AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260116
1. Urban Socio-Semantic Segmentation with Vision-Language Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: socio-semantic segmentation, vision-language model, reinforcement learning, cross-modal recognition, SocioSeg
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to achieve socio-semantic segmentation of urban surfaces from satellite imagery by employing a vision-language model that integrates cross-modal recognition and multi-stage reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces the Urban Socio-Semantic Segmentation dataset (SocioSeg) and proposes a novel vision-language reasoning framework called SocioReasoner, optimized through reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach outperforms current state-of-the-art models and demonstrates strong zero-shot generalization in segmenting socially defined categories.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10477

2. Rewarding the Rare: Uniqueness-Aware RL for Creative Problem Solving in LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, High-Level Solution Strategies, Exploration Collapse, Uniqueness-Aware Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance reinforcement learning for large language models by rewarding rare high-level reasoning strategies to improve diverse solution discovery.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Propose Uniqueness-Aware Reinforcement Learning with a rollout-level objective, utilizing an LLM-based judge to cluster rollouts by high-level strategies and reweight policy advantages.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach consistently improves pass@k performance and AUC@K across mathematics, physics, and medical reasoning benchmarks without sacrificing initial performance, while sustaining exploration and uncovering diverse solutions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.08763

3. VIBE: Visual Instruction Based Editor
🔑 Keywords: Instruction-based image editing, Diffusion model, Source consistency, AI Native, Image generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop a compact and efficient image editing system that achieves high-quality edits with low computational resources, while maintaining strict source consistency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a 2B-parameter Qwen3-VL model for guidance and a 1.6B-parameter diffusion model Sana1.5 for image generation.
– Design decisions focus on architecture, data processing, training configuration, and evaluation to ensure low-cost inference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method matches or exceeds the performance of larger models on the ImgEdit and GEdit benchmarks.
– Particularly strong in preserving the input image during various edit types such as attribute adjustment and object removal.
– The model efficiently runs on limited resources, fitting within 24 GB of GPU memory and generating high-resolution images rapidly without additional optimizations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02242

4. DanQing: An Up-to-Date Large-Scale Chinese Vision-Language Pre-training Dataset
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Pre-training, DanQing, cross-modal retrieval, Chinese image-text dataset, SigLIP2
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To advance vision-language pretraining in Chinese by introducing a large-scale, high-quality Chinese image-text dataset named DanQing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a comprehensive pipeline for constructing the dataset, utilizing data from 2024-2025 and employing a rigorous selection process to ensure superior data quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DanQing dataset enhances the performance of Chinese vision-language pretraining models like SigLIP2 in tasks such as zero-shot classification, cross-modal retrieval, and shows superior results across various downstream tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10305

5. CoF-T2I: Video Models as Pure Visual Reasoners for Text-to-Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-Frame reasoning, text-to-image generation, progressive visual refinement, CoF-T2I
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the potential of Chain-of-Frame (CoF) reasoning in enhancing text-to-image (T2I) generation through progressive visual refinement.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of CoF-T2I, a model integrating CoF reasoning into T2I generation, and creation of the CoF-Evol-Instruct dataset modeling semantic to aesthetic generation processes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CoF-T2I model significantly outperforms base video models and achieves competitive performance on benchmarks, emphasizing the potential for high-quality text-to-image generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10061

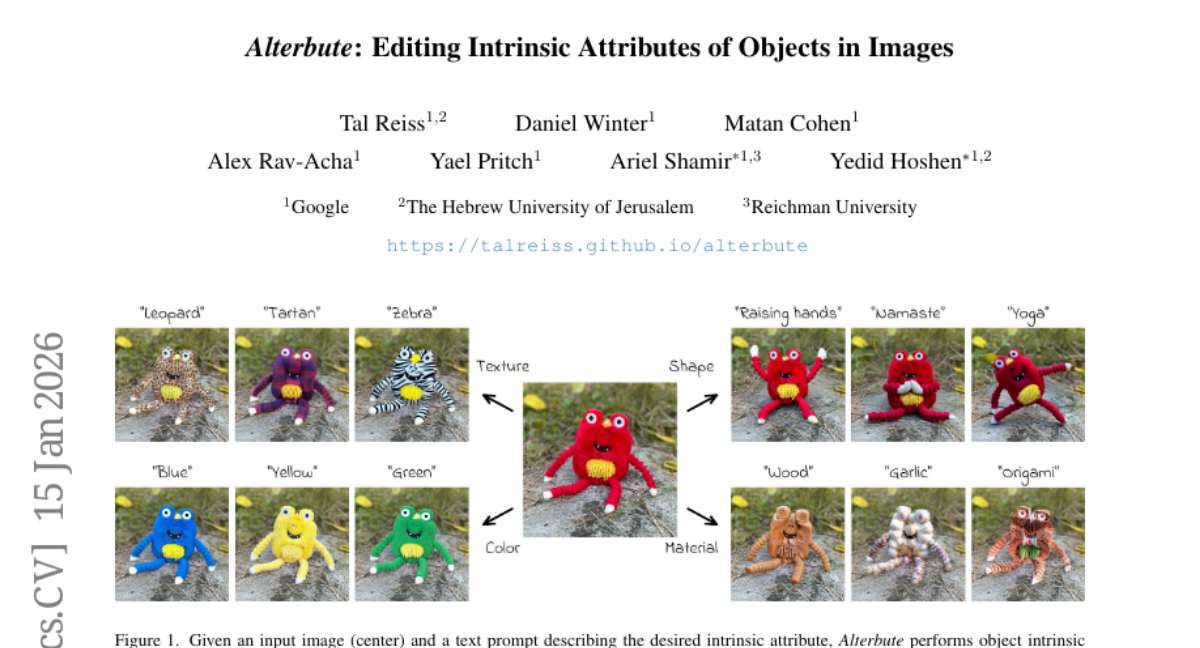
6. Alterbute: Editing Intrinsic Attributes of Objects in Images
🔑 Keywords: intrinsic attributes, identity-preserving, diffusion-based method, Visual Named Entities, vision-language model
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Alterbute, a diffusion-based method for editing an object’s intrinsic attributes while preserving identity and context.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes relaxed training objectives allowing changes in intrinsic and extrinsic attributes, conditioned on identity reference images and textual prompts.
– Employs Visual Named Entities and a vision-language model to extract identity-preserving data from large datasets for supervision.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Alterbute surpasses existing methods in effectively editing intrinsic attributes of objects while preserving identity.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10714
7. ToolSafe: Enhancing Tool Invocation Safety of LLM-based agents via Proactive Step-level Guardrail and Feedback
🔑 Keywords: LLM agents, tool invocation, safety detection, guardrail model, ReAct-style agents
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance safety and task performance of LLM agents by developing a guardrail model and reasoning framework to detect and prevent unsafe tool invocations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers developed a novel benchmark, TS-Bench, for assessing step-level tool invocation safety in LLM agents. Additionally, TS-Guard, a guardrail model using multi-task reinforcement learning, was created to detect and assess unsafe actions proactively.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Introduction of the TS-Flow framework led to a 65% reduction in harmful tool invocations and about a 10% improvement in benign task completion under adversarial conditions, specifically during prompt injection attacks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10156

8. Molmo2: Open Weights and Data for Vision-Language Models with Video Understanding and Grounding
🔑 Keywords: Molmo2, video-language models, video grounding, open-source, bi-directional attention
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop Molmo2, an open-source video-language model family that excels in video grounding tasks without relying on proprietary models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced 7 new video datasets and 2 multi-image datasets for model training, utilizing an efficient packing and message-tree encoding scheme.
– Applied bi-directional attention on vision tokens and a novel token-weight strategy to enhance performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Molmo2 surpasses existing open-weight models and some proprietary models in video grounding, point-driven grounding, and other related tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10611

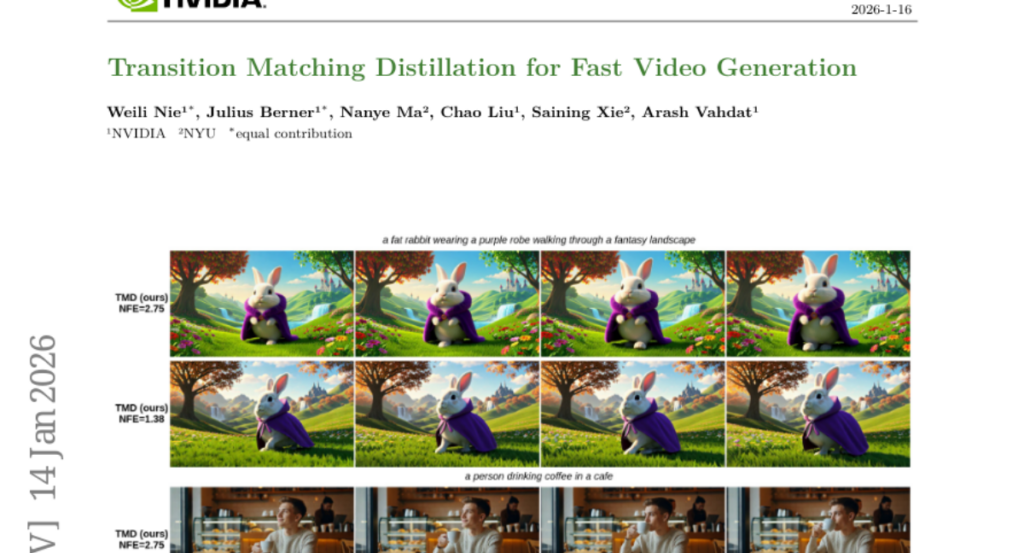
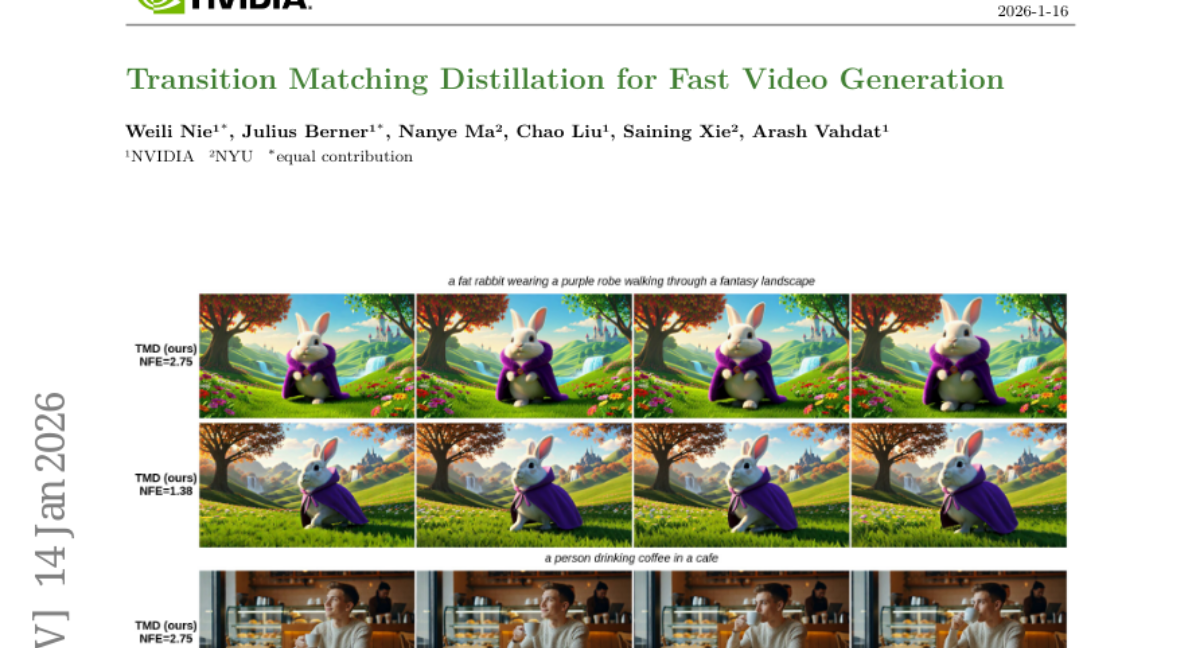
9. Transition Matching Distillation for Fast Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: Transition Matching, Distillation, Conditional Flow, Semantic Representation, Video Diffusion Models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop Transition Matching Distillation (TMD), a framework that enhances the efficiency of video diffusion models by transforming them into few-step generators.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– TMD works by aligning the multi-step denoising trajectory of a diffusion model with a few-step probability transition process using conditional flows and semantic representation decomposition.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The TMD framework provides a balance between generation speed and visual quality, outperforming existing distilled models in terms of visual fidelity and prompt adherence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09881
10. Action100M: A Large-scale Video Action Dataset
🔑 Keywords: Action100M, V-JEPA, video understanding, zero-shot performance, GPT-based reasoning
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a large-scale, open-vocabulary video action dataset to enhance machine intelligence in comprehending physical world actions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Construct Action100M using 1.2M instructional videos with V-JEPA embeddings and GPT-OSS-120B to create structured annotations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Action100M dataset shows promising data-scaling improvements and strong zero-shot performance across diverse action recognition benchmarks, making it a foundational tool for video understanding and modeling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10592

11. PRL: Process Reward Learning Improves LLMs’ Reasoning Ability and Broadens the Reasoning Boundary
🔑 Keywords: Process Reward Learning, Large Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, Reasoning Ability
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve reasoning abilities in Large Language Models through Process Reward Learning, which decomposes reinforcement learning objectives into intermediate steps for fine-grained supervision.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction and formulation of Process Reward Learning, which integrates a KL-divergence penalty into the reward maximization objective for enhanced exploration during reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PRL enhances average reasoning performance and broadens reasoning boundaries in LLMs, verified by improved average @ n and pass @ n metrics through extensive experimentation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10201

12. EvasionBench: Detecting Evasive Answers in Financial Q&A via Multi-Model Consensus and LLM-as-Judge
🔑 Keywords: EvasionBench, multi-model annotation framework, frontier LLMs, disagreement mining, implicit regularization
💡 Category: AI in Finance
🌟 Research Objective:
– To create a large-scale benchmark (EvasionBench) for detecting evasive responses in earnings calls, enhancing financial transparency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a multi-model annotation framework leveraging disagreements between advanced language models to identify challenging examples, employing a judge to resolve conflicts and outperform single-model distillation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The developed model, Eva-4B, achieved an accuracy of 81.3%, surpassing its base model by 25 percentage points, demonstrating the effectiveness of disagreement mining as implicit regularization and achieving high performance at reduced inference costs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09142
13. HeartMuLa: A Family of Open Sourced Music Foundation Models
🔑 Keywords: Music Foundation Models, audio-text alignment, lyric recognition, music generation, AI Native
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce open-source Music Foundation Models aimed at enhancing large-scale music understanding and generation across diverse tasks and modalities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed four components: HeartCLAP for audio-text alignment, HeartTranscriptor for lyric recognition, HeartCodec for efficient music coding, and HeartMuLa for song generation with user-controllable attributes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates the possibility of reproducing commercial-grade systems using academic-scale resources and establishes strong baselines for future multimodal content production research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10547

14. LaViT: Aligning Latent Visual Thoughts for Multi-modal Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: LaViT, Perception Gap, Visual Grounding, Multimodal Reasoning, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the perception gap in multimodal reasoning by aligning latent visual thoughts to improve visual grounding and model performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces LaViT, a framework that focuses on autoregressively reconstructing visual semantics and attention trajectories, using a curriculum sensory gating mechanism to avoid shortcut learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LaViT significantly enhances visual grounding, achieving up to +16.9% improvement in complex reasoning tasks, allowing a compact 3B model to outperform larger proprietary models like GPT-4o.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10129

15. Agent Skills in the Wild: An Empirical Study of Security Vulnerabilities at Scale
🔑 Keywords: AI agent frameworks, agent skills, security analysis, vulnerability taxonomy, data exfiltration
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Conduct a large-scale empirical security analysis to identify vulnerabilities in AI agent skills across major marketplaces.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized the SkillScan framework, integrating static analysis with LLM-based semantic classification on 31,132 skills.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– 26.1% of analyzed AI agent skills contain vulnerabilities with data exfiltration and privilege escalation being most common.
– Skills with executable scripts are significantly more prone to vulnerabilities, highlighting the need for better security practices.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10338

16. RigMo: Unifying Rig and Motion Learning for Generative Animation
🔑 Keywords: RigMo, generative framework, mesh sequences, latent space, auto-rigging
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce RigMo, a unified generative framework for simultaneously learning rig and motion from mesh sequences without human annotations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– RigMo utilizes per-vertex deformations encoded into two compact latent spaces for explicating rig and coherent motion.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RigMo achieves smooth, interpretable, and physically plausible rigs with superior reconstruction and category-level generalization over existing methods, establishing a new paradigm for dynamic 3D modeling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.06378
17. V-DPM: 4D Video Reconstruction with Dynamic Point Maps
🔑 Keywords: Dynamic Point Maps, V-DPM, 3D reconstruction, 4D reconstruction, video input
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to extend Dynamic Point Maps (DPMs) to video input through the V-DPM framework, enabling enhanced 3D and 4D reconstruction by recovering dynamic depth and full 3D motion of scene points.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors formulated DPMs for video input to maximize representational power and neural prediction, leveraging VGGT for adaptation with synthetic data to make it effective for V-DPM prediction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D and 4D reconstruction for dynamic scenes, effectively recovering both dynamic depth and full 3D motion unlike other dynamic extensions of VGGT.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09499

18. VQ-Seg: Vector-Quantized Token Perturbation for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
🔑 Keywords: vector quantization, Quantized Perturbation Module, dual-branch architecture, foundation model, medical image segmentation
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address limitations in dropout-based medical image segmentation by introducing VQ-Seg, which utilizes vector quantization for better control and efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a novel Quantized Perturbation Module to replace dropout with controllable perturbations.
– Developed a dual-branch architecture to mitigate potential information loss from quantization.
– Incorporated foundation model guidance using a Post-VQ Feature Adapter.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments on a newly collected Lung Cancer dataset and public benchmarks show VQ-Seg’s superior performance over state-of-the-art methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10124

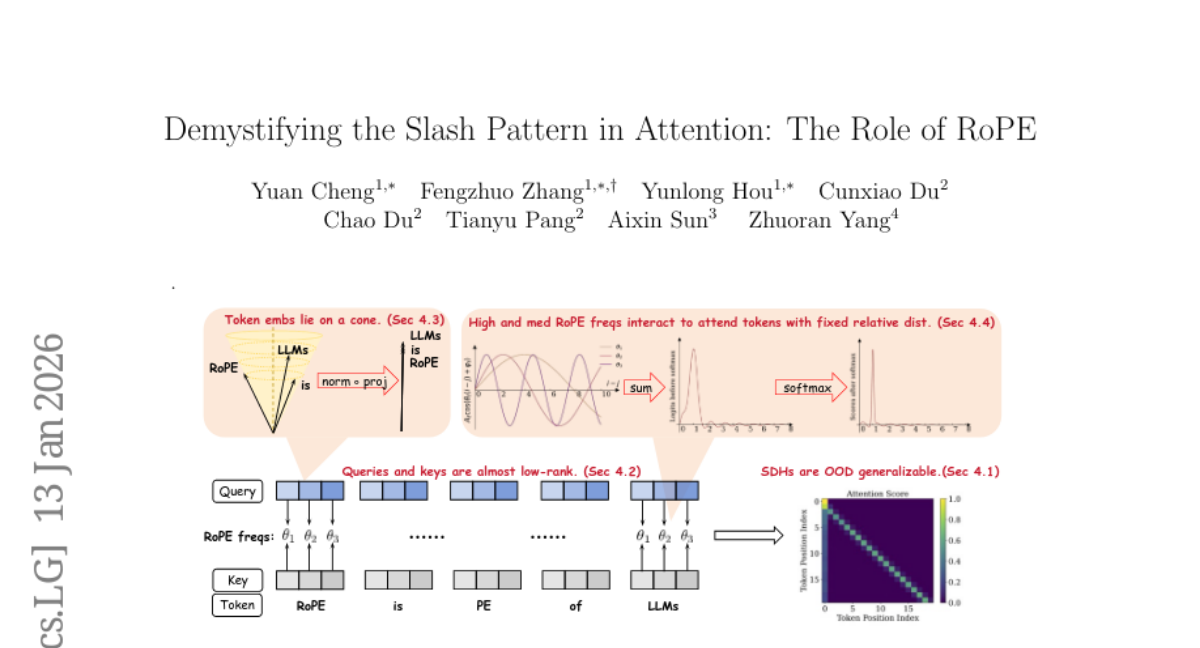
19. Demystifying the Slash Pattern in Attention: The Role of RoPE
🔑 Keywords: Slash-Dominant Heads, Large Language Models, Rank-One Queries/Keys, Rotary Position Embedding
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To demystify the emergence of Slash-Dominant Heads (SDHs) in Large Language Models (LLMs) from empirical and theoretical perspectives.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analytical review of open-source LLMs and theoretical proof using training dynamics in a shallow Transformer equipped with Rotary Position Embedding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SDHs are intrinsic features of LLMs generalizing to out-of-distribution prompts.
– SDHs emerge due to rank-one queries/keys and medium- to high-frequency components of Rotary Position Embedding, proven through gradient descent dynamics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.08297
20.

21. Memory Bank Compression for Continual Adaptation of Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Continual learning, memory bank, codebook optimization, Key-Value Low-Rank Adaptation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a memory-augmented continual learning approach for large language models that efficiently compresses memory banks to handle large-scale data streams.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a codebook optimization strategy and an online resetting mechanism for stable memory bank compression.
– Used Key-Value Low-Rank Adaptation in attention layers for efficient utilization of compressed memory representations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed MBC model significantly reduces memory bank size to 0.3% of the baseline while maintaining high retention accuracy during online adaptation learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.00756

22. Enhancing Sentiment Classification and Irony Detection in Large Language Models through Advanced Prompt Engineering Techniques
🔑 Keywords: Advanced prompting techniques, Large Language Models, Sentiment analysis, Few-shot learning, Chain-of-thought prompting
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate the use of advanced prompt engineering to enhance performance in sentiment analysis tasks using LLMs like GPT-4o-mini and gemini-1.5-flash.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluate advanced prompting techniques such as few-shot learning, chain-of-thought prompting, and self-consistency against a baseline in sentiment classification and aspect-based sentiment analysis.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Advanced prompting significantly improves the performance of sentiment analysis with specific strategies excelling in different models; few-shot learning is effective for GPT-4o-mini, while chain-of-thought prompting enhances irony detection in gemini-1.5-flash.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.08302

23. WildRayZer: Self-supervised Large View Synthesis in Dynamic Environments
🔑 Keywords: WildRayZer, novel view synthesis, dynamic environments, motion masking, analysis-by-synthesis
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to develop WildRayZer, a self-supervised framework designed for novel view synthesis in dynamic environments where both cameras and objects are in motion.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– WildRayZer employs an analysis-by-synthesis approach using a static renderer to manage rigid structures, while pseudo motion masks and motion estimators focus on transient regions. This enhances cross-view background completion by masking input tokens and gating loss gradients.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study concludes that WildRayZer consistently surpasses optimization-based and feed-forward baselines in removing transient regions and improving full-frame novel view synthesis quality with a single feed-forward pass. Additionally, a new dataset, Dynamic RealEstate10K, was curated for large-scale training and assessment of dynamic sequences.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10716

24. CaMeLs Can Use Computers Too: System-level Security for Computer Use Agents
🔑 Keywords: prompt injection attacks, architectural isolation, Computer Use Agents, Single-Shot Planning, control flow integrity
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address security challenges in Computer Use Agents (CUAs) by preventing prompt injection attacks using architectural isolation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce a Single-Shot Planning approach where a trusted planner pre-generates an execution graph with conditional branches to ensure security against malicious content.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Architectural isolation in CUAs is effective against instruction injections, but additional measures are needed for Branch Steering attacks. This approach retains up to 57% performance of frontier models, enhancing security without compromising utility in open-source models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09923

25. Deriving Character Logic from Storyline as Codified Decision Trees
🔑 Keywords: Role-playing agents, Decision Trees, Narrative data, Behavioral profiles, Deterministic retrieval
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop Codified Decision Trees (CDT) from narrative data to create robust and interpretable behavioral profiles for role-playing agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A data-driven framework is used to create decision trees from large-scale narrative data. The trees consist of conditional rules and are refined through validation and hierarchical specialization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CDT significantly outperforms traditional human-written profiles and previous induction methods, offering more reliable agent grounding for 85 characters across 16 artifacts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10080

26. Patient-Similarity Cohort Reasoning in Clinical Text-to-SQL
🔑 Keywords: text-to-SQL, EHR tables, temporal reasoning, patient similarity, AI in Healthcare
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce CLINSQL benchmark for evaluating text-to-SQL models on complex clinical tasks using real-world EHR data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluating 22 models with Chain-of-Thought self-refinement and rubric-based SQL analysis with execution checks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Despite advancements, current models struggle with clinical reliability; GPT-5-mini achieves 74.7% execution score, and other models show varied performance in complex query execution.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09876

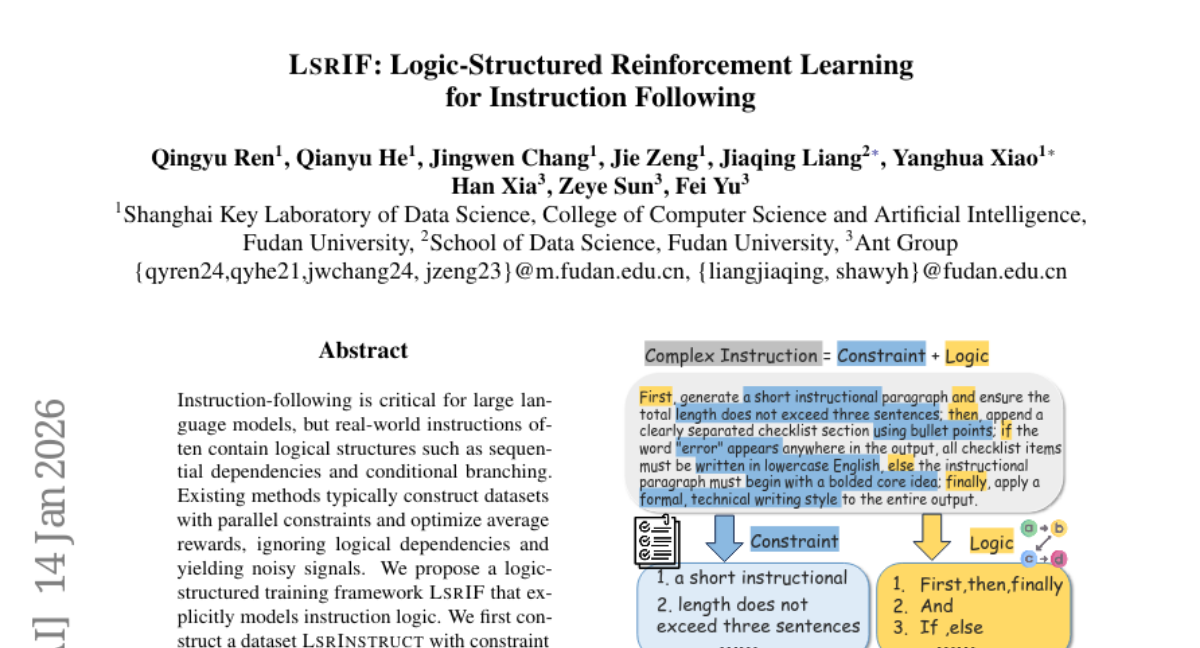
27. LSRIF: Logic-Structured Reinforcement Learning for Instruction Following
🔑 Keywords: Instruction-following, logical structures, sequential dependencies, conditional branching, LSRIF
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance instruction-following and reasoning capabilities of large language models by explicitly modeling instruction logic using a logic-structured training framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A novel dataset, LSRInstruct, is developed, incorporating constraint structures such as parallel, sequential, and conditional types.
– The newly designed structure-aware rewarding method LSRIF leverages average aggregation, failure-penalty propagation, and selective rewards to handle different logical structures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LSRIF significantly improves in-domain and out-of-domain instruction-following and general reasoning.
– Learning with explicit logic structures results in parameter updates in attention layers and enhances token-level attention to constraints and logical operators.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.06431
28. TAG-MoE: Task-Aware Gating for Unified Generative Mixture-of-Experts
🔑 Keywords: Mixture-of-Experts, semantic intent, task interference, Predictive Alignment Regularization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to inject semantic intent into the Mixture-of-Experts routing to address task interference in image generation and editing models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a Hierarchical Task Semantic Annotation scheme to structure task descriptors and designs Predictive Alignment Regularization to align routing decisions with high-level semantics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed model effectively resolves task interference, surpassing dense baseline models in fidelity and quality, with experts developing semantically correlated specializations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.08881

29. Inference-time Physics Alignment of Video Generative Models with Latent World Models
🔑 Keywords: Physics Plausibility, Latent World Model, Inference-Time Alignment, Video Generative Models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance the physics plausibility of video generation models by addressing inference-time strategies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a latent world model (specifically VJEPA-2) as a reward mechanism to improve the alignment of denoising trajectories during inference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method significantly improves physics plausibility across various generation settings, achieving first place in the ICCV 2025 Perception Test PhysicsIQ Challenge with a score of 62.64%.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10553

30. M^4olGen: Multi-Agent, Multi-Stage Molecular Generation under Precise Multi-Property Constraints
🔑 Keywords: Molecule Generation, Multi-Agent Reasoning, Group Relative Policy Optimization, Fragment-Level Edits, Multi-Property Constraints
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a framework for precise molecule generation under multiple physicochemical constraints using a two-stage process.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A fragment-level, retrieval-augmented framework with multi-agent reasoning for prototype generation.
– Use of Group Relative Policy Optimization for fine-grained optimization with controlled refinements.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach outperforms large language models and graph-based algorithms in satisfying multiple property constraints, demonstrating consistent gains in validity and precision.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10131
31. PACEvolve: Enabling Long-Horizon Progress-Aware Consistent Evolution
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Evolutionary Search, Context Pollution, Mode Collapse, PACEvolve
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a robust framework (PACEvolve) that addresses key failure modes in Large Language Models’ evolutionary search processes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of hierarchical context management to counteract context pollution.
– Use of momentum-based backtracking to overcome mode collapse.
– Introduction of a self-adaptive sampling policy for dynamic search coordination.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PACEvolve provides a systematic approach leading to consistent self-improvement.
– The framework achieves state-of-the-art results on benchmarks such as LLM-SR and KernelBench.
– PACEvolve successfully discovers superior solutions on Modded NanoGPT.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10657

32. FlowAct-R1: Towards Interactive Humanoid Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, MMDiT, chunkwise diffusion forcing, temporal consistency, real-time interaction
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop FlowAct-R1, a framework for real-time interactive humanoid video generation, achieving high-fidelity synthesis and low-latency responsiveness.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes MMDiT architecture and chunkwise diffusion forcing strategies to maintain continuous interaction while achieving long-term temporal consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FlowAct-R1 demonstrates exceptional behavioral vividness and perceptual realism, achieving stable video synthesis at 25fps and a TTFF of around 1.5 seconds across diverse character styles.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10103

33. A Safety Report on GPT-5.2, Gemini 3 Pro, Qwen3-VL, Doubao 1.8, Grok 4.1 Fast, Nano Banana Pro, and Seedream 4.5
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Multimodal Large Language Models, Safety Evaluation, Adversarial Evaluation, Model Safety Profiles
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To provide an integrated safety evaluation of 7 frontier language and vision models across multiple evaluation modes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing a unified protocol for evaluation, including benchmark, adversarial, multilingual, and compliance evaluations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Reveals a heterogeneous safety landscape across models, highlighting the need for standardized safety assessments to better evaluate real-world risks and guide development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10527

34. MatchTIR: Fine-Grained Supervision for Tool-Integrated Reasoning via Bipartite Matching
🔑 Keywords: Tool-Integrated Reasoning, Large Language Models, Fine-Grained Credit Assignment, Bipartite Matching, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to enhance the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in tool-integrated tasks by introducing a fine-grained credit assignment system, improving tool calls’ effectiveness.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework, named MatchTIR, utilizes bipartite matching for turn-level reward assignment and implements dual-level advantage estimation to differentiate between effective and redundant actions within task sequences.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MatchTIR demonstrates significant performance improvements on three benchmarks. Notably, the MatchTIR 4B model outperforms many 8B models, particularly excelling in complex, long-horizon, multi-turn tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10712

35. Think-Then-Generate: Reasoning-Aware Text-to-Image Diffusion with LLM Encoders
🔑 Keywords: Text-to-image diffusion models, Language model reasoning, think-then-generate, Dual-GRPO, Visual synthesis
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to enhance text-to-image diffusion models by integrating language model reasoning capabilities to improve factual consistency and semantic alignment through a think-then-generate paradigm.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers propose a think-then-generate paradigm where the language model-based text encoder reasons and rewrites user prompts, followed by a dual-gradient reinforcement optimization (Dual-GRPO) to ensure semantic and visual coherence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method shows substantial improvements in factual consistency, semantic alignment, and visual realism, achieving a WISE score of 0.79, closely aligning with GPT-4 capabilities. This represents a promising development towards next-generation models with enhanced reasoning, expression, and demonstration capacities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10332

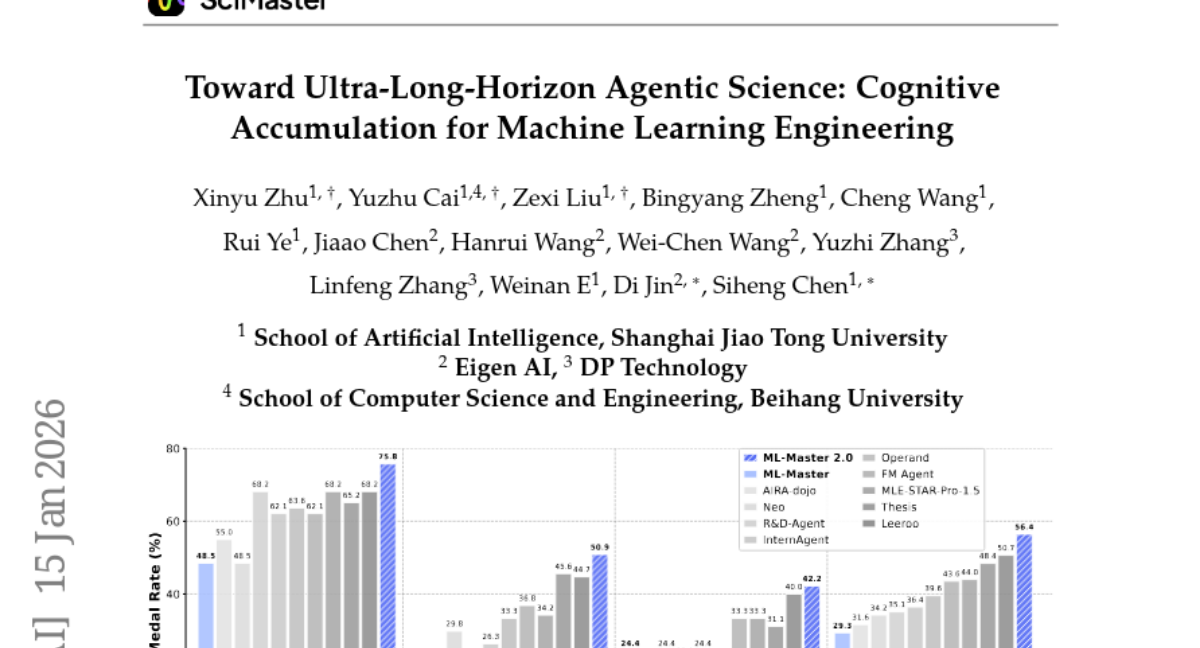
36. Toward Ultra-Long-Horizon Agentic Science: Cognitive Accumulation for Machine Learning Engineering
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, Hierarchical Cognitive Caching, ultra-long-horizon autonomy, machine learning engineering
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the challenge of ultra-long-horizon autonomy in machine learning engineering through a novel approach called ML-Master 2.0 utilizing Hierarchical Cognitive Caching.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of Hierarchical Cognitive Caching (HCC) to enable structural differentiation of experiences over time, allowing agents to manage context dynamically and distill execution traces into stable knowledge.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ML-Master 2.0 achieves a significant medal rate on OpenAI’s MLE-Bench, showcasing the potential of ultra-long-horizon autonomy as a framework for scalable autonomous exploration beyond existing complexities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10402
37. Beyond Static Tools: Test-Time Tool Evolution for Scientific Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Test-Time Tool Evolution, computational methods, scientific reasoning, cross-domain adaptation, AI for Science
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Test-Time Tool Evolution (TTE) to dynamically create and refine computational tools during inference, addressing limitations of static tool libraries in scientific domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a benchmark called SciEvo, with 1,590 scientific reasoning tasks and 925 evolved tools, to evaluate TTE’s efficacy in tool synthesis, verification, and evolution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TTE achieves state-of-the-art performance in accuracy and tool efficiency, effectively enabling cross-domain adaptation of computational tools.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.07641

38. Collaborative Multi-Agent Test-Time Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Multi-Agent Test-Time Reinforcement Learning, Structured Textual Experience, Consensus-Based Decision Making, AI Native, Credit Assignment
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a framework called Multi-Agent Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (MATTRL) to enhance multi-agent reasoning through structured textual experience and consensus-based decision-making.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MATTRL injects structured textual experience at inference time to form multi-expert teams for multi-turn discussions, retrieves test-time experiences, integrates them, and reaches consensus decision-making.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MATTRL improves accuracy by 3.67% over multi-agent baselines and 8.67% over single-agent baselines on various benchmarks, proving its effectiveness and stability in multi-agent reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09667

39. STEP3-VL-10B Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: multimodal intelligence, Perception Encoder, Qwen3-8B decoder, reinforcement learning, Parallel Coordinated Reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To redefine the balance between compact efficiency and frontier-level multimodal intelligence using STEP3-VL-10B.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed a unified pre-training strategy integrating a language-aligned Perception Encoder with a Qwen3-8B decoder.
– Implemented scaled post-training with over 1k iterations of reinforcement learning and Parallel Coordinated Reasoning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Despite its compact size, STEP3-VL-10B matches or outperforms significantly larger models in multimodal tasks.
– Achieves high performance metrics like 92.2% on MMBench and excels in complex reasoning.
– The model suite is released to provide the community with an efficient and reproducible baseline.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09668
