AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250407

1. Multi-SWE-bench: A Multilingual Benchmark for Issue Resolving
🔑 Keywords: Multi-SWE-bench, Large Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, AGI
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a multilingual issue-resolving benchmark called Multi-SWE-bench to evaluate LLMs across diverse software ecosystems.
– Launch the Multi-SWE-RL community to facilitate RL dataset construction for issue-resolving tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development and evaluation of Multi-SWE-bench featuring 1,632 instances across multiple programming languages.
– Analysis using state-of-the-art models with various methods including Agentless, SWE-agent, and OpenHands.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The introduction of Multi-SWE-bench and Multi-SWE-RL sets a foundation for future RL research.
– Open-source data production pipeline and tutorials aim to catalyze community contributions to the dataset, advancing RL towards AGI.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.02605

2. MegaMath: Pushing the Limits of Open Math Corpora
🔑 Keywords: Mathematical reasoning, Large Language Models, MegaMath, Open Dataset, Math Pre-training
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address the need for an open, large-scale, high-quality corpus tailored for math-centric pre-training in large language models (LLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Re-extracting mathematical documents from web data with HTML optimizations, fasttext-based filtering, and deduplication for higher-quality data.
– Identifying high-quality math-related code from a large code training corpus, enhancing data diversity.
– Synthesizing QA-style text, math-related code, and interleaved text-code blocks from web or code data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MegaMath provides 371 billion tokens, offering the largest and highest quality available among open math pre-training datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.02807

3. Agentic Knowledgeable Self-awareness
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Agentic Planning, Self-awareness, KnowSelf, Data-centric Approach
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces agentic knowledgeable self-awareness to enable LLM-based agents to regulate knowledge use autonomously.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A data-centric approach called KnowSelf is proposed, along with a heuristic situation judgement criterion to mark special tokens for training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– KnowSelf demonstrates superior performance across various tasks and models, achieving optimal planning with minimal external knowledge.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.03553
4. SynWorld: Virtual Scenario Synthesis for Agentic Action Knowledge Refinement
🔑 Keywords: LLM-based agents, multi-step action invocation, Monte Carlo Tree Search, SynWorld
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To empower LLM-based agents to autonomously explore environments and enhance their understanding of actions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of SynWorld framework using multi-step action invocation and Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) for action knowledge refinement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SynWorld proves to be an effective and general approach for learning action knowledge in new environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.03561
5. MME-Unify: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation Models
🔑 Keywords: Unified MLLMs, Multimodal Reasoning, Benchmarks, Evaluation Framework
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to create a comprehensive evaluation framework to systematically assess Unified MLLMs (U-MLLMs), addressing the challenges in benchmarking traditional and mixed-modality tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors propose a new benchmark including standardization of traditional tasks from 12 datasets covering 30 subtasks, introduction of five novel tasks for multimodal reasoning, and comprehensive model benchmarking on 12 leading U-MLLMs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study identifies significant performance gaps in existing U-MLLMs, emphasizing the necessity for more robust models that can effectively handle mixed-modality tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.03641
6. VARGPT-v1.1: Improve Visual Autoregressive Large Unified Model via Iterative Instruction Tuning and Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: VARGPT-v1.1, visual autoregressive model, reinforcement learning, Qwen2, image editing
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance VARGPT with advanced capabilities for unified visual understanding, generation, and image editing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– An integration of iterative visual instruction tuning with reinforcement learning using Direct Preference Optimization (DPO).
– Utilization of an expanded corpus of 8.3 million visual-generative instruction pairs and an upgraded language model backbone using Qwen2.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VARGPT-v1.1 achieves state-of-the-art performance in multimodal understanding and text-to-image instruction-following tasks.
– The model demonstrates significant improvements in comprehension and generation metrics, highlighting its potential for effective scalability and flexibility in training strategies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.02949

7. APIGen-MT: Agentic Pipeline for Multi-Turn Data Generation via Simulated Agent-Human Interplay
🔑 Keywords: AI Agents, Multi-Turn Interactions, APIGen-MT, Simulated Human-Agent Interplay, xLAM-2-fc-r
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop an effective framework, APIGen-MT, which generates high-quality, diverse multi-turn agent data for training AI agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementing a two-phase framework involving agentic pipeline for task blueprints and simulated human-agent interactions to create interaction trajectories. Training diverse models ranging from 1B to 70B parameters.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework successfully produces high-quality data, outperforms existing models like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5, and offers improved efficiency in multi-turn settings, with open-sourced models and data to facilitate further research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.03601

8. ShieldAgent: Shielding Agents via Verifiable Safety Policy Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Autonomous agents, Foundation models, Privacy breaches, ShieldAgent, Safety policy compliance
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose ShieldAgent, a guardrail agent designed to enforce explicit safety policy compliance for action trajectories of protected agents using logical reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Constructing a safety policy model with action-based probabilistic rule circuits and generating shielding plans for agents’ trajectories.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ShieldAgent achieves state-of-the-art results, reducing API queries and inference time significantly while maintaining high precision and efficiency in safeguarding autonomous agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2503.22738

9. TransMamba: Flexibly Switching between Transformer and Mamba
🔑 Keywords: Transformers, state space model, TransMamba, attention, sequence modeling
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper proposes TransMamba, a novel framework unifying Transformers and the Mamba state space model, aiming to enhance efficiency in sequence processing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces shared parameter matrices for dynamic switching between attention and SSM mechanisms, along with a Memory converter for seamless transitioning.
– Explores TransPoint scheduling for optimizing information integration.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TransMamba demonstrates superior training efficiency and performance over baselines, validating its potential as a scalable solution for next-generation sequence modeling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2503.24067

10. Comprehensive Relighting: Generalizable and Consistent Monocular Human Relighting and Harmonization
🔑 Keywords: Comprehensive Relighting, image prior, coarse-to-fine framework, diffusion models
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a generalizable model capable of both controlling and harmonizing lighting in images or videos of humans.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a pre-trained diffusion model as a general image prior and employed a coarse-to-fine framework.
– Introduced an unsupervised temporal lighting model to learn lighting cycle consistency.
– Combined temporal lighting with diffusion models using spatio-temporal feature blending; implemented guided refinement for high-frequency detail preservation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed Comprehensive Relighting approach shows strong generalizability and temporal coherence in lighting, outperforming existing methods for human relighting and harmonization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.03011

11. HumanDreamer-X: Photorealistic Single-image Human Avatars Reconstruction via Gaussian Restoration
🔑 Keywords: HumanDreamer-X, HumanFixer, PSNR, attention modulation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve single-image human reconstruction by enhancing geometric consistency and visual fidelity in 3D models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introducing a new framework, HumanDreamer-X, integrating multi-view human generation and reconstruction with 3D Gaussian Splatting as a representation method.
– Utilizing HumanFixer to restore renderings for photorealistic results and proposing an attention modulation strategy to enhance geometric identity consistency across multi-views.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach improves generation and reconstruction quality metrics (PSNR) by 16.45% and 12.65% respectively, achieving up to 25.62 dB. The method also demonstrates generalization capabilities and applicability to various human reconstruction models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.03536

12. EvMic: Event-based Non-contact sound recovery from effective spatial-temporal modeling
🔑 Keywords: Event Camera, High-Frequency Signals, Sound Recovery, Spatial-Temporal Information, Laser Matrix
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose a novel pipeline for non-contact sound recovery utilizing event camera data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Created a large training set with a novel simulation pipeline and designed a network leveraging event sparsity and Mamba for modeling temporal information. A spatial aggregation block was trained alongside an imaging system using a laser matrix for enhanced data collection.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method effectively recovers sound, as evidenced by experimental results on both synthetic and real-world data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.02402
13. MedSAM2: Segment Anything in 3D Medical Images and Videos
🔑 Keywords: 3D Image Segmentation, Medical Imaging, Segmentation Foundation Model, Human-in-the-loop, Cloud Deployment
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to create a promptable segmentation model for 3D image and video segmentation in precision medicine.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MedSAM2 was fine-tuned using a large dataset of over 455,000 3D image-mask pairs and 76,000 frames.
– Incorporates a human-in-the-loop pipeline for annotating medical image data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MedSAM2 outperforms previous models across various organs, lesions, and imaging modalities, reducing manual costs by over 85%.
– The tool is integrated into user-friendly platforms for local and cloud use, enhancing scalability and efficiency in healthcare and research environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.03600

14. BEATS: Bias Evaluation and Assessment Test Suite for Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Bias, Ethics, Fairness, Factuality, Responsible AI
💡 Category: AI Ethics and Fairness
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduction of the BEATS framework to evaluate Bias, Ethics, Fairness, and Factuality in Large Language Models (LLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a bias benchmark with 29 distinct metrics addressing demographic, cognitive, and social biases, along with ethical reasoning, group fairness, and factuality related misinformation risk.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Empirical results indicate significant bias in 37.65% of outputs from leading industry models, underscoring the risk in using these models for critical decision-making systems. The BEATS framework helps in diagnosing bias drivers and develops mitigation strategies, aiming for more socially responsible and ethically aligned AI models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2503.24310

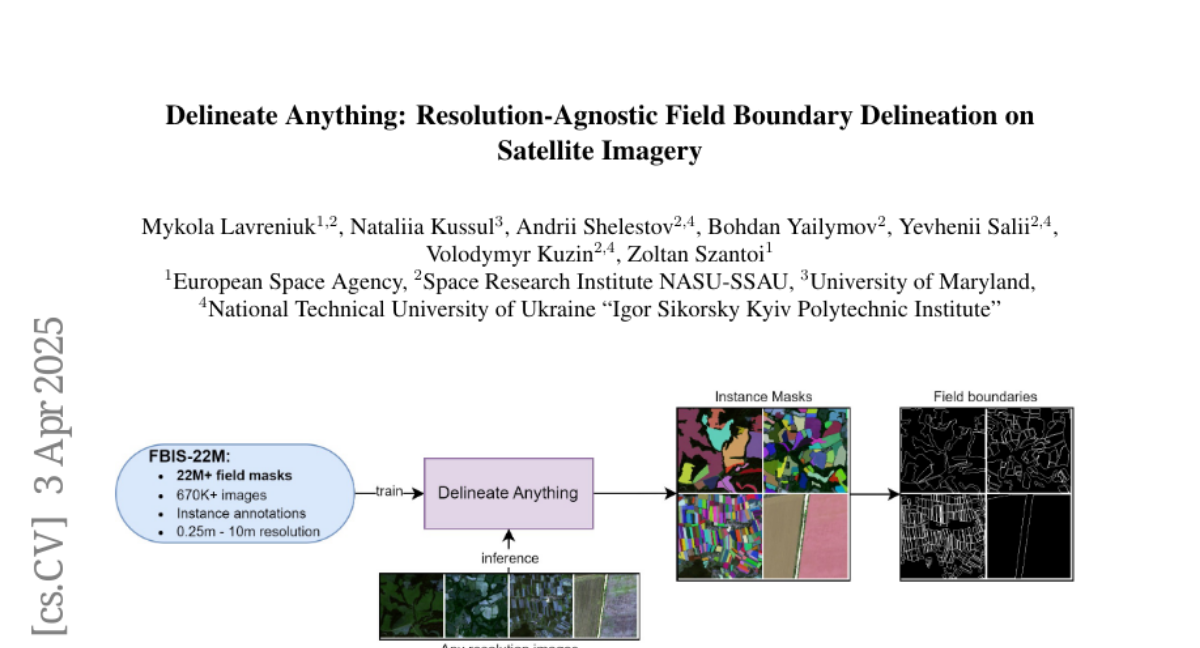
15. Delineate Anything: Resolution-Agnostic Field Boundary Delineation on Satellite Imagery
🔑 Keywords: Instance Segmentation, Satellite Imagery, Agricultural Field Boundaries, Zero-Shot Generalization, AI Native
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Reformulate the delineation of agricultural field boundaries using instance segmentation and introduce the large-scale FBIS-22M dataset.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop Delineate Anything, an instance segmentation model utilizing the FBIS-22M dataset, consisting of 672,909 image patches and 22,926,427 instance masks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed model achieves a new state-of-the-art with significant improvements in mAP metrics and offers faster inference and strong zero-shot generalization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.02534
16. Real-is-Sim: Bridging the Sim-to-Real Gap with a Dynamic Digital Twin for Real-World Robot Policy Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: Behavior Cloning, Dynamic Digital Twin, Real-World Applications, Simulator
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve the assessment of training performance in behavior cloning for robots by introducing a new framework named real-is-sim.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The proposed framework integrates a dynamic digital twin throughout policy development, including data collection, training, and deployment, by aligning simulations with the real world.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Validation on the PushT manipulation task shows that the success rates achieved in the simulator strongly correlate with real-world performance, offering a more practical evaluation approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.03597

17. SPF-Portrait: Towards Pure Portrait Customization with Semantic Pollution-Free Fine-tuning
🔑 Keywords: Semantic Pollution, Text-to-Image, Contrastive Learning, Semantic-Aware Fine Control Map, AI Native
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to eliminate Semantic Pollution while fine-tuning pre-trained Text-to-Image models for text-driven portrait customization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors introduce SPF-Portrait with a dual-path pipeline using contrastive learning and a Semantic-Aware Fine Control Map to spatially guide alignment, maintaining the original model’s performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SPF-Portrait achieves state-of-the-art performance by effectively preserving original model behavior and enhancing target attribute performance through a novel response enhancement mechanism.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.00396

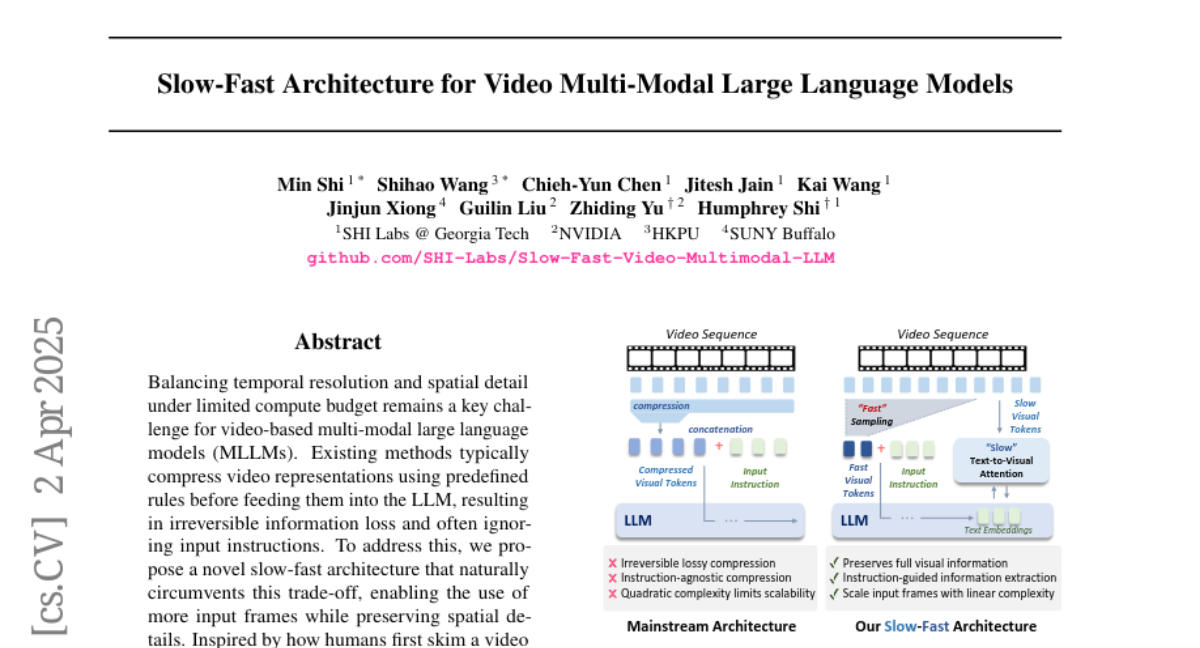
18. Slow-Fast Architecture for Video Multi-Modal Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Slow-Fast Architecture, Multi-Modal Large Language Models, Video Understanding
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the challenge of balancing temporal resolution and spatial detail under limited compute budgets in video-based multi-modal large language models (MLLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposed a novel slow-fast architecture using a dual-token strategy to optimize the input frames and preserve spatial details without irreversible information loss.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed model extends the input capacity significantly while maintaining computational efficiency, outperforming self-attention-only baselines and achieving state-of-the-art performance on video understanding benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.01328
19.
