AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250729

1. Agentic Reinforced Policy Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Agentic Reinforced Policy Optimization, Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Entropy-based Adaptive Rollout, Advantage Attribution
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Agentic Reinforced Policy Optimization (ARPO) to enhance multi-turn Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents by improving their reasoning capabilities and tool interactions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Incorporate entropy-based adaptive rollout and advantage attribution estimation to dynamically manage uncertainty and optimize stepwise interactions with external tools.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ARPO outperforms existing trajectory-level RL algorithms, achieving superior performance in computational and knowledge reasoning benchmarks while reducing resource usage.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.19849

2. Agentic Reinforced Policy Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Agentic Reinforced Policy Optimization, LLMs, Entropy-based Adaptive Rollout Mechanism, Advantage Attribution Estimation, Multi-turn Tool Interactions
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance multi-turn LLM-based agents using Agentic Reinforced Policy Optimization (ARPO) to manage adaptive uncertainty and advantage attribution effectively.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented an entropy-based adaptive rollout mechanism to balance global trajectory and step-level sampling for exploration post-tool interaction.
– Incorporated advantage attribution estimation to improve LLMs’ internalization of advantage differences during tool-use steps.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated ARPO’s superior performance over trajectory-level RL algorithms across 13 benchmarks in computational and knowledge reasoning and deep search domains.
– Achieved improved outcomes with only half the tool-use budget required by previous methods, offering scalability for real-time environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.19849

3. ARC-Hunyuan-Video-7B: Structured Video Comprehension of Real-World Shorts
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Model, Video Comprehension, Video Search, Video Reasoning, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop ARC-Hunyuan-Video, a multimodal model that processes visual, audio, and text signals for structured comprehension of real-world short videos, enhancing video search and recommendation capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a compact 7B-parameter model trained through pre-training, instruction fine-tuning, reinforcement learning, cold start, and final tuning using a high-quality automated annotation pipeline.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The ARC-Hunyuan-Video model demonstrates strong performance in video comprehension tasks, supporting zero-shot or fine-tuning with a few samples and improving user engagement and satisfaction with fast inference on real-world platforms.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.20939

4. SmallThinker: A Family of Efficient Large Language Models Natively Trained for Local Deployment
🔑 Keywords: SmallThinker, LLMs, deployment-aware architecture, GPU-free, sparse attention
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To design and deploy a family of large language models (LLMs) for local devices with limited computational resources, without relying on GPU hardware.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a two-level sparse structure with Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) and sparse feed-forward networks to reduce computational needs.
– Developed a pre-attention router to manage I/O bottlenecks and improve on-device inference efficiency.
– Utilized NoPE-RoPE hybrid sparse attention mechanism for enhanced memory efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SmallThinker models outperform larger LLMs in state-of-the-art performance, achieving over 20 tokens/s on standard CPUs with minimal memory usage, thus reducing the dependence on GPU hardware.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.20984

5. Rep-MTL: Unleashing the Power of Representation-level Task Saliency for Multi-Task Learning
🔑 Keywords: Multi-Task Learning, task saliency, negative transfer, shared representation space
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To optimize multi-task learning (MTL) by leveraging task saliency in shared representations to enhance complementarity and reduce negative transfer.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces Rep-MTL, which utilizes representation-level task saliency and focuses on entropy-based penalization and sample-wise cross-task alignment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Rep-MTL achieves competitive performance gains and efficiency on challenging MTL benchmarks, demonstrating its efficacy in balancing task-specific learning with cross-task sharing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.21049

6. Reconstructing 4D Spatial Intelligence: A Survey
🔑 Keywords: 4D spatial intelligence, computer vision, deep learning architectures, 4D scene reconstruction
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Organize methods for reconstructing 4D spatial intelligence into five progressive levels.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analyzed existing methods and structured them into progressive levels from basic 3D attributes to complex interactions and physical laws.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified key challenges and future research directions for each level of 4D spatial intelligence reconstruction.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.21045

7. A Survey of Self-Evolving Agents: On Path to Artificial Super Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, Self-evolving Agents, Continual Learning, Adaptive Agents, Artificial Super Intelligence
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To systematically review architectures and methods for self-evolving agents in continual learning environments, focusing on design considerations for adaptive, evolving systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Examination of evolutionary mechanisms across agent components, categorization of adaptation methods, and analysis of algorithmic and architectural designs for evolutionary adaptation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The paper highlights the importance of developing self-evolving agents capable of real-time adaptation, identifies evaluation metrics and benchmarks, and emphasizes applications in domains such as coding, education, and healthcare to pave the way for Artificial Super Intelligence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.21046

8. Geometric-Mean Policy Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Geometric-Mean Policy Optimization, Policy Updates, Token-Level Rewards, Multimodal Reasoning, AI Native
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to stabilize policy updates in large language models through Geometric-Mean Policy Optimization (GMPO), enhancing the performance on mathematical and multimodal reasoning benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– GMPO introduces the use of geometric mean for token-level rewards to provide a less sensitive approach to outliers and maintain stable importance sampling ratios. Comprehensive theoretical and experimental analyses are conducted to validate GMPO’s design and stability benefits.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GMPO demonstrates improved stability and a performance increase, surpassing GRPO by 4.1% on mathematical benchmarks and 1.4% on multimodal reasoning benchmarks like AIME24, AMC, MATH500, OlympiadBench, Minerva, and Geometry3K.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.20673
9. Region-based Cluster Discrimination for Visual Representation Learning
🔑 Keywords: RICE, Region Transformer, cluster discrimination loss, dense prediction, OCR
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance region-level visual and OCR capabilities with a novel method called Region-Aware Cluster Discrimination (RICE).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A novel Region Transformer layer is proposed to extract rich regional semantics and a unified region cluster discrimination loss is designed to support object and OCR learning within a single framework.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RICE consistently outperforms previous methods on segmentation, dense detection, and visual perception tasks for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs).
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.20025

10. GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M: A Million-Scale, GPT-Generated Image Dataset
🔑 Keywords: GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M, Large Multimodal Models, AI Native, Instruction-Guided Image Editing
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to introduce GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M, a publicly available large-scale image-editing corpus to bridge the gap in open-source research for instruction-guided image editing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Systematic construction of the dataset by unifying and refining three popular image-editing datasets (OmniEdit, HQ-Edit, UltraEdit), enhancing visual quality, and improving semantic clarity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Fine-tuned open-source models on the dataset demonstrated highly competitive performance across benchmarks, significantly advancing open-source methods and narrowing the gap with proprietary models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.21033

11. Met^2Net: A Decoupled Two-Stage Spatio-Temporal Forecasting Model for Complex Meteorological Systems
🔑 Keywords: deep learning, self-attention mechanism, multivariable fusion, shared latent space, state-of-the-art
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Improve weather prediction performance in end-to-end deep learning models by addressing representation inconsistency and capturing inter-variable dependencies in complex weather systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement an implicit two-stage training method using separate encoders and decoders for each variable, combined with a Translator to capture interactions and a self-attention mechanism for fusion.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method significantly enhances predictive accuracy, achieving a reduction in MSE for near-surface air temperature and humidity by 28.82% and 23.39% respectively, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.17189
12. UloRL:An Ultra-Long Output Reinforcement Learning Approach for Advancing Large Language Models’ Reasoning Abilities
🔑 Keywords: reinforcement learning, large language models, Ultra-Long Output Reinforcement Learning, dynamic masking, entropy collapse
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to improve the handling of ultra-long outputs in large language models to enhance their reasoning capabilities and training efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces an Ultra-Long Output Reinforcement Learning (UloRL) approach, which includes segmenting output decoding and utilizing dynamic masking of well-Mastered Positive Tokens to prevent inefficiencies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach significantly improves training speed and model performance, with the RL segment rollout achieving a 2.06x increase in training speed. Additionally, the performance on specific benchmarks like AIME2025 and BeyondAIME improved considerably, demonstrating the effectiveness of the methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.19766

13. ForCenNet: Foreground-Centric Network for Document Image Rectification
🔑 Keywords: Foreground-Centric Network (ForCenNet), document image rectification, curvature consistency loss
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address geometric deformations in photographed document images by emphasizing the importance of foreground elements for accurate text recognition and document image correction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a Foreground-Centric Network (ForCenNet) which uses a novel foreground-centric label generation method and mask mechanism to distinguish between readable and background regions.
– Implementation of curvature consistency loss to utilize detailed foreground labels, aiding the model in comprehending distorted geometric distributions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ForCenNet achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple benchmarks, efficiently correcting layout elements like text lines and table borders in document images.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.19804
14. ScenePainter: Semantically Consistent Perpetual 3D Scene Generation with Concept Relation Alignment
🔑 Keywords: 3D scene generation, ScenePainter, semantic drift, hierarchical graph structure, outpainting
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Addressing the issue of semantic drift in perpetual 3D scene generation for more consistent and coherent 3D view sequences.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the ScenePainter framework using a hierarchical graph structure known as SceneConceptGraph to guide outpainting and ensure semantic consistency and diversity in 3D scene generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework effectively mitigates semantic drift, producing more consistent and immersive 3D view sequences through extensive experiments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.19058

15. Music Arena: Live Evaluation for Text-to-Music
🔑 Keywords: Text-to-music, human preference evaluation, Music Arena, live evaluation
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce Music Arena, a platform for scalable human preference evaluation of text-to-music (TTM) models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing an LLM-based routing system and collecting detailed user preferences, including listening data and natural language feedback.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Music Arena provides a renewable source of preference data, enhancing transparency and aligning TTM systems with real-world user preferences.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.20900

16. Beyond Binary Rewards: Training LMs to Reason About Their Uncertainty
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Calibration, Language Models, Confidence Estimation, Brier Score
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve accuracy and confidence calibration of language models trained via reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce RLCR (Reinforcement Learning with Calibration Rewards), which augments binary correctness scores with Brier scores to incentivize calibrated predictions.
– Prove that RLCR yields accurate and well-calibrated predictions across diverse datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RLCR improves calibration without loss in accuracy, outperforming ordinary RL and post-hoc confidence score classifiers in both in-domain and out-of-domain evaluations.
– Verbalized confidence at test time can enhance accuracy and calibration through confidence-weighted scaling methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.16806

17. JAM: A Tiny Flow-based Song Generator with Fine-grained Controllability and Aesthetic Alignment
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, flow-matching, lyrics-to-song generation, word-level control, aesthetic alignment
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance lyrics-to-song generation by providing word-level control over vocal timing and duration, improving the quality of generated songs through aesthetic alignment.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers implemented Direct Preference Optimization for aesthetic alignment using a synthetic dataset, eliminating the need for manual data annotations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The flow-matching-based model JAM surpasses current models in music-specific attributes by offering fine-grained vocal control and achieving better aesthetic alignment with human preferences.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.20880
18. Goal Alignment in LLM-Based User Simulators for Conversational AI
🔑 Keywords: Conversational AI, User Goal State Tracking, Goal-Oriented Behavior, User Simulators, Goal-Aligned Responses
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to introduce a novel framework, User Goal State Tracking (UGST), to enhance goal-oriented behavior in user simulators within conversational AI systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study presents a three-stage methodology using UGST for developing user simulators that autonomously track and reason about goal progression to generate goal-aligned responses.
– Comprehensive evaluation metrics are established for assessing goal alignment, demonstrating substantial improvements across benchmarks like MultiWOZ 2.4 and {\tau}-Bench.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The introduction of UGST addresses a critical gap in conversational AI, establishing it as essential for developing goal-aligned user simulators and enhancing the reliability of user simulation in multi-turn conversations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.20152

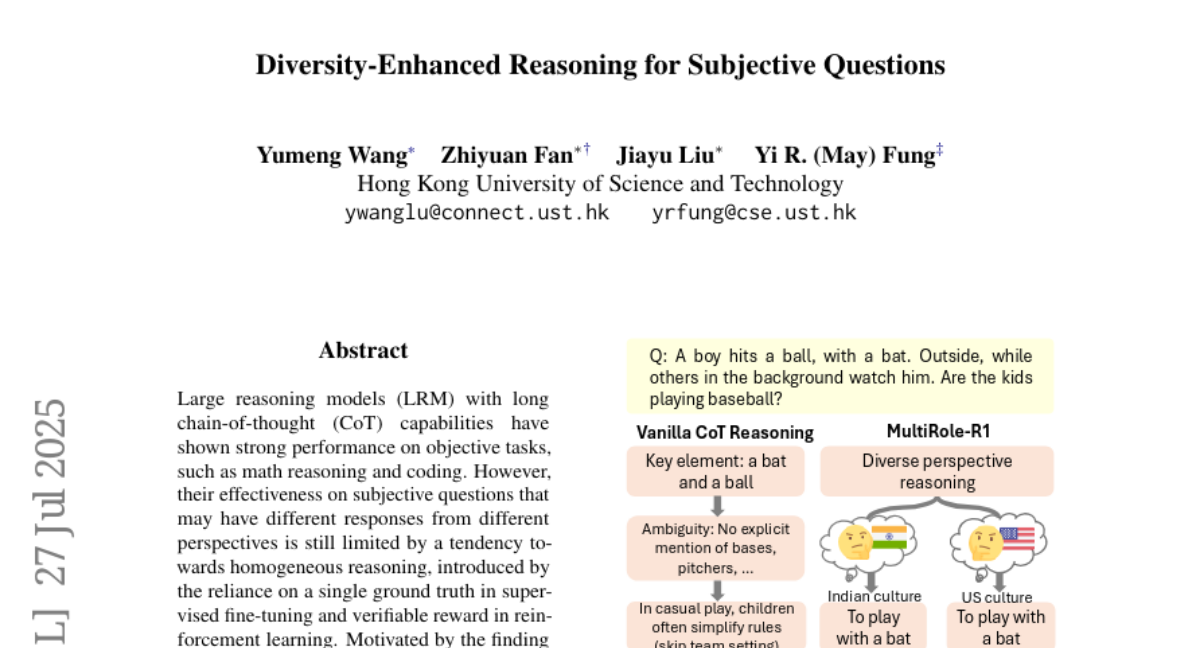
19. Diversity-Enhanced Reasoning for Subjective Questions
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Large reasoning models, subjective reasoning, diversity-enhanced framework, reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve accuracy and diversity in subjective reasoning tasks by introducing a diversity-enhanced framework named MultiRole-R1.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of unsupervised data construction to generate reasoning chains with diverse role perspectives.
– Employment of reinforcement learning using Group Relative Policy Optimization with reward shaping to enhance diversity as a significant reward signal.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MultiRole-R1 improves performance on subjective tasks by incorporating diverse perspectives, demonstrating effectiveness and generalizability across multiple benchmarks.
– The study establishes a positive relationship between reasoning diversity and accuracy, showcasing the potential of diversity-enhanced training in Large Reasoning Models (LRMs).
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.20187
20. SAND-Math: Using LLMs to Generate Novel, Difficult and Useful Mathematics Questions and Answers
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Mathematical Reasoning, SAND-Math, Difficulty Hiking, Benchmark Performance
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to overcome the lack of difficult and novel training data for developing high-performing mathematical reasoning language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a pipeline, SAND-Math, which generates and enhances the complexity of synthetic mathematical problems.
– Conducting an ablation study to analyze the impact of increasing problem difficulty on model performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SAND-Math dataset significantly improves model performance, surpassing existing synthetic datasets.
– The Difficulty Hiking component effectively raises problem difficulty, boosting performance on the AIME25 benchmark.
– The complete pipeline, including the dataset and fine-tuned model, offers a scalable solution for enhanced mathematical reasoning capabilities in language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.20527

21. GenoMAS: A Multi-Agent Framework for Scientific Discovery via Code-Driven Gene Expression Analysis
🔑 Keywords: LLM-based agents, gene expression analysis, workflow reliability, autonomous adaptability, GenoMAS
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance gene expression analysis by integrating workflow reliability and autonomous adaptability to improve preprocessing and identification accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of LLM-based agents in a system named GenoMAS, employing typed message-passing protocols and a guided-planning framework for task execution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved a Composite Similarity Correlation of 89.13% for data preprocessing and F_1 of 60.48% for gene identification, surpassing previous methods significantly and uncovering biologically plausible gene-phenotype associations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.21035

22. Running in CIRCLE? A Simple Benchmark for LLM Code Interpreter Security
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, code interpreters, cybersecurity threats, benchmarks, OpenAI
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate interpreter-specific cybersecurity risks in large language models (LLMs) with native code execution capabilities using a proposed benchmark named CIRCLE.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a benchmark with 1,260 prompts targeting system resources to assess vulnerabilities in LLMs. Automated evaluation framework was used to test code execution and correctness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified significant inconsistencies in vulnerabilities among commercial models, highlighting the need for cybersecurity benchmarks and tools for safe LLM integrations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.19399

23.
