AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251125

1. General Agentic Memory Via Deep Research
🔑 Keywords: JIT compilation, Reinforcement Learning, light-weight memorizer, AI-generated summary, large language models
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose the General Agentic Memory (GAM) framework to improve memory efficiency and task completion for AI agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Leverages JIT compilation principles, features a duo-design with components—Memorizer and Researcher—to handle offline and online memory tasks efficiently.
– Utilizes reinforcement learning to optimize performance with large language models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates significant improvements in memory-grounded task completion scenarios compared to existing memory systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18423

2. AutoEnv: Automated Environments for Measuring Cross-Environment Agent Learning
🔑 Keywords: AutoEnv, AutoEnv-36, cross-environment learning, heterogeneous environments, learning methods
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the lack of standardized frameworks and datasets for evaluating cross-environment learning in AI agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of AutoEnv, an automated framework for creating heterogeneous worlds.
– Construction of AutoEnv-36, a dataset with 36 environments and 358 levels.
– Formalization of agent learning as a component-centric process and evaluation of eight learning methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Single learning methods do not scale effectively across numerous heterogeneous environments.
– Environment-adaptive selection of learning methods improves performance but faces diminishing returns with expanding method space.
– AutoEnv and AutoEnv-36 serve as valuable testbeds for studying cross-environment agent learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19304

3. Computer-Use Agents as Judges for Generative User Interface
🔑 Keywords: Computer-Use Agents, Graphical User Interfaces, coding-oriented language models, task solvability, CUA Dashboard
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate whether Computer-Use Agents can assist coding-oriented language models in the automatic design of Graphical User Interfaces.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed AUI-Gym, a benchmark for GUI development across 52 applications, synthesizing 1560 tasks using language models. Additionally, created a verifier to ensure task executability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Introduced a framework where Coder acts as Designer and CUA serves as Judge to enhance GUI design efficiency. Achievements in interface design prioritize task solvability and agent-native efficiency, pushing agents towards active participation in digital environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.15567
4. DeCo: Frequency-Decoupled Pixel Diffusion for End-to-End Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: Pixel diffusion, frequency-DeCoupled, diffusion transformer, frequency-aware flow-matching loss, ImageNet
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance image generation efficiency and quality by separating high-frequency details from low-frequency semantics using a frequency-DeCoupled pixel diffusion framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The proposal includes leveraging a lightweight pixel decoder for high-frequency details and introducing a frequency-aware flow-matching loss to emphasize visually salient frequencies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The frequency-DeCoupled framework achieves superior performance in pixel diffusion models, evidenced by a lower FID score on ImageNet and a high GenEval score for a text-to-image model.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19365

5. DR Tulu: Reinforcement Learning with Evolving Rubrics for Deep Research
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Evolving Rubrics, Deep Research Models, Long-Form Tasks, AI-Generated Summary
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enable deep research models to efficiently handle long-form tasks through Reinforcement Learning with Evolving Rubrics (RLER).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of RLER to evolve rubrics alongside policy models during training, allowing for dynamic and on-policy feedback.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The newly developed DR Tulu-8B model demonstrates superior performance in long-form deep research across multiple domains and is cost-effective compared to existing models and proprietary systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19399

6. UltraFlux: Data-Model Co-Design for High-quality Native 4K Text-to-Image Generation across Diverse Aspect Ratios
🔑 Keywords: UltraFlux, Diffusion Transformers, Positional Encoding, 4K Resolution, VAE Compression
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address failures in diffusion transformers at 4K resolution through enhancements like positional encoding and VAE compression.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement a co-design approach with UltraFlux, a Flux-based DiT trained on a 4K dataset, using strategies like Resonance 2D RoPE for positional encoding and a simple VAE post-training scheme for better reconstruction fidelity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UltraFlux consistently outperforms existing models in fidelity and aesthetics, effectively handling different aspect ratios, and even matching or surpassing proprietary solutions like Seedream 4.0.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18050

7. In-Video Instructions: Visual Signals as Generative Control
🔑 Keywords: Video generative models, In-Video Instruction, AI-generated summary, spatial-aware
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the capability of video generative models in controllable image-to-video generation using In-Video Instruction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Examined the interpretation of visual signals embedded within frames using overlaid text, arrows, or trajectories.
– Conducted extensive experiments with state-of-the-art video generators like Veo 3.1, Kling 2.5, and Wan 2.2.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Video models effectively interpret and execute visually embedded instructions, improving control over image-to-video generation, especially in complex multi-object scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19401

8. Budget-Aware Tool-Use Enables Effective Agent Scaling
🔑 Keywords: Budget Awareness, Tool-Augmented Agents, Cost-Performance, AI Systems and Tools, Budget Aware Test-time Scaling
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve scaling of tool-augmented agents by introducing continuous budget awareness and adaptive planning for better cost-performance trade-offs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A lightweight plug-in called Budget Tracker is developed to provide continuous budget awareness.
– An advanced framework named BATS (Budget Aware Test-time Scaling) is introduced, leveraging budget awareness for dynamic planning and verification.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Budget-aware methods lead to more favorable scaling curves and advance the cost-performance Pareto frontier of tool-augmented agents.
– The study provides a systematic exploration of budget-constrained agents, offering insights into transparent and principled scaling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.17006

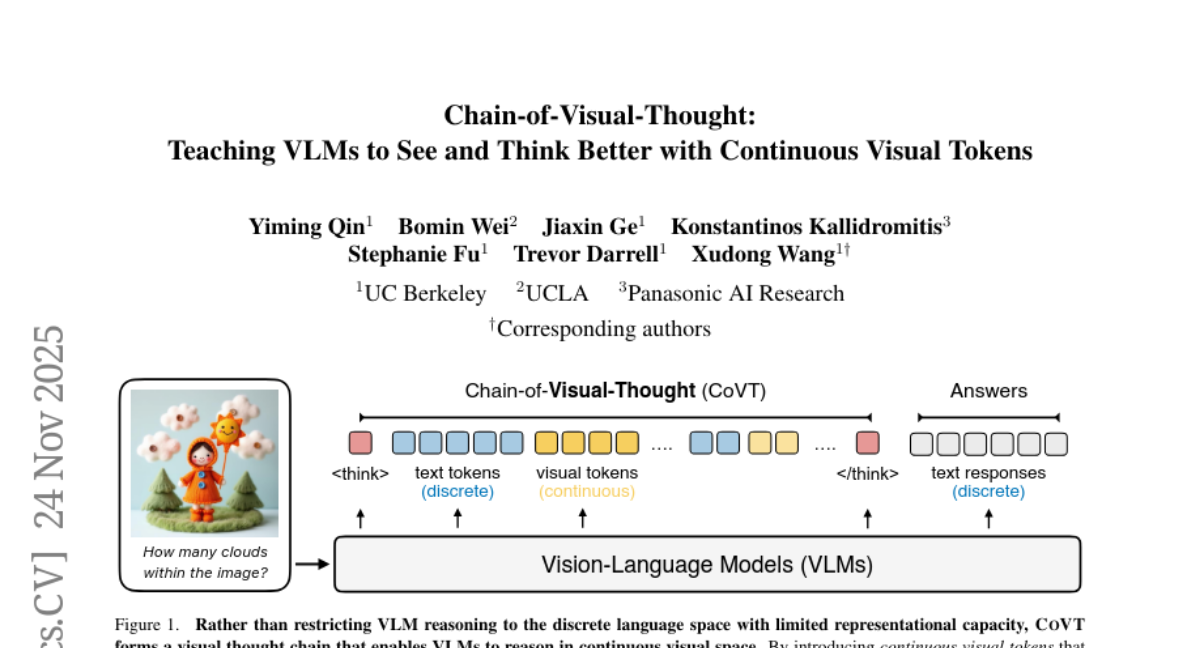
9. Chain-of-Visual-Thought: Teaching VLMs to See and Think Better with Continuous Visual Tokens
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-Visual-Thought, Vision-Language Models, visual tokens, dense supervision signals, multimodal intelligence
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to enhance Vision-Language Models (VLMs) by enabling them to reason with visual tokens, thus improving performance on perceptual tasks by capturing dense visual information.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces Chain-of-Visual-Thought (COVT), which distills knowledge from lightweight vision experts into compact visual tokens that encode rich perceptual cues. The VLM with COVT makes predictions in continuous visual token space and is trained to reconstruct dense supervision signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Integrating COVT into strong VLMs consistently enhances performance across various perception benchmarks by 3% to 16%, showcasing that compact continuous visual thinking supports more precise, grounded, and interpretable multimodal intelligence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19418
10. Pillar-0: A New Frontier for Radiology Foundation Models
🔑 Keywords: Radiology Foundation Model, RATE, AUROC, Brain Hemorrhage Detection, Clinical Practice
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce Pillar-0, a radiology foundation model that enhances performance across a wide array of radiology tasks and extends capabilities to new applications utilizing RATE for labeling with high accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Pretraining Pillar-0 on large datasets including abdomen-pelvis CTs, chest CTs, head CTs, and breast MRIs, and using RATE, a framework to extract structured labels with near-perfect accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Pillar-0 outperforms existing models like MedGemma, MedImageInsight, Lingshu, and Merlin with higher AUROC scores. It excels in brain hemorrhage detection with significant efficiency and generalizes well to new tasks, showcasing a clinically rigorous platform for advanced radiology systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.17803

11. Plan-X: Instruct Video Generation via Semantic Planning
🔑 Keywords: Plan-X, Semantic Planner, visual hallucinations, multimodal semantic tokens, video generation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To integrate a Semantic Planner with diffusion models to reduce visual hallucinations and align video generation with instructions using multimodal semantic tokens.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A learnable multimodal language model is used to create text-grounded spatio-temporal semantic tokens, enhancing video diffusion model synthesis.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Plan-X significantly decreases visual hallucinations and enables detailed, instruction-aligned video generation that consistently adheres to multimodal context.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.17986

12. HunyuanVideo 1.5 Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: HunyuanVideo 1.5, DiT architecture, video super-resolution, text-to-video, open-source
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a lightweight video generation model with state-of-the-art visual quality and motion coherence.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized DiT architecture with SSTA and video super-resolution network, enhanced by selective and sliding tile attention, glyph-aware text encoding, and progressive pre-training and post-training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HunyuanVideo 1.5 establishes a new state-of-the-art in open-source video generation, offering high-performance capabilities on consumer-grade GPUs and accessible advanced video generation to a broader audience.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18870

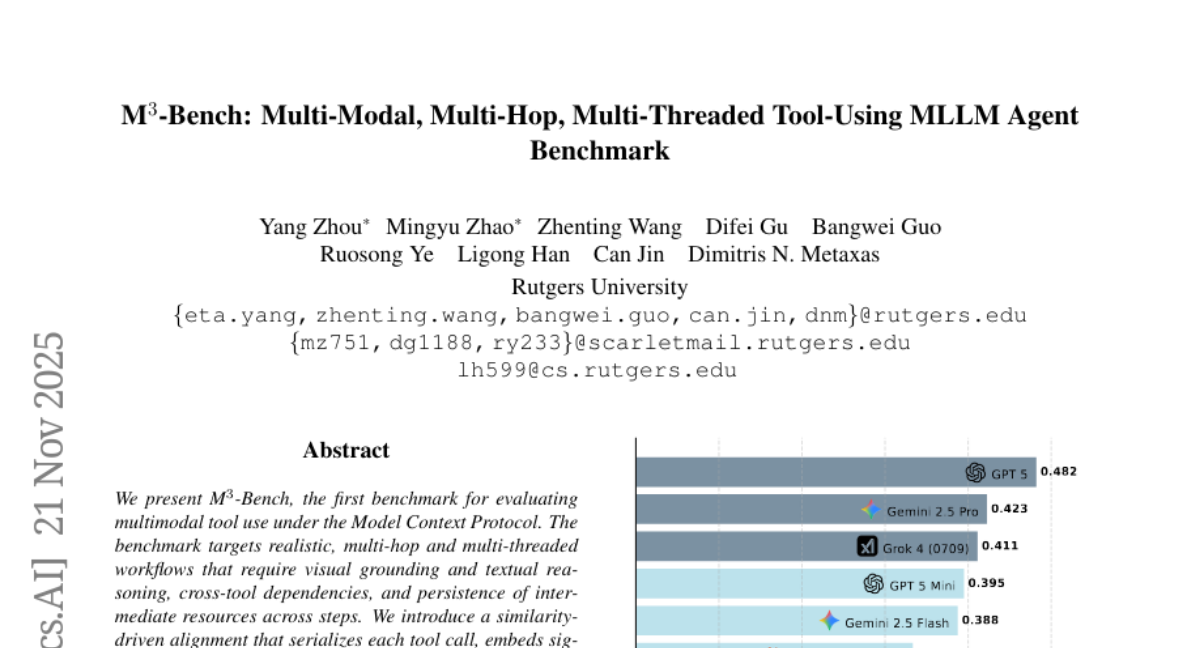
13. M3-Bench: Multi-Modal, Multi-Hop, Multi-Threaded Tool-Using MLLM Agent Benchmark
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, multimodal tool use, visual grounding, textual reasoning, Multimodal LLMs
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce M^3-Bench, a benchmark evaluating multimodal tool use with focus on visual grounding, textual reasoning, and cross-tool dependencies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ similarity-driven alignment using sentence encoders and Hungarian matching to establish one-to-one correspondences.
– Utilize an Executor & Judge pipeline with human verification for standardized trajectories.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current multimodal MLLMs reveal gaps in argument fidelity and structure consistency, indicating a need for improved joint reasoning methods over images, text, and tool graphs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.17729
14. Multi-Agent Deep Research: Training Multi-Agent Systems with M-GRPO
🔑 Keywords: M-GRPO, Multi-agent systems, Group Relative Policy Optimization, trajectory-alignment, decoupled training pipeline
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The introduction of M-GRPO to enhance stability and efficiency in hierarchical multi-agent systems, particularly in tool-augmented reasoning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– M-GRPO employs a hierarchical extension of Group Relative Policy Optimization, involving trajectory alignment and a decoupled training pipeline to manage heterogeneous trajectories and server-separated agent deployment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– In tests involving real-world benchmarks, M-GRPO demonstrates superior stability and sample efficiency compared to existing single-agent and multi-agent GRPO approaches, indicating enhanced performance in tool-augmented reasoning tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.13288

15. MIST: Mutual Information Via Supervised Training
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Neural Network, Quantile Regression, Meta-dataset, Mutual Information (MI)
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to design Mutual Information (MI) estimators using a fully data-driven approach parameterized by a neural network.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves training a neural network on a large meta-dataset of synthetic joint distributions using two-dimensional attention and optimizing for quantile regression loss.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed MI estimators outperform classical baselines and offer better-calibrated confidence intervals compared to existing methods, with significantly faster inference speeds.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18945

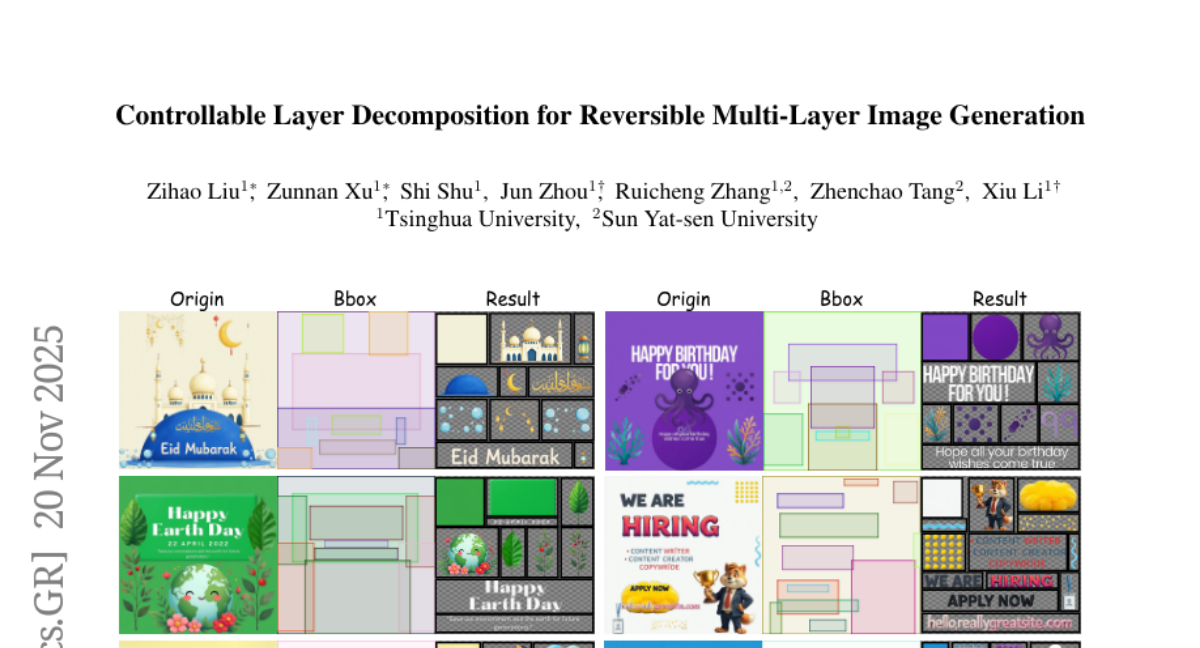
16. Controllable Layer Decomposition for Reversible Multi-Layer Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: Controllable Layer Decomposition, layer separation, image matting, segmentation precision, conditional generation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Controllable Layer Decomposition (CLD) for fine-grained, controllable separation of raster images into RGBA layers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed two key modules: LayerDecompose-DiT (LD-DiT) for image element decoupling and Multi-Layer Conditional Adapter (MLCA) for precise conditional generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CLD demonstrates superior decomposition quality and controllability compared to existing methods. It enhances practical applicability by allowing manipulation of separated layers in common design tools like PowerPoint.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.16249
17. MASS: Motion-Aware Spatial-Temporal Grounding for Physics Reasoning and Comprehension in Vision-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Vision Language Models, physics-driven reasoning, spatial-temporal signals, 3D motion tracking, MASS-Bench
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the performance of Vision Language Models on physics-driven video reasoning tasks by integrating spatial-temporal signals and motion tracking.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a benchmark called MASS-Bench with 4,350 videos and 8,361 question-answer pairs focusing on physics comprehension.
– Introduced a model-agnostic method called MASS which injects spatial-temporal signals through depth-based 3D encoding and visual grounding, enhanced by a motion tracker.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The refined Vision Language Models significantly outperform comparable and larger baselines in physics reasoning, validating the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18373

18. PRInTS: Reward Modeling for Long-Horizon Information Seeking
🔑 Keywords: PRInTS, Information-Seeking, Generative PRM, Dense Scoring, Trajectory Summarization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces PRInTS, a generative process reward model aimed at enhancing information-seeking abilities in AI agents by overcoming limitations in existing models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– PRInTS is trained with dual capabilities: dense scoring to evaluate step quality across multiple dimensions and trajectory summarization to compress and retain essential step information.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive evaluations demonstrate that PRInTS improves the information-seeking capabilities of AI agents, matching or surpassing the performance of frontier models with smaller backbones, outperforming existing strong reward modeling baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19314

19. EvoVLA: Self-Evolving Vision-Language-Action Model
🔑 Keywords: EvoVLA, Vision-Language-Action, triplet contrastive learning, sim-to-real transfer, stage hallucination
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper presents EvoVLA, a self-supervised framework designed to improve long-horizon robotic manipulation by addressing stage hallucination through advanced learning techniques.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– EvoVLA utilizes triplet contrastive learning, pose-based exploration, and long-horizon memory to enhance accuracy and efficiency in robotic tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework significantly reduces stage hallucination and achieves better task success rates and sample efficiency in both simulation and real-world environments compared to existing models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.16166

20. Upsample Anything: A Simple and Hard to Beat Baseline for Feature Upsampling
🔑 Keywords: test-time optimization, Vision Foundation Models, anisotropic Gaussian kernel, semantic segmentation, depth estimation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a lightweight test-time optimization framework, Upsample Anything, that enhances low-resolution features to high-resolution outputs without training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method employs an anisotropic Gaussian kernel for precise high-resolution reconstruction, effectively combining Gaussian Splatting and Joint Bilateral Upsampling.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Upsample Anything achieves state-of-the-art performance in tasks such as semantic segmentation and depth estimation, running in approximately 0.419 seconds per 224×224 image.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.16301

21. AICC: Parse HTML Finer, Make Models Better — A 7.3T AI-Ready Corpus Built by a Model-Based HTML Parser
🔑 Keywords: language model, semantic understanding, two-stage formatting pipeline, structured element preservation, multilingual corpus
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study focuses on improving web data quality for training large language models through an innovative HTML extraction pipeline called MinerU-HTML.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MinerU-HTML is developed as a novel extraction pipeline that treats content extraction as a sequence labeling problem, utilizing a 0.6B-parameter language model with semantic understanding for improved document structure preservation.
– It employs a two-stage formatting pipeline that categorizes semantic elements before converting them to Markdown, offering scalability over traditional heuristic methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The new method demonstrates superior performance on MainWebBench, achieving higher ROUGE-N F1 scores and preserving structured elements like formulas and code blocks better than existing extractors.
– Models trained on AICC (AI-ready Common Crawl) outperform those trained on Trafilatura-extracted data across numerous benchmarks, confirming that higher extraction quality enhances model capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.16397

22. Target-Bench: Can World Models Achieve Mapless Path Planning with Semantic Targets?
🔑 Keywords: Target-Bench, world models, mapless path planning, fine-tuning, robotics
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aimed to evaluate world models on mapless path planning using a new benchmark called Target-Bench, targeting real-world semantic planning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers used Target-Bench, containing 450 robot-collected video sequences and SLAM-based ground truth trajectories, to evaluate state-of-the-art models on their path planning capabilities. Metrics measured included target-reaching capability, trajectory accuracy, and directional consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The results revealed significant limitations in current world models, with the best off-the-shelf model achieving only a 0.299 score. Fine-tuning improved a 5B-parameter model to a 0.345 score, a 400% improvement over its baseline and 15% better than the best off-the-shelf model. The study supports the effectiveness of fine-tuning on specialized benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.17792
23. One4D: Unified 4D Generation and Reconstruction via Decoupled LoRA Control
🔑 Keywords: 4D generation, Unified Masked Conditioning, Decoupled LoRA Control, RGB frames, pointmaps
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to present One4D, a unified framework for generating and reconstructing dynamic 4D content as synchronized RGB frames and pointmaps.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a Unified Masked Conditioning mechanism and Decoupled LoRA Control to handle varying sparsities and ensure pixel-level consistency between RGB frames and pointmaps.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– One4D effectively produces high-quality RGB frames and accurate pointmaps from both synthetic and real 4D datasets, advancing general, high-quality 4D world modeling using video diffusion models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18922
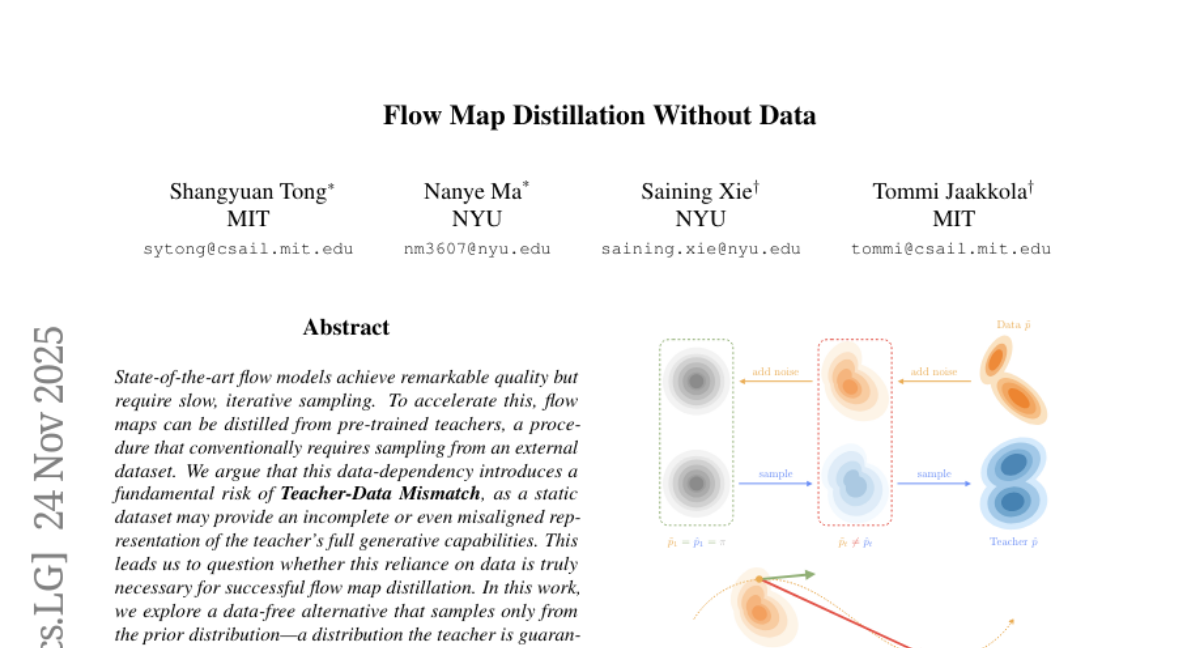
24. Flow Map Distillation Without Data
🔑 Keywords: data-free framework, flow map distillation, prior distribution, Teacher-Data Mismatch, FID
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Explore a data-free alternative to traditional flow map distillation methods that sample from prior distribution to achieve high fidelity without data dependency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce a framework that mimics the teacher’s sampling path while correcting its own errors, achieving high-quality results with minimal sampling steps.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method surpasses data-based alternatives and establishes a new state-of-the-art in flow map distillation, achieving FID of 1.45 and 1.49 on ImageNet with only 1 sampling step.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19428
25. Representational Stability of Truth in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Representational Stability, Linear Probe, Epistemic Familiarity, Truth Judgements
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To assess how stably large language models (LLMs) encode true, false, and neither-true-nor-false content in their internal representations through the concept of representational stability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized perturbation analysis and trained a linear probe on LLM activations to differentiate true from not-true statements, measuring the boundary shifts under controlled label changes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Found that epistemic familiarity influences representational stability more than linguistic form, indicating that familiar fictional contexts result in more coherent truth assignments, while unfamiliar content produces significant instabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19166

26. MSRNet: A Multi-Scale Recursive Network for Camouflaged Object Detection
🔑 Keywords: Camouflaged object detection, Pyramid Vision Transformer, Attention-Based Scale Integration Units, Multi-Granularity Fusion Units, recursive-feedback decoding strategy
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve camouflaged object detection by enhancing feature extraction and recursive feature refinement through a Multi-Scale Recursive Network.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The proposed method uses a Pyramid Vision Transformer backbone and Attention-Based Scale Integration Units for selective feature merging. A recursive-feedback decoding strategy is implemented to refine features and improve global context understanding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art results on two benchmark datasets for camouflaged object detection and ranks second on two others, demonstrating its effectiveness in handling small and multiple camouflaged objects.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.12810

27. Extracting Interaction-Aware Monosemantic Concepts in Recommender Systems
🔑 Keywords: Sparse Autoencoder, Monosemantic Neurons, Latent Dimensions, User-Item Affinity Predictions
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to extract interpretable latent dimensions from embeddings in recommender systems to support controllable personalization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a Sparse Autoencoder to identify semantic structures within pretrained representations, with a prediction-aware training objective to align the latent structure with user-item affinity predictions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method captures meaningful dimensions such as genre and popularity, enabling operations like targeted filtering and content promotion without altering the base model.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18024

28. Fidelity-Aware Recommendation Explanations via Stochastic Path Integration
🔑 Keywords: Explanation fidelity, SPINRec, path-integration, stochastic baseline sampling, recommendation systems
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance explanation fidelity in recommender systems using SPINRec, a model-agnostic approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper introduces a stochastic baseline sampling method along with path-integration techniques to better capture interactions in recommendation systems.
– Conducts a comprehensive fidelity evaluation across different models and datasets, using counterfactual metrics for validation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SPINRec consistently outperforms existing methods and sets a new benchmark for faithful explainability in recommendation systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18047

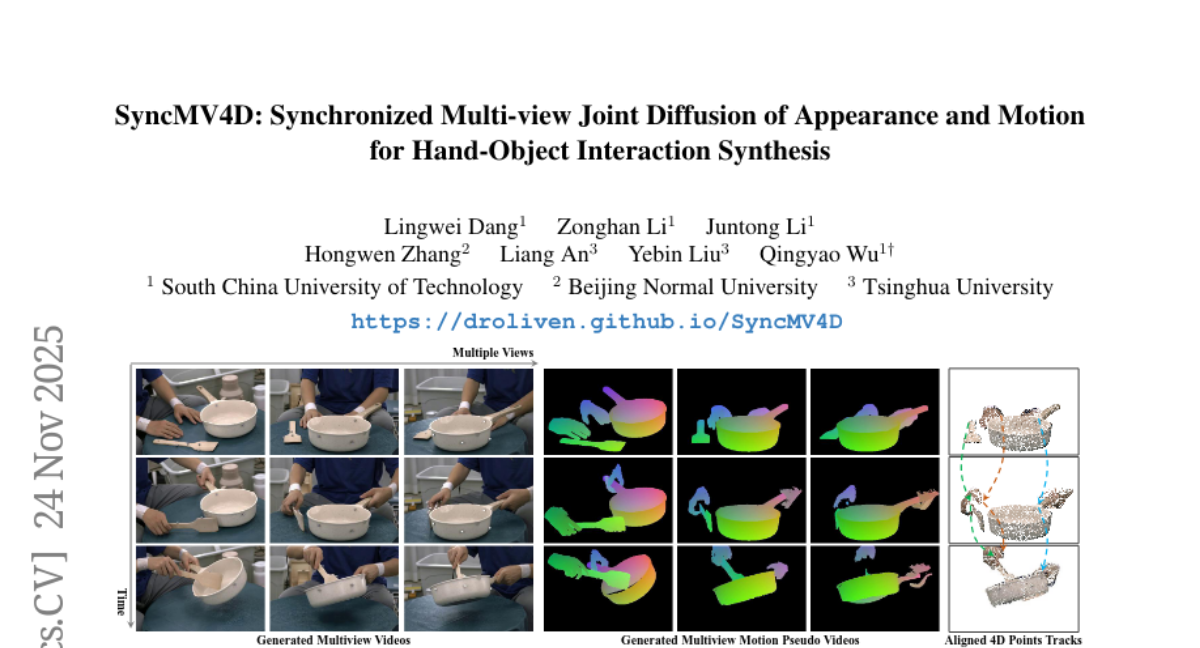
29. SyncMV4D: Synchronized Multi-view Joint Diffusion of Appearance and Motion for Hand-Object Interaction Synthesis
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, SyncMV4D, Hand-Object Interaction, 4D motions, Multi-view geometry
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to overcome current limitations in generating 3D Hand-Object Interaction by introducing SyncMV4D, a model that integrates visual priors, motion dynamics, and multi-view geometry to generate synchronized multi-view HOI videos and 4D motions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a Multi-view Joint Diffusion model to co-generate HOI videos and intermediate motions.
– Implementation of a Diffusion Points Aligner to refine intermediate motions into globally aligned 4D metric point tracks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SyncMV4D framework exhibits superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods in achieving visual realism, motion plausibility, and multi-view consistency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19319
30.
