AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260202

1. ASTRA: Automated Synthesis of agentic Trajectories and Reinforcement Arenas
🔑 Keywords: ASTRA, tool-augmented language models, multi-step decision making, verifiable reinforcement learning, synthetic data
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop an automated framework, ASTRA, to enhance multi-step decision-making capabilities of tool-augmented language models through synthetic data and verifiable reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– ASTRA employs a two-component system: a pipeline for synthesizing tool-use trajectories from tool-call graphs, and an environment synthesis framework to create rule-verifiable environments, supporting deterministic multi-turn reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ASTRA-trained models achieve state-of-the-art performance in agentic tool-use benchmarks and maintain core reasoning abilities, comparable to closed-source systems. The authors provide all pipelines, environments, and trained models publicly.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21558

2. Golden Goose: A Simple Trick to Synthesize Unlimited RLVR Tasks from Unverifiable Internet Text
🔑 Keywords: Golden Goose, Reinforcement Learning, Verifiable Rewards, Large Language Models, Cybersecurity
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to overcome the limitation of verifiable data in Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) by synthesizing unlimited RLVR tasks from unverifiable internet text.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Golden Goose synthesizes questions from internet text by converting fill-in-the-middle tasks into multiple-choice question-answering versions, creating a large-scale dataset, GooseReason-0.7M, for RLVR training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Golden Goose improves RLVR performance under continuous training, achieving state-of-the-art results across various domains, including cybersecurity, demonstrating the potential of utilizing unverifiable text for data expansion.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22975

3. TTCS: Test-Time Curriculum Synthesis for Self-Evolving
🔑 Keywords: Test-Time Training, Large Language Models, Question Synthesizer, Reasoning Solver, Self-Consistency Rewards
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective was to enhance the reasoning abilities of large language models by developing a co-evolving test-time training framework, TTCS, that utilizes challenging question variants and updates a reasoning solver with self-consistency rewards.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– TTCS initializes two policies from a pretrained model: a question synthesizer and a reasoning solver, which co-evolve through iterative optimization. The synthesizer creates challenging question variants, and the solver updates using self-consistency rewards based on both test and synthetic questions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TTCS strengthens reasoning abilities on difficult mathematical benchmarks and transfers enhancements to general-domain tasks across different LLM backbones, paving a scalable path for dynamically constructing test-time curricula for self-evolution.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22628

4. PaperBanana: Automating Academic Illustration for AI Scientists
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, agentic framework, VLMs, image generation models, publication-ready illustrations
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduction of PaperBanana, a framework for automating the creation of academic illustrations using advanced vision-language models and image generation techniques.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of specialized agents for reference retrieval, planning, rendering, and iterative refinement via self-critique.
– Evaluation using PaperBananaBench with 292 test cases from NeurIPS 2025 covering diverse domains and styles.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PaperBanana surpasses current baselines in various parameters like faithfulness, conciseness, readability, and aesthetics.
– Effective extension of method to generate high-quality statistical plots, streamlining the creation of publication-ready illustrations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.23265

5. ReGuLaR: Variational Latent Reasoning Guided by Rendered Chain-of-Thought
🔑 Keywords: Variational Auto-Encoding, Latent Reasoning, Chain-of-Thought, Large Language Models, Multi-Modal Reasoning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– ReGuLaR aims to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of reasoning processes in AI models by compressing them into a latent space, while maintaining performance through image-rendered explicit reasoning chains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study utilizes a Rendered CoT-Guided Variational Latent Reasoning approach within the Variational Auto-Encoding framework, integrating visual-semantic representations to regularize poster distribution for efficient compression.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ReGuLaR significantly surpasses existing latent reasoning methods and even outperforms Chain-of-Thought through multi-modal reasoning, offering a novel solution to latent reasoning challenges.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.23184

6. DreamActor-M2: Universal Character Image Animation via Spatiotemporal In-Context Learning
🔑 Keywords: DreamActor-M2, in-context learning, self-bootstrapped data synthesis, generative prior, AW Bench
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a universal character animation framework, DreamActor-M2, that resolves motion injection trade-offs and pose prior limitations for enhanced generalization across diverse characters.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce a two-stage paradigm: integrating reference appearance and motion cues into a unified latent space and employing a self-bootstrapped data synthesis pipeline with cross-identity training pairs for seamless end-to-end RGB-driven animation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DreamActor-M2 achieves state-of-the-art performance with superior visual fidelity and robust cross-domain generalization, evaluated using the versatile AW Bench benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21716

7. DenseGRPO: From Sparse to Dense Reward for Flow Matching Model Alignment
🔑 Keywords: DenseGRPO, sparse reward problem, flow matching models, dense rewards, step-wise reward gain
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the sparse reward problem in flow matching models by introducing DenseGRPO, which incorporates dense rewards to evaluate fine-grained contributions at each denoising step.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a reward model that predicts step-wise reward gain using an ODE-based approach.
– Adaptive exploration calibration through a reward-aware scheme that adjusts timestep-specific stochasticity injection in the SDE sampler.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DenseGRPO effectively aligns human preference with dense rewards, demonstrating improved training and model alignment on multiple standard benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20218

8. RM -RF: Reward Model for Run-Free Unit Test Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: RM-RF, reward model, run-free evaluation, code coverage, mutation kill rate
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces RM-RF, a lightweight reward model designed to predict execution outcomes from source code, for run-free evaluation of automatically generated unit tests.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Instead of traditional methods, RM-RF predicts three execution-derived signals from source and test code and uses a multilingual dataset labeled by an execution-based pipeline for training and evaluation. Various tuning regimes were tested.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RM-RF offers significantly reduced latency and infrastructure costs while maintaining competitive predictive fidelity compared to conventional methods, enabling scalable feedback for test generation and RL-based code optimization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13097

9. TAM-Eval: Evaluating LLMs for Automated Unit Test Maintenance
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, test suite maintenance, TAM-Eval, automation, software testing
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Evaluate large language models on comprehensive test suite maintenance tasks, including creation, repair, and updating across multiple programming languages using the TAM-Eval framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a benchmark comprising 1,539 scenarios from Python, Java, and Go projects, employing a system-agnostic evaluation protocol based on test suite pass rate, code coverage, and mutation testing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Large Language Models currently demonstrate limited capabilities in handling realistic test maintenance processes and yield only marginal improvements in test effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.18241

10. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5: Towards a Multi-Task 0.9B VLM for Robust In-the-Wild Document Parsing
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Model, State-of-the-Art (SOTA), Benchmarking, Compact Model, AI-generated Summary
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce and evaluate PaddleOCR-VL-1.5, focusing on achieving SOTA accuracy on document understanding tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized specialized benchmarks such as OmniDocBench and proposed Real5-OmniDocBench to evaluate model robustness against real-world distortions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 achieved 94.5% accuracy, maintained compactness at 0.9B parameters, and extended functionalities to include seal recognition and text spotting while achieving high efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21957

11. NativeTok: Native Visual Tokenization for Improved Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: NativeTok, tokenization, causal dependencies, Meta Image Transformer, Mixture of Causal Expert Transformer
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to introduce a novel visual tokenization method, NativeTok, that enforces causal dependencies during the image encoding process to enhance image generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a Meta Image Transformer for latent image modeling and a Mixture of Causal Expert Transformer to generate tokens conditioned on previous tokens and latent features.
– Implements a Hierarchical Native Training strategy to ensure training efficiency by only updating new expert blocks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments demonstrated that NativeTok is effective in achieving efficient and coherent image reconstruction while embedding relational constraints within token sequences.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22837

12. DIFFA-2: A Practical Diffusion Large Language Model for General Audio Understanding
🔑 Keywords: DIFFA-2, diffusion-based large audio language model, audio understanding, dual adapters
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop DIFFA-2, a diffusion-based large audio language model, that improves efficiency and maintains competitive audio understanding performance compared to autoregressive counterparts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of an upgraded speech encoder and dual semantic and acoustic adapters, with a four-stage training curriculum that includes semantic and acoustic alignment, large-scale supervised fine-tuning, and preference optimization using open-source data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DIFFA-2 outperforms its predecessor DIFFA and proves competitive against strong autoregressive LALMs while ensuring diffusion-based modeling is a feasible approach for large-scale audio understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.23161

13. Revisiting Diffusion Model Predictions Through Dimensionality
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Models, High-Dimensional Settings, X-Prediction, K-Diff, Generative Performance
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– This research aims to establish a theoretical framework for understanding why direct data prediction (x-prediction) outperforms traditional noise and velocity prediction in high-dimensional settings and proposes a method to learn optimal prediction parameters automatically.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces a generalized prediction formulation accommodating various output targets and proposes the k-Diff framework, which uses a data-driven approach to learn optimal prediction parameters from data without estimating dimensions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The results show that x-prediction is superior when the ambient dimension exceeds the data’s intrinsic dimension. The k-Diff framework, through extensive experiments, consistently outperforms fixed-target baselines in image generation, enhancing generative performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21419
14. Robust Tool Use via Fission-GRPO: Learning to Recover from Execution Errors
🔑 Keywords: Large language models, multi-turn execution, reinforcement learning, Fission-GRPO, error recovery
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces a framework, Fission-GRPO, aimed at improving the multi-turn tool execution abilities of large language models by transforming execution errors into corrective supervision during reinforcement learning training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The core mechanism involves fissioning each failed trajectory into new training instances, enhancing them with diagnostic feedback from a fine-tuned Error Simulator, and subsequently resampling recovery rollouts on-policy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Fission-GRPO improved the error recovery rate by 5.7% for the Qwen3-8B model and achieved a 4% overall accuracy increase, outperforming GRPO and specialized tool-use agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15625

15. Real-Time Aligned Reward Model beyond Semantics
🔑 Keywords: RLHF, reward overoptimization, policy models, reward models, policy feedback
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address reward overoptimization in Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) by introducing a novel framework, R2M, which incorporates real-time policy feedback for dynamic reward modeling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– R2M utilizes real-time evolving hidden states of the policy, known as policy feedback, to align with the policy’s distribution shift during the reinforcement learning process, providing an alternative to reliance on semantic representations of a pretrained language model.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The introduction of R2M offers a promising new direction for enhancing reward model performance by employing real-time feedback from policy models, moving beyond traditional reward models that depend solely on surface semantics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22664

16. KAPSO: A Knowledge-grounded framework for Autonomous Program Synthesis and Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Autonomous Program Synthesis, Iterative Optimization, Knowledge Integration, Cognitive Memory, git-native experimentation engine
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce and evaluate KAPSO, a modular framework designed to enhance autonomous program synthesis by iteratively improving code generation over extended tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes iterative optimization loops with components such as ideation, code synthesis, execution, and evaluation; incorporates a git-native experimentation engine, a structured knowledge system, and a cognitive memory layer.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– KAPSO addresses long-horizon failures in coding agents by providing reproducible artifacts and preserving experimental states; it successfully improves performance in various benchmark tasks, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing autonomous program synthesis.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21526

17. ExpAlign: Expectation-Guided Vision-Language Alignment for Open-Vocabulary Grounding
🔑 Keywords: vision-language alignment, multiple instance learning, open-vocabulary detection, zero-shot instance segmentation, energy-based multi-scale consistency regularization
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance open-vocabulary detection and zero-shot instance segmentation through improved vision-language alignment without additional annotations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper introduces ExpAlign, a vision-language alignment framework that employs multiple instance learning and attention-based soft MIL pooling.
– Development of an energy-based multi-scale consistency regularization scheme, with a focus on a Top-K multi-positive contrastive objective and a Geometry-Aware Consistency Objective.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ExpAlign demonstrates superior performance in open-vocabulary detection and zero-shot instance segmentation, especially in long-tail categories, achieving notable results on the LVIS minival split while maintaining lightweight and efficient inference capability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22666

18. Machine Learning for Energy-Performance-aware Scheduling
🔑 Keywords: Bayesian Optimization, Gaussian Processes, Pareto Frontier, Sensitivity Analysis, Multi-core Systems
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To automate scheduling configuration optimization on heterogeneous multi-core systems using Bayesian Optimization, focusing on energy-time trade-offs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of Gaussian Processes to approximate the Pareto Frontier and incorporate Sensitivity Analysis to provide interpretability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach identifies dominant hardware parameters that influence system performance by comparing covariance kernels like Matérn and RBF.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.23134

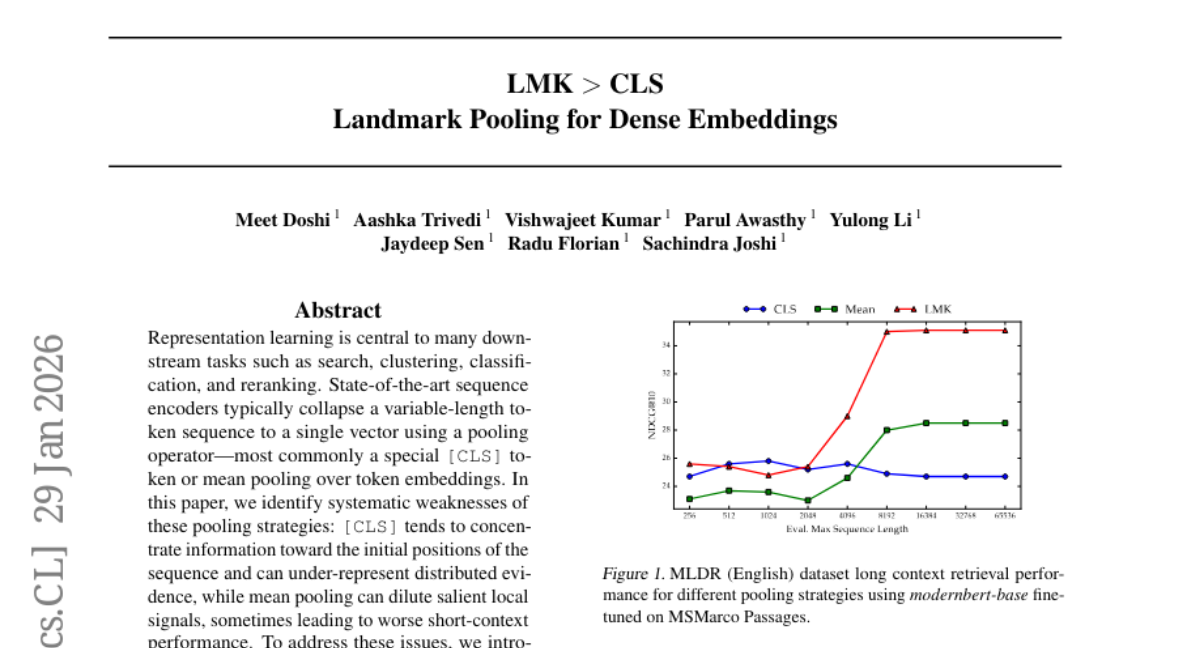
19. LMK > CLS: Landmark Pooling for Dense Embeddings
🔑 Keywords: Landmark pooling, sequence encoders, representation learning, long-context extrapolation, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance long-context representation learning by employing Landmark pooling to better preserve global and local information in sequences.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of Landmark (LMK) pooling, which partitions sequences into chunks and inserts landmark tokens to mean-pool their embeddings for improved context representation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LMK pooling demonstrates significant improvements in long-context tasks while maintaining performance on short-context retrieval tasks, making it a practical and scalable alternative to traditional pooling methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21525
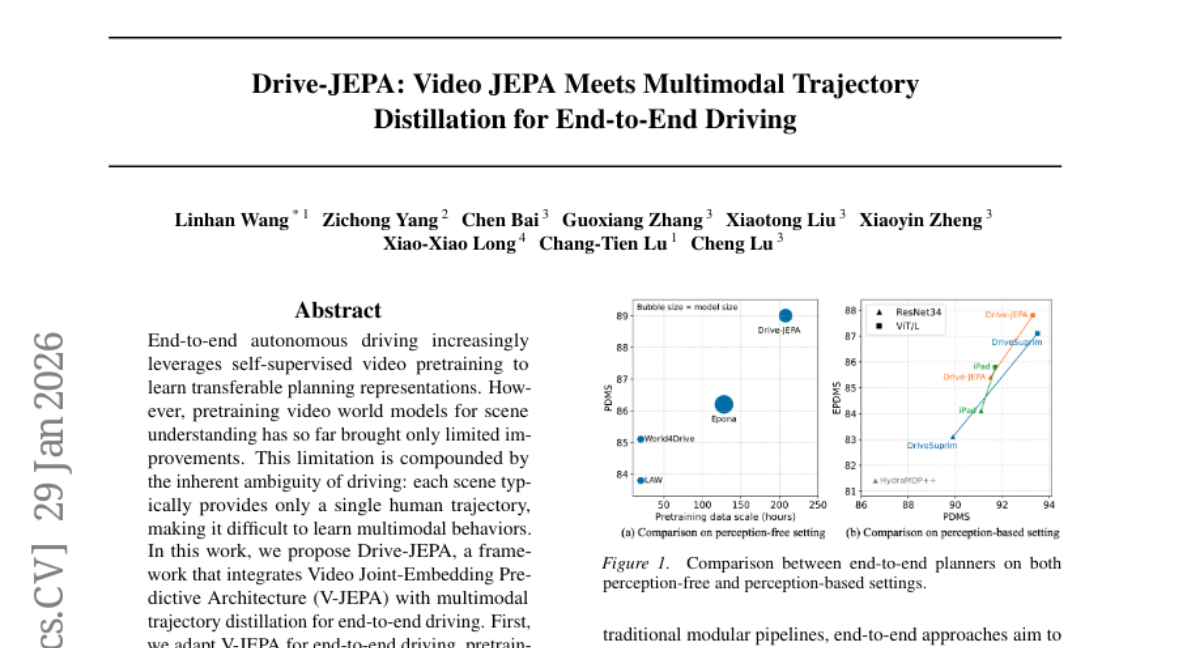
20. Drive-JEPA: Video JEPA Meets Multimodal Trajectory Distillation for End-to-End Driving
🔑 Keywords: Drive-JEPA, V-JEPA, multimodal trajectory distillation, autonomous driving, Video Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim is to enhance end-to-end autonomous driving performance by leveraging Drive-JEPA, which combines V-JEPA video pretraining with multimodal trajectory distillation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Drive-JEPA pretrains a ViT encoder on large-scale driving videos to create predictive representations for trajectory planning.
– A proposal-centric planner is introduced to distill a variety of simulator-generated and human trajectories, utilizing a momentum-aware selection mechanism for improved driving behavior.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Drive-JEPA framework, evaluated on NAVSIM, outperforms prior methods, achieving new state-of-the-art results with 93.3 PDMS on v1 and 87.8 EPDMS on v2 in perception-free settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22032
21.

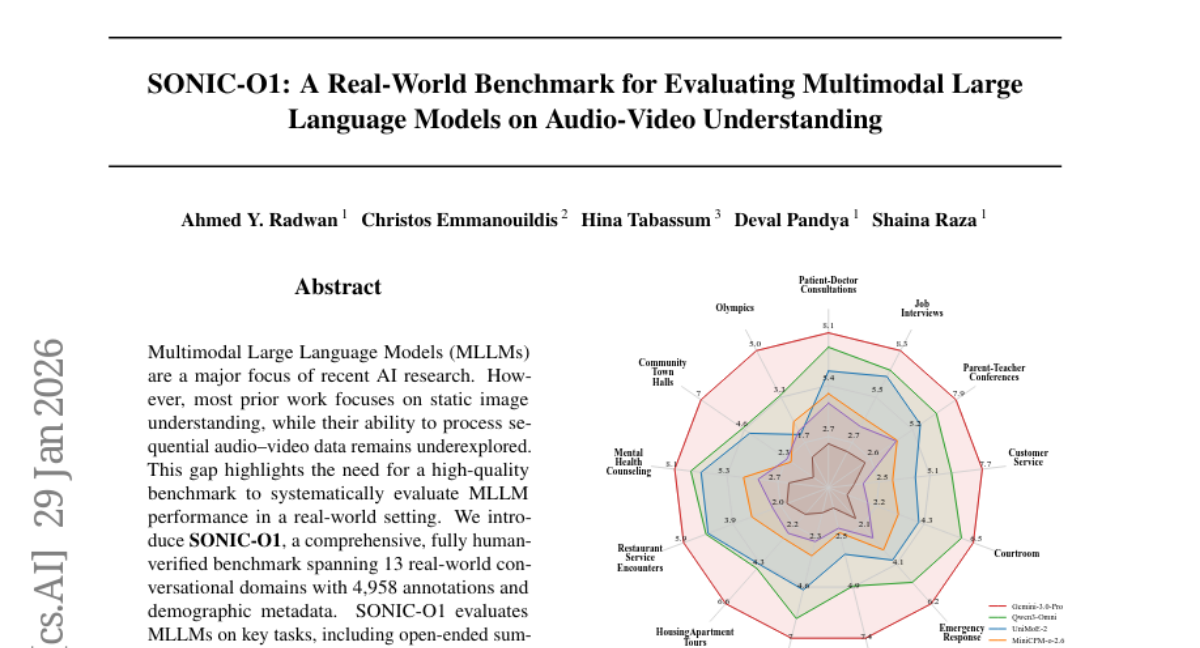
22. SONIC-O1: A Real-World Benchmark for Evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models on Audio-Video Understanding
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Large Language Models, audio-video data, temporal localization, demographic disparities
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces a comprehensive benchmark named SONIC-O1 to evaluate Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) on sequential audio-video data in real-world conversational domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– SONIC-O1 is presented with 4,958 human-verified annotations and demographic metadata, focusing on tasks like open-ended summarization, multiple-choice question answering, and temporal localization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Significant performance differences are observed in temporal localization between best-performing closed-source and open-source models, and across demographic groups, indicating persistent disparities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21666
23. Value-Based Pre-Training with Downstream Feedback
🔑 Keywords: V-Pretraining, self-supervised learning, downstream task, token efficiency, language models
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate the impact of using downstream task gradients to enhance pretraining objectives, improving model performance with minimal labeled data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce the method of V-Pretraining, a value-based, modality-agnostic approach that aligns pretraining tasks with downstream task gradients to maximize performance efficiently.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– V-Pretraining improved the performance of language models in reasoning tasks, achieving significant performance gains with reduced data and computational resources.
– In vision self-supervised learning, it achieved state-of-the-art results on benchmarks such as ADE20K and improved efficiency and accuracy on datasets like NYUv2 and ImageNet.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22108

24. Visual Personalization Turing Test
🔑 Keywords: Visual Personalization Turing Test, VPTT Framework, Perceptual Indistinguishability, VPRAG, Generative AI
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
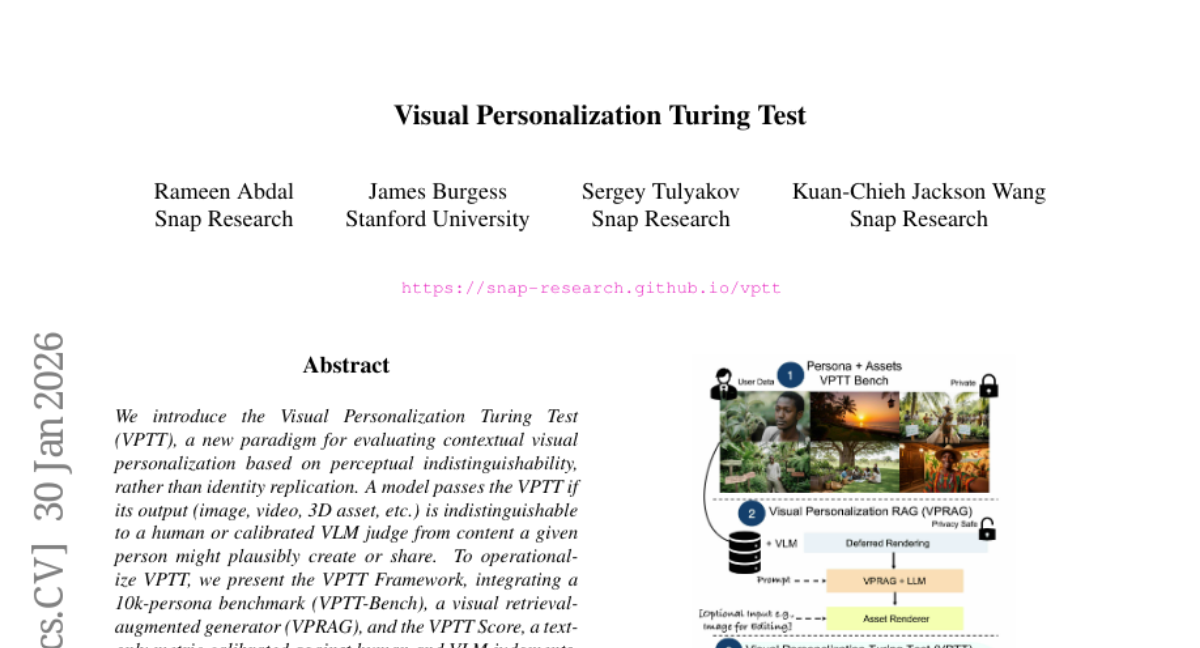
– To introduce the Visual Personalization Turing Test (VPTT) as a paradigm for evaluating contextual visual personalization based on perceptual indistinguishability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Operationalizing VPTT with a 10k-persona benchmark, a visual retrieval-augmented generator (VPRAG), and a VPTT Score calibrated against human and VLM judgments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VPRAG achieves the best balance of alignment and originality, confirming the VPTT Score as a reliable perceptual proxy for evaluating personalized generative AI.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22680
25. Memorization Dynamics in Knowledge Distillation for Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Knowledge Distillation, Large Language Models, Memorization, Privacy-Preserving, Hard Distillation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study investigates how Knowledge Distillation affects training data memorization and explores its utility as a privacy-preserving method compared to standard fine-tuning techniques.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs Knowledge Distillation across three large language model families (Pythia, OLMo-2, Qwen-3) and analyzes memorization patterns using datasets (FineWeb, Wikitext, Nemotron-CC-v2), evaluating features like zlib entropy, KL divergence, and perplexity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Distilled models demonstrate over 50% reduction in training data memorization compared to standard fine-tuning.
– A small fraction of easily memorizable examples accounts for a large portion of memorization during distillation.
– Student memorization is predictable before distillation using specific data features.
– Hard distillation poses a higher risk by inheriting significantly more teacher-specific examples than soft distillation, while overall offering improved generalization and reduced memorization risk.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15394

26. Why Attention Patterns Exist: A Unifying Temporal Perspective Analysis
🔑 Keywords: Temporal Attention Pattern Predictability Analysis, large language models, attention patterns, query self-similarity, Rotary Positional Embeddings
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– TAPPA introduces a unifying framework to understand and analyze attention patterns in large language models through a temporal perspective.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Differentiates attention patterns into predictable and unpredictable based on mathematical formulations and query self-similarity.
– Provides a detailed mathematical analysis focusing on predictable patterns and examines the effect of queries, keys, and Rotary Positional Embeddings.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TAPPA’s framework is validated through tasks like KV cache compression and LLM pruning, showing improved performance with a simple TAPPA-driven metric over baseline methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21709

27. Routing the Lottery: Adaptive Subnetworks for Heterogeneous Data
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, adaptive pruning, adaptive tickets, subnetwork collapse, subnetwork similarity score
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Routing the Lottery (RTL), an adaptive pruning framework that identifies multiple specialized subnetworks tailored to various data conditions, outperforming traditional methods while using fewer parameters.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– RTL framework discovers adaptive tickets for different data classes, semantic clusters, or environments, and introduces a subnetwork similarity score for diagnosing oversparsification without labels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RTL achieves superior balanced accuracy and recall compared to single- and multi-model baselines, addresses performance drop due to subnetwork collapse, and showcases the potential for modular and context-aware deep learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22141
28. Continual GUI Agents
🔑 Keywords: Continual GUI Agents, GUI-Anchoring in Flux, Reinforcement Fine-tuning, Continual Learning, Anchoring Rewards
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address performance degradation in dynamic digital environments by introducing a framework for Continual GUI Agents to learn under shifting domains and resolutions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of GUI-AiF framework featuring two novel reinforcement fine-tuning rewards: Anchoring Point Reward in Flux and Anchoring Region Reward in Flux to stabilize continual learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GUI-AiF framework outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, establishing the first continual learning framework for GUI agents and highlighting the potential of reinforcement fine-tuning in this domain.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20732

29. Deep Search with Hierarchical Meta-Cognitive Monitoring Inspired by Cognitive Neuroscience
🔑 Keywords: Deep search agents, hierarchical metacognitive monitoring, reasoning, retrieval, corrective intervention
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance reasoning and retrieval performance in deep search agents through hierarchical metacognitive monitoring.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces DS-MCM, a framework that incorporates a Fast Consistency Monitor for quick checks and a Slow Experience-Driven Monitor for guiding corrective actions based on past experiences.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DS-MCM improves performance and robustness across various deep search benchmarks and backbone models by effectively embedding monitoring within the reasoning-retrieval loop.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.23188

30. Latent Chain-of-Thought as Planning: Decoupling Reasoning from Verbalization
🔑 Keywords: Latent Reasoning, Large Language Models, Planning with Latent Thoughts, Inference-time Search
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce PLaT, a framework to decouple reasoning from verbalization for enhanced scalability and dynamic termination in latent reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Reformulate latent reasoning as planning by modeling reasoning as a deterministic trajectory of latent planning states, with a Decoder for necessary verbalization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PLaT achieves lower greedy accuracy but offers superior scalability in reasoning diversity, supporting a broader and robust solution space for inference-time search.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21358

31. Scaling Multiagent Systems with Process Rewards
🔑 Keywords: Multiagent systems, credit assignment, sample efficiency, AI feedback, per-action process rewards
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
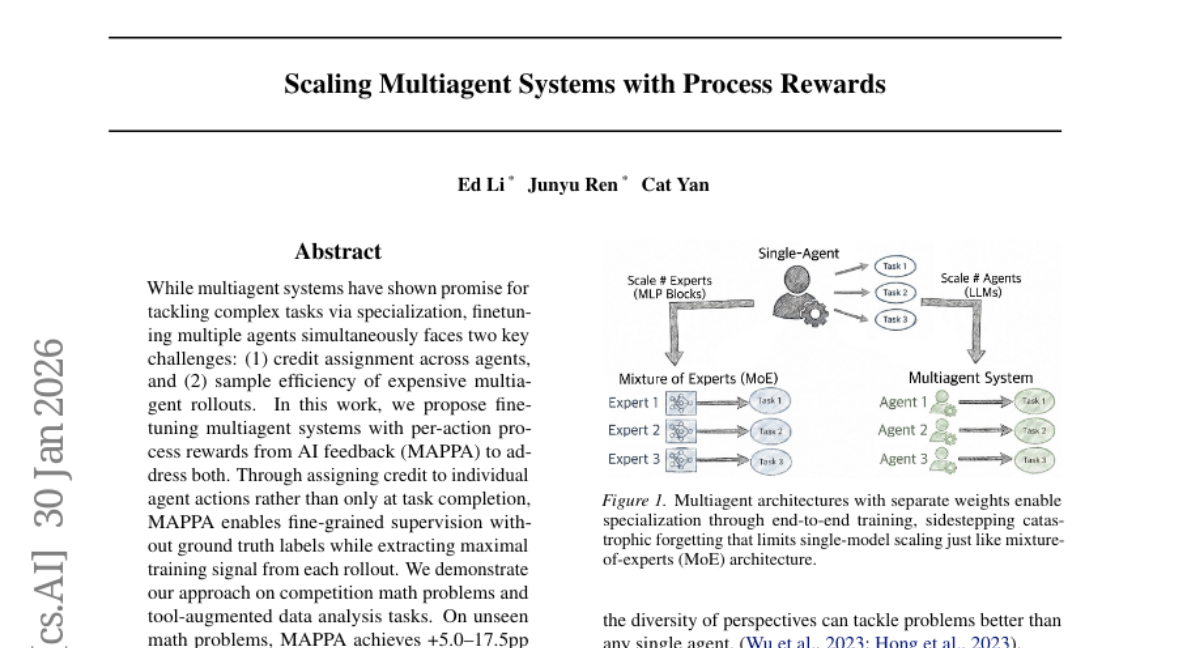
– To enhance multiagent systems by addressing credit assignment and sample efficiency challenges using per-action process rewards from AI feedback (MAPPA).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employing finetuning of multiagent systems with per-action process rewards to improve supervision and extract maximal training signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MAPPA demonstrates significant improvements in solving competition math problems and tool-augmented data analysis tasks, showing enhancements in unseen math problem performance and data analysis success rates, indicating its effectiveness in scaling multiagent systems for complex tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.23228
32. MemOCR: Layout-Aware Visual Memory for Efficient Long-Horizon Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: MemOCR, multimodal memory agent, visual layout, reinforcement learning, context utilization
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce MemOCR to enhance long-horizon reasoning by efficiently compressing interaction histories into adaptive visual layouts under tight context budgets.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize structured rich-text memory transformed into images for memory access.
– Employ reinforcement learning with budget-aware objectives to maintain robustness across various memory budgets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MemOCR outperforms text-based baselines in long-context question-answering tasks, demonstrating superior context utilization even under extreme budget constraints.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21468

33. Pushing the Boundaries of Natural Reasoning: Interleaved Bonus from Formal-Logic Verification
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, formal logic verification, symbolic verification, natural language generation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
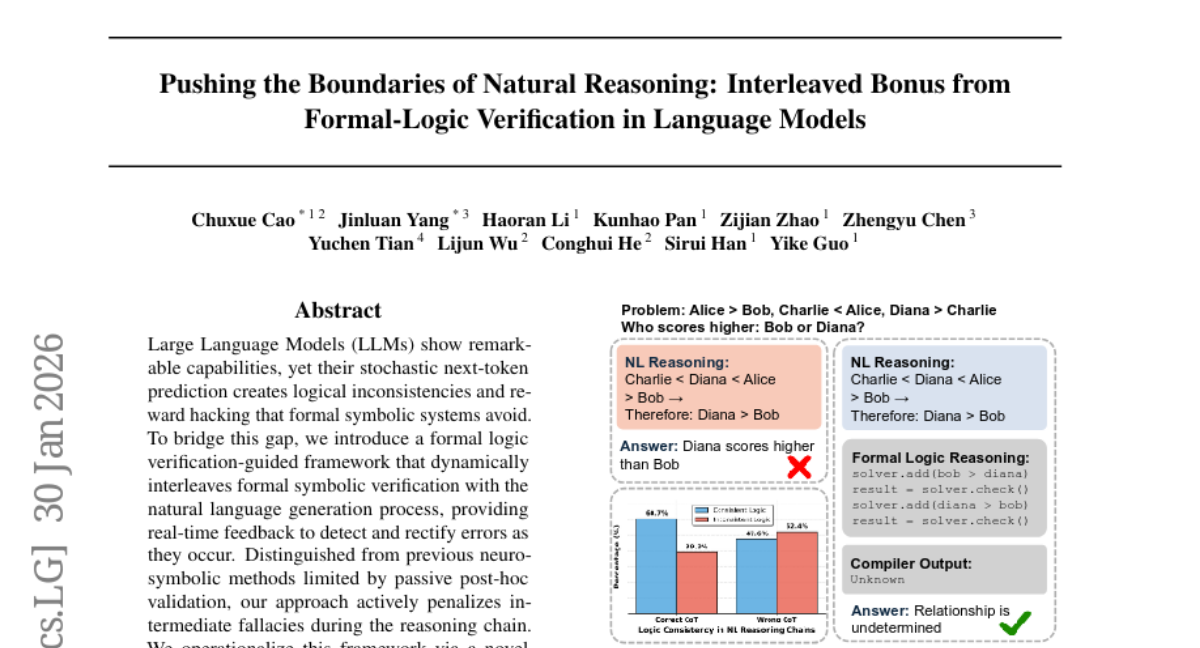
– Improve reasoning accuracy and reduce errors in large language models by dynamically interleaving formal logic verification with natural language generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement a two-stage training pipeline that integrates formal logic verification-guided supervised fine-tuning and policy optimization to provide real-time feedback and actively penalize intermediate fallacies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework enhances performance of 7B and 14B models, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines by 10.4% and 14.2% on average across six reasoning benchmarks, illustrating that formal verification can significantly push the performance boundaries of advanced LLM reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22642
34. DINO-SAE: DINO Spherical Autoencoder for High-Fidelity Image Reconstruction and Generation
🔑 Keywords: DINO-SAE, generative autoencoders, semantic alignment, Riemannian Flow Matching
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance generative autoencoder performance by combining semantic representation with pixel-level reconstruction using a spherical latent space.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a Hierarchical Convolutional Patch Embedding module and Cosine Similarity Alignment objective to maintain semantic consistency while preserving detail.
– Utilization of Riemannian Flow Matching for training a Diffusion Transformer on a spherical latent manifold.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction quality with 0.37 rFID and 26.2 dB PSNR on ImageNet-1K.
– Efficient convergence of the Riemannian Flow Matching-based DiT, achieving a gFID of 3.47 at 80 epochs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22904

35. Statistical Estimation of Adversarial Risk in Large Language Models under Best-of-N Sampling
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, adversarial prompting, Best-of-N sampling, jailbreak vulnerability, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces SABER, a scaling-aware risk estimation method, for predicting large-scale adversarial vulnerability in language models, particularly assessing jailbreak vulnerability under Best-of-N sampling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– SABER employs a Beta distribution to model sample-level success probabilities, deriving an analytic scaling law to predict large-N attack success rates with reduced computational costs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SABER significantly decreases estimation error compared to the baseline, revealing that models perceived as robust can experience nonlinear risk amplification under adversarial pressure, providing an efficient methodology for assessing LLM safety.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22636

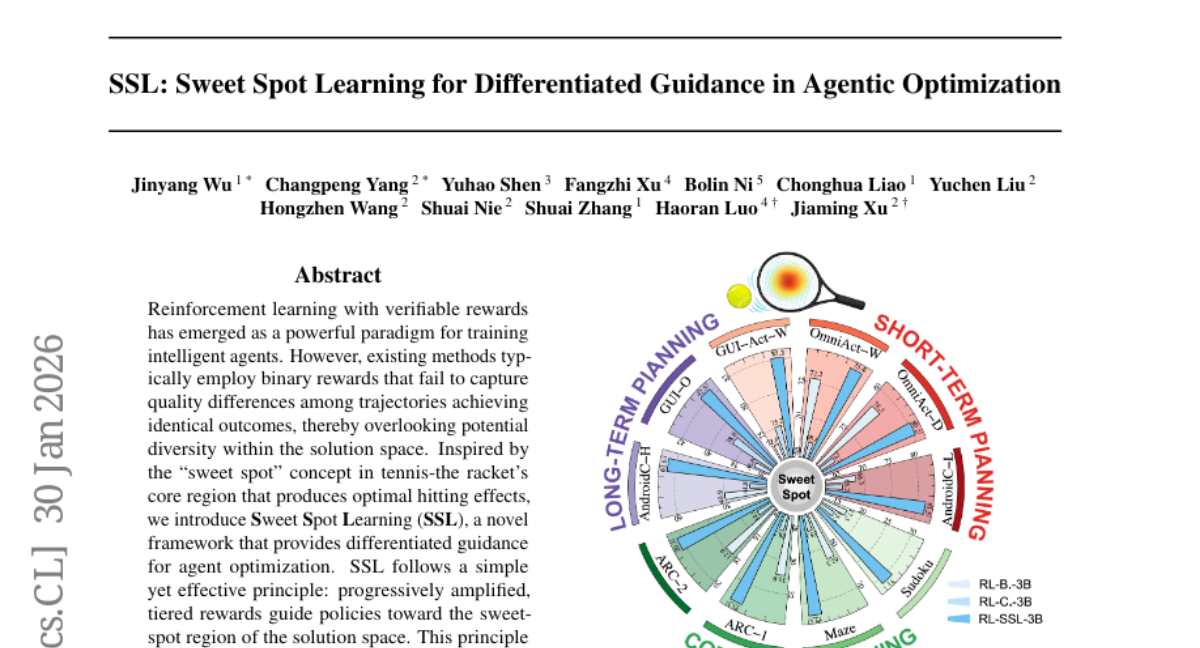
36. SSL: Sweet Spot Learning for Differentiated Guidance in Agentic Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Sweet Spot Learning, Reinforcement Learning, Sample Efficiency, Cross-Task Transferability, Gradient Signal-to-Noise Ratio
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a novel framework called Sweet Spot Learning (SSL) aimed at improving sample efficiency and cross-task transferability through tiered rewards in reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement continuous and tiered reward systems that provide differentiated guidance to optimize agent behavior toward optimal regions of the solution space, verified through theoretical demonstration of improved gradient signal-to-noise ratio.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SSL demonstrated consistent improvements over strong baselines in multiple domains, enhancing sample efficiency by up to 2.5 times and showing effective cross-task transferability across 12 benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22491
37. Causal World Modeling for Robot Control
🔑 Keywords: video world modeling, autoregressive diffusion framework, shared latent space, closed-loop rollout mechanism, AI Native
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces a new approach in video world modeling to enhance robot learning by predicting frames and executing policies using a shared latent space and feedback mechanisms.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study implements LingBot-VA, an autoregressive diffusion framework featuring three key designs: a shared latent space integrating vision and action tokens using a Mixture-of-Transformers architecture, a closed-loop rollout mechanism for environmental feedback, and an asynchronous inference pipeline for efficient control.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model demonstrates significant potential in long-horizon manipulation and data efficiency in both simulation and real-world scenarios, with strong generalizability to new configurations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21998

38. FourierSampler: Unlocking Non-Autoregressive Potential in Diffusion Language Models via Frequency-Guided Generation
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Language Models, Frequency-Domain Analysis, FourierSampler, Low-Frequency Components, High-Frequency Components
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The investigation delves into the spectral characteristics of diffusion language models to address positional bias and enhance arbitrary generation capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs frequency-domain analysis to distinguish between low-frequency components, which encode global structures, and high-frequency components, which detail local features. The FourierSampler with a dynamic frequency-domain sliding window is introduced to optimize generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FourierSampler significantly improves inference outcomes, achieving notable performance over autoregressive models and other strategies in benchmarks such as LLADA and SDAR, with specific improvements of 20.4% and 16.0% on different datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.23182

39. Do Reasoning Models Enhance Embedding Models?
🔑 Keywords: RLVR, Embedding Models, HRSA, Local Geometry Reorganization, Manifold Realignment
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To determine if embedding models initialized from RLVR-tuned reasoning models have a performance advantage over base models in semantic representation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluation on MTEB and BRIGHT datasets using Hierarchical Representation Similarity Analysis (HRSA) to analyze similarity across representation, geometry, and function levels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Embedding models initialized from RLVR-tuned backbones show no consistent performance advantage over base models. Although RLVR reorganizes local geometry and preserves global manifold geometry, subsequent contrastive learning aligns base- and reasoning-initialized models effectively.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21192

40. THINKSAFE: Self-Generated Safety Alignment for Reasoning Models
🔑 Keywords: ThinkSafe, Large Reasoning Models, Safety Alignment, Lightweight Refusal Steering, Computational Cost
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to enhance safety in large reasoning models without impairing their performance or increasing computational costs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The ThinkSafe framework utilizes lightweight refusal steering and fine-tuning on self-generated responses to realign safety without dependency on external teachers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ThinkSafe significantly boosts safety while maintaining reasoning proficiency, achieving superior safety comparable to existing methods with reduced computational expenses.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.23143
41. Quartet II: Accurate LLM Pre-Training in NVFP4 by Improved Unbiased Gradient Estimation
🔑 Keywords: NVFP4, NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs, quantized training, gradient estimation, LLM training
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance the utilization of the NVFP4 format for pre-training large language models, focusing on improving quantized training through a novel routine, MS-EDEN, and a new scheme, Quartet II.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a novel unbiased quantization routine called MS-EDEN, integrated into a fully-NVFP4 quantization scheme named Quartet II, which is applied to linear layers to enhance gradient estimation and matrix multiplication processes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Quartet II shows improved gradient estimation and execution speed, achieving up to a 4.2x speedup over BF16 on NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs. This method also performs well in end-to-end LLM training on vast sets of parameters and tokens.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22813
