AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20250924

1. Baseer: A Vision-Language Model for Arabic Document-to-Markdown OCR
🔑 Keywords: Arabic document OCR, vision-language model, decoder-only fine-tuning, WER, domain-specific adaptation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a vision-language model, Baseer, specifically fine-tuned for Arabic document OCR to enhance performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a decoder-only fine-tuning strategy on a multimodal large language model, leveraging a large-scale dataset of synthetic and real-world documents.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Baseer achieves state-of-the-art results with a WER of 0.25, outperforming existing open-source and commercial solutions, and highlights the advantages of domain-specific adaptation of general-purpose multimodal large language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.18174

2. Reinforcement Learning on Pre-Training Data
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Pre-Training, large language models, RLPT, generalizable reasoning skills
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to optimize large language models by using Reinforcement Learning on Pre-Training data (RLPT) to enhance reasoning skills without human annotation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– RLPT utilizes autonomous exploration of pre-training data trajectories, using a next-segment reasoning objective for deriving reward signals directly from data, eliminating the need for human annotation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments demonstrate RLPT’s effectiveness with notable improvements across various benchmarks, showcasing promise for further scaling and advancement of large language models’ reasoning abilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19249

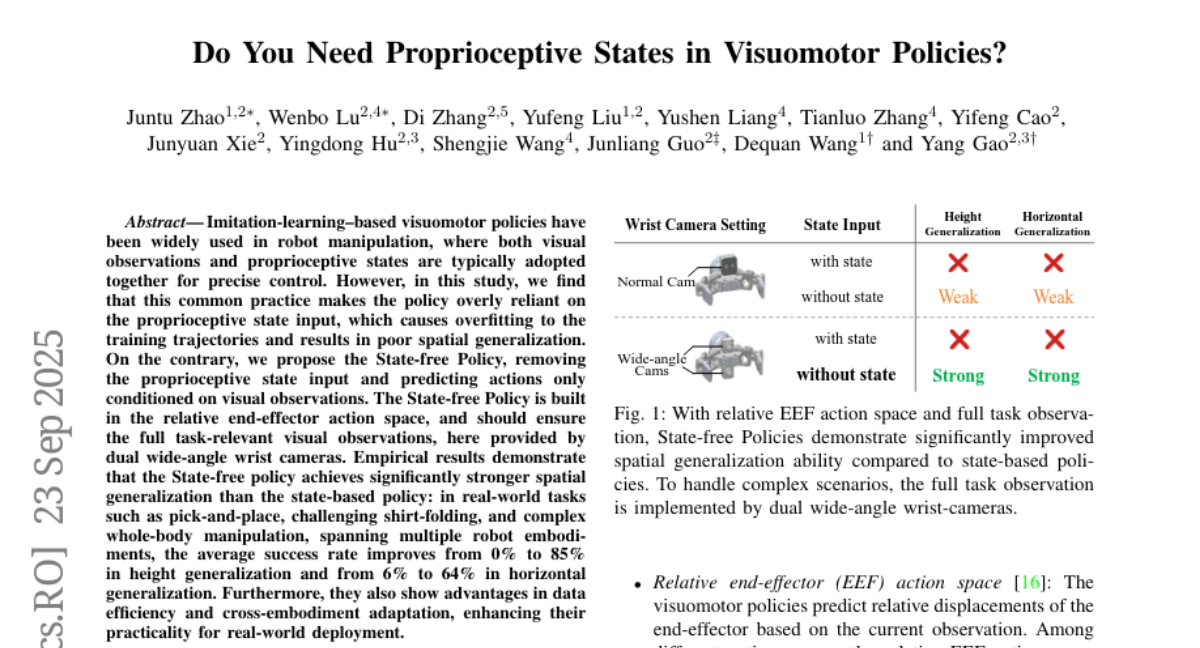
3. Do You Need Proprioceptive States in Visuomotor Policies?
🔑 Keywords: State-free Policy, spatial generalization, overfitting, proprioceptive state input, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve spatial generalization and data efficiency in robot manipulation tasks by employing a State-free Policy that relies solely on visual observations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a State-free Policy in a relative end-effector action space, utilizing visual observations from dual wide-angle wrist cameras without relying on proprioceptive state input.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The State-free Policy demonstrates significantly stronger spatial generalization compared to state-based policies, with improved success rates in real-world tasks, and shows advantages in data efficiency and cross-embodiment adaptation, proving its practicality for real-world deployment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.18644
4. MiniCPM-V 4.5: Cooking Efficient MLLMs via Architecture, Data, and Training Recipe
🔑 Keywords: MiniCPM-V 4.5, Multimodal Large Language Models, 3D-Resampler, Unified Learning Paradigm, Hybrid Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the efficiency and performance of multimodal large language models, making them more accessible and scalable.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a unified 3D-Resampler model architecture for compact encoding.
– Employed a unified learning paradigm for document and text recognition.
– Used a hybrid reinforcement learning strategy for improved reasoning modes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MiniCPM-V 4.5 surpasses well-known models like GPT-4o-latest in performance while maintaining remarkable efficiency.
– State-of-the-art results achieved in VideoMME benchmark among models under 30B, with significantly reduced GPU memory and inference time.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.18154

5. MAPO: Mixed Advantage Policy Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Mixed Advantage Policy Optimization, Reinforcement Learning, Advantage Function, GRPO, Foundation Models
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose a new strategy called Mixed Advantage Policy Optimization (MAPO) to improve trajectory ranking in reinforcement learning for foundation models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a dynamic reweighting mechanism for the advantage function to adapt to sample-specific characteristics and address issues with advantage reversion and advantage mirror problems.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MAPO proved effective in trajectory ranking with improved performance in comparison with state-of-the-art methods, as validated by ablation studies on different advantage variants.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.18849

6. Hyper-Bagel: A Unified Acceleration Framework for Multimodal Understanding and Generation
🔑 Keywords: Hyper-Bagel, speculative decoding, multi-stage distillation, multimodal understanding, image editing
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To accelerate multimodal understanding and generation tasks efficiently without sacrificing quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a unified acceleration framework, Hyper-Bagel, using speculative decoding for next-token prediction and a multi-stage distillation process for diffusion denoising.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Hyper-Bagel achieves significant performance gains, including a 16.67x speedup in text-to-image generation and a 22x speedup in image editing while maintaining output quality. A highly efficient model is developed for real-time interaction through advanced adversarial distillation and human feedback learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.18824

7. VolSplat: Rethinking Feed-Forward 3D Gaussian Splatting with Voxel-Aligned Prediction
🔑 Keywords: VolSplat, voxel-aligned Gaussians, 3D reconstruction, novel view synthesis, geometric consistency
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve novel view synthesis and 3D reconstruction quality by addressing the limitations of pixel-aligned Gaussian prediction methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of VolSplat, a multi-view feed-forward model using voxel-aligned Gaussians that predicts Gaussians from a 3D voxel grid for superior multi-view consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VolSplat achieves state-of-the-art performance with improved geometric consistency and novel-view rendering quality, offering a scalable framework for robust 3D reconstruction.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19297
8. What Characterizes Effective Reasoning? Revisiting Length, Review, and Structure of CoT
🔑 Keywords: Large reasoning models, Chain-of-thought, Failed-Step Fraction, AI-generated summary, structure-aware
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate what characterizes effective chain-of-thought (CoT) in large reasoning models, emphasizing fewer failed steps and better structural quality rather than length or review.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted a systematic evaluation across ten large reasoning models on math and scientific reasoning.
– Introduced a graph view of CoT to extract structure and identify the Failed-Step Fraction (FSF).
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study finds that naive lengthening of CoT and increased review lead to lower accuracy.
– Effective CoT fails less, with the Failed-Step Fraction outperforming other metrics for correctness and supporting structure-aware test-time scaling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19284

9. Lyra: Generative 3D Scene Reconstruction via Video Diffusion Model Self-Distillation
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, video diffusion models, 3D Gaussian Splatting, dynamic 3D scene generation, real-time rendering
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to transform implicit 3D knowledge from **video diffusion models** into an explicit **3D Gaussian Splatting** representation, allowing for the generation of 3D scenes from text or images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces a **self-distillation framework** that utilizes a 3DGS decoder supervised by an RGB decoder, enabling the framework to train with synthetic data and produce 3D scenes without needing multi-view training data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework achieves **state-of-the-art** performance in both static and dynamic 3D scene generation, demonstrating the ability to synthesize 3D scenes from a text prompt or a single image for real-time rendering.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19296

10. Large Language Models Discriminate Against Speakers of German Dialects
🔑 Keywords: language models, dialect naming bias, dialect usage bias, AI Ethics, German dialects
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To assess whether large language models (LLMs) exhibit dialect naming and usage bias against German dialect speakers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized sociolinguistic literature on dialect perception to analyze traits associated with dialect speakers.
– Conducted association and decision tasks to evaluate LLM biases using a novel evaluation corpus pairing sentences from seven regional German dialects with their standard German counterparts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– All evaluated LLMs exhibit significant dialect naming and usage bias, associating negative adjectives with German dialect speakers.
– The explicit labeling of linguistic demographics, like German dialect speakers, amplifies bias more than implicit cues.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.13835

11. Soft Tokens, Hard Truths
🔑 Keywords: reinforcement learning, continuous tokens, chain-of-thought, language models, discrete tokens
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to introduce a scalable method for learning continuous chain-of-thought (CoT) tokens using reinforcement learning, improving performance and diversity over discrete tokens.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A novel reinforcement learning approach is utilized with “soft” tokens, integrating mixtures of tokens and noise on the input embedding to facilitate RL exploration while minimizing computational overhead.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Continuous CoT tokens enhance performance on math reasoning benchmarks and preserve out-of-domain predictions, offering a more versatile and efficient model deployment using discrete tokens for inference.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19170

12. HyRF: Hybrid Radiance Fields for Memory-efficient and High-quality Novel View Synthesis
🔑 Keywords: Hybrid Radiance Fields, AI-generated summary, neural fields, high-frequency parameters, hybrid rendering scheme
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop Hybrid Radiance Fields (HyRF) that combine explicit Gaussians and neural fields to achieve high-quality rendering with reduced memory overhead and real-time performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a decoupled neural field architecture to separately model geometry and view-dependent color, and a hybrid rendering scheme to effectively composite Gaussian splatting with a neural field-predicted background.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HyRF achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality while reducing model size by over 20 times compared to traditional 3D Gaussian Splatting, maintaining real-time performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.17083
13. OpenGVL – Benchmarking Visual Temporal Progress for Data Curation
🔑 Keywords: OpenGVL, AI-generated summary, vision-language models, robotics datasets
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop OpenGVL as a benchmark for predicting task progress in robotics using vision-language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluate publicly available open-source and closed-source vision-language models on temporal progress prediction tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Open-source models significantly underperform compared to closed-source models, reaching only about 70% of their performance.
– OpenGVL can be used for automated data curation and efficient quality assessment of large-scale robotics datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.17321
14. CAR-Flow: Condition-Aware Reparameterization Aligns Source and Target for Better Flow Matching
🔑 Keywords: Conditional generative modeling, Flow-based methods, Probability path, Image data, FID
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance conditional generative modeling by repositioning distributions for faster training and improved performance on image data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Condition-Aware Reparameterization for Flow Matching (CAR-Flow), which is a lightweight, learned shift that conditions distributions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CAR-Flow shortens the probability path the model must learn, effectively accelerating training.
– On ImageNet-256, CAR-Flow reduces FID from 2.07 to 1.68, while adding less than 0.6% additional parameters to the model.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19300

15. CommonForms: A Large, Diverse Dataset for Form Field Detection
🔑 Keywords: CommonForms, Form Field Detection, Object Detection, FFDNet-Small, FFDNet-Large
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce CommonForms, a web-scale dataset for form field detection, classifying fields into Text Input, Choice Button, and Signature.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing a filtering process on Common Crawl to create a diverse dataset of 55k documents from an initial 8 million.
– Deploying FFDNet-Small and FFDNet-Large models that achieve high precision in detecting form fields.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Ablation studies highlight the importance of high-resolution inputs and data cleaning for efficient form field detection.
– The proposed models outperform commercial PDF readers, effectively predicting diverse form fields including checkboxes.
– Released the first large-scale dataset and open-source models for form field detection, available on GitHub.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.16506

16. Better Late Than Never: Evaluation of Latency Metrics for Simultaneous Speech-to-Text Translation
🔑 Keywords: SimulST, YAAL, LongYAAL, SoftSegmenter, latency metrics
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to analyze SimulST latency metrics and identify segmentation bias to improve latency evaluation accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of YAAL and LongYAAL as refined latency metrics for both short-form and unsegmented audio, and SoftSegmenter for improved alignment quality in translations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– YAAL and LongYAAL provide more accurate latency evaluations compared to existing metrics, while SoftSegmenter enhances alignment quality in long-form evaluations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.17349

17. RadEval: A framework for radiology text evaluation
🔑 Keywords: RadEval, LLM-based evaluators, radiology texts, AI-generated summary, zero-shot retrieval
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to introduce and establish RadEval as a comprehensive framework for evaluating radiology texts with diverse metrics to ensure reproducibility and robust benchmarking.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– RadEval utilizes a range of metrics including n-gram overlap, contextual measures, and advanced LLM-based evaluators.
– It refines and extends implementations, supports multiple imaging modalities, and includes pretrained domain-specific radiology encoders.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework provides statistical testing tools and baseline model evaluations, enhancing reproducibility.
– It includes an expertly annotated dataset with clinically significant error labels, aligning metric correlations with radiologist judgment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.18030

18. GeoSVR: Taming Sparse Voxels for Geometrically Accurate Surface Reconstruction
🔑 Keywords: GeoSVR, sparse voxels, surface reconstruction, Voxel-Uncertainty Depth Constraint, Surface Regularization
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce GeoSVR, a voxel-based framework designed to improve the accuracy and detail of surface reconstruction by leveraging sparse voxels with depth constraints and surface regularization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed the Voxel-Uncertainty Depth Constraint to enhance scene constraints using monocular depth cues while maintaining geometric precision.
– Designed Sparse Voxel Surface Regularization to promote geometric consistency and facilitate the formation of sharp, detailed surfaces.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GeoSVR demonstrated superior performance over existing methods in terms of geometric accuracy, detail preservation, and reconstruction completeness across various scenarios, while ensuring high efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.18090

19. VIR-Bench: Evaluating Geospatial and Temporal Understanding of MLLMs via Travel Video Itinerary Reconstruction
🔑 Keywords: VIR-Bench, MLLMs, geospatial-temporal intelligence, itinerary recommendations, travel videos
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to introduce VIR-Bench, a new benchmark designed to evaluate and enhance the geospatial-temporal intelligence of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to improve real-world applications like itinerary recommendations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study presents VIR-Bench, consisting of 200 travel videos, framing itinerary reconstruction as a challenging task to push the geospatial-temporal intelligence of MLLMs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results show that state-of-the-art MLLMs struggle with the complexities of long-distance travel videos, suggesting areas for improvement, and insights from VIR-Bench lead to a prototype travel-planning agent that shows improved itinerary recommendations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19002

20. Zero-Shot Multi-Spectral Learning: Reimagining a Generalist Multimodal Gemini 2.5 Model for Remote Sensing Applications
🔑 Keywords: Multi-spectral imagery, Remote Sensing, multimodal models, Zero-Shot, Gemini2.5
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to enable generalist multimodal models to process multi-spectral imagery in a zero-shot manner, enhancing performance in remote sensing tasks without the need for additional training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach involves introducing new multi-spectral data as inputs to generalist multimodal models, which are typically trained on RGB inputs. It leverages the models’ understanding of visual space and injects domain-specific information as instructions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Gemini2.5 model demonstrates strong zero-shot performance on remote sensing benchmarks, highlighting the potential for easy adaptability and accelerated work for geospatial professionals using specialized sensor data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19087

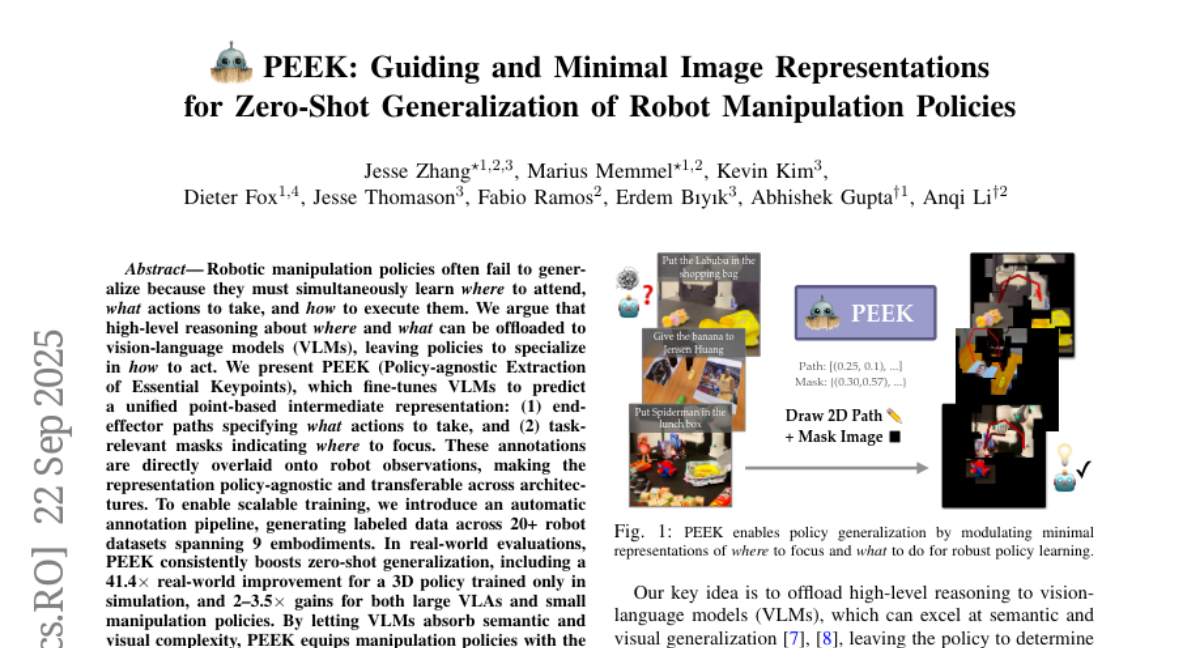
21. PEEK: Guiding and Minimal Image Representations for Zero-Shot Generalization of Robot Manipulation Policies
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Models, Zero-Shot Generalization, Robotic Manipulation, Policy-Agnostic, Keypoints
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces PEEK, a method for enhancing robotic manipulation by fine-tuning vision-language models to assist in predicting keypoints crucial for various policies and robotic embodiments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– PEEK employs a policy-agnostic intermediate representation to instruct end-effector paths and task-relevant masks, using an automatic annotation pipeline that labels data from over 20 robot datasets across 9 embodiments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PEEK significantly boosts zero-shot generalization abilities in robotics, demonstrated by real-world improvements such as a 41.4x performance gain for a 3D policy trained only in simulations and notable gains for both large and small manipulation policies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.18282
22. DRISHTIKON: A Multimodal Multilingual Benchmark for Testing Language Models’ Understanding on Indian Culture
🔑 Keywords: multimodal, multilingual, cultural understanding, generative AI systems, text-image pairs
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce DRISHTIKON, a unique multimodal and multilingual benchmark designed solely to evaluate the cultural understanding of generative AI systems within the diverse cultural spectrum of India.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a dataset with over 64,000 aligned text-image pairs covering 15 languages and various cultural themes to evaluate various vision-language models, including both proprietary and open-source systems, in zero-shot and chain-of-thought settings.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current models exhibit significant limitations in reasoning over culturally grounded, multimodal inputs, especially in low-resource languages, identifying a need for more inclusive AI research to develop culturally aware multimodal language technologies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2509.19274

23.
