AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250605

1. MiMo-VL Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: MiMo-VL-7B-SFT, MiMo-VL-7B-RL, Multimodal Reasoning, Mixed On-policy Reinforcement Learning, Chain-of-Thought
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop and open-source two state-of-the-art vision-language models, MiMo-VL-7B-SFT and MiMo-VL-7B-RL, that excel in general visual understanding and multimodal reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized four-stage pre-training on 2.4 trillion tokens combined with Mixed On-policy Reinforcement Learning, incorporating high-quality reasoning data and diverse reward signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MiMo-VL-7B-RL significantly outperforms larger models, including Qwen2.5-VL-7B, across 35 out of 40 tasks and sets new performance benchmarks in GUI grounding applications, highlighting the efficacy of mixed RL and long Chain-of-Thought data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03569

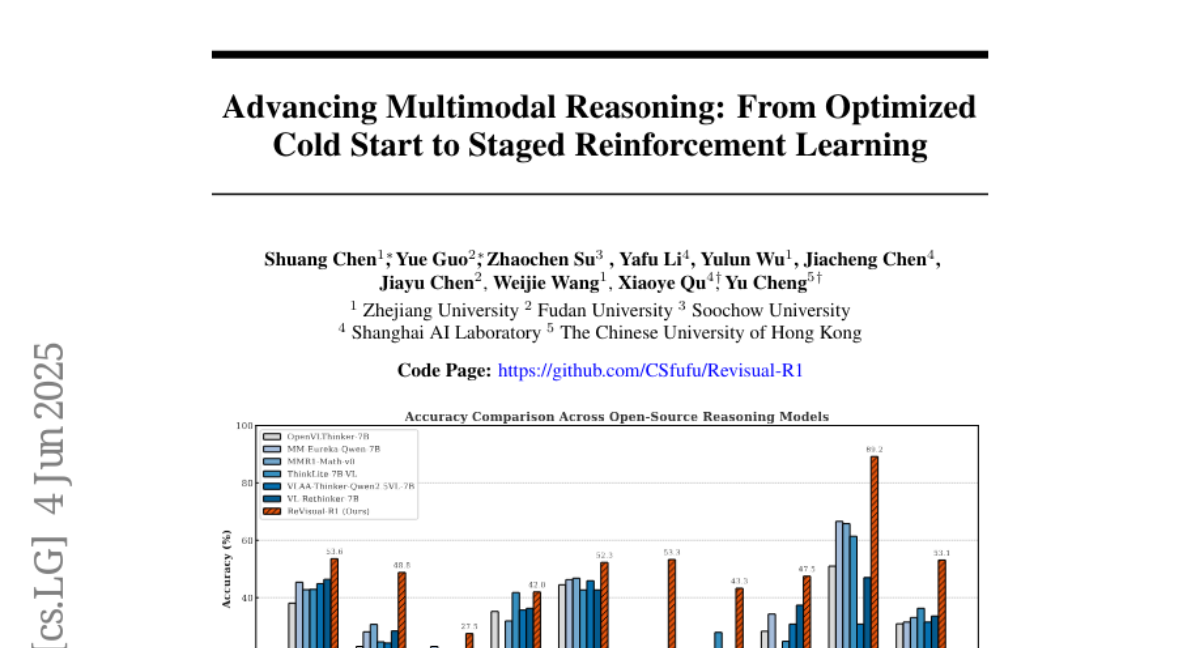
2. Advancing Multimodal Reasoning: From Optimized Cold Start to Staged Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Large Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, Cold Start Initialization, Multimodal Reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance reasoning capabilities in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by examining and improving current training pipelines.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Investigated the impact of effective cold start initialization with exclusively text data.
– Identified issues such as gradient stagnation in standard GRPO within multimodal RL.
– Employed a staged training method incorporating text-only RL post multimodal RL phase.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Found that carefully selected text data initialization can improve MLLM performance, even outperforming some recent models before applying multimodal RL.
– Highlighted that sequential multimodal followed by text-only RL phases significantly enhance MLLM reasoning capabilities.
– Introduced ReVisual-R1 achieving state-of-the-art performance on several challenging benchmarks for open-source 7B MLLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04207
3. AmbiK: Dataset of Ambiguous Tasks in Kitchen Environment
🔑 Keywords: Ambiguous Instructions, Large Language Models, AmbiK, Human-validated, Dataset
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to provide a unified platform, AmbiK, for comparing ambiguity detection methods in kitchen robots by collecting and validating ambiguous instructions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers utilized Large Language Models to assist in collecting and human-validating a dataset. The dataset contains 1000 pairs of ambiguous tasks and their unambiguous counterparts, categorized by ambiguity type.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The dataset, AmbiK, is expected to enable researchers to perform comprehensive comparisons of current and future task ambiguity detection methods in autonomous systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04089

4. A Controllable Examination for Long-Context Language Models
🔑 Keywords: LongBioBench, long-context language models, seamless context, controllable setting, sound evaluation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces LongBioBench, a benchmark designed to evaluate long-context language models across understanding, reasoning, and trustworthiness dimensions by using artificially generated biographies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized controlled settings with 18 long-context language models for experimental evaluation to test semantic understanding, reasoning, and trustworthiness as context lengths increase.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LongBioBench shows a better trade-off between mirroring authentic language tasks and maintaining controllability compared to previous synthetic benchmarks. Most models showed deficiencies in semantic understanding and elementary reasoning and became less trustworthy with longer context lengths.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.02921

5. MMR-V: What’s Left Unsaid? A Benchmark for Multimodal Deep Reasoning in Videos
🔑 Keywords: MMR-V, Multimodal Reasoning, Multi-frame Reasoning, AI-Generated Summary, Chain-of-Thought
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces MMR-V, a new benchmark designed to challenge multimodal large language models in long-range, multi-frame reasoning and hidden information processing in videos.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The MMR-V benchmark involves tasks requiring models to infer and analyze evidence frames distant from the question frame, beyond direct perception through reasoning over hidden information.
– Manual annotation of tasks for reliability, referencing real-world user understanding to align with common perceptions, and inclusion of distractors to reduce model shortcuts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments show that current models, including the best-performing o4-mini, struggle with multimodal reasoning, achieving only 52.5% accuracy.
– Existing reasoning enhancement strategies like Chain-of-Thought offer limited improvements due to differences between multi-modal and textual reasoning requirements.
– MMR-V aims to inspire further research to improve multimodal reasoning capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04141

6. SuperWriter: Reflection-Driven Long-Form Generation with Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: SuperWriter-Agent, Long-form text generation, AI-generated summary, Hierarchical Direct Preference Optimization, Monte Carlo Tree Search
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the quality and consistency of long-form text generation in large language models using the SuperWriter-Agent framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of structured planning and refinement stages into the generation pipeline.
– Training a 7B SuperWriter-LM model with a supervised fine-tuning dataset.
– Development of a hierarchical Direct Preference Optimization procedure using Monte Carlo Tree Search.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SuperWriter-LM achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing larger baseline models in automatic and human evaluations.
– Hierarchical Direct Preference Optimization and structured thinking steps significantly improve the quality of long-form text generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04180

7. Establishing Trustworthy LLM Evaluation via Shortcut Neuron Analysis
🔑 Keywords: shortcut neurons, data contamination, trustworthy evaluation, Large Language Models, benchmarks
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– This research aims to tackle data contamination in large language models by analyzing the mechanisms of contaminated models themselves.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors propose a novel method for identifying shortcut neurons through comparative and causal analysis.
– They introduce an evaluation method called shortcut neuron patching to suppress these shortcut neurons.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in mitigating contamination, with a high Spearman coefficient correlation exceeding 0.95 against a trustworthy benchmark, MixEval.
– The method demonstrates strong generalizability across various benchmarks and hyperparameter settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04142
8. OpenThoughts: Data Recipes for Reasoning Models
🔑 Keywords: OpenThoughts project, Reasoning models, Open-source datasets, AIME, LiveCodeBench
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective of the OpenThoughts project is to develop open-source datasets for training reasoning models that can match or exceed the current benchmarks in math, code, and science domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Systematic investigation and enhancement of each step in the data generation pipeline with over 1,000 controlled experiments, leading to the creation of improved datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The OpenThoughts project successfully developed datasets and models, notably OpenThinker3-7B, achieving state-of-the-art results on standard reasoning benchmarks such as AIME and LiveCodeBench, with significant percentages recorded such as 53% on AIME 2025.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04178

9. IllumiCraft: Unified Geometry and Illumination Diffusion for Controllable Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: IllumiCraft, diffusion framework, 3D point tracks, HDR video maps
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– IllumiCraft aims to generate high-fidelity, temporally coherent videos by integrating geometric cues within a diffusion framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves using three complementary inputs: HDR video maps for lighting control, synthetically relit frames for appearance cues, and precise 3D point tracks for geometric information.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– IllumiCraft achieves superior fidelity and coherence in video generation compared to existing methods, supporting both background-conditioned and text-conditioned video relighting.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03150

10. VisCoder: Fine-Tuning LLMs for Executable Python Visualization Code Generation
🔑 Keywords: VisCode-200K, Python-based visualization, iterative code correction, feedback-driven learning, plot generation
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve plot generation performance for visualization tasks using the VisCode-200K dataset which integrates execution-grounded supervision and iterative code correction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a large-scale instruction tuning dataset named VisCode-200K for Python-based visualization and self-correction, including validated plotting code and multi-turn correction dialogues.
– Fine-tuned the Qwen2.5-Coder-Instruct model on this dataset to create VisCoder, which was evaluated using PandasPlotBench.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VisCoder significantly outperforms open-source models and rivals proprietary models like GPT-4o-mini in plot generation, highlighting the effectiveness of feedback-driven learning for generating executable and visually accurate code.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03930

11. Voyager: Long-Range and World-Consistent Video Diffusion for Explorable 3D Scene Generation
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated, 3D scenes, video diffusion, camera path, world-consistent
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop Voyager, a video diffusion framework capable of generating world-consistent 3D point-cloud sequences from a single image, facilitating long-range 3D scene exploration along custom camera paths.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of a unified architecture that generates aligned RGB and depth video sequences, auto-regressive inference with smooth video sampling for scene extension, and an automated video reconstruction pipeline for scalable training data curation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Voyager outperforms existing methods in visual quality and geometric accuracy, offering versatile applications by eliminating the need for traditional 3D reconstruction pipelines and manual data annotation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04225
12. Unleashing the Reasoning Potential of Pre-trained LLMs by Critique Fine-Tuning on One Problem
🔑 Keywords: Critique Fine-Tuning, reasoning potential, model performance, GPU efficiency
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore a more efficient way to enhance reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) without high computational costs inherent in reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of Critique Fine-Tuning using diverse model-generated solutions on a single problem, critiqued by teacher LLMs, and applied to models like Qwen and Llama to improve reasoning tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Critique Fine-Tuning on a single problem leads to significant performance improvement in LLMs on various reasoning tasks, requiring only a fraction of the computational resources compared to reinforcement learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03295

13. Image Editing As Programs with Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Transformer, Image Editing As Programs, vision-language model, atomic operations, lightweight adapter
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a unified image editing framework called IEAP to address challenges encountered by diffusion models in instruction-driven image editing, particularly with structurally inconsistent edits.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce IEAP, which leverages the Diffusion Transformer (DiT) architecture, by decomposing complex image editing instructions into sequences of atomic operations.
– Each operation is handled by a lightweight adapter using the same DiT backbone, programmed by a vision-language model (VLM)-based agent.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– IEAP outperforms state-of-the-art methods on standard benchmarks, providing superior accuracy and semantic fidelity, especially for complex multi-step instructions across various editing tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04158

14. Ψ-Sampler: Initial Particle Sampling for SMC-Based Inference-Time Reward Alignment in Score Models
🔑 Keywords: Psi-Sampler, SMC-based framework, reward alignment, score-based generative model, preconditioned Crank-Nicolson Langevin (pCNL)
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to improve reward alignment performance in score-based generative models using the Psi-Sampler framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study utilizes Psi-Sampler, an SMC-based framework that incorporates pCNL for effective posterior sampling and inference-time reward alignment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Initializing particles from a reward-aware posterior instead of Gaussian prior significantly enhances sampling efficiency and alignment performance across various tasks, including layout-to-image generation and aesthetic-preference generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.01320
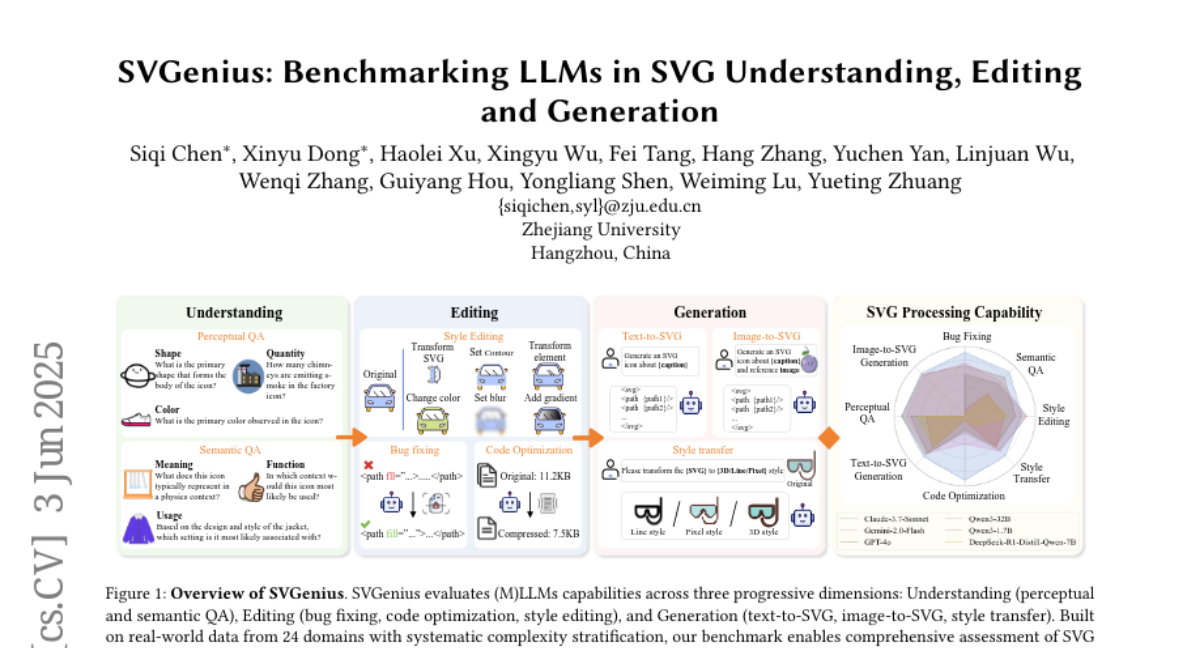
15. SVGenius: Benchmarking LLMs in SVG Understanding, Editing and Generation
🔑 Keywords: SVGenius, Large Language Models, Multimodal LLMs, complexity stratification, reasoning-enhanced training
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to evaluate Large Language Models and Multimodal LLMs for SVG processing across three dimensions: understanding, editing, and generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed SVGenius, a benchmark with 2,377 queries, using real-world data from 24 application domains, evaluated across 8 task categories and 18 metrics to assess 22 mainstream models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Proprietary models outperform open-source models but all struggle against increased complexity.
– Reasoning-enhanced training is more effective than scaling, but style transfer remains challenging across models.
– SVGenius offers the first comprehensive framework for SVG processing, advancing vector graphics models and automated graphic design.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03139
16. LayerFlow: A Unified Model for Layer-aware Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: LayerFlow, text-to-video, layer embeddings, multi-stage training strategy, smooth videos
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to create a unified framework, LayerFlow, for generating layer-aware videos from text prompts, enabling versatile video generation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach involves using a text-to-video diffusion transformer and organizing videos into sub-clips with layer embeddings. A multi-stage training strategy is employed, including training with low-quality video data and fine-tuning LoRA models for smooth integration of layered images.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LayerFlow successfully generates videos with transparent foregrounds, clean backgrounds, and blended scenes. The framework’s flexible design supports decomposing blended videos and generating appropriate backgrounds, achieving high-quality layer-aware video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04228

17. DenseDPO: Fine-Grained Temporal Preference Optimization for Video Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), text-to-video diffusion models, DenseDPO, Vision Language Models (VLMs), motion generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) process for text-to-video diffusion models by addressing bias and annotation precision issues.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– DenseDPO method introduced with three contributions: aligning video pairs by denoising, labeling preferences on segments rather than clips, and utilizing Vision Language Models for automatic annotation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DenseDPO significantly improves motion generation with less data while maintaining text alignment, visual quality, and temporal consistency. It also facilitates automatic preference annotation using Vision Language Models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03517

18. TimeHC-RL: Temporal-aware Hierarchical Cognitive Reinforcement Learning for Enhancing LLMs’ Social Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: Temporal-aware Hierarchical Cognitive Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, social intelligence, post-training, System 1 and System 2
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance the social intelligence of Large Language Models by leveraging Temporal-aware Hierarchical Cognitive Reinforcement Learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Comparison of TimeHC-RL with other post-training paradigms and test-time intervention paradigms across eight datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TimeHC-RL significantly improves the performance of LLMs in social domains, outperforming the traditional System 2 RL method.
– The approach allows a 7B model to match the capabilities of advanced models like DeepSeek-R1 and OpenAI-O3.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.24500
19. Beyond the Surface: Measuring Self-Preference in LLM Judgments
🔑 Keywords: DBG score, self-preference bias, large language models, gold judgments, attention-based perspective
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces the DBG score to accurately measure self-preference bias in large language models by using gold judgments to differentiate response quality from bias.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Comprehensive experiments are conducted using DBG score across different versions and sizes of large language models to assess self-preference bias.
– Investigates factors like response text style and post-training data that influence self-preference bias.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The implementation of DBG score effectively mitigates the confounding effect of response quality on bias measurement.
– Explores potential underlying mechanisms of self-preference bias from an attention-based perspective.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.02592

20. Rectified Sparse Attention
🔑 Keywords: Rectified Sparse Attention, Large Language Models, Sparse Decoding, KV Cache Misalignment, Dense Rectification
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to improve the efficiency and quality of long-sequence generation in Large Language Models by addressing the issue of KV cache misalignment.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves combining block-sparse attention with periodic dense rectification, refreshing the KV cache at fixed intervals to maintain alignment and limit error accumulation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ReSA significantly enhances efficiency, delivering up to 2.42 times speedup for long-context inference while preserving near-lossless generation quality across various tasks. The method proves practical for scalable applications and the code is provided for further use.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04108

21. TalkingMachines: Real-Time Audio-Driven FaceTime-Style Video via Autoregressive Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: audio-driven avatar, real-time performance, audio large language model, infinite video streaming, asymmetric knowledge distillation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To transform pretrained image-to-video models into audio-driven avatar generators for real-time applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Adaptation of a SOTA image-to-video model with 18 billion parameters to support audio-driven avatar generation.
– Implementation of infinite video streaming using asymmetric knowledge distillation from a bidirectional teacher model to a sparse causal, autoregressive student model.
– Design of a high-throughput, low-latency inference pipeline with optimized engineering including device disaggregation, CUDA stream communication, and elimination of redundant computations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework enables natural conversational experiences with significant engineering optimizations, allowing efficient and seamless audio-driven character animation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03099

22. Orak: A Foundational Benchmark for Training and Evaluating LLM Agents on Diverse Video Games
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Model (LLM), game characters, game benchmarks, agentic modules, fine-tuning datasets
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop Orak, a benchmark for training and evaluating LLM agents in diverse real-world video games, addressing the gaps in existing game benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a plug-and-play interface using the Model Context Protocol (MCP) for seamless integration of LLMs with games and proposes a fine-tuning dataset from LLM gameplay trajectories.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Orak provides a comprehensive evaluation framework including game score leaderboards, LLM battle arenas, and analyses of agentic strategies and fine-tuning effects, aiming to build generic gaming agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03610

23. DiffDecompose: Layer-Wise Decomposition of Alpha-Composited Images via Diffusion Transformers
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion models, AI-generated summary, Layer-Wise Decomposition, AlphaBlend dataset, DiffDecompose
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a novel task of Layer-Wise Decomposition of Alpha-Composited Images to recover constituent layers from single overlapped images with semi-transparent/transparent alpha layer occlusion.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed AlphaBlend, a large-scale dataset for transparent and semi-transparent layer decomposition.
– Presented DiffDecompose, a framework using diffusion Transformer-based methods to learn the posterior over possible layer decompositions under semantic prompts and blending types.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated DiffDecompose’s effectiveness through extensive experiments on the AlphaBlend and public LOGO datasets.
– The model predicts one or multiple layers without per-layer supervision and maintains pixel-level correspondence across layers.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.21541

24. Critique-GRPO: Advancing LLM Reasoning with Natural Language and Numerical Feedback
🔑 Keywords: Critique-GRPO, Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Natural Language Feedback, Policy Exploration
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance reasoning capabilities of large language models by combining numerical and natural language feedback in a novel RL framework called Critique-GRPO.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed an online RL framework integrating both numeric and natural language critiques.
– Conducted extensive experiments on Qwen2.5-7B-Base and Qwen3-8B-Base across various tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Critique-GRPO outperforms traditional RL and supervised learning methods in reasoning tasks.
– Notably improves pass@1 scores and surpasses baselines incorporating expert demonstrations.
– Identified that higher entropy and longer responses do not ensure efficient learning or better exploration.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03106

25. Robustness in Both Domains: CLIP Needs a Robust Text Encoder
🔑 Keywords: Adversarial Finetuning, CLIP Models, Text Encoders, Multimodal Retrieval, Zero-shot Accuracy
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the robustness of CLIP text encoders against adversarial noise.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced LEAF, an efficient adversarial finetuning method for text encoders capable of scaling to large CLIP models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LEAF improves zero-shot adversarial accuracy in text domains and enhances recall in multimodal retrieval tasks under adversarial noise.
– Demonstrated improvements in text-to-image generation quality and better reconstruction of input text from embedding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03355
26. CapSpeech: Enabling Downstream Applications in Style-Captioned Text-to-Speech
🔑 Keywords: CapSpeech, CapTTS, text-to-speech synthesis, AI-generated summary, high-fidelity
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce CapSpeech, a large benchmark dataset aimed at improving style, accent, emotion, and chat-agent synthesis in text-to-speech tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a dataset comprising over 10 million machine-annotated and 0.36 million human-annotated audio-caption pairs; conducted experiments using autoregressive and non-autoregressive models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CapSpeech is identified as the largest available comprehensive dataset for CapTTS-related tasks, demonstrating high-fidelity and intelligible speech synthesis, providing insights into the challenges of developing CapTTS systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.02863
27. Adapt before Continual Learning
🔑 Keywords: Continual Learning, Pre-trained Models, Plasticity, Stability, ACL
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research proposes the ACL framework to enhance Continual Learning by improving the plasticity of Pre-trained Models while maintaining stability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a plug-and-play adaptation phase for PTMs before the core CL process to balance the stability-plasticity trade-off.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments confirm that ACL significantly improves Continual Learning performance across benchmarks, offering a versatile solution for PTM-based CL.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03956
28. DLP: Dynamic Layerwise Pruning in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Dynamic Layerwise Pruning (DLP), Large Language Models (LLMs), Non-uniform Layerwise Pruning, Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT), Sparsity
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to develop a pruning method, Dynamic Layerwise Pruning (DLP), that adaptively determines layer importance in Large Language Models (LLMs) to maintain performance at high sparsity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methodology integrates model weights with input activation information to assign pruning rates dynamically according to the relative importance of each layer.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DLP preserves model performance effectively at high sparsity levels, achieving a perplexity reduction of 7.79 and an accuracy improvement of 2.7% in LLaMA2-7B at 70% sparsity compared to existing methods. Additionally, it is compatible with LLM compression techniques and can be integrated into the Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) framework.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.23807

29. BenchHub: A Unified Benchmark Suite for Holistic and Customizable LLM Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: BenchHub, large language models, benchmark repository, domain-specific models, domain-aware benchmarking
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce BenchHub, a dynamic benchmark repository to improve evaluations of large language models by aggregating and classifying datasets across various domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– BenchHub facilitates scalable data management and integrates 303K questions from 38 benchmarks, supporting continuous updates and customized evaluations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates significant performance variation across domain-specific model subsets and highlights the importance of domain-aware benchmarking to encourage better dataset reuse and transparent model comparisons.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.00482

30. Improving Knowledge Distillation Under Unknown Covariate Shift Through Confidence-Guided Data Augmentation
🔑 Keywords: diffusion-based data augmentation, knowledge distillation, covariate shift, spurious feature resilience
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve the robustness of knowledge distillation by using a diffusion-based data augmentation strategy to generate challenging samples.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a novel diffusion-based data augmentation strategy that creates images maximizing the disagreement between the teacher and student models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method significantly enhances worst group and mean group accuracy on CelebA and SpuCo Birds datasets, as well as spurious mAUC on spurious ImageNet under covariate shift, surpassing current state-of-the-art diffusion-based data augmentation baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.02294

31. Quantitative LLM Judges
🔑 Keywords: LLM-as-a-judge, large language model, regression models, predictive power
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The framework aims to enhance the alignment between existing LLM evaluation scores and human scores using quantitative LLM judges, thus improving predictive power and efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach involves training regression models to use LLM judges’ textual evaluations and scores, presenting four quantitative judges for diverse types of feedback while showcasing computational and statistical efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study empirically demonstrates that quantitative judges can effectively boost the predictive power of existing judges through post-hoc modeling across four datasets with two base judges.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.02945

32. RefEdit: A Benchmark and Method for Improving Instruction-based Image Editing Model on Referring Expressions
🔑 Keywords: RefEdit, Instruction-based Editing, Complex Scene Editing, Synthetic Data, State-of-the-art
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the limitations of existing editing models in handling complex scenes with multiple entities by introducing RefEdit.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed RefEdit, an instruction-based editing model, trained on a scalable synthetic data generation pipeline with only 20,000 editing triplets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RefEdit surpasses models like Flux/SD3 trained on millions of samples in performance on complex scene editing and referring expression tasks, achieving state-of-the-art results comparable to closed-source methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03448

33. Follow the Flow: Fine-grained Flowchart Attribution with Neurosymbolic Agents
🔑 Keywords: FlowPathAgent, neurosymbolic agent, Fine-grained Flowchart Attribution, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the reliability and explainability of LLM predictions in flowchart interpretation through Fine-grained Flowchart Attribution.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a neurosymbolic agent called FlowPathAgent for post hoc attribution using graph-based reasoning.
– Segmentation and conversion of flowcharts into structured symbolic graphs for dynamic interaction and attribution path generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FlowPathAgent significantly reduces visual hallucinations in LLM-generated flowchart QA answers, improving performance by 10-14% on the FlowExplainBench benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.01344

34. Video-Skill-CoT: Skill-based Chain-of-Thoughts for Domain-Adaptive Video Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-Thought, domain-adaptive video reasoning, skill-aware CoT, expert learning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve domain-adaptive video reasoning using a novel framework called Video-SKoT, which incorporates skill-aware Chain-of-Thought supervisions and expert modules.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework constructs skill-based CoT annotations and develops a skill-specific expert learning system that utilizes lightweight adapters for training on various reasoning skills.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Video-SKoT consistently outperforms strong baselines in video understanding benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of its approach. It also offers an in-depth comparative analysis of CoT annotation pipelines and learned skills across multiple video domains.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03525

35. POSS: Position Specialist Generates Better Draft for Speculative Decoding
🔑 Keywords: Position Specialists, Large Language Model, Speculative Decoding, Token Prediction, Draft Model
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve the token prediction accuracy and acceptance rate in Large Language Model inference using Position Specialists with position-specialized draft layers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces Position Specialists, consisting of multiple specialized draft layers to focus on specific positions, mitigating feature deviation and improving prediction accuracies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiment results indicate that Position Specialists enhance token acceptance rates at later positions and provide improvements in average acceptance length and speed-up ratio compared to baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03566

36. HTSC-2025: A Benchmark Dataset of Ambient-Pressure High-Temperature Superconductors for AI-Driven Critical Temperature Prediction
🔑 Keywords: High-temperature superconducting materials, AI-based discovery, HTSC-2025, Benchmark dataset, Ethical AI
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduction of HTSC-2025, a benchmark dataset for high-temperature superconducting materials to improve AI-based discoveries.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Compilation of superconducting materials data from 2023 to 2025 based on BCS superconductivity theory, including various theoretical systems.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HTSC-2025 provides a crucial benchmark for accelerating the discovery of superconducting materials using AI methods and is accessible for continuous updates.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03837

37. TRiSM for Agentic AI: A Review of Trust, Risk, and Security Management in LLM-based Agentic Multi-Agent Systems
🔑 Keywords: Agentic AI, LLMs, TRiSM, Governance, Explainability
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To provide a structured analysis of Trust, Risk, and Security Management (TRiSM) in LLM-based agentic multi-agent systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Examined agentic AI architectural foundations and emerging system designs.
– Detailed four pillars—governance, explainability, ModelOps, and privacy/security within agentic LLMs context.
– Developed a comprehensive risk taxonomy and included case studies to illustrate vulnerabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified unique threat vectors and introduced trust-building mechanisms.
– Evaluated metrics for trust, interpretability, and human-centered performance.
– Proposed a roadmap for responsible agentic AI deployment aligned with robust TRiSM principles.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04133

38. Segment Policy Optimization: Effective Segment-Level Credit Assignment in RL for Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Segment Policy Optimization, Advantage Estimation, Monte Carlo, Chain of Thought
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the reasoning capabilities of large language models using reinforcement learning by improving advantage estimation strategies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the Segment Policy Optimization (SPO) framework, which utilizes segment-level advantage estimation. The framework features flexible segment partition, accurate segment advantage estimation, and introduces a probability-mask strategy for policy optimization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SPO achieves superior accuracy improvements (6-12 percentage points for short chains and 7-11 percentage points for long chains) over existing methods like PPO and GRPO, while reducing computational costs in specific contexts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2505.23564

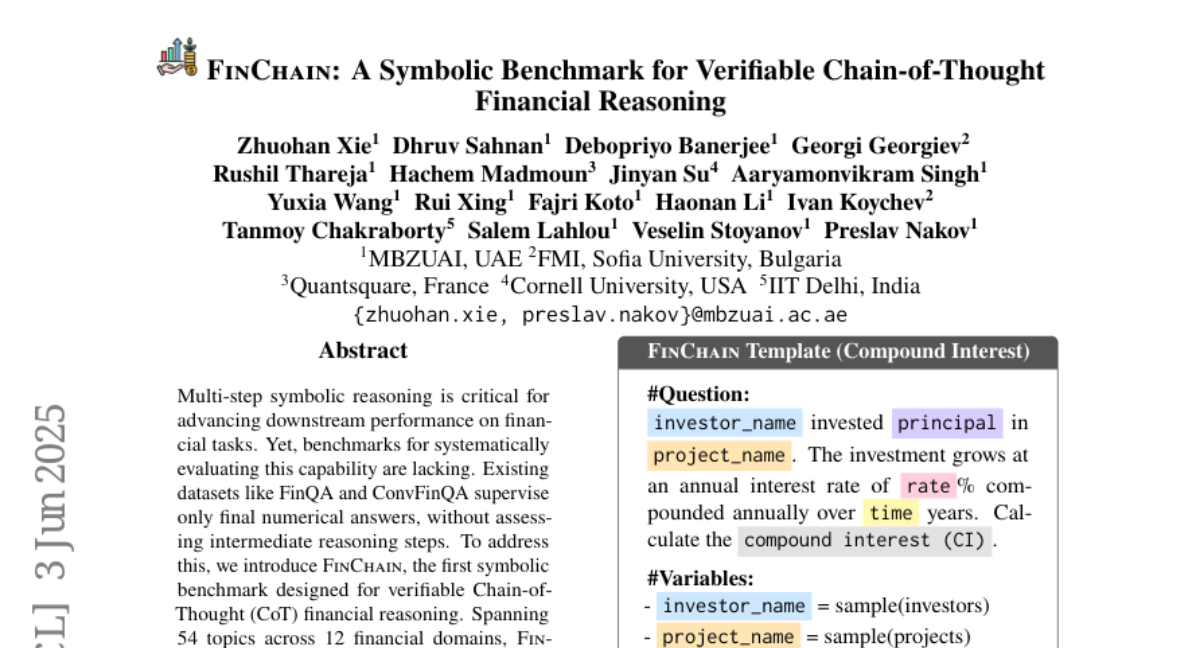
39. FinChain: A Symbolic Benchmark for Verifiable Chain-of-Thought Financial Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: FinChain, ChainEval, multi-step symbolic reasoning, financial tasks, Chain-of-Thought
💡 Category: AI in Finance
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce FinChain, a benchmark for evaluating multi-step symbolic reasoning in financial tasks focused on both intermediate reasoning steps and final answers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed FinChain across 54 topics in 12 financial domains, incorporating parameterized templates and executable Python traces for versatile data generation.
– Introduced ChainEval as a metric for automatic evaluation of reasoning processes and final answers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Found that even state-of-the-art Language Models (LLMs) have substantial room for improvement in multi-step financial reasoning.
– FinChain provides comprehensive resources available for use at the project GitHub repository.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.02515
40. VLMs Can Aggregate Scattered Training Patches
🔑 Keywords: Visual Stitching, VLMs, Data Moderation, Adversarial Data Poisoning, AI Safety
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the visual stitching ability in Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and its role in evading data moderation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Demonstration of visual stitching in common open-source VLMs through tests on three datasets, manipulating image-ID pairs into (patch, ID) pairs for finetuning, and simulating adversarial data poisoning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Confirmed that VLMs can integrate fragmented visual information and reconstruct harmful content, posing significant safety risks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03614

41. CRAWLDoc: A Dataset for Robust Ranking of Bibliographic Documents
🔑 Keywords: CRAWLDoc, metadata extraction, web documents, layout-independent ranking
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce CRAWLDoc for ranking linked web documents by embedding resources and metadata into a unified representation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Retrieve and embed resources, anchor texts, and URLs from publication URLs, along with ORCID profiles and supplementary materials into a unified representation. Evaluate using a manually labeled dataset of 600 publications.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CRAWLDoc demonstrates robust, layout-independent ranking of relevant documents across diverse publishers and data formats. It provides a foundation for improved metadata extraction from various web document layouts and formats.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03822

42. Rethinking the Stability-Plasticity Trade-off in Continual Learning from an Architectural Perspective
🔑 Keywords: Dual-Arch, Continual Learning, stability-plasticity dilemma
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the stability-plasticity dilemma in Continual Learning by leveraging network architecture.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce the Dual-Arch framework using two specialized networks focusing on plasticity and stability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Dual-Arch framework enhances existing CL methods’ performance while reducing parameter size by up to 87%.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03951

43. Rex-Thinker: Grounded Object Referring via Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: CoT reasoning, interpretability, object referring, AI-generated summary, Rex-Thinker
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance object referring through step-by-step reasoning to improve interpretability and rejection of unmatched queries.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed Rex-Thinker, a CoT-based model, supported by a large-scale dataset HumanRef-CoT, with structured reasoning plans.
– Training in two stages: cold-start supervised fine-tuning and GRPO-based reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Rex-Thinker outperforms standard baselines in precision and interpretability.
– Demonstrates strong generalization and improved ability to reject hallucinated outputs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04034

44. RiOSWorld: Benchmarking the Risk of Multimodal Compter-Use Agents
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal large language models, Safety alignment, Autonomous computer-use agents, Safety risks, Real-world computer tasks
💡 Category: AI Ethics and Fairness
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce RiOSWorld, a benchmark for evaluating potential risks of MLLM-based agents during real-world computer tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Categorization of risks into User-originated risks and Environmental risks along with evaluating safety risks from the perspectives of risk goal intention and completion.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Findings indicate significant safety risks faced by current computer-use agents in real-world scenarios and emphasize the necessity for safety alignment to develop trustworthy agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.00618

45. Small Language Models are the Future of Agentic AI
🔑 Keywords: Small Language Models, Agentic AI, LLM-to-SLM Conversion, AI Agent Industry, AI Resources
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To advocate for the use of small language models (SLMs) in agentic AI systems, highlighting their suitability, power, and economic benefits over large language models (LLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analysis of current capabilities of SLMs, common agentic system architectures, and the economics of language model deployment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SLMs are proposed as the future of agentic AI due to their operational and economic advantages. The paper suggests heterogeneous systems using multiple models for tasks requiring general conversational capabilities, and discusses potential adoption barriers and an LLM-to-SLM conversion approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.02153

46. Solving Inverse Problems with FLAIR
🔑 Keywords: Flow-based generative models, Inverse problems, Variational framework, Regularization, Sample diversity
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce FLAIR, a training-free variational framework that uses flow-based generative models to enhance solutions of inverse problems in imaging.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a variational objective focused on flow matching to address various types of degradation and incorporate deterministic trajectory adjustments for recovering unusual data modes.
– Decouple optimization of data fidelity and regularization, employing a time-dependent calibration scheme to modulate the strength of regularization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FLAIR consistently surpasses existing diffusion- and flow-based methods in terms of reconstruction quality and diversity in standard imaging benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.02680
47. Robust Neural Rendering in the Wild with Asymmetric Dual 3D Gaussian Splatting
🔑 Keywords: Asymmetric Dual 3DGS, 3D reconstruction, consistency constraint, divergent masking, Dynamic EMA Proxy
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve 3D reconstruction from in-the-wild images by developing a novel framework that leverages consistency constraints and divergent masking to improve efficiency and reduce artifacts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework trains two 3D Gaussian Splatting models in parallel with consistency constraints and introduces a divergent masking strategy to ensure asymmetric training and minimize shared error modes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method outperforms existing approaches, providing stable and efficient 3D reconstruction, and the authors plan to release the codes and trained models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03538

48. Survey of Active Learning Hyperparameters: Insights from a Large-Scale Experimental Grid
🔑 Keywords: Active Learning, hyperparameter space, hyperparameter grid, experiment results, reproducibility
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to explore the impact of hyperparameters on the performance of Active Learning to enhance its practical application and reproducibility.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Compiled a large hyperparameter grid of over 4.6 million combinations, analyzed performance in a comprehensive AL study, and examined the impact of each hyperparameter.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Provides recommendations on hyperparameter influence, highlights the significant effect of the AL strategy implementation, and outlines a study design for more reproducible AL experiments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.03817
49. Sounding that Object: Interactive Object-Aware Image to Audio Generation
🔑 Keywords: interactive object-aware audio generation, object-centric learning, multi-modal attention
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research objective of this study is to develop an interactive object-aware audio generation model that aligns sounds with user-selected visual objects in images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method integrates object-centric learning into a conditional latent diffusion model utilizing multi-modal attention, allowing for the association of image regions with their corresponding sounds and enabling interactive sound generation at the object level via image segmentation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study concludes that the proposed model outperforms baseline models, achieving better alignment between selected objects and their associated sounds, validated through theoretical analysis and both quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2506.04214
