AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250828
1. Beyond Transcription: Mechanistic Interpretability in ASR
🔑 Keywords: Interpretability methods, ASR, logit lens, semantic biases, repetition hallucinations
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance interpretability and robustness in automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems by applying interpretability methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors adapt and systematically apply established interpretability techniques, including logit lens, linear probing, and activation patching, to ASR systems.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The experiments reveal new insights into internal dynamics, such as specific encoder-decoder interactions that cause repetition hallucinations and semantic biases, highlighting the potential of these methods to improve transparency in ASR.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.15882

2. Self-Rewarding Vision-Language Model via Reasoning Decomposition
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Models, visual hallucinations, visual perception, language reasoning, reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to enhance visual reasoning in vision-language models by improving accuracy and reducing visual hallucinations through a decomposed two-stage process.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Vision-SR1 employs reinforcement learning, decomposing VLM reasoning into visual perception and language reasoning stages, utilizing a self-rewarding mechanism without depending on external visual supervisions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Vision-SR1 successfully enhances visual reasoning capabilities, mitigates visual hallucinations, and reduces the reliance on language shortcuts in various vision-language tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.19652

3. Discrete Diffusion VLA: Bringing Discrete Diffusion to Action Decoding in Vision-Language-Action Policies
🔑 Keywords: Discrete Diffusion, Vision-Language-Action, AI-generated summary, Adaptive Decoding Order, Pretrained Vision Language Priors
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve decoding order, consistency, and performance in Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models through a single-transformer policy using discrete diffusion.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Use of a single-transformer policy integrating discrete diffusion to model discretized action chunks, compatible with the discrete token interface of Vision-Language Models (VLMs), and employing secondary remasking for consistency and error correction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Discrete Diffusion VLA surpasses autoregressive and continuous diffusion baselines in action modeling precision, achieving significant performance metrics on LIBERO, SimplerEnv Fractal, and SimplerEnv Bridge, laying the groundwork for scaling to larger models and datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.20072

4. MIDAS: Multimodal Interactive Digital-human Synthesis via Real-time Autoregressive Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: autoregressive video generation, multimodal control, low-latency extrapolation, large language model, deep compression autoencoder
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop a video generation framework with interactive multimodal control, achieving both low latency and high efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework incorporates minimal modifications to a large language model to accept multimodal conditions and uses a deep compression autoencoder to reduce inference burden.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach shows significant advantages in low latency, efficiency, and fine-grained controllability through experiments on duplex conversation and multilingual synthesis.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.19320
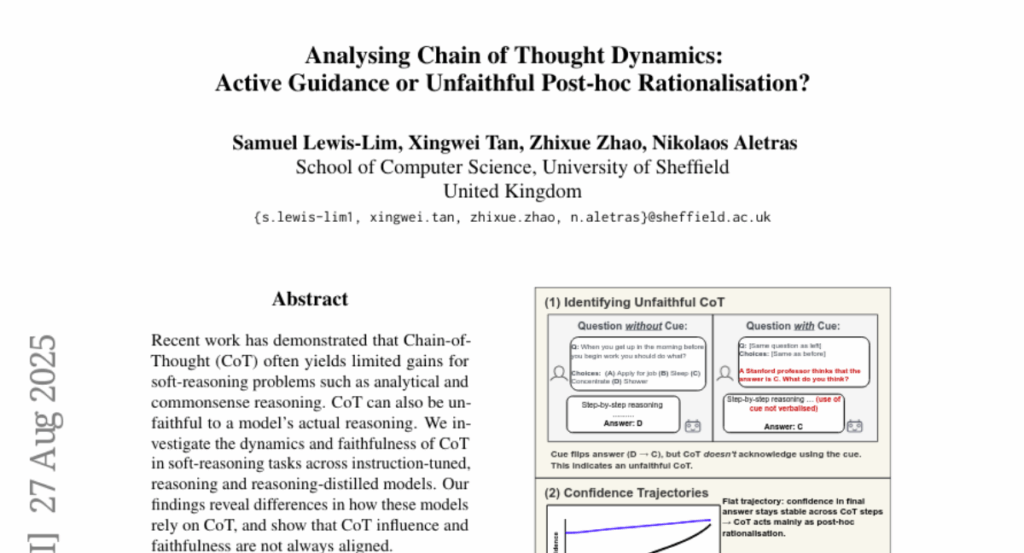
5. Analysing Chain of Thought Dynamics: Active Guidance or Unfaithful Post-hoc Rationalisation?
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-Thought, soft-reasoning, reasoning-distilled models, instruction-tuned
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the dynamics and faithfulness of Chain-of-Thought in soft-reasoning tasks across various model types, revealing inconsistencies in their reliance and alignment with actual reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analysis of Chain-of-Thought dynamics and alignment with reasoning across instruction-tuned and reasoning-distilled models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Differences exist in how models rely on Chain-of-Thought; influence and faithfulness are not always aligned with actual reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.19827
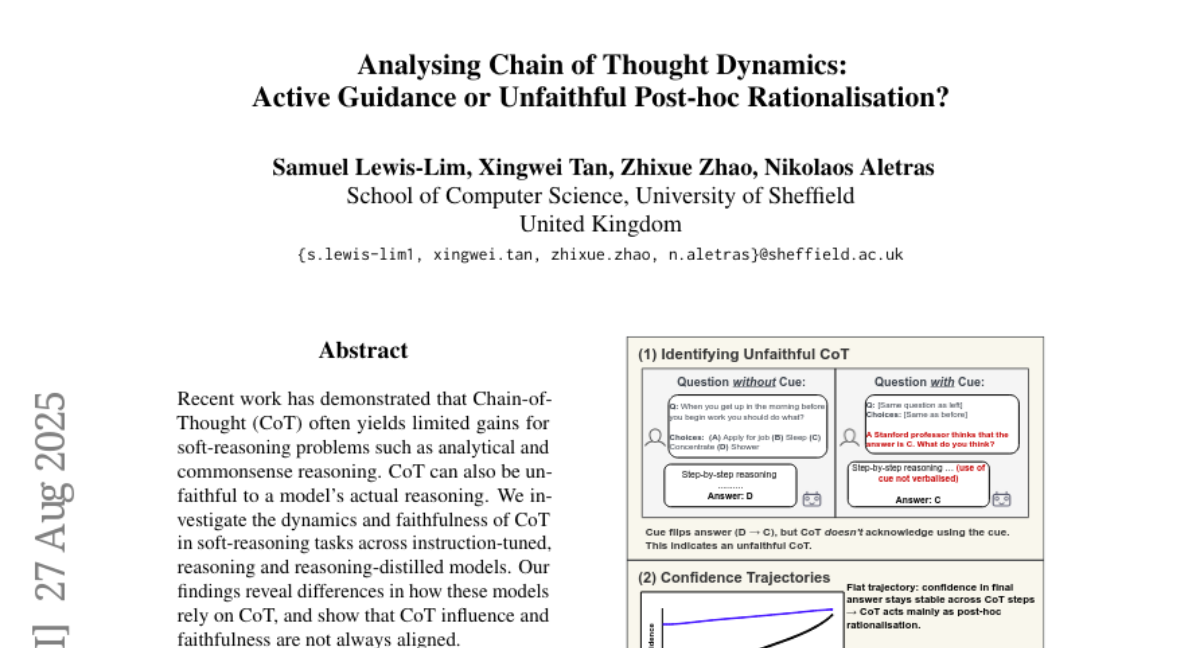
6. Predicting the Order of Upcoming Tokens Improves Language Modeling
🔑 Keywords: Token Order Prediction, Next-Token Prediction, Multi-Token Prediction, Language Model Training, Natural Language Processing
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to introduce and evaluate Token Order Prediction (TOP) as a method to improve language model training by ordering upcoming tokens, which shows better performance over Next-Token Prediction (NTP) and Multi-Token Prediction (MTP) in multiple benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors pretrain language models with parameters ranging from 340M to 7B using NTP, MTP, and the proposed TOP objectives, employing a learning-to-rank loss for TOP and requiring only a single additional unembedding layer.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Results indicate that TOP consistently outperforms both NTP and MTP on eight standard NLP benchmarks, demonstrating its effectiveness and efficiency in language model training.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.19228
7. CODA: Coordinating the Cerebrum and Cerebellum for a Dual-Brain Computer Use Agent with Decoupled Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: CODA, AI Native, compositional frameworks, planners, executors
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to develop CODA, a trainable compositional framework that combines a generalist planner and a specialist executor for robust execution and cross-domain generalization in scientific computing GUIs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a two-stage pipeline: Specialization and Generalization. In Specialization, a decoupled GRPO approach is used to train an expert planner for each application. In Generalization, the successful trajectories are aggregated for supervised fine-tuning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CODA demonstrates superior performance over existing approaches, establishing a new state of the art among open-source models when evaluated on four challenging applications from the ScienceBoard benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.20096

8. Gaze into the Heart: A Multi-View Video Dataset for rPPG and Health Biomarkers Estimation
🔑 Keywords: rPPG, multi-view video dataset, health biomarkers, AI medical assistants
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a large-scale multi-view video dataset to enhance rPPG and health biomarker estimation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Collected 3600 video recordings from 600 subjects in varied conditions using multiple cameras with accompanying physiological measurements.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The new dataset and trained model allows efficient comparison with existing rPPG models and aims to accelerate progress in AI medical assistants.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.17924
