AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251127

1. Multimodal Evaluation of Russian-language Architectures
🔑 Keywords: Mera Multi, Multimodal Evaluation Framework, Russian Language, AI-Generated Summary, Benchmark Leakage
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the lack of multimodal benchmarks for Russian-spoken architectures by introducing Mera Multi, a comprehensive framework with 18 newly constructed evaluation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of an instruction-based benchmark that includes text, image, audio, and video modalities. Development of a universal taxonomy of multimodal abilities and creation of datasets with Russian cultural and linguistic specificity. Implementation of methodologies to prevent benchmark leakage through watermarking and licensing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– This framework enables a better understanding of the intelligence, limitations, and risks of multimodal large language models in the context of the Russian language and offers a replicable methodology for constructing similar benchmarks for other languages, particularly within the Slavic family.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.15552

2. Latent Collaboration in Multi-Agent Systems
🔑 Keywords: LatentMAS, Multi-agent systems, Large language models, latent space, collaboration
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces LatentMAS, a framework enabling efficient and effective collaboration among large language model (LLM) agents using latent space representations to enhance reasoning quality and reduce computational costs without training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework involves auto-regressive latent thoughts generation and the use of a shared latent working memory to preserve and transfer each agent’s internal representations, ensuring lossless information exchange.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Theoretical analyses and empirical evaluations across various benchmarks demonstrate that LatentMAS achieves higher accuracy, reduces output token usage, and provides faster inference compared to traditional text-based multi-agent systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20639

3. Inferix: A Block-Diffusion based Next-Generation Inference Engine for World Simulation
🔑 Keywords: Inferix, semi-autoregressive, video generation, world models, interactive video streaming
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Inferix is developed as a next-generation inference engine aimed at immersive world synthesis using semi-autoregressive decoding methods, focusing on high-quality and real-time video generation and interaction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper introduces a novel decoding paradigm combining diffusion and autoregressive methods, allowing the generation of coherent and stable video sequences through block-diffusion techniques and KV Cache management.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Inferix distinctly sets itself apart by supporting real-time interaction and accurate world dynamics modeling. Integration with LV-Bench offers efficient benchmarking for minute-long video generation, encouraging community collaboration to enhance its capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20714

4. Harmony: Harmonizing Audio and Video Generation through Cross-Task Synergy
🔑 Keywords: Generative AI, audio-visual synchronization, Cross-Task Synergy, Global-Local Decoupled Interaction Module, Synchronization-Enhanced CFG
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to address and improve audio-visual synchronization in generative AI through innovative frameworks and methodologies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a Cross-Task Synergy training paradigm enhancing supervisory signals from audio-driven video and video-driven audio generation tasks.
– Developed a Global-Local Decoupled Interaction Module to achieve efficient temporal-style alignment.
– Created a Synchronization-Enhanced Classifier-Free Guidance (SyncCFG) to amplify alignment signals during inference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Harmony framework significantly outperforms existing methods, establishing new benchmarks in generation fidelity and fine-grained audio-visual synchronization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.21579

5. Revisiting Generalization Across Difficulty Levels: It’s Not So Easy
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Generalization, Task Difficulties, Data Curation, Evaluation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate how well large language models generalize across different task difficulties to enhance data curation and evaluation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conduct systematic evaluations of LLMs using datasets and groups of example difficulty.
– Utilize Item Response Theory to rank dataset examples based on the capabilities of several LLMs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Cross-difficulty generalization is found to be limited; consistent improvements cannot be achieved by training on solely easy or hard data.
– Highlights the importance of incorporating a range of difficulties in both training and evaluation datasets for LLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.21692

6. NVIDIA Nemotron Parse 1.1
🔑 Keywords: OCR, Document Parsing, Encoder-Decoder Architecture, Huggingface, NIM Container
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Nemotron-Parse-1.1 aims to enhance the capabilities of OCR and document parsing, including markdown formatting, structured table parsing, and text extraction from images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes an encoder-decoder architecture with 885M parameters, featuring a compact 256M-parameter language decoder, and releases model weights on Huggingface.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Nemotron-Parse-1.1 achieves competitive accuracy on public benchmarks and offers a lightweight OCR solution, with a special version, Nemotron-Parse-1.1-TC, providing a 20% speed improvement with minimal quality loss.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20478

7. Monet: Reasoning in Latent Visual Space Beyond Images and Language
🔑 Keywords: Monet, MLLMs, latent visual space, continuous embeddings, Visual-latent Policy Optimization
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introducing Monet, a training framework to enhance multimodal large language models (MLLMs) in latent visual reasoning using continuous embeddings.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a three-stage distillation-based supervised fine-tuning pipeline to address computational cost and supervision challenges.
– Development of Visual-latent Policy Optimization, a reinforcement learning method for improving latent reasoning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Monet-7B model demonstrates significant improvements in abstract visual reasoning tasks and outperforms in real-world benchmarks, with strong out-of-distribution generalization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.21395

8. Terminal Velocity Matching
🔑 Keywords: Terminal Velocity Matching, Generative Modeling, Diffusion Timesteps, Fusible Attention Kernel, 2-Wasserstein Distance
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Terminal Velocity Matching (TVM), a generalized approach to flow matching, aiming to improve high-fidelity generative modeling with minimal computational steps.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– TVM models transitions between diffusion timesteps, regularizing behavior at terminal time.
– Introduces minor architectural adjustments to Diffusion Transformers for single-stage training stability.
– Implements a fused attention kernel to efficiently handle Jacobian-Vector Products in transformer architectures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art performance on ImageNet datasets with impressive FID scores, notably 3.29 FID with one NFE and 1.99 FID with four NFEs on ImageNet-256×256.
– Demonstrates scalability and effectiveness for high-fidelity one/few-step models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19797

9. UniGame: Turning a Unified Multimodal Model Into Its Own Adversary
🔑 Keywords: Unified Multimodal Models, self-adversarial, post-training framework, consistency, robustness
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces UniGame, a self-adversarial post-training framework designed to address inconsistencies in Unified Multimodal Models by using a lightweight perturber at the shared token interface.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a lightweight perturber in the model’s token interface, enabling the generation branch to challenge fragile understanding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UniGame enhances model consistency by 4.6%, improves understanding (3.6%) and generation (0.02), and increases robustness against adversarial shifts (4.8% on NaturalBench and 6.2% on AdVQA).
– The framework is architecture-agnostic, with minimal additional parameters, and can be integrated with existing post-training methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19413

10. G^2VLM: Geometry Grounded Vision Language Model with Unified 3D Reconstruction and Spatial Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: G^2VLM, Vision-Language Models, Spatial Understanding, 3D Reconstruction, In-Context Learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces G^2VLM, a model designed to integrate 3D geometry learning with vision-language capabilities to enhance spatial understanding and reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– G^2VLM utilizes a combination of learned 3D visual geometry features, multi-view image, and video data to improve spatial tasks and employs in-context and interleaved reasoning strategies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study demonstrates G^2VLM’s effectiveness in spatial 3D reconstruction and understanding, achieving results comparable or better than existing models, positioning it as a strong baseline for future research in this domain.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.21688

11. MobileVLA-R1: Reinforcing Vision-Language-Action for Mobile Robots
🔑 Keywords: vision-language-action framework, chain-of-thought (CoT), GRPO reinforcement learning, supervised chain-of-thought alignment, quadruped robots
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Development of MobileVLA-R1, a unified vision-language-action framework to enhance reasoning and control for quadruped robots in complex environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of MobileVLA-CoT, a large-scale dataset providing structured reasoning via multi-granularity chain-of-thought.
– Implementation of a two-stage training paradigm combining supervised CoT alignment with GRPO reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MobileVLA-R1 demonstrates superior performance over strong baselines with a 5% improvement in VLN and VLA tasks.
– Real-world deployment on quadruped robots validates robust performance and stability in complex environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.17889

12. Block Cascading: Training Free Acceleration of Block-Causal Video Models
🔑 Keywords: Block Cascading, parallelization, sequential pipelines, interactive generation, inference speed
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address the speed-quality trade-off in block-causal video generation by introducing Block Cascading, which uses parallelization to enhance video block generation speed without compromising quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach involves training-free parallelization, where future video blocks start generation with partially denoised context from predecessors, allowing multiple blocks to denoise simultaneously, leveraging temporal parallelism across GPUs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Block Cascading achieves approximately 2x speed acceleration for both small and large models while maintaining generation quality, and it eliminates the context switch overhead in interactive generation scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20426
13. Image-Free Timestep Distillation via Continuous-Time Consistency with Trajectory-Sampled Pairs
🔑 Keywords: TBCM, diffusion models, trajectory-based framework, knowledge transfer, self-contained distillation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the Trajectory-Backward Consistency Model (TBCM) to enhance efficiency and reduce data dependency in diffusion models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– TBCM extracts latent representations from the teacher model’s generation trajectory, eliminating the need for external datasets and improving distillation simplicity and efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TBCM achieves impressive FID and CLIP scores while significantly reducing training time and GPU memory usage, indicating its potential for scalable and efficient deployment in resource-limited scenarios.
– The study reveals diffusion-generation space discrepancies and examines sampling strategies’ impact on performance, contributing insights for future distillation research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20410

14. RAISECity: A Multimodal Agent Framework for Reality-Aligned 3D World Generation at City-Scale
🔑 Keywords: RAISECity, Reality-Aligned, agentic framework, multimodal tools, perceptual quality
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose RAISECity to develop high-quality, city-scale 3D worlds with real-world alignment.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes an agentic framework with diverse multimodal foundation tools for building complex 3D scenes.
– Incorporates iterative self-reflection and refinement to enhance performance and minimize errors.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RAISECity demonstrates superior performance in real-world alignment, shape precision, and texture fidelity compared to existing baselines.
– Achieves over a 90% win-rate in perceptual quality against current methods, positioning RAISECity as a significant advancement for applications in immersive media and embodied intelligence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18005

15. NAF: Zero-Shot Feature Upsampling via Neighborhood Attention Filtering
🔑 Keywords: Neighborhood Attention Filtering, Vision Foundation Models, Upsampling, Zero-shot, Image Restoration
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Neighborhood Attention Filtering (NAF), designed to upsample features from Vision Foundation Models without retraining.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– NAF leverages Cross-Scale Neighborhood Attention and Rotary Position Embeddings, guided by high-resolution input images, offering a VFM-agnostic approach.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– NAF achieves state-of-the-art upsampling performance across various pixel-level tasks with high efficiency and also demonstrates strong abilities in image restoration. It operates at 18 FPS, handling up to 2K feature maps.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18452
16. Reinforcing Action Policies by Prophesying
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action, Reinforcement Learning, World Model, FlowScale, Prophet
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance Vision-Language-Action policies using ProphRL, focusing on improving data efficiency and optimization stability through a learned world model and tailored RL.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce Prophet, a robot actuation model trained on large datasets, allowing for few-shot adaptation to new scenarios.
– Implement Flow-action-GRPO (FA-GRPO) and FlowScale to optimize VLA actions with reweighted gradients.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ProphRL shows increased performance, with success gains of 5-17% on public benchmarks and 24-30% on real robots across various VLA implementations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20633

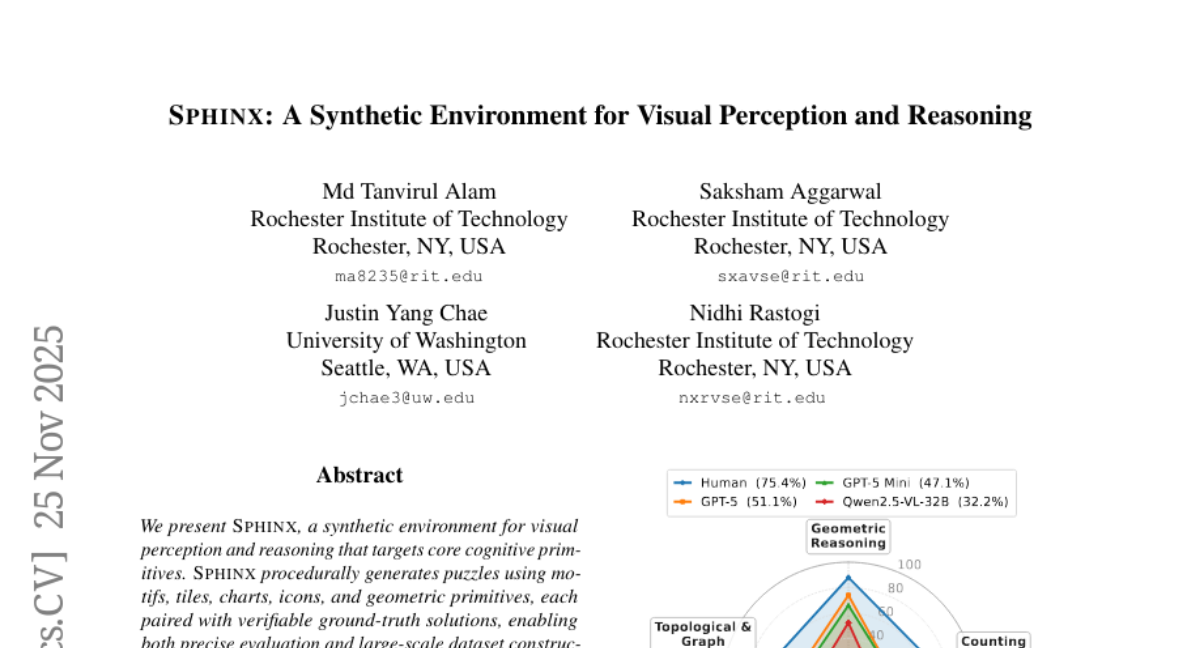
17. SPHINX: A Synthetic Environment for Visual Perception and Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Sphinx, Visual Perception, Reinforcement Learning, Large Vision-Language Models, Multimodal Reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to introduce Sphinx, a synthetic environment designed to evaluate and enhance performance of large vision-language models through a range of visual tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Sphinx generates puzzles with verifiable solutions and uses motifs, tiles, charts, icons, and geometric primitives for task creation. It employs reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards to improve model accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Evaluation of large vision-language models, including state-of-the-art models like GPT-5, shows a significant underperformance compared to human benchmarks. However, applying reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards significantly improves accuracy on visual tasks, demonstrating potential for advancements in multimodal reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20814
18. Frequency-Adaptive Sharpness Regularization for Improving 3D Gaussian Splatting Generalization
🔑 Keywords: Frequency-Adaptive Sharpness Regularization, 3D Gaussian Splatting, generalization, novel view synthesis
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the generalization of 3D Gaussian Splatting in synthesizing novel viewpoints, addressing its limitations in few-shot scenarios.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Frequency-Adaptive Sharpness Regularization (FASR) to adjust regularization based on local image frequency, aiming to improve generalization solutions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FASR effectively addresses the challenge of generalizing 3D Gaussian Splatting to novel viewpoints by preventing artifacts and enabling fine detail reconstruction, outperforming traditional Sharpness-Aware Minimization approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.17918

19. Position: The Complexity of Perfect AI Alignment — Formalizing the RLHF Trilemma
🔑 Keywords: RLHF, Alignment Trilemma, epsilon-representativeness, polynomial tractability, delta-robustness
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To formalize and analyze the Alignment Trilemma in Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), which demonstrates the infeasibility of simultaneously achieving representativeness, tractability, and robustness.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A complexity-theoretic analysis combining statistical learning theory and robust optimization was employed to prove the computational limits of achieving representativeness and robustness for global-scale populations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current RLHF systems struggle with trade-offs, mainly favoring tractability over representativeness and robustness. Strategic relaxations in alignment requirements are suggested to navigate these trade-offs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19504

20. I-GLIDE: Input Groups for Latent Health Indicators in Degradation Estimation
🔑 Keywords: RaPP, Uncertainty Quantification, RUL Prediction, Multi-sensor Systems, I-GLIDE
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a novel framework to enhance RUL prediction accuracy and interpretability in multi-sensor systems by leveraging RaPP and uncertainty quantification.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Adaptation of RaPP as a health indicator (HI) and augmentation with aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty quantification using Monte Carlo dropout and probabilistic latent spaces.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach improves RUL-prediction robustness and provides mechanism-specific diagnostics, achieving outstanding accuracy and generalizability compared to existing HI methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.21208

21.
