AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250805
1. Qwen-Image Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Qwen-Image, data pipeline, progressive training, dual-encoding mechanism, visual fidelity
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Present Qwen-Image, a model in the Qwen series, to enhance complex text rendering and precise image editing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a comprehensive data pipeline for data collection, filtering, annotation, synthesis, and balancing.
– Implement progressive training that scales from simple to complex text rendering.
– Introduce a dual-encoding mechanism to balance semantic consistency and visual fidelity in image editing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Qwen-Image achieves state-of-the-art performance in both image generation and editing across multiple benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.02324

2. SitEmb-v1.5: Improved Context-Aware Dense Retrieval for Semantic Association and Long Story Comprehension
🔑 Keywords: situated embedding models, retrieval performance, context window, embedding models, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance retrieval performance by conditioning short text chunks on broader context windows, outperforming state-of-the-art models with fewer parameters.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a new training paradigm and developed situated embedding models (SitEmb) to address the limitations of current embedding models in encoding context effectively.
– Evaluated the method using a curated book-plot retrieval dataset designed to assess situated retrieval capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SitEmb-v1 model based on BGE-M3 significantly outperformed existing state-of-the-art embedding models, with only 1B parameters, including models with up to 7-8B parameters.
– The 8B SitEmb-v1.5 model further improved performance by over 10%, demonstrating strong results across different languages and various downstream applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.01959

3. CellForge: Agentic Design of Virtual Cell Models
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Multi-Agent Framework, Single-Cell Multi-Omics Data, Virtual Cells, LLM Agents
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To transform raw single-cell multi-omics data into optimized computational models for virtual cells, improving prediction accuracy in single-cell perturbation experiments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing a multi-agent framework with three core modules: Task Analysis, Method Design (collaborative agentic approaches), and Experiment Execution to automate model and code generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CellForge consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in single-cell perturbation prediction, showcasing the effective collaboration among agents and the power of iterative interactions over direct modeling challenges.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.02276
4. Beyond the Trade-off: Self-Supervised Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning Models’ Instruction Following
🔑 Keywords: self-supervised RL, reasoning models, instruction following, scalability, cost-effectiveness
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance instruction following in reasoning models without relying on external supervision, maintaining reasoning performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a self-supervised RL framework leveraging reasoning models’ internal signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework significantly improves instruction following capabilities and offers a scalable, cost-effective approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.02150

5. Llama-3.1-FoundationAI-SecurityLLM-8B-Instruct Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Foundation-Sec-8B-Instruct, Cybersecurity, Large Language Models, Instruction-following, Conversational Capabilities
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aimed to introduce Foundation-Sec-8B-Instruct, a cybersecurity-focused LLM designed for chat-style interactions and instruction-following, to address limitations in the integration of large language models within the cybersecurity domain.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Foundation-Sec-8B-Instruct was developed by training the existing Foundation-Sec-8B model to enhance its performance in general-purpose cybersecurity dialogue and instruction-following tasks, incorporating domain-specific knowledge with conversational capabilities and alignment with human preferences.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Comprehensive evaluations demonstrated that Foundation-Sec-8B-Instruct outperforms existing models like Llama 3.1-8B-Instruct in cybersecurity tasks and aligns with GPT-4o-mini’s performance on cyber threat intelligence and instruction-following tasks. This model is envisioned as an essential tool for cybersecurity professionals.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.01059

6. InstructVLA: Vision-Language-Action Instruction Tuning from Understanding to Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: InstructVLA, Vision-Language-Action, Multimodal Training, Vision-Language Models, Mixture-of-Experts Adaptation
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to introduce InstructVLA, an end-to-end vision-language-action (VLA) model that preserves vision-language reasoning and enhances manipulation performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a novel training paradigm called Vision-Language-Action Instruction Tuning (VLA-IT) with multimodal training and mixture-of-experts adaptation to optimize textual reasoning and action generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– InstructVLA significantly improves manipulation performance over existing models, achieving a 30.5% improvement over SpatialVLA, and outperforms other benchmarks like OpenVLA and action expert systems by significant margins. It shows potential for enhancing human-robot interaction with efficient policy learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.17520

7. Fitness aligned structural modeling enables scalable virtual screening with AuroBind
🔑 Keywords: AuroBind, virtual screening, atomic-level structural model, ligand-bound structures, binding fitness
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a scalable virtual screening framework, AuroBind, that fine-tunes atomic-level structural models to predict ligand-bound structures and assess binding fitness for disease-relevant targets.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized direct preference optimization, self-distillation from high-confidence complexes, and a teacher-student acceleration strategy for joint prediction of ligand-bound structures and binding fitness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AuroBind outperforms state-of-the-art models in structural and functional benchmarks, enabling significantly faster screenings across vast compound libraries and achieving impressive hit rates for both agonists and antagonists in disease-relevant targets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.02137

8. VeOmni: Scaling Any Modality Model Training with Model-Centric Distributed Recipe Zoo
🔑 Keywords: Omni-Modal LLMs, 3D Parallelism, Modular Training Framework, Model-Centric Distributed Recipes, Flexible Configuration Interface
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To accelerate the development of omni-modal large language models (LLMs) by enhancing training frameworks with efficient 3D parallelism and flexible system configurations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a modular and efficient training framework, \veomni, which decouples communication from computation, enabling efficient 3D parallelism.
– Implemented a flexible configuration interface to allow seamless integration of new modalities with minimal coding effort.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that \veomni efficiently trains a 30B parameter omni-modal mixture-of-experts (MoE) model with exceptional throughput, achieving superior efficiency and scalability for large omni-modal LLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.02317

9. A Glimpse to Compress: Dynamic Visual Token Pruning for Large Vision-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Large Vision-Language Models, Visual token compression, dynamic pruning, GlimpsePrune, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve efficiency in Large Vision-Language Models by introducing a dynamic pruning framework, GlimpsePrune, that adaptively removes irrelevant visual tokens without degrading performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves a data-driven approach inspired by human cognition, which prunes irrelevant visual tokens in a single forward pass before generating answers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GlimpsePrune effectively prunes 92.6% of visual tokens while maintaining baseline performance on VQA tasks. Enhanced fine-tuning capabilities allow improved performance, reaching 110% of baseline performance with a high pruning rate.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.01548

10. Dynaword: From One-shot to Continuously Developed Datasets
🔑 Keywords: Dynaword, Danish Dynaword, community collaboration, open datasets, quality assurance
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop a framework, Dynaword, and its implementation, Danish Dynaword, to enable the creation and continuous update of large-scale, open natural language datasets through community collaboration.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methods involve introducing the Dynaword approach as a framework and showcasing the Danish Dynaword as a practical implementation that validates the framework’s potential. The datasets are updated continuously via community contributions, ensuring openness and scalability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Dynaword framework addresses challenges such as reliance on ambiguously licensed sources, static dataset releases, and limited quality assurance processes. Danish Dynaword exemplifies the success of this approach by amassing four times more tokens than similar datasets, openly licensed, and incorporating contributions from industry and research. The framework includes tests to ensure data quality and sustainability of contributions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.02271
11. Personalized Safety Alignment for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: Personalized Safety Alignment, Text-to-image diffusion models, User-specific control, Harmful content suppression, Cross-attention mechanism
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a framework for integrating personalized user profiles into text-to-image diffusion models to align content with individual safety preferences.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of the Personalized Safety Alignment framework using a cross-attention mechanism and a new dataset, Sage, to adjust models according to user-specific safety profiles.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Personalized Safety Alignment enhances the suppression of harmful content and improves alignment with user constraints, achieving higher Win Rate and Pass Rate scores.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.01151

12. Voxlect: A Speech Foundation Model Benchmark for Modeling Dialects and Regional Languages Around the Globe
🔑 Keywords: Voxlect, Speech Foundation Models, Dialect Classification, ASR Performance, Speech Generation Systems
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The introduction of Voxlect as a benchmark for evaluating speech foundation models on dialect classification and their applications across multiple languages and dialects.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized over 2 million training utterances from 30 publicly available speech corpora, evaluating performance in dialect classification under noisy conditions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated Voxlect’s utility in augmenting speech recognition datasets with dialect information and evaluating the performance of speech generation systems. Voxlect is publicly available under the RAIL license.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.01691

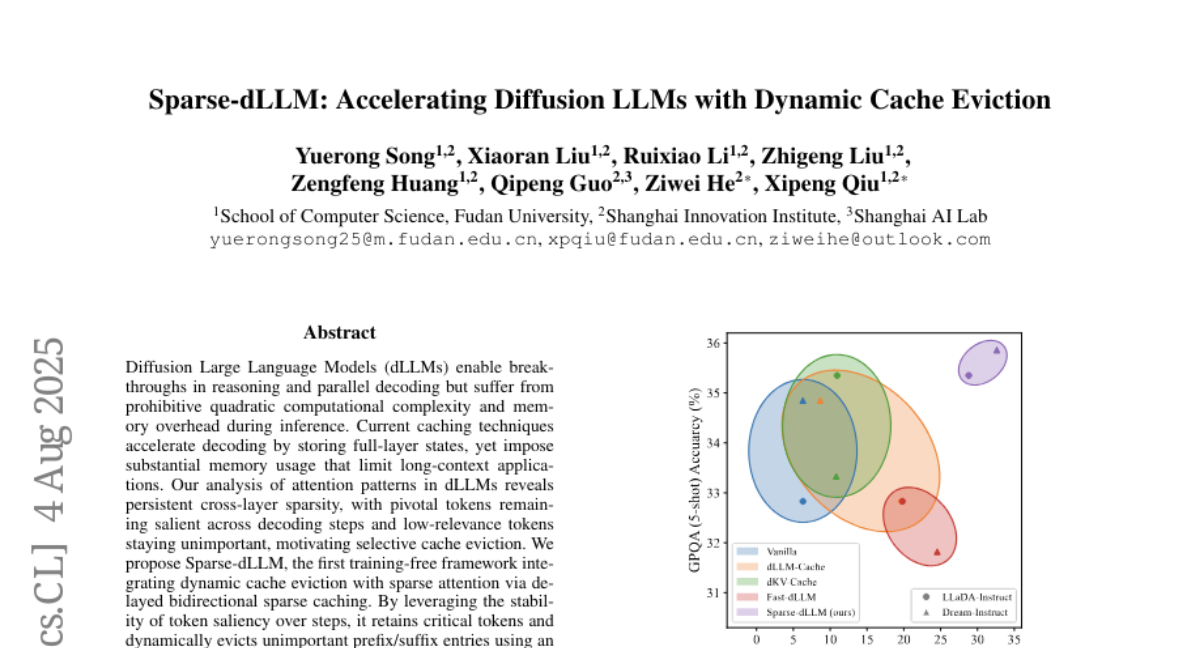
13. Sparse-dLLM: Accelerating Diffusion LLMs with Dynamic Cache Eviction
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Large Language Models, Sparse Attention, Dynamic Cache Eviction, Throughput, Token Saliency
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance the efficiency of Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) by integrating dynamic cache eviction and sparse attention without compromising performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analyzed attention patterns in dLLMs leading to the development of Sparse-dLLM framework by implementing delayed bidirectional sparse caching.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Sparse-dLLM achieves up to 10 times higher throughput compared to traditional dLLMs while maintaining comparable performance and memory costs, showing superior efficiency and effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.02558
14. Artificial Intelligence and Misinformation in Art: Can Vision Language Models Judge the Hand or the Machine Behind the Canvas?
🔑 Keywords: vision language models, AI-generated images, artist attribution, canvas attribution, misinformation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate the capability of vision language models in accurately attributing artists and distinguishing AI-generated images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Experimental study using state-of-the-art AI models on a dataset with close to 40,000 paintings from 128 artists.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Vision language models have limited capabilities in performing artist attribution and identifying AI-generated images, indicating the need for improvements to prevent misinformation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.01408

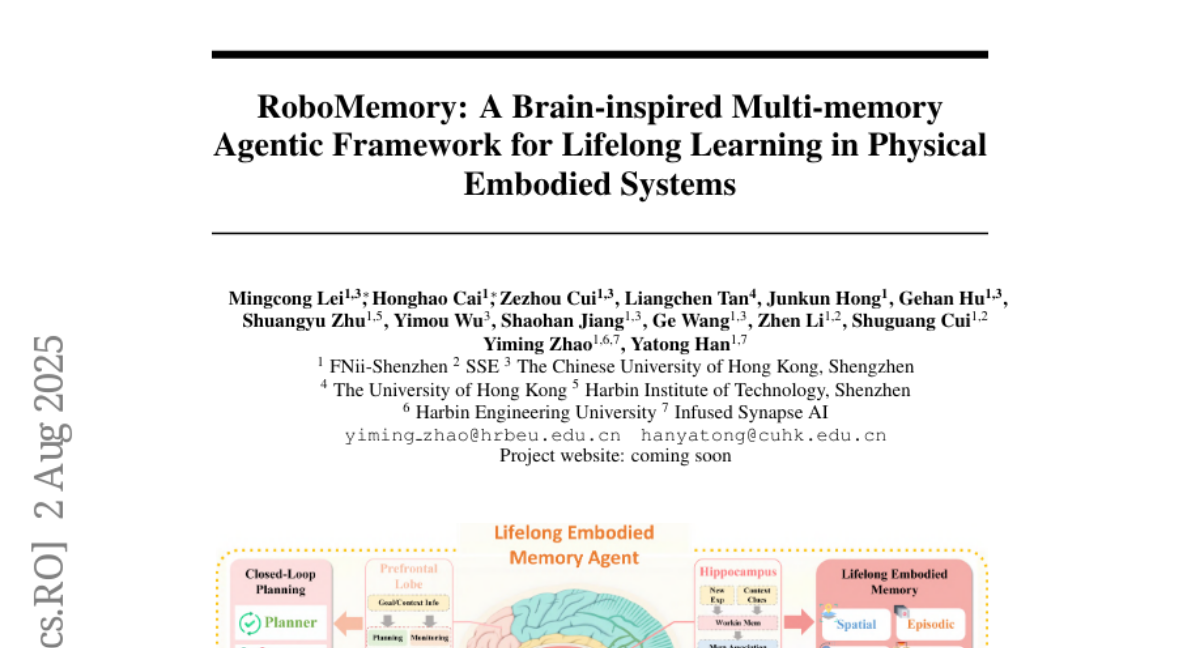
15. RoboMemory: A Brain-inspired Multi-memory Agentic Framework for Lifelong Learning in Physical Embodied Systems
🔑 Keywords: RoboMemory, Lifelong Learning, Cognitive Neuroscience, Embodied Systems, Multi-Modal Memory
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance lifelong learning in physical robots by developing RoboMemory, a brain-inspired multi-memory framework based on cognitive neuroscience principles.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– RoboMemory integrates four core modules resembling various brain components to support continuous learning and task execution. The Lifelong Embodied Memory System is central, facilitating fast parallelized updates and retrievals across different memory submodules and utilizing a dynamic Knowledge Graph for enhanced memory consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RoboMemory surpasses existing baselines by significant margins in success rates, establishing a new state-of-the-art for physical robots. Ablation studies validate its components, and real-world deployments confirm its effectiveness in repeated tasks, alleviating latency issues and ensuring scalability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.01415
16. Cyber-Zero: Training Cybersecurity Agents without Runtime
🔑 Keywords: Cyber-Zero, Runtime-Free Cybersecurity LLMs, Agent Trajectories, CTF Writeups
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a runtime-free framework, Cyber-Zero, to synthesize agent trajectories for training cybersecurity LLMs, achieving high performance without actual runtime environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes CTF writeups and persona-driven LLM simulation to reverse-engineer runtime behaviors, creating realistic interaction sequences.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Cyber-Zero-trained models outperform baseline models by up to 13.1% on key CTF benchmarks like InterCode-CTF, showing state-of-the-art results while being cost-effective and challenging proprietary systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.00910

17. Exploitation Is All You Need… for Exploration
🔑 Keywords: Meta-reinforcement learning, Exploration-exploitation dilemma, Emergent exploratory behavior, Recurring Environmental Structure, Pseudo-Thompson Sampling
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate whether a meta-reinforcement learning agent can exhibit exploratory behavior with a solely greedy objective, given certain conditions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted experiments using stochastic multi-armed bandits and temporally extended gridworlds to test the presence of exploratory behavior under specific conditions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Exploratory behavior emerges in agents trained with a greedy objective when Recurring Environmental Structure and Agent Memory are present. Long-Horizon Credit Assignment is not always necessary, suggesting exploration and exploitation can coexist under a unified reward-maximization process.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.01287

18. AgentTTS: Large Language Model Agent for Test-time Compute-optimal Scaling Strategy in Complex Tasks
🔑 Keywords: AgentTTS, LLM, Test-time scaling, Multi-stage complex tasks, Compute-optimal scaling
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the efficiency and robustness of compute allocation in multi-stage complex tasks using an LLM-agent-based framework called AgentTTS.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted extensive pilot experiments on four tasks across six datasets to derive empirical insights.
– Employed an iterative feedback-driven interaction approach for compute-optimal allocations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AgentTTS significantly improves search efficiency and robustness compared to traditional and other LLM-based methods.
– Demonstrates enhanced adaptability to varying training set sizes and offers greater interpretability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.00890
19. Embedding-Aware Quantum-Classical SVMs for Scalable Quantum Machine Learning
🔑 Keywords: Quantum Advantage, Vision Transformer, Quantum Machine Learning, Quantum Support Vector Machines, Embedding Choice
💡 Category: Quantum Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To demonstrate the importance of embedding choice in achieving quantum advantage for classification tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A quantum-classical pipeline using class-balanced k-means distillation combined with pretrained Vision Transformer embeddings was proposed to improve accuracy over classical SVMs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Vision Transformer embeddings uniquely enable quantum advantage with significant accuracy improvements on Fashion-MNIST and MNIST datasets, showcasing dependence on embedding choice and synergy between transformer attention and quantum feature spaces.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.00024

20. Platonic Representations for Poverty Mapping: Unified Vision-Language Codes or Agent-Induced Novelty?
🔑 Keywords: multimodal framework, satellite imagery, LLM, socio-economic indicators, AI agent
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to determine whether socio-economic indicators such as household wealth can be predicted effectively using satellite imagery and LLM-generated text data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers used a multimodal framework comprising five different pipelines to predict household wealth, integrating satellite imagery and textual data, with a focus on improving the prediction accuracy compared to vision-only models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The fusion of vision and LLM-generated text outperformed vision-only baselines in predicting wealth. The study demonstrated moderate correlation in the fused embeddings from vision and language modalities, supporting a shared latent representation of wealth while maintaining complementary details. The release of a large-scale multimodal dataset includes more than 60,000 DHS clusters linked to relevant imagery and textual data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.01109

21. SHAMI-MT: A Syrian Arabic Dialect to Modern Standard Arabic Bidirectional Machine Translation System
🔑 Keywords: Bidirectional Machine Translation, AraT5v2-base-1024, Nabra dataset, MADAR corpus, Dialectal Arabic Translation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Bridge the communication gap between Modern Standard Arabic and the Syrian dialect using a specialized machine translation system, SHAMI-MT.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of two models for MSA-to-Shami and Shami-to-MSA translation based on AraT5v2-base-1024 architecture, fine-tuned on the Nabra dataset and evaluated using the MADAR corpus.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The MSA-to-Shami model achieved a high-quality score of 4.01 out of 5.0 based on GPT-4.1 assessments, effectively producing dialectally authentic translations and advancing dialectal Arabic translation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.02268
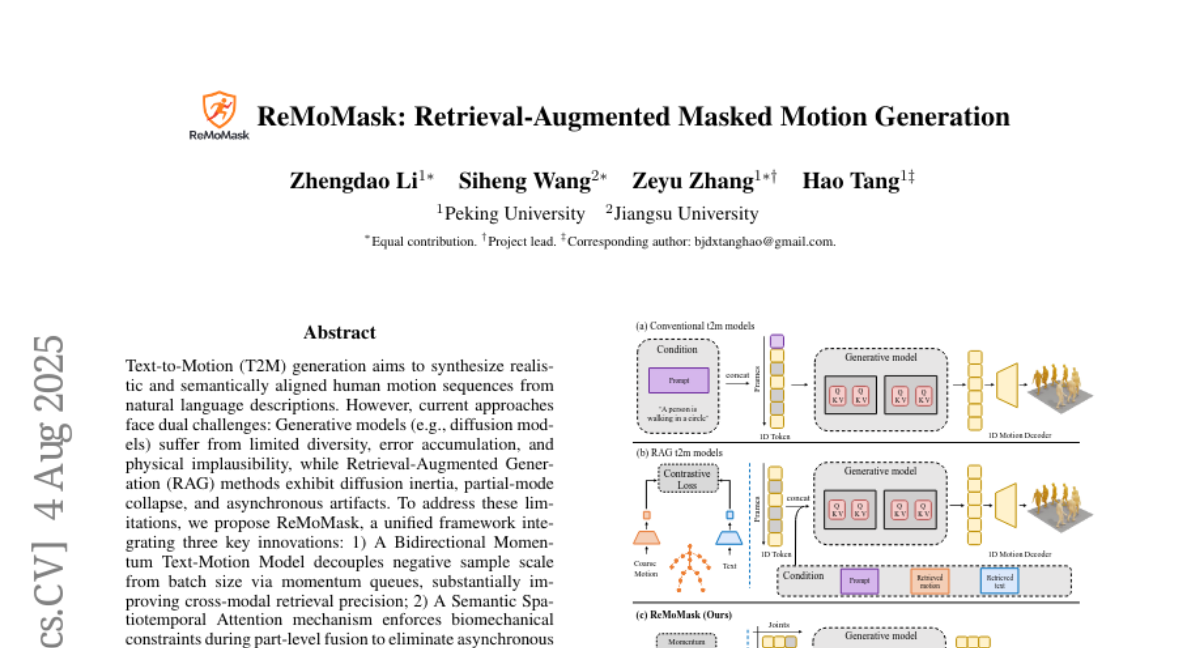
22. ReMoMask: Retrieval-Augmented Masked Motion Generation
🔑 Keywords: ReMoMask, Text-to-Motion, Bidirectional Momentum Text-Motion Model, Semantic Spatio-temporal Attention, RAG-Classier-Free Guidance
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the challenges of generating realistic and semantically aligned human motion sequences from natural language descriptions by introducing a unified framework called ReMoMask.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of a Bidirectional Momentum Text-Motion Model to enhance cross-modal retrieval precision.
– Use of Semantic Spatio-temporal Attention to enforce biomechanical constraints and eliminate artifacts.
– Implementation of RAG-Classier-Free Guidance to improve generative capabilities without classifiers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ReMoMask achieves state-of-the-art performance on the HumanML3D and KIT-ML benchmarks, with notable improvements in FID scores compared to previous methods.
– Demonstrates efficient generation of temporally coherent motions in fewer steps.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.02605
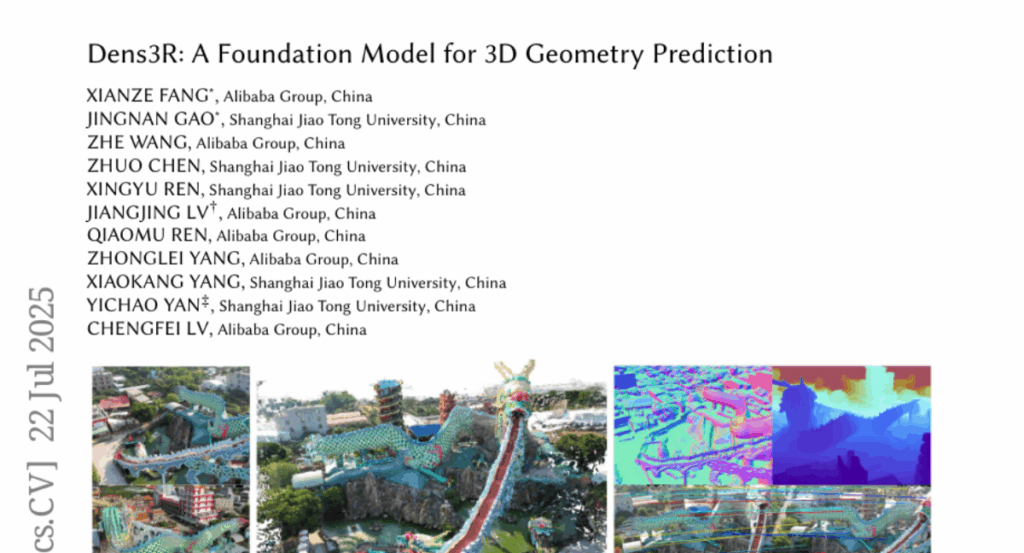
23. Dens3R: A Foundation Model for 3D Geometry Prediction
🔑 Keywords: 3D foundation model, dense 3D reconstruction, geometric quantities, joint regression, intrinsic invariance
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Dens3R, a 3D foundation model designed for consistent and accurate joint geometric dense prediction across multiple geometric quantities such as depth and surface normals.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a two-stage training framework with a lightweight shared encoder-decoder backbone and position-interpolated rotary positional encoding to enhance robustness and expressiveness, integrating image-pair matching features.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates superior performance in various dense 3D prediction tasks and showcases the potential for broader applications through a geometrically consistent multi-view inference pipeline.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.16290

24. Uncertainty-Based Methods for Automated Process Reward Data Construction and Output Aggregation in Mathematical Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Uncertainty-driven framework, Process-Level Reward Models, Mathematical reasoning, Data generation, Output aggregation
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of Process-Level Reward Models in mathematical reasoning tasks through an automated uncertainty-driven framework for reward data construction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– An uncertainty-driven framework is proposed to automate process reward data construction and annotation. Additionally, two output aggregation methods, Hybrid Majority Reward Vote and Weighted Reward Frequency Vote, are introduced to enhance existing methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework and aggregation methods show significant improvements in mathematical reasoning abilities across diverse Process-Level Reward Models, as evidenced by experiments on ProcessBench, MATH, and GSMPlus datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.01773

25.
