AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260121
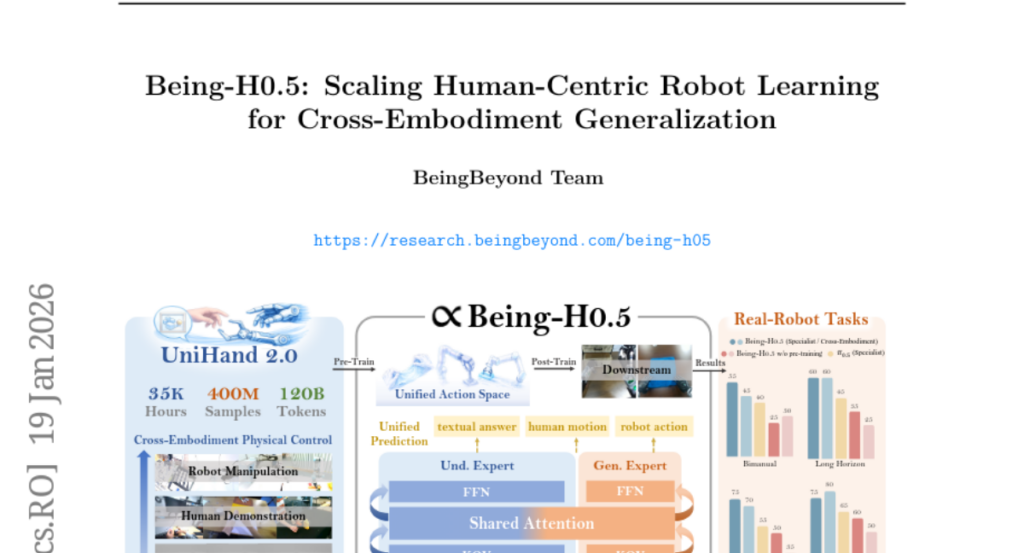
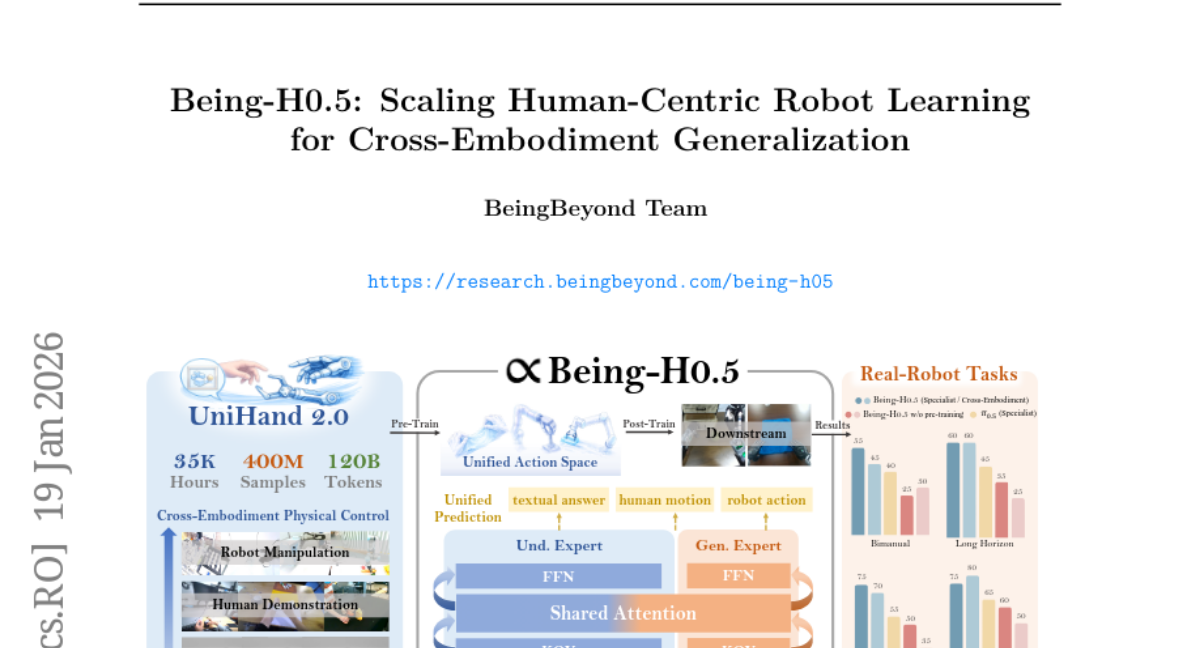
1. Being-H0.5: Scaling Human-Centric Robot Learning for Cross-Embodiment Generalization
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action, cross-embodiment generalization, human-centric learning, Mixture-of-Transformers, multimodal data
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Being-H0.5, a Vision-Language-Action model aimed at achieving robust cross-embodiment generalization across diverse robotic platforms through a novel learning approach and architectural design.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper proposes a human-centric learning paradigm utilizing human interaction traces as a foundational language for physical interaction. It also leverages a Mixture-of-Transformers architecture with specialized embodiment handling and includes the largest embodied pre-training dataset called UniHand-2.0.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Being-H0.5 demonstrates state-of-the-art results on simulated benchmarks, achieving significant performance on LIBERO and RoboCasa, and shows compelling cross-embodiment capabilities across multiple robotic platforms.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.12993
2. OmniTransfer: All-in-one Framework for Spatio-temporal Video Transfer
🔑 Keywords: OmniTransfer, spatio-temporal video transfer, appearance consistency, temporal control, multi-view information
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop a unified framework, OmniTransfer, for spatio-temporal video transfer that enhances appearance consistency and temporal control.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method leverages multi-view information and multimodal semantic guidance to achieve task-aware positional bias, reference-decoupled causal learning, and task-adaptive multimodal alignment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OmniTransfer outperforms existing methods in enhancing appearance and temporal transfer, setting a new standard for flexible, high-fidelity video generation without relying on pose-guided techniques.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14250
3. UniX: Unifying Autoregression and Diffusion for Chest X-Ray Understanding and Generation
🔑 Keywords: Unified Medical Foundation Model, Visual Understanding, Generation Tasks, Cross-Modal Self-Attention, Diffusion Models
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Present UniX, a unified medical foundation model that effectively decouples visual understanding and generation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes distinct autoregressive and diffusion branches with a cross-modal self-attention mechanism to guide the generation process with understanding features.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves significant improvements in both understanding performance and generation quality on chest X-rays, establishing a scalable paradigm for synergistic medical image understanding and generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11522

4. MemoryRewardBench: Benchmarking Reward Models for Long-Term Memory Management in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: MemoryRewardBench, memory management, reward models, large language models, long-context comprehension
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce MemoryRewardBench to evaluate reward models’ effectiveness in assessing long-term memory management across varying context lengths and memory patterns in large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Systematic evaluation involving 10 distinct settings with context lengths ranging from 8K to 128K tokens to assess both long-context comprehension and long-form generation tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Performance evaluations on 13 state-of-the-art reward models reveal a diminishing performance gap between open-source and proprietary models, with newer-generation models outperforming predecessors.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11969
5. Think3D: Thinking with Space for Spatial Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: 3D reasoning, Vision-Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, Multimodal Agents, Spatial Intelligence
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Think3D framework to enhance Vision-Language Models’ 3D reasoning capabilities by enabling interactive spatial exploration.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize 3D reconstruction models for recovering point clouds and camera poses.
– Implement ego/global-view switching and reinforcement learning to improve spatial exploration.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Think3D improves spatial reasoning performance significantly without additional training.
– Demonstrates that smaller models benefit from reinforcement learning policies, enhancing tool usage effectiveness.
– Suggests training-free, tool-augmented spatial exploration as a path to flexible, human-like 3D reasoning in multimodal agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13029

6. Aligning Agentic World Models via Knowledgeable Experience Learning
🔑 Keywords: WorldMind, LLMs, physical hallucinations, symbolic World Knowledge Repository, cross-environment transferability
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– WorldMind aims to address the modal disconnect in Large Language Models (LLMs) by autonomously constructing a symbolic World Knowledge Repository to enhance physical feasibility and task optimality through experience-based learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– It synthesizes environmental feedback to unify Process Experience for enforcing physical feasibility and Goal Experience to guide task optimality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– WorldMind demonstrates superior performance over baselines in experiments on EB-ALFRED and EB-Habitat, with notable cross-model and cross-environment transferability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13247
7. A BERTology View of LLM Orchestrations: Token- and Layer-Selective Probes for Efficient Single-Pass Classification
🔑 Keywords: Lightweight probes, hidden states, safety, sentiment analysis, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve classification tasks like safety and sentiment analysis by using lightweight probes trained on hidden states of LLMs without adding computational overhead.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implements a two-stage aggregator for representation selection over the full token-layer hidden-state tensor. Introduces a combination of direct pooling, scoring-attention gate, and downcast multi-head self-attention probe.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach enhances performance on safety and sentiment benchmarks compared to logit-only reuse and is competitive with larger task-specific models, achieving this while minimizing VRAM and latency costs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13288

8. LightOnOCR: A 1B End-to-End Multilingual Vision-Language Model for State-of-the-Art OCR
🔑 Keywords: LightOnOCR-2-1B, vision-language model, multilingual, localization, RLVR
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce LightOnOCR-2-1B, a compact 1B-parameter vision-language model designed for efficient, multilingual document image-to-text conversion.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes specialized training techniques with a large-scale, high-quality distillation mix, and employs a resume strategy and RLVR for improved localization and robustness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art performance on OlmOCR-Bench, being significantly smaller and faster than prior models, and publicly releases models and datasets under open licenses.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14251

9. DARC: Decoupled Asymmetric Reasoning Curriculum for LLM Evolution
🔑 Keywords: DARC, Self-Play, Large Language Models, AI-Generated Summary, Asymmetric Self-Distillation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The goal is to stabilize the self-play framework in large language models, addressing optimization instability and enhancing reasoning performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a two-stage framework named DARC, which involves decoupling question generation and using an asymmetric self-distillation mechanism with document-augmented teachers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DARC proves model-agnostic, significantly improving reasoning benchmarks by 10.9 points, outperforming baselines and closely competing with fully supervised models without human annotations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13761
10. Which Reasoning Trajectories Teach Students to Reason Better? A Simple Metric of Informative Alignment
🔑 Keywords: Rank-Surprisal Ratio (RSR), reasoning trajectories, distillation, student likelihood, token-wise rank
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a novel metric, Rank-Surprisal Ratio (RSR), to improve the assessment of reasoning trajectories for knowledge distillation in large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Propose RSR as a metric, defined as the ratio of a trajectory’s average token-wise rank to its average negative log-likelihood, tested across five student models and trajectories from 11 teachers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RSR effectively balances learning signal strength and behavioral alignment, outperforming existing metrics with a strong correlation to post-training performance (average Spearman 0.86).
– Demonstrates practical utility in trajectory and teacher selection.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14249

11. Uncertainty-Aware Gradient Signal-to-Noise Data Selection for Instruction Tuning
🔑 Keywords: GRADFILTERING, Instruction tuning, Large language models, Data selection, Gradient Signal-to-Noise Ratio
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce an uncertainty-aware data selection framework, GRADFILTERING, to enhance the adaptation efficiency and performance of LLMs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a small GPT-2 proxy with a LoRA ensemble and aggregate per-example gradients into a Gradient Signal-to-Noise Ratio (G-SNR) utility for data selection.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GRADFILTERING matches or exceeds existing methods in LLM-as-a-judge evaluations and human assessments, with faster convergence under the same compute budget due to uncertainty-aware scoring.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13697

12. Fundamental Limitations of Favorable Privacy-Utility Guarantees for DP-SGD
🔑 Keywords: Differentially Private Stochastic Gradient Descent, f-differential privacy, shuffled sampling, Gaussian noise multiplier, adversarial advantage
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To analyze the privacy-utility trade-offs in Differentially Private Stochastic Gradient Descent (DP-SGD) within the framework of f-differential privacy and shuffled sampling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study derives an explicit suboptimal upper bound on the trade-off curve to assess the privacy implications under worst-case adversarial models. It examines the required noise multiplier for meaningful privacy protection in both shuffled and Poisson subsampling scenarios.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research identifies a critical bottleneck in achieving strong privacy without degrading utility in DP-SGD, as the required Gaussian noise levels for shuffled sampling result in significant accuracy degradation, thereby underscoring a fundamental trade-off under adversarial assumptions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10237
13. A Hybrid Protocol for Large-Scale Semantic Dataset Generation in Low-Resource Languages: The Turkish Semantic Relations Corpus
🔑 Keywords: AI classification, FastText embeddings, semantic relationships, low-resource languages, Turkish NLP
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to generate a large-scale semantic relationship dataset for low-resource languages, specifically demonstrated in Turkish.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methodology incorporates FastText embeddings and Agglomerative Clustering to identify semantic clusters, uses Gemini 2.5-Flash for automated classification, and integrates curated dictionary sources.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The resulting dataset includes 843,000 unique Turkish semantic pairs, validated by achieving 90% top-1 retrieval accuracy and 90% F1-macro in downstream tasks. The approach addresses data scarcity in Turkish NLP and is applicable to other low-resource languages. The dataset and models are publicly released.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13253
14. METIS: Mentoring Engine for Thoughtful Inquiry & Solutions
🔑 Keywords: AI mentor, Research writing, METIS, LLM judges, Stage-aware routing
💡 Category: AI in Education
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to evaluate if an AI mentor can effectively guide undergraduates from forming an idea to writing a full research paper, through the development of METIS.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– METIS, a tool-augmented and stage-aware assistant, is compared against GPT-5 and Claude Sonnet 4.5 using several metrics such as LLM-as-a-judge pairwise preferences, student-persona rubrics, and multi-turn tutoring.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– METIS surpasses GPT-5 and Claude Sonnet 4.5 in supporting undergraduate research writing, showing higher student scores and improved document-grounded outputs, although challenges remain in areas like tool routing and stage classification.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13075

15. RemoteVAR: Autoregressive Visual Modeling for Remote Sensing Change Detection
🔑 Keywords: Remote sensing change detection, visual autoregressive models, multi-resolution feature fusion, cross-attention, autoregressive training
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces RemoteVAR, a framework aiming to enhance remote sensing change detection through an improved visual autoregressive approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework utilizes multi-resolution feature fusion and cross-attention mechanisms, specifically tailored for change map prediction through autoregressive training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments demonstrate that RemoteVAR consistently improves upon existing strong baselines, presenting a competitive alternative in the field of remote sensing change detection.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11898
16. LIBERTy: A Causal Framework for Benchmarking Concept-Based Explanations of LLMs with Structural Counterfactuals
🔑 Keywords: Concept-based explanations, Counterfactuals, LLM-based Intervention, Structured Causal Models, Order-faithfulness
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to create a framework for generating structured counterfactual pairs using LLMs and SCMs to improve evaluation and analysis of concept-based explanations in high-stakes domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of LIBERTy, a framework grounded in structured causal models for text generation, involving interventions on concepts to produce counterfactuals with LLMs.
– Three datasets (disease detection, CV screening, and workplace violence prediction) are created, alongside a new metric, order-faithfulness, to evaluate various models and methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LIBERTy provides a comprehensive benchmark for developing more faithful explainability methods.
– The study finds proprietary LLMs exhibit reduced sensitivity to demographic concepts, likely due to post-training mitigation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.10700
17.

18. Finally Outshining the Random Baseline: A Simple and Effective Solution for Active Learning in 3D Biomedical Imaging
🔑 Keywords: Active Learning, 3D Biomedical Image Segmentation, Class-Stratified Querying, Power Noising, Segmentation Quality
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce ClaSP PE, an active learning strategy that improves 3D biomedical image segmentation by addressing class imbalance and selection redundancy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– ClaSP PE combines class-stratified querying and log-scale power noising with decaying schedule to enhance query diversity and exploitation in early-stage active learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ClaSP PE significantly outperforms improved random baselines in segmentation quality and annotation efficiency. It generalizes well to novel datasets without manual adaptation, showing its robustness in practical applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13677

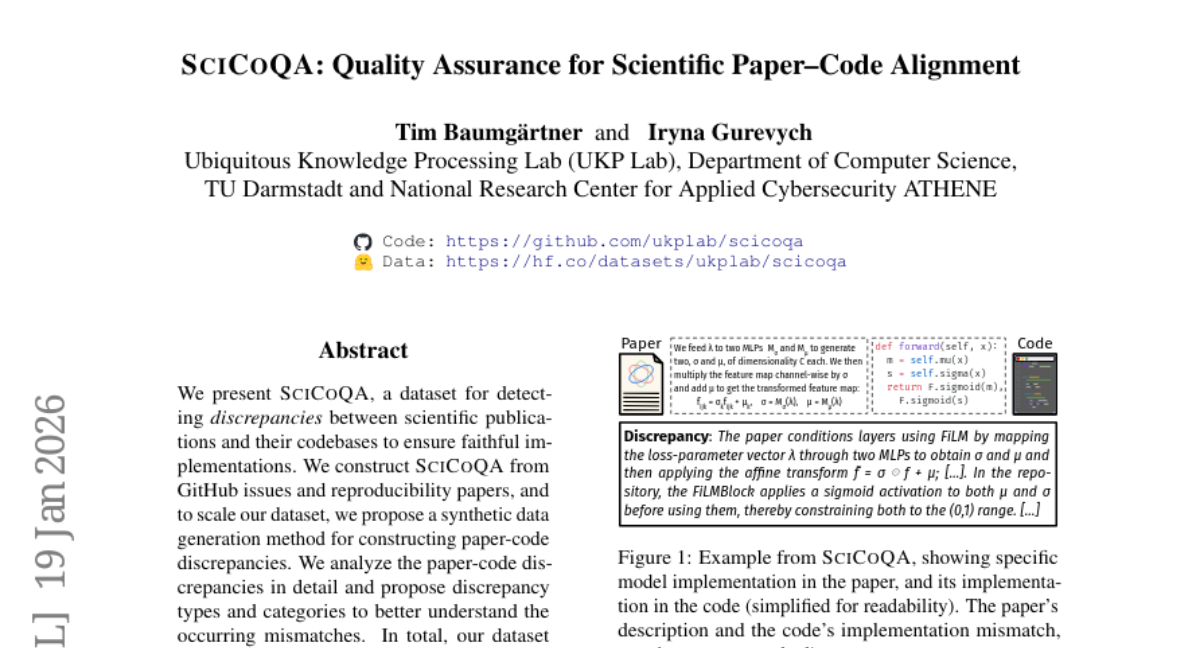
19. SciCoQA: Quality Assurance for Scientific Paper–Code Alignment
🔑 Keywords: SciCoQA, paper-code discrepancies, reproducibility, AI, computational science
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Create a dataset to detect discrepancies between scientific publications and their code implementations across various disciplines.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize GitHub issues and reproducibility papers to construct the SciCoQA dataset.
– Implement a synthetic data generation method to expand the dataset.
– Conduct a detailed analysis of paper-code discrepancies to categorize them.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SciCoQA comprises 611 discrepancies, with 81 real and 530 synthetic examples.
– Evaluation of 21 LLMs shows the challenges of detecting discrepancies, with the top model, GPT-5, achieving only a 45.7% detection rate of real discrepancies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.12910
20. Beyond Cosine Similarity: Taming Semantic Drift and Antonym Intrusion in a 15-Million Node Turkish Synonym Graph
🔑 Keywords: Neural Embeddings, Semantic Clustering, Semantic Drift, Synonymy, Antonymy
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve the differentiation between synonyms and antonyms using a large-scale semantic clustering system, overcoming limitations of traditional neural embeddings.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a labeled dataset of 843,000 concept pairs including synonymy, antonymy, and co-hyponymy, verified by human-curated resources.
– Implemented a specialized three-way semantic relation discriminator achieving 90% macro-F1.
– Introduced a novel soft-to-hard clustering algorithm to prevent semantic drift and resolve polysemy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Successfully generated 2.9 million high-precision semantic clusters which enhance semantic search and retrieval, particularly for low-resource languages.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13251

21. DSAEval: Evaluating Data Science Agents on a Wide Range of Real-World Data Science Problems
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Environment Perception, Multi-Query Interactions, Multi-Dimensional Evaluation, unstructured data, data science agents
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to evaluate LLM-based data agents across various data science tasks using a benchmark, DSAEval, which covers structured and unstructured data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of DSAEval, a benchmark featuring 641 real-world data science problems based on 285 datasets, with three key features for evaluation: Multimodal Environment Perception, Multi-Query Interactions, and Multi-Dimensional Evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research reveals that Claude-Sonnet-4.5 achieves the highest overall performance, GPT-5.2 is the most efficient, and MiMo-V2-Flash is the most cost-effective among 11 evaluated LLMs. Multimodal perception aids performance improvement in vision-related tasks, yet challenges remain in unstructured domains. Future research directions are proposed to enhance data science agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13591

22. On the Evidentiary Limits of Membership Inference for Copyright Auditing
🔑 Keywords: Membership Inference Attacks, Large Language Models, Paraphrasing Framework, Semantic Content, SAE-Guided Extraction
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate the reliability of Membership Inference Attacks in detecting copyrighted text usage in Large Language Models when training data is obfuscated while maintaining semantic content.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of SAGE, a Structure-Aware SAE-Guided Extraction framework, which uses Sparse Autoencoders to paraphrase training data, altering lexical structure but preserving semantic content and downstream utility.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– State-of-the-art Membership Inference Attacks degrade in robustness against semantics-preserving transformations, making them insufficient as standalone mechanisms for copyright auditing of Large Language Models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.12937

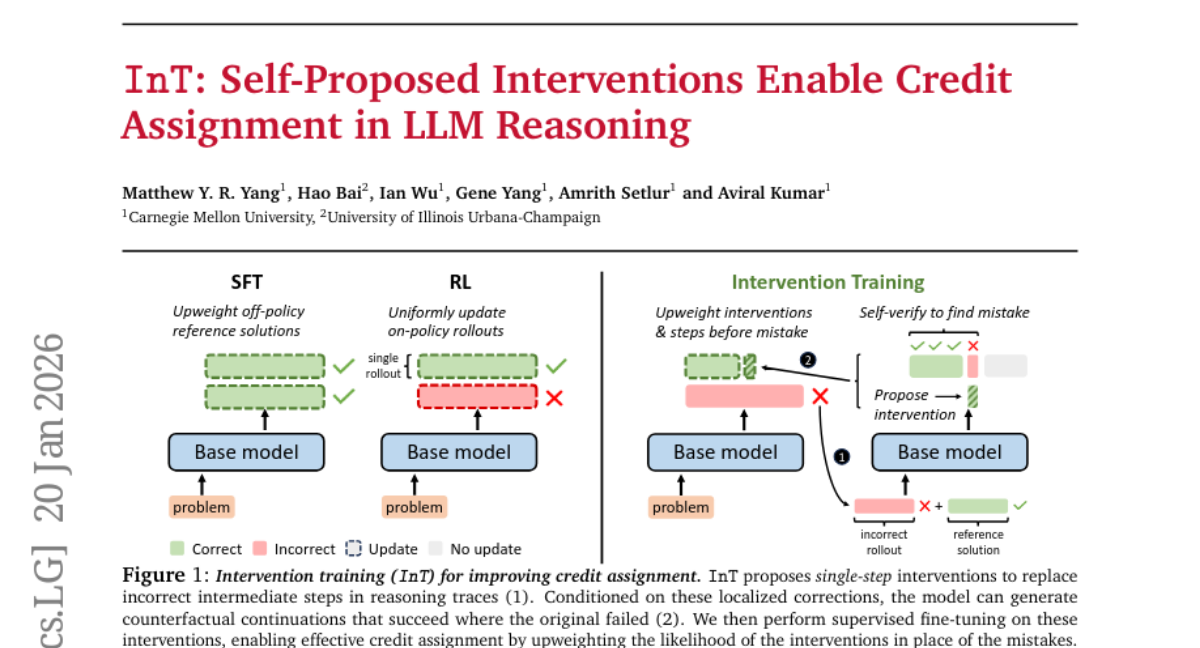
23. InT: Self-Proposed Interventions Enable Credit Assignment in LLM Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Intervention Training, Credit Assignment, Reinforcement Learning, Reasoning Traces, AI-generated Summary
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by introducing Intervention Training to facilitate fine-grained credit assignment and enhance performance in reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a novel training paradigm called Intervention Training where the model proposes targeted corrections to redirect reasoning trajectories toward higher rewards, using reference solutions from mathematical reasoning datasets and supervised fine-tuning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The implementation of Intervention Training combined with reinforcement learning and fine-tuning enhances the accuracy by nearly 14% over a 4B-parameter base model, surpassing larger open-source models like gpt-oss-20b.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14209
24. FantasyVLN: Unified Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reasoning for Vision-Language Navigation
🔑 Keywords: Vision-and-Language Navigation, Chain-of-Thought, Real-time Navigation, Implicit Reasoning, Latent Space
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a unified implicit reasoning framework named FantasyVLN, aimed at enhancing reasoning in Vision-and-Language Navigation without explicit token overhead, enabling real-time performance with improved accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework encodes imagined visual tokens into a compact latent space using a pretrained Visual AutoRegressor during Chain-of-Thought reasoning training. It jointly learns from textual, visual, and multimodal Chain-of-Thought modes using a unified multi-CoT strategy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The FantasyVLN framework significantly improves success rates and efficiency in Vision-and-Language Navigation while reducing inference latency by an order of magnitude compared to explicit Chain-of-Thought methods, achieving reasoning-aware yet real-time navigation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13976

25. PRiSM: Benchmarking Phone Realization in Speech Models
🔑 Keywords: PRiSM benchmark, phonetic perception, cross-lingual speech processing, transcription accuracy, multilingual domains
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce PRiSM, an open-source benchmark for evaluating phonetic perception in speech models across diverse domains including clinical, educational, and multilingual applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of transcription-based metrics and representation probes to evaluate the performance of Phone Recognition (PR) systems, with a focus on intrinsic and extrinsic assessments of phonetic perception.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Diverse language exposure during training enhances PR performance.
– Encoder-CTC models demonstrate high stability.
– Specialized PR models outperform Large Audio Language Models in effectiveness.
– PRiSM provides resources such as code and datasets to advance multilingual speech models with strong phonetic capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14046

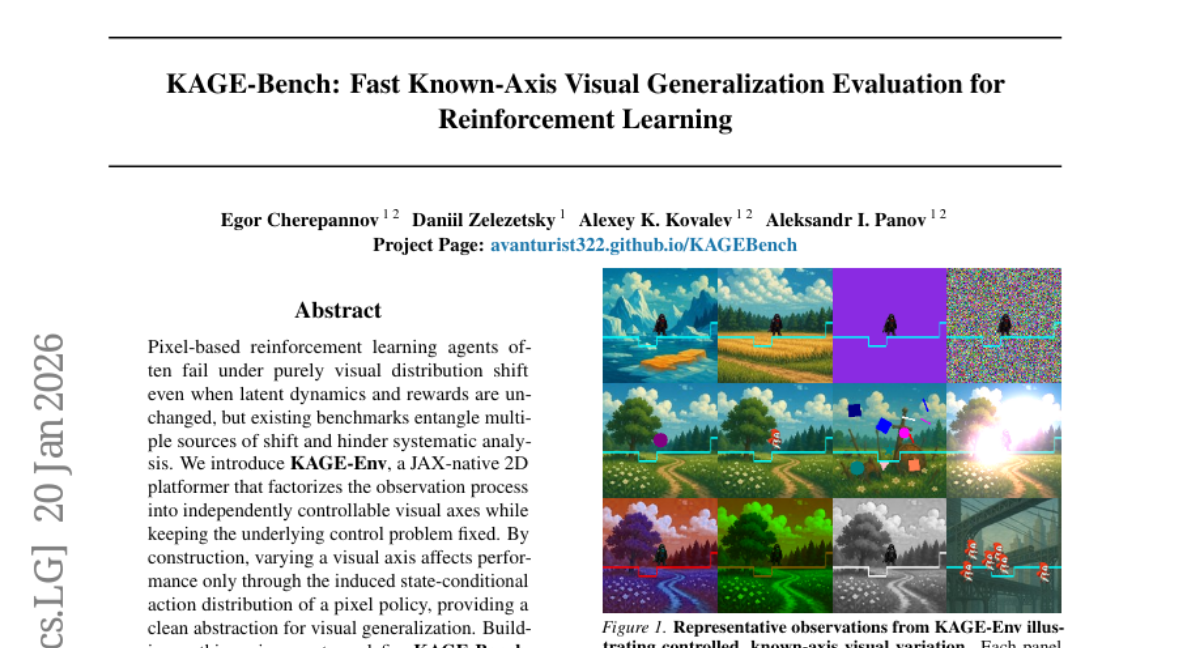
26. KAGE-Bench: Fast Known-Axis Visual Generalization Evaluation for Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, visual generalization, JAX-native, visual distribution shift, reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study focuses on isolating visual shifts from underlying control problems to analyze visual generalization in reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of KAGE-Env, a JAX-native 2D platformer environment, which factorizes the observation process into independently controllable visual axes without altering the underlying control problem.
– Development of KAGE-Bench, a benchmark comprising six known-axis suites and 34 train-evaluation pairs to isolate individual visual shifts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study found axis-dependent failures with background and photometric shifts significantly impacting performance, while agent-appearance shifts were less detrimental.
– Some visual shifts resulted in failures that obscured task completion despite preserving forward motion, indicating that relying on returns alone can misrepresent generalization failure.
– The fully vectorized JAX implementation allows for rapid and reproducible analysis with up to 33 million environment steps per second on a single GPU.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14232
27. Agentic-R: Learning to Retrieve for Agentic Search
🔑 Keywords: Agentic search, multi-step reasoning, on-demand retrieval, iterative training strategy, answer correctness
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To design a novel retriever training framework specifically tailored for agentic search that improves on traditional similarity-based retrievers by incorporating both local query-passage relevance and global answer correctness.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of an iterative optimization approach between the search agent and the retriever, allowing continuous improvements using evolving and higher-quality queries.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed retriever consistently outperforms strong baselines across various search agents, demonstrating superior performance in single-hop and multi-hop QA benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11888

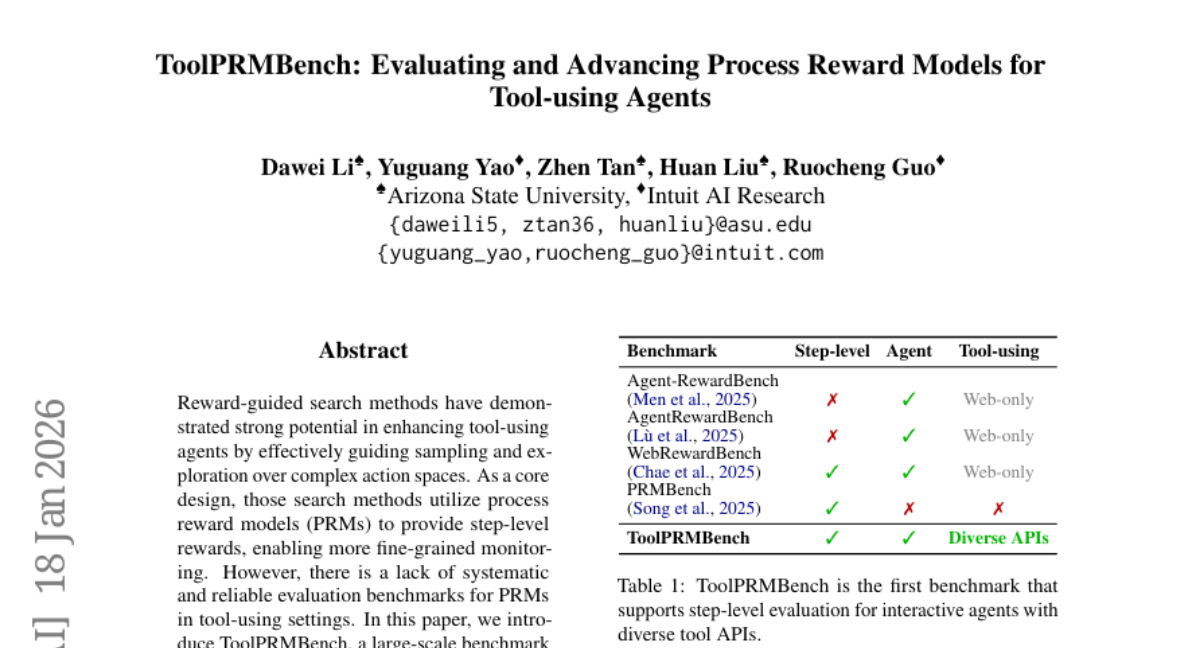
28. ToolPRMBench: Evaluating and Advancing Process Reward Models for Tool-using Agents
🔑 Keywords: ToolPRMBench, process reward models, tool-using agents, multi-LLM verification, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce ToolPRMBench, a large-scale benchmark specifically designed for evaluating process reward models (PRMs) in tool-using agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study utilizes steps including converting agent trajectories into step-level test cases and employing multi-LLM verification to ensure data quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The experiments revealed differences in PRM effectiveness and highlighted the potential for specialized PRMs in tool-using scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.12294
29. Locate, Steer, and Improve: A Practical Survey of Actionable Mechanistic Interpretability in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Mechanistic Interpretability, Large Language Models, Localizing, Steering, Alignment
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To establish a systematic framework for actionable intervention in Large Language Models using Mechanistic Interpretability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Structured the approach around a pipeline: “Locate, Steer, and Improve” with formal categorization of diagnosis (Localizing) and intervention (Steering) methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated improvements in Alignment, Capability, and Efficiency, operationalizing Mechanistic Interpretability as a methodology for optimizing model performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14004

30. FutureOmni: Evaluating Future Forecasting from Omni-Modal Context for Multimodal LLMs
🔑 Keywords: FutureOmni, Multimodal Large Language Models, future forecasting, audio-visual cues, cross-modal reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce FutureOmni as the first benchmark to evaluate the ability of multimodal models to forecast future events from audio-visual data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluates 13 omni-modal and 7 video-only models using a scalable LLM-assisted, human-in-the-loop pipeline with 919 videos and 1,034 QA pairs across 8 domains.
– Proposes a new Omni-Modal Future Forecasting (OFF) training strategy to improve prediction accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current systems struggle with future forecasting from audio-visual data, particularly in speech-heavy scenarios, achieving a best accuracy of 64.8%.
– The proposed OFF strategy enhances future forecasting and generalization capabilities in the evaluated models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13836

31. Toward Efficient Agents: Memory, Tool learning, and Planning
🔑 Keywords: agentic systems, large language models, efficiency, memory, tool learning
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study evaluates the efficiency in agentic systems, with a focus on the components of memory, tool learning, and planning, while analyzing the trade-offs between effectiveness and computational costs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs optimization strategies, benchmarks, and examines a range of recent approaches to agentic systems, focusing on methods such as reinforcement learning, controlled search mechanisms, and context compression to enhance efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The paper characterizes efficiency by comparing effectiveness under a fixed cost budget and cost at a comparable level of effectiveness, and examines benchmarks and evaluation protocols, discussing major challenges and future directions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14192

32. Advances and Frontiers of LLM-based Issue Resolution in Software Engineering: A Comprehensive Survey
🔑 Keywords: large language models, autonomous coding agents, training-free frameworks, supervised fine-tuning, reinforcement learning
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To survey the emerging domain of autonomous coding agents in addressing software issue resolution.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analysis of data construction pipelines, examining both automated collection and synthesis approaches.
– Investigation of methodologies, including training-free frameworks and training-based techniques like supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The paper discusses critical analyses of data quality and agent behavior and outlines practical applications, identifying key challenges and promising directions for future research.
– An open-source repository is provided to serve as a dynamic resource in this field.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11655
