AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260120

1. ABC-Bench: Benchmarking Agentic Backend Coding in Real-World Development
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, agentic backend coding, executable workflow, development lifecycle, containerized services
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to evaluate LLM agents on backend coding tasks requiring comprehensive development lifecycle management, addressing the gap in current benchmarks which overlook dynamic, real-world engineering requirements.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces ABC-Bench, a benchmark specifically designed to assess backend coding within a realistic and executable workflow. It involves 224 tasks across 8 languages and 19 frameworks, requiring agents to manage tasks from repository exploration to service deployment and API testing using a scalable automated pipeline.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The evaluation shows that even state-of-the-art models have difficulties delivering reliable performance on holistic backend tasks, underscoring a significant gap between model capabilities and practical engineering demands.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11077

2. NAACL: Noise-AwAre Verbal Confidence Calibration for LLMs in RAG Systems
🔑 Keywords: confidence calibration, Noise-AwAre Confidence CaLibration (NAACL), retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), supervised fine-tuning (SFT)
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address poor confidence calibration in retrieval-augmented generation for large language models by introducing a noise-aware calibration framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted a systematic study across four benchmarks to analyze calibration performance influenced by noisy retrieved contexts.
– Developed NAACL, a framework that utilizes noise-aware rules and supervised fine-tuning on approximately 2K HotpotQA examples to improve model calibration without relying on stronger teacher models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– NAACL significantly enhances calibration performance, improving ECE scores by 10.9% in-domain and 8.0% out-of-domain, thereby making large language models more epistemically reliable.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11004

3. Spurious Rewards Paradox: Mechanistically Understanding How RLVR Activates Memorization Shortcuts in LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Verifiable Rewards, Perplexity Paradox, Neural Circuit Analysis
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the phenomenon where models achieve gains despite spurious rewards in reinforcement learning, particularly focusing on the “Perplexity Paradox.”
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of Path Patching, Logit Lens, JSD analysis, and Neural Differential Equations to discover and analyze a hidden neural circuit facilitating the memorization shortcut.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identification of a Functional Anchor and Structural Adapters facilitating a memorization shortcut in LLMs when exposed to spurious rewards, and demonstration of how scaling MLP keys can control contamination-driven performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11061

4. The Assistant Axis: Situating and Stabilizing the Default Persona of Language Models
🔑 Keywords: persona space, Assistant Axis, persona drift, large language models
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate the structure of the space of model personas to understand how large language models default to an Assistant identity and explore the Assistant Axis’s impact on model behavior.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Examined activation directions related to diverse character archetypes across several models to determine the leading component of the persona space and its influence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified the Assistant Axis as a determinant of model behavior, revealing that steering towards it enhances helpfulness, while steering away may result in persona drift, leading to atypical or harmful behaviors. Stability along this axis can mitigate adversarial attempts and stabilize model behavior.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10387

5. PubMed-OCR: PMC Open Access OCR Annotations
🔑 Keywords: OCR-centric corpus, PubMed Central, Google Cloud Vision, scientific articles, layout-aware modeling
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To create an OCR-centric corpus from PubMed Central PDFs that supports layout-aware modeling and coordinate-grounded QA.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Each page image is annotated with Google Cloud Vision, with annotations provided in a JSON schema including word-, line-, and paragraph-level bounding boxes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PubMed-OCR corpus spans 209.5K articles and is valuable for evaluating OCR-dependent pipelines, despite limitations like reliance on a single OCR engine and heuristic line reconstruction.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11425

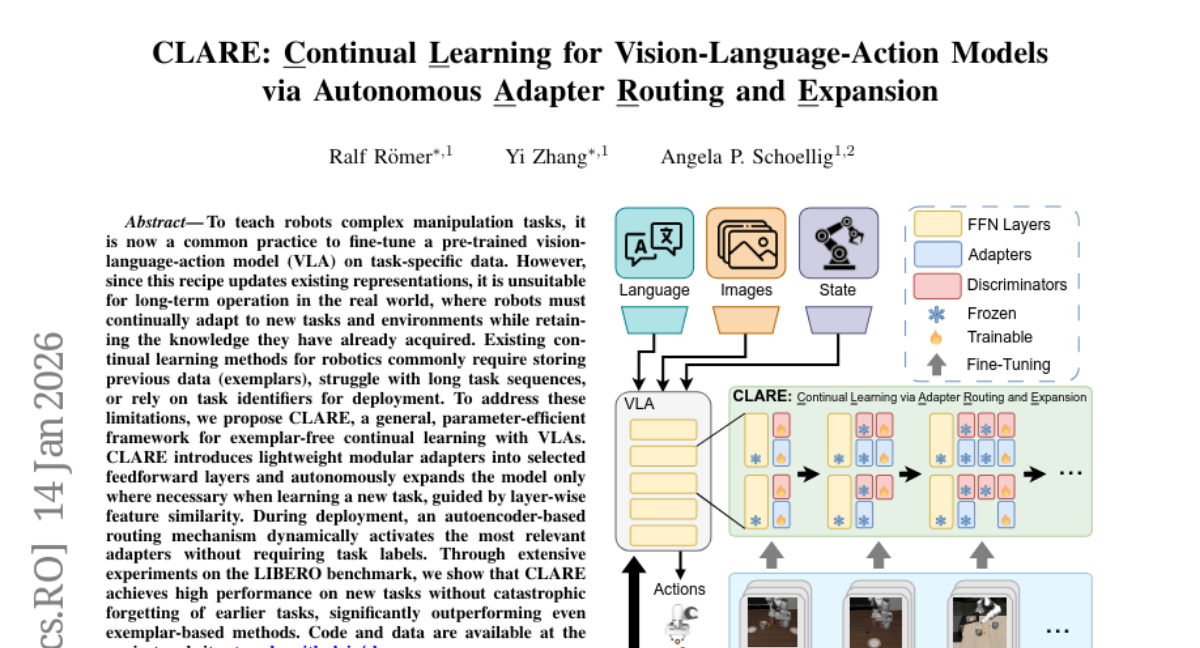
6. CLARE: Continual Learning for Vision-Language-Action Models via Autonomous Adapter Routing and Expansion
🔑 Keywords: Continual Learning, Modular Adapters, Feature Similarity, Autoencoder-based Routing, LIBERO Benchmark
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop CLARE, a parameter-efficient, exemplar-free continual learning framework for vision-language-action models, enabling robots to adapt to new tasks while preserving previously learned knowledge.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– CLARE integrates lightweight modular adapters into selected feedforward layers and employs an autoencoder-based routing mechanism to dynamically activate relevant adapters without needing task labels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CLARE achieves high performance on new tasks without catastrophic forgetting of past tasks and significantly outperforms exemplar-based methods, as demonstrated on the LIBERO benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09512
7.

8. SIN-Bench: Tracing Native Evidence Chains in Long-Context Multimodal Scientific Interleaved Literature
🔑 Keywords: Fish-in-the-Ocean paradigm, SIN-Bench, evidence chains, multimodal language models, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the Fish-in-the-Ocean paradigm and SIN-Bench dataset to assess the reasoning abilities of multimodal language models over scientific documents using evidence chains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a “Fish-in-the-Ocean” paradigm requiring construction of explicit cross-modal evidence chains in native scientific documents.
– Build SIN-Data, a scientifically interleaved corpus, and construct SIN-Bench with tasks covering evidence discovery, hypothesis verification, grounded QA, and evidence-anchored synthesis.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments reveal that grounding is a primary bottleneck for accuracy; Gemini-3-pro achieves the best average score, while GPT-5 excels in answer accuracy but lacks in evidence-aligned scores.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10108

9. YaPO: Learnable Sparse Activation Steering Vectors for Domain Adaptation
🔑 Keywords: Sparse Autoencoder, Sparse Codes, Steering Large Language Models, Activation Interventions, Cultural Alignment
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective of the research is to propose Yet another Policy Optimization (YaPO) that learns sparse steering vectors for more effective and stable control of large language model behaviors.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach leverages sparse autoencoder latent space optimization to learn disentangled, interpretable, and efficient steering directions, improving over dense methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– YaPO demonstrates faster convergence, stronger performance, and enhanced training stability compared to dense steering baselines. It effectively generalizes to various alignment-related behaviors without degrading general knowledge.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.08441

10. CoDance: An Unbind-Rebind Paradigm for Robust Multi-Subject Animation
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Unbind-Rebind framework, pose shift encoder, stochastic perturbations, semantic guidance
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– CoDance aims to address the challenges in character image animation with multi-subject rendering, especially when dealing with arbitrary subject counts, diverse character types, and spatial misalignment.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introducing the Unbind-Rebind framework with an Unbind module using a novel pose shift encoder, and a Rebind module using semantic and spatial guidance to control animation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CoDance demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in multi-subject character animation and generalizes well across different subjects and spatial layouts. The framework, experiments, and datasets are supported by CoDanceBench.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11096

11. Medical SAM3: A Foundation Model for Universal Prompt-Driven Medical Image Segmentation
🔑 Keywords: Medical SAM3, foundation model, fine-tuning, prompt-driven segmentation, medical imaging
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Adapt the SAM3 foundation model for universal prompt-driven medical image segmentation by fine-tuning on diverse medical imaging datasets.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Fine-tuning SAM3 on 33 datasets covering 10 medical imaging modalities to handle domain shifts and complex anatomical structures.
– Utilize paired segmentation masks and text prompts to acquire robust domain-specific representations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Medical SAM3 demonstrates consistent and significant performance gains across various challenging scenarios, establishing its efficacy as a universal, text-guided segmentation tool for medical imaging.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10880

12. Multiplex Thinking: Reasoning via Token-wise Branch-and-Merge
🔑 Keywords: Multiplex Thinking, stochastic soft reasoning, continuous multiplex token, reinforcement learning, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Multiplex Thinking, a stochastic soft reasoning mechanism to optimize reasoning trajectories with reinforcement learning while maintaining shorter sequences than traditional methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized stochastic soft reasoning at each thinking step to sample and aggregate multiple candidate tokens into a continuous multiplex token, allowing for optimized multiplex trajectories through on-policy reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Multiplex Thinking outperforms strong discrete CoT and RL baselines in complex reasoning benchmarks while producing shorter token sequences.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.08808
