AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260209
1. OdysseyArena: Benchmarking Large Language Models For Long-Horizon, Active and Inductive Interactions
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, autonomous agents, OdysseyArena, transition laws, agent evaluation
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce OdysseyArena, a framework to evaluate large language models in long-horizon, inductive agent tasks that focus on autonomous discovery of environmental transition laws.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Formalize four primitives, translating abstract transition dynamics into interactive environments.
– Establish OdysseyArena-Lite for standardized benchmarking with 120 tasks and OdysseyArena-Challenge for stress-testing agent stability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Highlighted a critical bottleneck in leading LLMs’ performance in inductive scenarios, emphasizing the need for further development in long-horizon, strategic agentic foresight.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.05843

2. F-GRPO: Don’t Let Your Policy Learn the Obvious and Forget the Rare
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Verifiable Rewards, Group Sampling, Difficulty-Aware Advantage Scaling, Focal Loss
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the performance of Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) by introducing a difficulty-aware advantage scaling technique without increasing computational cost.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analyze the bias caused by group sampling in RLVR methods and derive probability behavior concerning group size.
– Introduce a difficulty-aware advantage scaling coefficient inspired by Focal Loss to adjust updates on high-success prompts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed scaling method enhances performance on both in-domain and out-of-domain benchmarks across multiple algorithms, improving metrics significantly without increasing group size or computational expenses.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06717

3. On the Entropy Dynamics in Reinforcement Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Entropy Dynamics, Large Language Models, Reinforcement Fine-Tuning, AI Native, Exploration-Exploitation Balance
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to establish a theoretical framework for analyzing entropy dynamics during the reinforcement fine-tuning of large language models, with a specific focus on deriving expressions for entropy change and proposing entropy control methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors use discriminant analysis to quantify entropy change under a single logit update, leading to a derivation of a first-order expression and extension to Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). Empirical evidence supports the derived methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study provides novel insights into reinforcement fine-tuning training dynamics, offering theoretical support and practical strategies for improving the exploration-exploitation balance during large language model fine-tuning. It introduces effective entropy-discriminator clipping methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03392
4. Pisets: A Robust Speech Recognition System for Lectures and Interviews
🔑 Keywords: Speech-to-Text, Wav2Vec2, Whisper, Audio Spectrogram Transformer, curriculum learning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve transcription accuracy and reduce hallucinations in Russian speech recognition by integrating multiple models and strategies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study uses a three-component system combining Wav2Vec2, AST, and Whisper models, with curriculum learning and advanced uncertainty modeling techniques.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– By implementing this architecture, the system, “Pisets,” robustly transcribes long audio data effectively across various acoustic conditions, outshining other models like WhisperX.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.18415

5. Self-Improving World Modelling with Latent Actions
🔑 Keywords: SWIRL, self-improvement framework, Forward World Modelling, Inverse Dynamics Modelling, reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce SWIRL, a self-improvement framework that learns world models from state-only sequences without the need for costly action-labelled trajectories.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Alternates between Forward World Modelling and Inverse Dynamics Modelling using Variational Information Maximisation and ELBO Maximisation.
– Trains models through reinforcement learning, especially GRPO, with the opposite model’s log-probability as a reward signal.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SWIRL demonstrates improved performance on reasoning and planning benchmarks, achieving gains of up to 28% on various tasks such as AURORABench and ByteMorph.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06130

6. Back to Basics: Revisiting Exploration in Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning via Generative Probabilities
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Entropy Collapse, Large Language Models, Generative Diversity, Advantage Re-weighting Mechanism
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address entropy collapse in reasoning for Large Language Models by equilibrating confidence levels and enhancing generative diversity through dynamic reward shaping.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers propose a novel Advantage Re-weighting Mechanism (ARM) that incorporates Prompt Perplexity and Answer Confidence into the advantage estimation, which dynamically reshapes the reward signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Empirical results show the approach significantly improves generative diversity and response entropy while maintaining accuracy, outperforming existing methods like GRPO, particularly noted in mathematical and coding benchmarks with models like Qwen2.5.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.05281

7. Self-Improving Multilingual Long Reasoning via Translation-Reasoning Integrated Training
🔑 Keywords: TRIT, multilingual reasoning, translation training, cross-lingual alignment, response generation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to improve multilingual reasoning and question understanding by jointly training translation and reasoning components through the TRIT framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The TRIT framework integrates translation training into multilingual reasoning without using external feedback or additional multilingual data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The TRIT framework enhances multilingual question understanding and response generation, outperforming various baselines by 7 percentage points. It improves cross-lingual question alignment and translation quality significantly, achieving gains up to 8.4 COMET points.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.05940

8. Canzona: A Unified, Asynchronous, and Load-Balanced Framework for Distributed Matrix-based Optimizers
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, matrix-based optimizers, tensor fragmentation, distributed frameworks, Canzona
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the conflict between matrix-based optimizers and distributed tensor fragmentation to improve efficiency and reduce latency in Large Language Models (LLMs) training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposes Canzona, a unified asynchronous framework that decouples logical optimizer assignment from physical parameter distribution. Utilizes an alpha-Balanced Static Partitioning strategy for data parallelism and an Asynchronous Compute pipeline with Micro-Group Scheduling for tensor parallelism.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates a significant improvement in efficiency, achieving a 1.57x speedup in end-to-end iteration time and a 5.8x reduction in optimizer step latency compared to the baseline on the Qwen3 model family.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06079

9. RaBiT: Residual-Aware Binarization Training for Accurate and Efficient LLMs
🔑 Keywords: RaBiT, Residual binarization, Quantization-aware training, Inference speed-up, RTX 4090
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address feature co-adaptation in quantized large language models (LLMs) through a novel residual binarization framework RaBiT that enhances accuracy-efficiency trade-offs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of hierarchical path derivation and robust initialization in quantization-aware training, utilizing binary layer stacking and sequential error correction to resolve co-adaptation issues.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RaBiT redefines the 2-bit accuracy-efficiency frontier for LLMs, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance and achieving a 4.49 times inference speed-up over full-precision models, rivaling more hardware-intensive methods like Vector Quantization on RTX 4090.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.05367

10. PlanViz: Evaluating Planning-Oriented Image Generation and Editing for Computer-Use Tasks
🔑 Keywords: Unified Multimodal Models, computer-use planning, Image Generation, PlanViz, PlanScore
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study proposes PlanViz, a benchmark designed to evaluate the image generation and editing capabilities of Unified Multimodal Models (UMMs) for computer-use planning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research emphasizes the evaluation of UMMs through sub-tasks such as route planning, work diagramming, and web&UI displaying, utilizing a task-adaptive scoring system called PlanScore for assessing correctness, visual quality, and efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The findings underscore the challenges and opportunities in assessing the capabilities of UMMs in planning tasks, highlighting the need for further research in this domain.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06663

11. Uncovering Cross-Objective Interference in Multi-Objective Alignment
🔑 Keywords: Multi-objective alignment, Large Language Models, cross-objective interference, scalarization algorithms, Covariance Targeted Weight Adaptation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate multi-objective alignment issues in Large Language Models where improving one objective may degrade others.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted a systematic study of cross-objective interference using scalarization algorithms and derived a local covariance law to explain the phenomenon.
– Proposed Covariance Targeted Weight Adaptation (CTWA) to maintain positive covariance between objective rewards and training signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Interference is model-dependent and pervasive, but can be mitigated by CTWA.
– Provided a global convergence analysis demonstrating conditions for achieving global convergence in non-convex scalarized optimization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06869
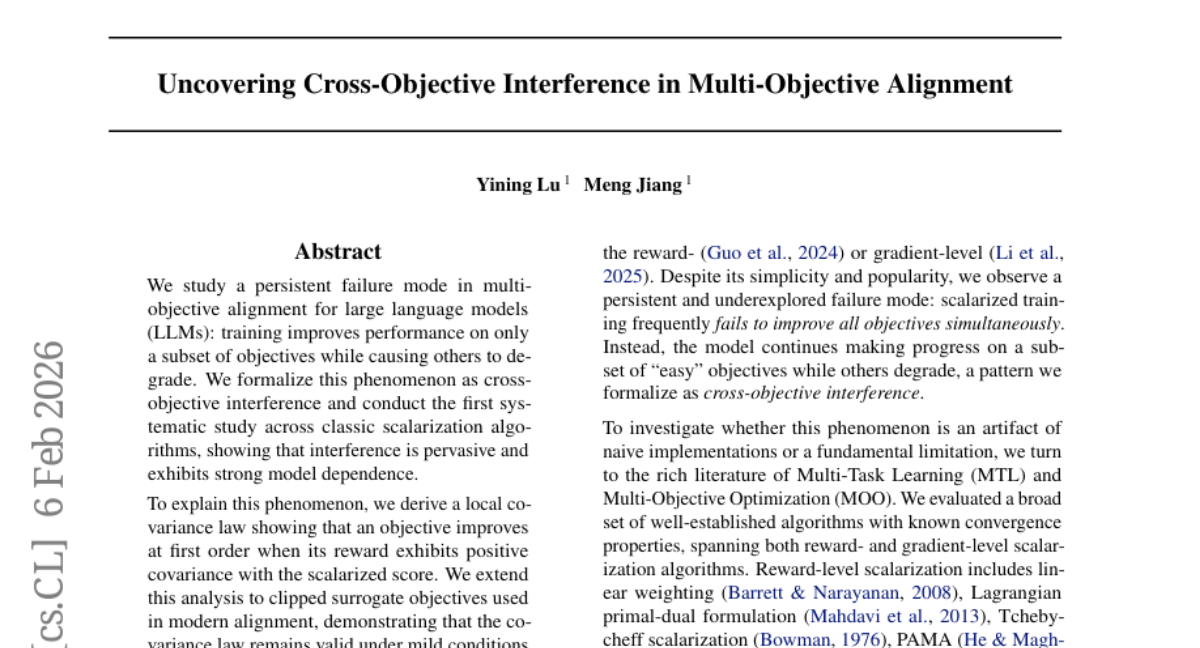
12. QuantLRM: Quantization of Large Reasoning Models via Fine-Tuning Signals
🔑 Keywords: QuantLRM, Large Reasoning Models, Weight Updates, Channel Importance, Fine-Tuning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve quantization of Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) by utilizing weight update magnitude signals from fine-tuning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a method called QuantLRM which employs weight-only quantization by estimating channel importance through fitting simple restricted quadratic functions on weight updates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– QuantLRM consistently enhances the performance of LRM quantization with a significant average improvement, particularly noted as 6.55% on a reinforcement learning fine-tuned model. It also effectively gathers signals via pseudo-fine-tuning for non-fine-tuned LRMs, broadening its applicability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02581
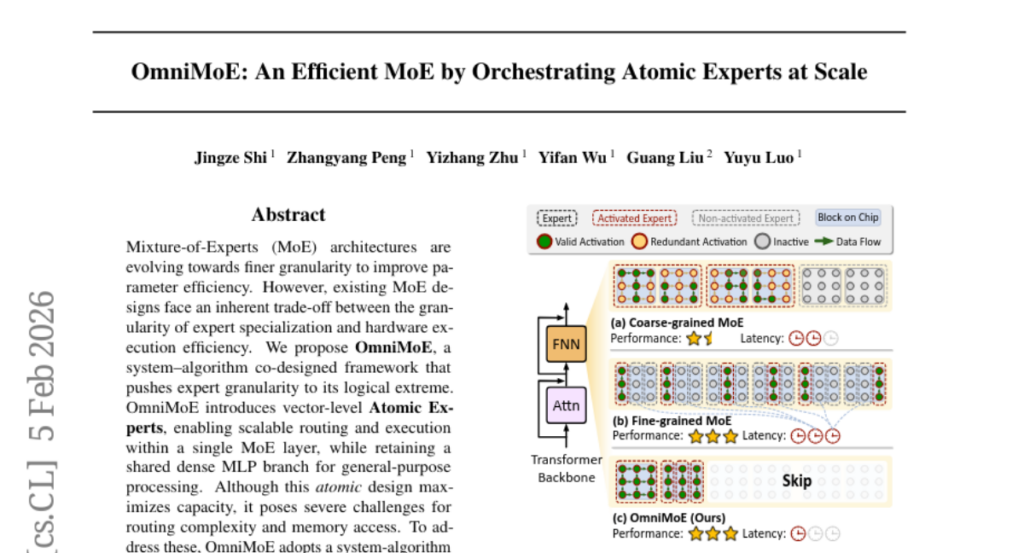
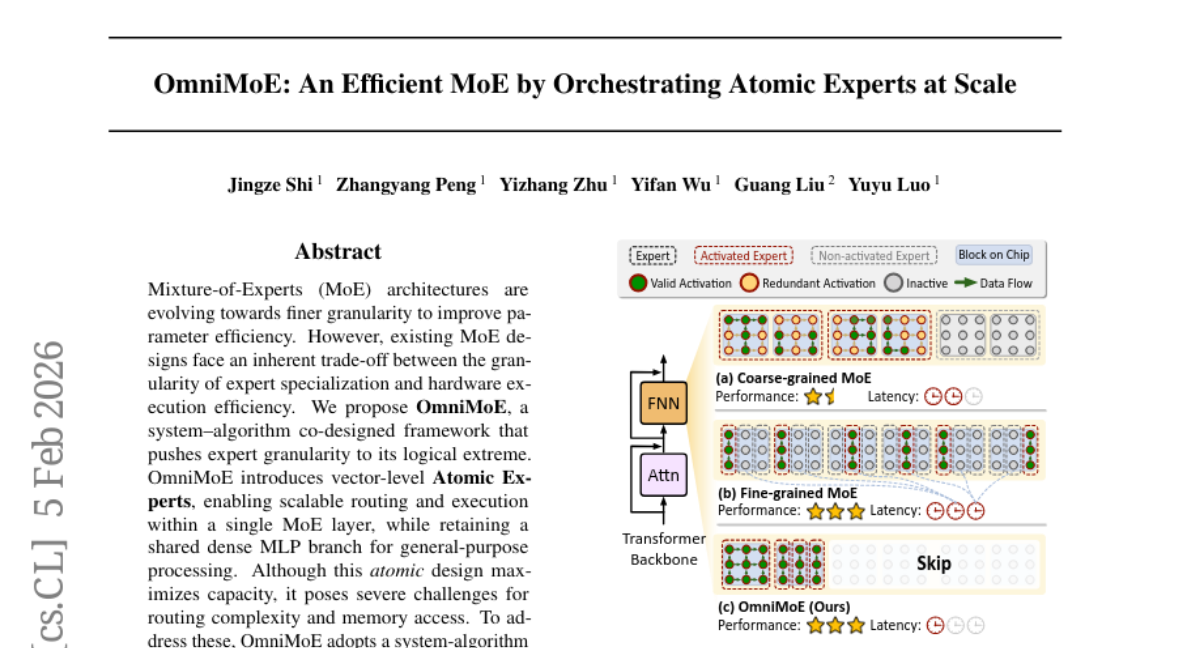
13. OmniMoE: An Efficient MoE by Orchestrating Atomic Experts at Scale
🔑 Keywords: OmniMoE, Mixture-of-Experts, vector-level Atomic Experts, routing complexity, inference latency
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce OmniMoE, a co-designed framework to enhance expert specialization in Mixture-of-Experts architectures by pushing expert granularity to the limit.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a system-algorithm co-design employing vector-level Atomic Experts for scalable routing and execution.
– Implement a Cartesian Product Router to reduce routing complexity and Expert-Centric Scheduling to optimize memory-bound lookups into efficient operations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OmniMoE, with 1.7B active parameters, achieves significant improvements in zero-shot accuracy and inference latency, outperforming existing baselines and demonstrating fast and accurate massive-scale fine-grained MoE.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.05711
14. Large Language Model Reasoning Failures
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, reasoning capabilities, reasoning failures, categorization framework, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to systematically analyze reasoning failures in Large Language Models, classifying them into embodied and non-embodied types along with subcategories and providing a comprehensive survey.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a novel categorization framework to distinguish and classify reasoning failures in LLMs. The paper analyzes existing studies, explores root causes, and presents mitigation strategies for these failures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– By unifying fragmented research efforts, the paper offers a structured perspective on systemic weaknesses in LLM reasoning, providing insights and guiding future research towards more reliable reasoning capabilities. A GitHub repository has been released to support further exploration.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06176

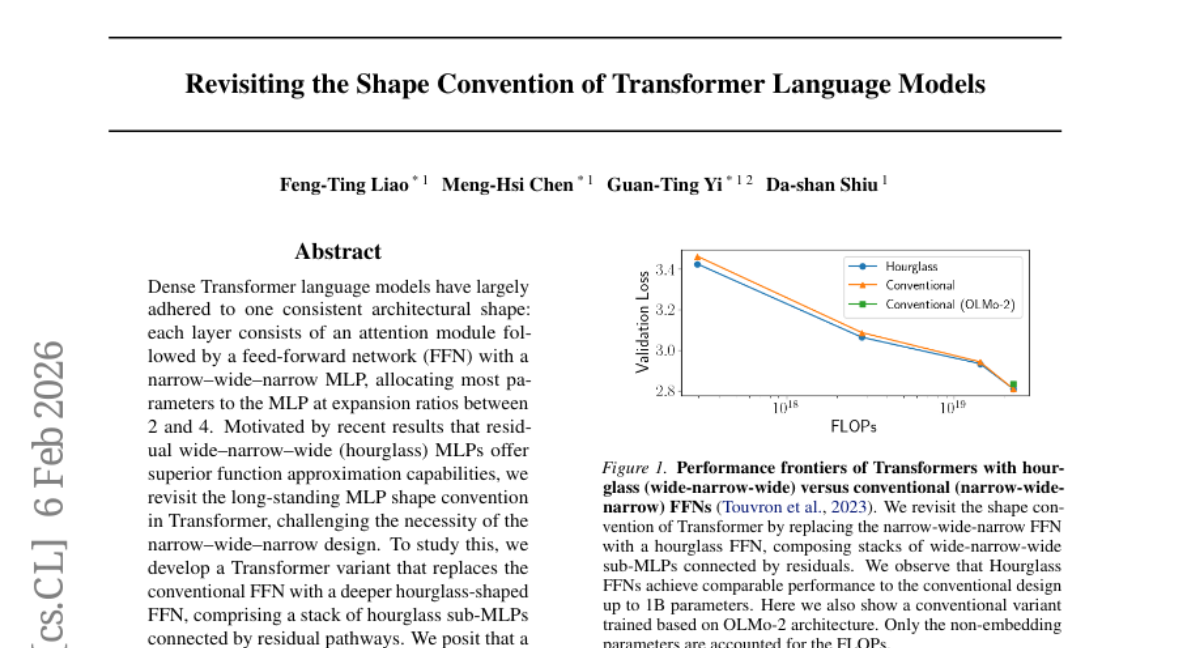
15. Revisiting the Shape Convention of Transformer Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Hourglass MLP, Transformers, Feed-Forward Network, Model Efficiency, Parameter Utilization
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the use of hourglass-shaped MLPs in replacing conventional FFNs within Transformers, examining their potential to enhance model efficiency and parameter utilization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a Transformer variant utilizing deeper hourglass-shaped FFNs connected by residual pathways, comparing its performance with traditional FFNs across various model scales.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Hourglass FFNs demonstrate superior performance to conventional FFNs in models up to 400M parameters and remain competitive in larger models up to 1B parameters. They also promote a better balance between attention and FFN parameters under fixed budgets, prompting a reevaluation of traditional MLP design conventions in modern language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06471
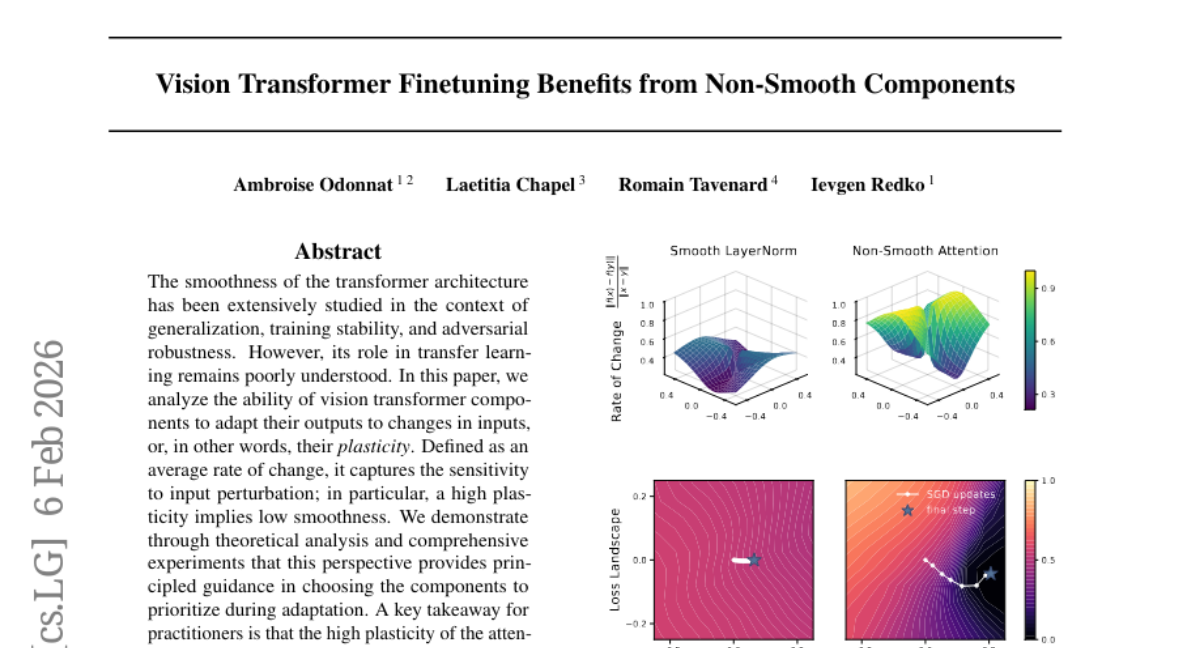
16. Vision Transformer Finetuning Benefits from Non-Smooth Components
🔑 Keywords: Vision Transformer, Plasticity, Smoothness, Finetuning Performance, Transfer Learning
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to analyze the plasticity of vision transformer components and its correlation with finetuning performance, particularly in the context of transfer learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs theoretical analysis combined with comprehensive experiments to evaluate the plasticity of attention modules and feedforward layers of vision transformers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research concludes that high plasticity in attention modules and feedforward layers of vision transformers leads to improved finetuning performance, challenging the traditional view that smoothness is always beneficial.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06883
17. Table-as-Search: Formulate Long-Horizon Agentic Information Seeking as Table Completion
🔑 Keywords: Table-as-Search, Information Seeking, Structured Planning, Table Completion, Search States
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve long-horizon search robustness by reformulating Information Seeking tasks as table completion problems using the Table-as-Search (TaS) framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The TaS framework structures search tasks into tables, with rows for search candidates and columns for constraints. It manages search states by recording history and search results in filled cells and proposes new search plans with empty cells.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TaS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in deep, wide, and deepwide search benchmarks. It demonstrates superior robustness, efficiency, scalability, and flexibility in long-horizon Information Seeking tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06724

18. Urban Spatio-Temporal Foundation Models for Climate-Resilient Housing: Scaling Diffusion Transformers for Disaster Risk Prediction
🔑 Keywords: diffusion-transformer framework, spatio-temporal urban data, climate-risk indicators, transportation-network structure, intelligent vehicles
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Skjold-DiT, a diffusion-transformer framework designed to predict building-level climate risks and incorporate transportation network structures for emergency response applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Skjold-DiT harnesses heterogeneous spatio-temporal urban data employing components like Fjell-Prompt for cross-city transfer, Norrland-Fusion for cross-modal attention mechanism integration, and Valkyrie-Forecast for counterfactual simulation to unify data into a shared latent representation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The introduction of the Baltic-Caspian Urban Resilience (BCUR) dataset allows for the evaluation of predictive capacity, cross-city adaptation, and calibration. It assesses outcomes such as reachability and hazard-conditioned travel times to assist intelligent-vehicle routing and emergency dispatch systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06129

19. SE-Bench: Benchmarking Self-Evolution with Knowledge Internalization
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, Self-Evolution, Knowledge Internalization, Open-Book Paradox, SE-Bench
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– SE-Bench aims to evaluate agents’ abilities to store and utilize novel knowledge without documentation, focusing on challenges in knowledge retention and internalization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces SE-Bench, a diagnostic environment that obfuscates the NumPy library, requiring agents to internalize a pseudo-novel API for simple coding tasks without access to documentation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Three key insights were found: training with reference documentation can inhibit knowledge retention (Open-Book Paradox), standard Reinforcement Learning struggles with knowledge internalization (RL Gap), and Self-Play proves viable for learning from self-generated tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04811

20. Avoiding Premature Collapse: Adaptive Annealing for Entropy-Regularized Structural Inference
🔑 Keywords: Optimal Transport, Premature Mode Collapse, Sinkhorn fixed-point map, gradient explosions, Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– This research aims to identify and address premature mode collapse in optimal transport-based structural prediction models by preventing gradient explosions during large-scale training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study uses an adaptive stability control algorithm called Efficient Piecewise Hybrid Adaptive Stability Control (EPH-ASC) to monitor the stability of the inference process and stabilize Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections during training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed algorithm, EPH-ASC, effectively prevents late-stage gradient explosions by enforcing a linear stability law, making it essential for stabilizing models during large-scale training.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.23039

21. AtlasPatch: An Efficient and Scalable Tool for Whole Slide Image Preprocessing in Computational Pathology
🔑 Keywords: AI-driven computational pathology, Whole-slide image, Tissue detection, Patch extraction, Segment-Anything model
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop an efficient and scalable framework, AtlasPatch, for whole-slide image preprocessing, enhancing tissue detection and patch extraction while minimizing computational overhead.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of the fine-tuned Segment-Anything model for tissue detection on a diverse dataset of approximately 30,000 WSI thumbnails and efficient parallelization across CPUs and GPUs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AtlasPatch achieves state-of-the-art performance in tissue detection and patch extraction with significantly reduced computational costs, offering an open-source solution for AI-driven computational pathology workflows.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03998

22.

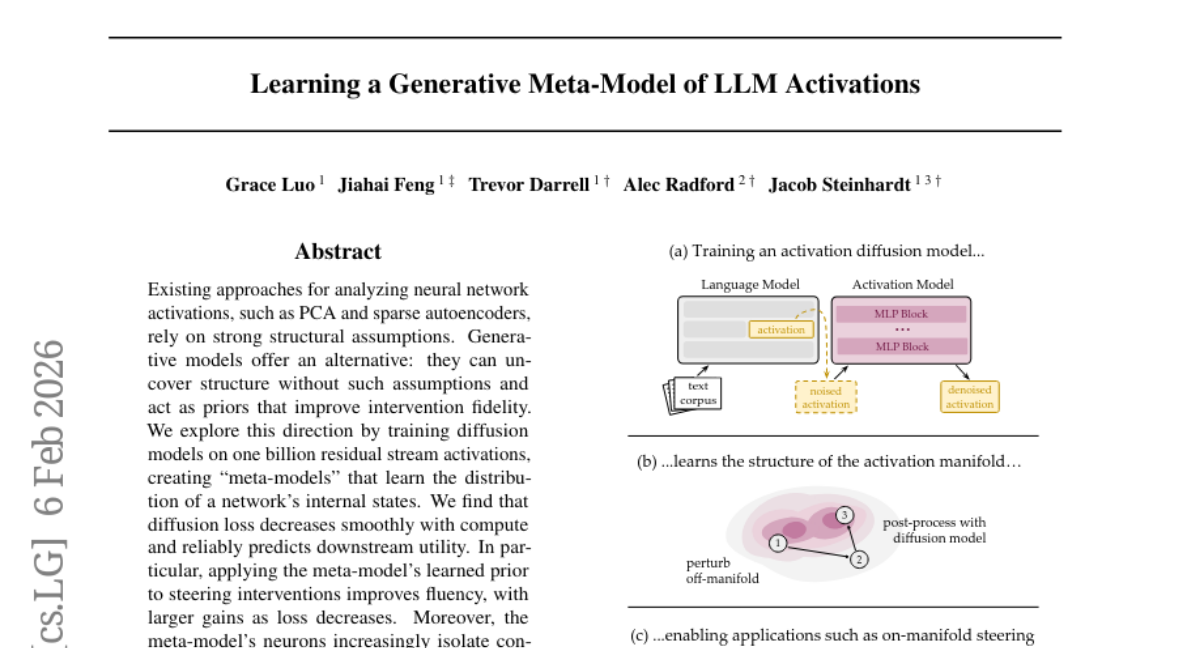
23. Learning a Generative Meta-Model of LLM Activations
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Generative Models, Diffusion Models, Meta-models, Intervention Fidelity
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to explore the creation of meta-models by training diffusion models on neural network activations to improve intervention fidelity without relying on conventional structural assumptions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Diffusion models are trained on one billion residual stream activations to uncover the distribution of a network’s internal states and learn a prior that enhances intervention processes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Results indicate that the decrease in diffusion loss correlates with improved downstream utility and fluency in interventions.
– Meta-model neurons show increased ability to isolate concepts into individual units, enhancing interpretability without restrictive assumptions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06964
24. Exploring Knowledge Purification in Multi-Teacher Knowledge Distillation for LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Knowledge Purification, Knowledge distillation, Large language models, Teacher models, Knowledge conflicts
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce and explore Knowledge Purification to resolve conflicts in multi-teacher large language model distillation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Propose and evaluate five distinct Knowledge Purification methods to consolidate rationales and improve distillation efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that purification methods enhance distilled model performance and reduce knowledge conflicts, with router-based methods showcasing strong generalization capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.01064

25. Seg-ReSearch: Segmentation with Interleaved Reasoning and External Search
🔑 Keywords: Seg-ReSearch, segmentation, interleaved reasoning, external search, hierarchical reward design
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce Seg-ReSearch, a novel segmentation approach that addresses the limitations of frozen MLLM knowledge and enhances performance on video object segmentation benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Seg-ReSearch combines interleaved reasoning and external search, and utilizes a hierarchical reward design to effectively train segmentation systems for dynamic, open-world queries.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Seg-ReSearch significantly improves the state-of-the-art in video object segmentation, as demonstrated by experiments on the challenging OK-VOS benchmark and other existing reasoning segmentation benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04454

26. SPARC: Separating Perception And Reasoning Circuits for Test-time Scaling of VLMs
🔑 Keywords: SPARC, vision-language models, visual perception, reasoning, test-time scaling
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To create a modular framework, SPARC, that decouples visual perception from reasoning in vision-language models to enhance test-time scaling and visual reasoning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implements a two-stage pipeline inspired by brain processing, where visual perception is separated from reasoning, allowing for targeted computational allocation and adaptability to varying computational needs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SPARC outperforms traditional monolithic vision-language models and strong visual-grounding approaches, showing improved accuracy on benchmarks like Qwen3VL-4B while reducing computational token budget significantly.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06566
27. SEAD: Self-Evolving Agent for Multi-Turn Service Dialogue
🔑 Keywords: SEAD framework, service dialogue agents, user modeling, task completion rate, dialogue efficiency
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance service dialogue agents by developing the SEAD framework, which allows agents to learn effective strategies without relying on large-scale human annotations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– This study decouples user modeling into a Profile Controller and a User Role-play Model, enabling agents to manage diverse training scenarios and simulate realistic role-playing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SEAD framework significantly outperforms existing models by improving task completion rate by 17.6% and dialogue efficiency by 11.1%, highlighting its superior performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03548

28. ReMiT: RL-Guided Mid-Training for Iterative LLM Evolution
🔑 Keywords: ReMiT, Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Mid-Training, Iterative Feedback Loop
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce a bidirectional training approach using ReMiT that enhances the pre-training and post-training performance of large language models through feedback loops.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed ReMiT that dynamically reweights tokens during the mid-training phase by leveraging RL-tuned model reasoning priors.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ReMiT achieved an average improvement of 3% on 10 pre-training benchmarks and sustained a gain of over 2% throughout the post-training pipeline, validating the iterative feedback approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03075

29. SeeUPO: Sequence-Level Agentic-RL with Convergence Guarantees
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, Reinforcement Learning, convergence guarantees, multi-turn scenarios, critic-free
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address the convergence issues of existing reinforcement learning algorithms in multi-turn agent interactions by introducing SeeUPO, a critic-free method with convergence guarantees.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Sequential decision-making in multi-turn scenarios is modeled as multi-agent bandit problems.
– Policy updates are conducted through backward induction to ensure monotonic improvement and convergence to the global optimal solution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SeeUPO demonstrates substantial improvements over existing algorithms, showing relative gains of 43.3%-54.6% on Qwen3-14B and 24.1%-41.9% on Qwen2.5-14B, along with superior training stability, proving the effectiveness of the proposed method.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06554

30. OmniVideo-R1: Reinforcing Audio-visual Reasoning with Query Intention and Modality Attention
🔑 Keywords: OmniVideo-R1, audio-visual understanding, multimodal reasoning, self-supervised learning, contrastive learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance audio-visual understanding through a novel framework that integrates self-supervised and contrastive learning for improved multimodal reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework utilizes query-intensive grounding based on self-supervised learning and modality-attentive fusion built upon contrastive learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OmniVideo-R1 consistently outperforms strong baselines on multiple benchmarks, demonstrating its effectiveness and robust generalization capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.05847

31. SEMA: Simple yet Effective Learning for Multi-Turn Jailbreak Attacks
🔑 Keywords: SEMA, multi-turn jailbreaks, adversarial prompts, Reinforcement Learning, AI safety
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces a novel framework, SEMA, designed to effectively train multi-turn attackers for large language models without relying on existing strategies or external data, aiming for high attack success rates.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– SEMA employs a two-stage process: Prefilling self-tuning and Reinforcement Learning with intent-drift-aware reward, which includes using self-generated multi-turn adversarial prompts for training while stabilizing learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SEMA achieves state-of-the-art attack success rates across multiple datasets and models, outperforming both single-turn and multi-turn baselines. It serves as a robust stress test for LLM safety, enabling more effective automatic redteaming to expose failure modes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06854

32. Group-Evolving Agents: Open-Ended Self-Improvement via Experience Sharing
🔑 Keywords: Group-Evolving Agents, open-ended self-improvement, evolutionary units, experience sharing, exploratory diversity
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Group-Evolving Agents (GEA), aiming to enhance open-ended self-improvement by treating groups of agents as fundamental evolutionary units, enabling efficient experience sharing and robust coding performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors evaluate GEA against challenging coding benchmarks, contrasting its performance with state-of-the-art self-evolving methods and human-designed agent frameworks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GEA significantly outperforms existing self-evolving paradigms and human-designed frameworks in coding tasks by effectively converting early-stage exploratory diversity into sustained progress and demonstrating consistent transferability and robustness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04837

33. compar:IA: The French Government’s LLM arena to collect French-language human prompts and preference data
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, Large Language Models, human preference data, multilingual model training, human-AI interaction
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop an open-source platform, compar:IA, to collect large-scale human preference data and improve performance in non-English languages for language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a blind pairwise comparison interface to gather human preferences from a predominantly French-speaking audience, enabling evaluation across diverse language models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– compar:IA has successfully gathered significant preference data and prompts, especially in French, and has released datasets under open licenses. It serves as an international digital public good, facilitating multilingual language model training and evaluation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06669

34. InftyThink+: Effective and Efficient Infinite-Horizon Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Iterative Reasoning, Summarization, Chain-of-Thought, Inference Latency
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Improve accuracy and efficiency in large language models through the optimization of iterative reasoning processes using InftyThink+.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a reinforcement learning framework with a two-stage training scheme, starting with supervised learning followed by trajectory-level reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– InftyThink+ improves accuracy by 21% on AIME24, outperforms traditional methods, reduces inference latency, and enhances reasoning efficiency while generalizing better to out-of-distribution benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06960

35. EgoAVU: Egocentric Audio-Visual Understanding
🔑 Keywords: Multi-modal large language models, EgoAVU, audio-visual narrations, Token-based video filtering, cross-modal correlation modeling
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the joint understanding of audio and visual signals in egocentric videos by multi-modal large language models using a new scalable data engine and dataset called EgoAVU.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of EgoAVU, a scalable data engine to generate audio-visual narrations, questions, and answers, utilizing cross-modal correlation modeling and Token-based video filtering.
– Development of a large-scale training dataset EgoAVU-Instruct and an evaluation split EgoAVU-Bench for performance assessment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EgoAVU-Bench highlights existing MLLMs’ bias towards visual signals neglecting audio cues. Fine-tuning with EgoAVU-Instruct results in up to 113% improvement, with benefits extending to other benchmarks like EgoTempo and EgoIllusion.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06139

36. MemGUI-Bench: Benchmarking Memory of Mobile GUI Agents in Dynamic Environments
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, memory-centric benchmark, LLM-as-judge evaluation, state-of-the-art agents, design implications
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address memory capability gaps in mobile GUI agents by introducing MemGUI-Bench, a benchmark focusing on comprehensive memory assessment.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– 128 tasks across 26 applications are designed to challenge memory via cross-temporal and cross-spatial retention. A systematic memory taxonomy was used, evaluating 11 agents across 5 architectures, supplemented by an automated pipeline with Progressive Scrutiny and 7 hierarchical metrics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The experiments identified significant memory deficits across the systems tested, revealed 5 distinct failure modes, and synthesized 5 actionable design implications, with all resources made fully open-sourced for further research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06075
37. POINTS-GUI-G: GUI-Grounding Journey
🔑 Keywords: GUI agents, vision-language models, GUI grounding, Reinforcement Learning, Data Engineering
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop GUI agents with enhanced grounding abilities for automating digital tasks, starting from base models with minimal initial grounding capability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ refined data engineering including augmentation, filtering, and difficulty grading.
– Apply improved training strategies focusing on continuous fine-tuning and resolution consistency.
– Integrate Reinforcement Learning with verifiable rewards to boost GUI grounding accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The newly introduced POINTS-GUI-G-8B model achieves state-of-the-art performance in GUI agent tasks, proving the effectiveness of the integrated data engineering, training strategies, and reinforcement learning approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06391

38. Judging What We Cannot Solve: A Consequence-Based Approach for Oracle-Free Evaluation of Research-Level Math
🔑 Keywords: Consequence-Based Utility, reasoning models, oracle-free evaluator, LLM judges, correct-wrong separation
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve the evaluation of mathematical solutions by introducing a method that assesses their utility in solving related problems, thereby optimizing their selection based on quality and accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study proposes Consequence-Based Utility, an oracle-free approach that evaluates candidate solutions by testing their applicability as exemplars in solving verifiable similar questions. It evaluates this methodology on research-level math problems with both expert and LLM-generated solutions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Consequence-Based Utility outperforms traditional reward models and LLM judges in ranking solution quality and ensuring stronger correct-wrong separation, demonstrated by improved Acc@1 and AUC metrics, notably for models like GPT-OSS-120B.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06291

39. DreamDojo: A Generalist Robot World Model from Large-Scale Human Videos
🔑 Keywords: DreamDojo, world model, continuous latent actions, real-time distillation, robotic tasks
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop a foundation world model, DreamDojo, which is designed to simulate dexterous robotic tasks effectively by leveraging 44k hours of egocentric human videos.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach involves utilizing continuous latent actions to handle the scarcity of action labels and a distillation pipeline to achieve real-time performance, enhancing the transfer of interaction knowledge from unlabeled videos.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DreamDojo displays a nuanced understanding of physics and precise action control, facilitating applications such as live teleoperation, policy evaluation, and model-based planning. It is validated through systematic evaluation on challenging out-of-distribution benchmarks, indicating its potential for developing general-purpose robotic models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06949
40. MSign: An Optimizer Preventing Training Instability in Large Language Models via Stable Rank Restoration
🔑 Keywords: large language models, training instability, gradient explosions, MSign, Jacobian alignment
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study examines training failures in large language models, specifically targeting instability and gradient explosions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers identified two phenomena causing training collapse: decline in weight matrix stable rank and increasing alignment between layer Jacobians. They proposed MSign, an optimizer that applies matrix sign operations to maintain stable rank.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments confirmed that MSign effectively prevents training failures in models ranging from 5M to 3B parameters with less than 7.0% computational overhead.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.01734

41. AudioSAE: Towards Understanding of Audio-Processing Models with Sparse AutoEncoders
🔑 Keywords: Sparse Autoencoders, Whisper, HuBERT, Feature Steering, EEG Activity
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research investigates the effectiveness of Sparse Autoencoders trained on Whisper and HuBERT models in extracting and disentangling acoustic and semantic information in audio processing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Training Sparse Autoencoders across all encoder layers of Whisper and HuBERT models, evaluating their stability, interpretability, and practical utility in audio processing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Sparse Autoencoders achieve over 50% feature consistency across random seeds and preserve reconstruction quality.
– SAE features capture and disentangle general acoustic, semantic information, and specific audio events effectively.
– Feature steering reduces Whisper’s false speech detections by 70% with minimal increase in Word Error Rate (WER).
– SAE features correlate with human EEG activity during speech perception, aligning them with human neural processing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.05027

42. Baichuan-M3: Modeling Clinical Inquiry for Reliable Medical Decision-Making
🔑 Keywords: Baichuan-M3, large language model, clinical decision support, long-horizon reasoning, hallucination suppression
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop Baichuan-M3, a medical-enhanced large language model that shifts from passive question-answering to active clinical decision support with improved capabilities like long-horizon reasoning and proactive information gathering.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a specialized training pipeline modeling the physician’s workflow, incorporating features like proactive information acquisition, long-horizon reasoning, and adaptive hallucination suppression.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Baichuan-M3 achieves state-of-the-art results on several health-related benchmarks, significantly outperforming GPT-5.2 in clinical inquiry, advisory, and safety, and is publicly available on Hugging Face.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06570
