesis to improve model training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The initial benchmark comprises over 11,000 instances from various programming languages. It demonstrates measurable improvements in model performance by fine-tuning on these instances, providing a scalable, multilingual evaluation benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17419

9. Meta-RL Induces Exploration in Language Agents
🔑 Keywords: Meta-RL, Large Language Model, Exploration, Adaptation, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance LLM agents’ abilities in exploration and adaptation in reinforcement learning tasks through the Meta-RL framework, LaMer.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced LaMer with two components: cross-episode training for exploration and rewards optimization, and in-context policy adaptation for real-time learning without gradient updates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LaMer significantly outperforms RL baselines by improving performance and generalization in diverse environments, achieving performance gains of 11%-19% in tasks like Sokoban, MineSweeper, and Webshop.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16848
10. A Benchmark and Agentic Framework for Omni-Modal Reasoning and Tool Use in Long Videos
🔑 Keywords: LongShOTBench, Multimodal Reasoning, Long-form Video Understanding, MLLMs, AI-generated Summaries
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces LongShOTBench, a diagnostic benchmark designed to evaluate long-form multimodal video understanding through open-ended dialogues and reasoning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– LongShOTBench is developed using a scalable, human-validated pipeline to ensure the coverage and reproducibility of its multimodal reasoning tasks which integrate video, audio, and speech.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– State-of-the-art models show significant performance gaps when tested on LongShOTBench, highlighting the challenges in real-world long-form video understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16978

11. Robust-R1: Degradation-Aware Reasoning for Robust Visual Understanding
🔑 Keywords: Robust-R1, Multimodal Large Language Models, visual degradations, supervised fine-tuning, dynamic reasoning depth scaling
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance the robustness of Multimodal Large Language Models to visual degradations using a novel framework, Robust-R1.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework includes techniques such as supervised fine-tuning, reward-driven alignment, and dynamic reasoning depth scaling.
– A specialized 11K dataset with realistic degradations across four visual processing stages was used.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Robust-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance on real-world degradation benchmarks, surpassing existing robust baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17532

12.

13. MineTheGap: Automatic Mining of Biases in Text-to-Image Models
🔑 Keywords: Text-to-Image models, bias score, genetic algorithm, societal impacts, diversity
💡 Category: AI Ethics and Fairness
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces MineTheGap, a method designed to identify prompts that cause biases in Text-to-Image models, aiming to reduce redundancy and enhance diversity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method utilizes a genetic algorithm to iteratively refine a pool of prompts, identifying those that expose biases. A novel bias score ranks these biases by severity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MineTheGap goes beyond mere bias detection, improving prompt diversity while addressing the societal impacts of biased outputs in TTI models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13427
14. 3D-RE-GEN: 3D Reconstruction of Indoor Scenes with a Generative Framework
🔑 Keywords: 3D scene generation, textured mesh scenes, scene reconstruction, generative models, differentiable optimization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To create a compositional framework, 3D-RE-GEN, that reconstructs single images into modifiable 3D textured mesh scenes with comprehensive backgrounds.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of state-of-the-art models for asset detection, reconstruction, and placement beyond their original domains.
– Using generative models for obtaining occluded objects and applying scene-level reasoning.
– Implementation of a novel 4-DoF differentiable optimization for physically realistic scene layouts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in single-image 3D scene reconstruction, producing coherent and modifiable scenes.
– 3D-RE-GEN facilitates realistic lighting and simulation tasks in visual effects and game development by generating a comprehensive background and accurate spatial organization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17459
15. StageVAR: Stage-Aware Acceleration for Visual Autoregressive Models
🔑 Keywords: Visual Autoregressive, computational complexity, stage-aware acceleration, semantic irrelevance
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to accelerate visual autoregressive models by selectively pruning or approximating less critical stages to achieve significant speedup with minimal quality loss.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A systematic analysis was conducted, showing early steps in the VAR process are essential for semantic and structural consistency, while later steps can be modified for acceleration. The StageVAR framework introduces a plug-and-play acceleration strategy without additional training requirements.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– StageVAR achieves up to 3.4x speedup with minor quality impacts, outperforming existing acceleration methods for efficient visual autoregressive image generation, highlighting stage-aware design as a key principle.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16483

16. Bolmo: Byteifying the Next Generation of Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Bolmo, byte-level language models, byteification, subword-level models, character understanding
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Bolmo, a new family of byte-level language models at 1B and 7B parameter scales that convert existing subword-level models to overcome character understanding and efficiency limitations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Use Byteification to transform subword-level models into byte-level models, employing an effective exact distillation objective to achieve this transformation with minimal resource investment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Bolmo surpasses prior byte-level models and matches or exceeds the performance of subword-level models in character understanding and some coding tasks, while maintaining competitive inference speeds.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15586
17. Animate Any Character in Any World
🔑 Keywords: AniX, controllable-entity models, conditional autoregressive video generation, 3D environments, natural language
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The goal of this research is to develop AniX, a framework that synthesizes temporally coherent videos by extending controllable-entity models to enable user-defined character interactions within 3D environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– AniX utilizes conditional autoregressive video generation, leveraging a pre-trained video generator to support character interactions directed via natural language, while maintaining visual fidelity and motion dynamics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The results demonstrate AniX’s effectiveness in generating videos with high visual quality, character consistency, and action controllability, achieving long-horizon coherence across various actions and characters.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17796
18. Turn-PPO: Turn-Level Advantage Estimation with PPO for Improved Multi-Turn RL in Agentic LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Turn-PPO, Reinforcement Learning, Multi-Turn Tasks, Long-Horizon Reasoning, Advantage Estimation
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve advantage estimation and performance in multi-turn reinforcement learning tasks, particularly those requiring long-horizon reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Turn-PPO, a variant of Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) tailored for turn-level multi-turn tasks.
– Conducted experiments using the WebShop and Sokoban datasets to validate the approach.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Turn-PPO demonstrates enhanced robustness and effectiveness over Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) in environments with long reasoning components.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17008

19. Physics of Language Models: Part 4.1, Architecture Design and the Magic of Canon Layers
🔑 Keywords: Canon layers, reasoning depth, reasoning breadth, AI-generated summary, synthetic tasks
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Canon layers as lightweight architectural components that enhance reasoning capabilities in language models during pretraining tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized controlled synthetic pretraining tasks to isolate and evaluate core model capabilities, integrating Canon layers into various architectures like Transformers and linear attention models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Canon layers improve reasoning depth and breadth, enhance knowledge manipulation, and elevate weaker architectures to compete with state-of-the-art models, validated through both synthetic and real-world pretraining settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17351
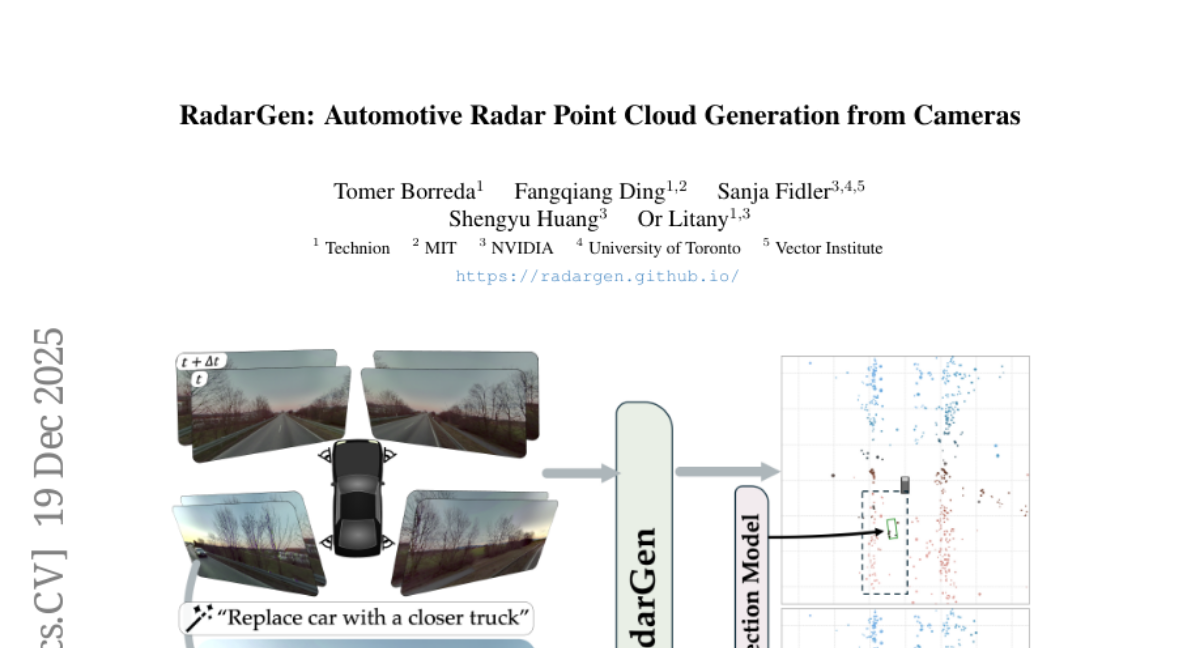
20. RadarGen: Automotive Radar Point Cloud Generation from Cameras
🔑 Keywords: RadarGen, diffusion models, radar point clouds, BEV-aligned, multimodal generative simulation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop RadarGen, a diffusion model for synthesizing realistic radar point clouds from multi-view camera imagery.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Adapts image-latent diffusion to radar domain; utilizes BEV-aligned depth, semantic, and motion cues from pretrained models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RadarGen improves radar measurement distribution reproduction, advancing toward unified generative simulation across sensing modalities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17897
21. 4D-RGPT: Toward Region-level 4D Understanding via Perceptual Distillation
🔑 Keywords: 4D-RGPT, Multimodal LLM, Perceptual 4D Distillation, R4D-Bench, depth-aware
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance 4D perception in video inputs using a specialized multimodal LLM called 4D-RGPT.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces Perceptual 4D Distillation, a training framework that transfers 4D representations from a frozen expert model into 4D-RGPT for improved temporal perception.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The developed 4D-RGPT demonstrates significant improvements on existing 4D Video Question Answering benchmarks and the newly proposed R4D-Bench, a benchmark for depth-aware dynamic scenes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17012

22. Seed-Prover 1.5: Mastering Undergraduate-Level Theorem Proving via Learning from Experience
🔑 Keywords: Seed-Prover 1.5, agentic reinforcement learning, formal theorem proving, test-time scaling, Lean
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present Seed-Prover 1.5, a model for formal theorem proving using large-scale agentic reinforcement learning and efficient test-time scaling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Seed-Prover 1.5 utilizes agentic reinforcement learning and interacts with formal languages like Lean to enhance theorem proving capabilities, complemented by an efficient test-time scaling workflow.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Seed-Prover 1.5 outperforms state-of-the-art methods, solving a significant percentage of undergraduate and graduate-level mathematical problems with reduced computational resources. Scaling learning from experience presents great potential for formal mathematical reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17260

23. PhysBrain: Human Egocentric Data as a Bridge from Vision Language Models to Physical Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: Egocentric2Embodiment, AI-generated, PhysBrain, evidence grounding, temporal consistency
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to translate human egocentric videos into structured training data for robots, enhancing their egocentric understanding and task performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces the Egocentric2Embodiment pipeline that transforms first-person videos into multi-level, schema-driven VQA supervision with enforced evidence grounding and temporal consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Training on the constructed E2E-3M dataset results in the PhysBrain, which significantly improves egocentric understanding and planning on EgoThink, demonstrating successful transfer from human egocentric supervision to robot control.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16793