AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250512
1. Bielik v3 Small: Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: parameter-efficient, Polish language processing, generative text models, token efficiency, Adaptive Learning Rate
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To optimize parameter-efficient generative text models for Polish language processing, achieving high performance with fewer computational resources.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a custom Polish tokenizer (APT4) to improve token efficiency.
– Implementation of Weighted Instruction Cross-Entropy Loss to balance learning.
– Use of Adaptive Learning Rate to dynamically adjust based on training progress.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Smaller, well-optimized generative models (1.5B and 4.5B parameters) can achieve performance comparable with much larger models.
– These models establish new benchmarks in parameter-efficient language modeling for less-represented languages like Polish.
– The 4.5B model achieves competitive results with models 2-3 times its size, and the 1.5B model maintains strong performance in a compact profile.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.02550

2. Bielik 11B v2 Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Bielik 11B v2, Polish text processing, Weighted Instruction Cross-Entropy Loss, Adaptive Learning Rate
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to optimize a language model, Bielik 11B v2, for Polish text processing, exhibiting exceptional performance across Polish language benchmarks with strong cross-lingual abilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model leverages two key innovations: Weighted Instruction Cross-Entropy Loss, which optimizes learning using quality-based weights on diverse instruction types, and Adaptive Learning Rate, which adjusts dynamically based on context length.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Bielik 11B v2 outperforms larger models with significantly fewer parameters, especially in tasks requiring linguistic understanding and complex reasoning, while being efficient in terms of parameter usage and versatile in deploying across various hardware configurations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.02410

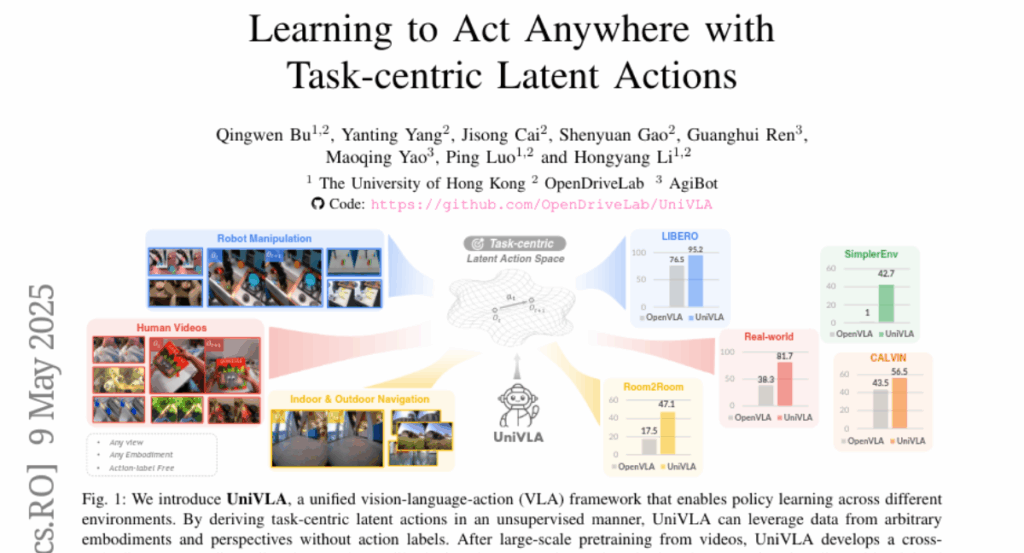
3. UniVLA: Learning to Act Anywhere with Task-centric Latent Actions
🔑 Keywords: UniVLA, vision-language-action, latent action model, DINO feature space, scalable robot policy learning
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper presents UniVLA, a framework to learn cross-embodiment vision-language-action (VLA) policies, addressing limitations of existing methods constrained by single physical specifications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– UniVLA derives task-centric action representations from videos utilizing a latent action model, incorporating language instructions, and establishing a latent action model within the DINO feature space.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UniVLA achieves state-of-the-art results in manipulation and navigation benchmarks, is efficient in deployment on various robots, and outperforms previous frameworks with significantly reduced pretraining compute and data requirements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.06111
4. G-FOCUS: Towards a Robust Method for Assessing UI Design Persuasiveness
🔑 Keywords: Design Persuasiveness, Vision-Language Models, Pairwise UI Evaluation, G-FOCUS
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce and validate an approach for evaluating user interface (UI) design persuasiveness beyond traditional aesthetic considerations, focusing on comparative effectiveness using Vision-Language Models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A benchmark named WiserUI-Bench is introduced for Pairwise UI Design Persuasiveness Assessment, featuring 300 labeled real-world UI image pairs. Additionally, a novel inference strategy called G-FOCUS is proposed to enhance evaluation accuracy and reduce position bias during VLM-based assessments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results indicate that G-FOCUS improves upon existing inference methodologies by enhancing consistency and accuracy in pairwise UI evaluation. This approach aims to augment traditional A/B testing by offering a scalable model for UI preference modeling and design optimization, with plans for publicly releasing the associated code and data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.05026

5. Sailing AI by the Stars: A Survey of Learning from Rewards in Post-Training and Test-Time Scaling of Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Learning from Rewards, Reinforcement Learning, Active Learning, Reward Models
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To provide a comprehensive overview of the paradigm of Learning from Rewards in the context of Large Language Models (LLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper categorizes and analyzes strategies across training, inference, and post-inference stages and discusses benchmarks for reward models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The survey highlights the challenges and future directions in enabling LLMs transition from passive to active learning with aligned preferences and deep reasoning capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.02686

6. Healthy LLMs? Benchmarking LLM Knowledge of UK Government Public Health Information
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, public health information, PubHealthBench, Multiple Choice Question Answering, free form responses
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To understand the domain-specific knowledge of Large Language Models (LLMs) in UK public health and assess their ability to provide relevant, accurate, and current information.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a new benchmark, PubHealthBench, featuring over 8000 questions for evaluating LLMs in both Multiple Choice Question Answering (MCQA) and free form responses to public health queries.
– Creation of an automated pipeline to develop these queries and the release of a dataset comprising extracted UK Government public health guidance documents.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The latest private LLMs like GPT-4.5 and GPT-4.1 show high accuracy in MCQA, outperforming humans using search engines.
– There is lower performance in free form responses, indicating additional safeguards or tools may be necessary for accurately providing public health information.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.06046

7. A Preliminary Study for GPT-4o on Image Restoration
🔑 Keywords: GPT-4o, multi-modal, image restoration, visual priors
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper investigates GPT-4o’s performance and impact on various image restoration tasks within the image restoration community.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Systematic evaluation of GPT-4o’s outputs across diverse restoration tasks and case studies on image dehazing, derainning, and low-light enhancement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Although visually appealing, GPT-4o’s restoration outputs often lack pixel-level structural fidelity compared to ground-truth images.
– GPT-4o’s outputs, serving as visual priors, can significantly enhance existing dehazing networks, and the study provides practical guidelines for integration into future image restoration pipelines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.05621

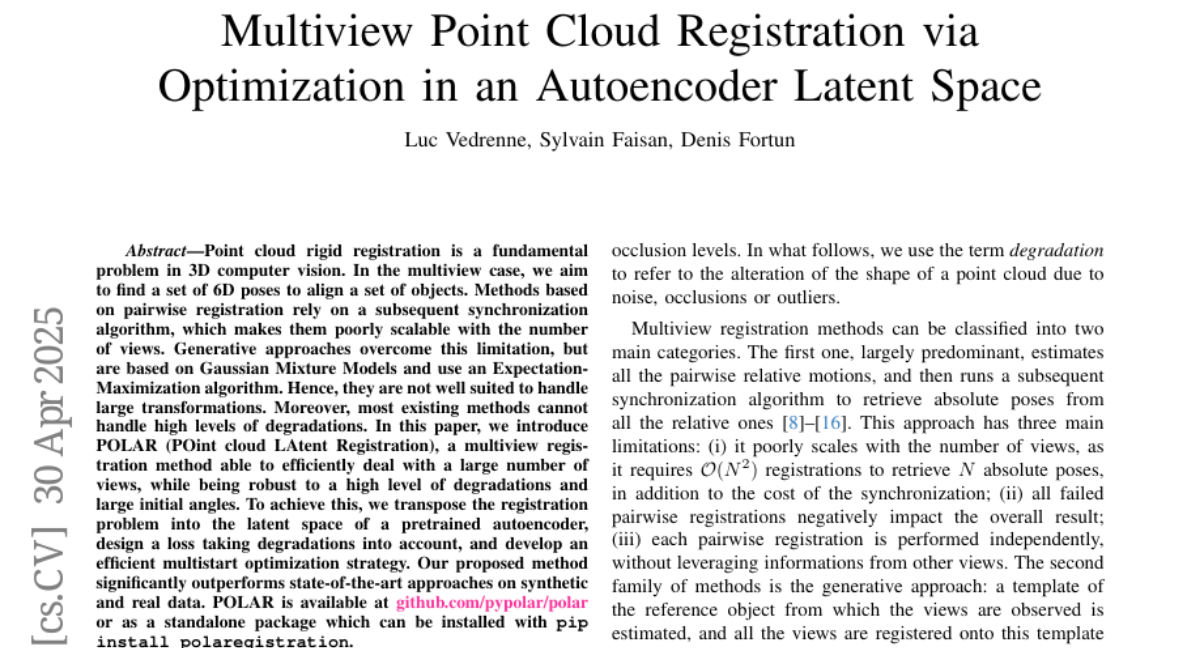
8. Multiview Point Cloud Registration via Optimization in an Autoencoder Latent Space
🔑 Keywords: Point cloud rigid registration, multiview case, 6D poses, latent space, pretrained autoencoder
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce POLAR, a multiview registration method for efficiently handling a large number of views, robust against high levels of degradations and large initial angles in 3D computer vision.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Transposing the registration problem into the latent space of a pretrained autoencoder and designing a loss function that takes into account degradations, along with developing an efficient multistart optimization strategy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– POLAR significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches on both synthetic and real data, offering a scalable and robust solution for multiview point cloud registration, and is available as an open-source package.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.21467
9.
