AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251202
1. From Code Foundation Models to Agents and Applications: A Practical Guide to Code Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, Large Language Models, Code Specialization, Research-Practice Gap, Software Development
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Provide a comprehensive guide and practical synthesis of code LLMs, covering the full lifecycle from data curation to deployment, including methods, trade-offs, and the research-practice gap.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analyze the capabilities of general and code-specialized LLMs through analytic and probing experiments.
– Critically examine design decisions and trade-offs, mapping research directions to practical software development needs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Highlight the advancements in code LLMs, their impact on automated software development, and suggest directions to bridge the gap between academic research and practical deployment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.18538
2. LongVT: Incentivizing “Thinking with Long Videos” via Native Tool Calling
🔑 Keywords: LongVT, Multimodal Chain-of-Tool-Thought, LMMs, video reasoning, global-to-local reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to enhance video reasoning in long-form videos through the LongVT framework, utilizing a Multimodal Chain-of-Tool-Thought approach for global-to-local reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs interleaved multimodal reasoning with large multimodal models (LMMs) to simulate human-like skimming and detail-oriented analysis in long videos. It includes a novel training strategy with a curated dataset called VideoSIAH.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LongVT consistently outperforms strong baselines in long-video understanding and reasoning benchmarks, facilitated by a three-stage training strategy and empirical validation, with all resources publicly available.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20785

3. Envision: Benchmarking Unified Understanding & Generation for Causal World Process Insights
🔑 Keywords: Envision-a, spatiotemporal consistency, multi-frame reasoning, multimodal models, causal event progression
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces a benchmark called Envision-a for chained text-to-multi-image generation to address limitations in current models by emphasizing spatiotemporal causality and dynamic causal processes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Envision-a redefines evaluation with 1,000 four-stage prompts from various domains, and introduces the Envision-Score, a holistic metric assessing multi-dimensional consistency, physicality, and aesthetics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Unified multimodal models outperform specialized text-to-image models, especially in causal narrative coherence, though they still struggle with spatiotemporal consistency, impacting their ability to model dynamic world processes effectively.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01816

4. Stabilizing Reinforcement Learning with LLMs: Formulation and Practices
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Token-Level Objective, Mixture-of-Experts, Importance Sampling Correction
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to provide a theoretical framework for optimizing sequence-level rewards in Reinforcement Learning using token-level objectives, focusing on large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes theoretical insights such as first-order approximation to explain how importance sampling correction, clipping, and Routing Replay stabilize training, specifically through the application in Mixture-of-Experts models.
– Conducts extensive experiments with a 30 billion parameter Mixture-of-Experts model to assess training stabilization techniques in both on-policy and off-policy updates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Found that minimizing training-inference discrepancy and policy staleness is crucial for effective training.
– Demonstrated that once training stability is achieved, prolonged optimization leads to consistent performance outcomes, mitigating cold-start initialization effects.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01374

5. How Far Are We from Genuinely Useful Deep Research Agents?
🔑 Keywords: Deep Research Agents, report synthesis, evidence integration, verification, reasoning-resilient planning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of this research is to improve the effectiveness of Deep Research Agents (DRAs) by introducing a new benchmark called FINDER, designed to address existing limitations in task complexity and subjective metrics for report synthesis.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs the introduction of FINDER, a benchmark with 100 human-curated research tasks and 419 structured checklist items, as well as the creation of the Deep rEsearch Failure Taxonomy (DEFT) to identify failure modes in DRAs using grounded theory and human-LLM co-annotating.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study concludes that current DRAs face challenges not in task comprehension but specifically in evidence integration, verification, and reasoning-resilient planning, as evidenced by the experimental findings using DEFT.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01948

6. What about gravity in video generation? Post-Training Newton’s Laws with Verifiable Rewards
🔑 Keywords: NewtonRewards, video diffusion models, verifiable rewards, optical flow, Newtonian kinematic constraint
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To bridge the gap between visual realism and physical realism in video diffusion models by introducing NewtonRewards, a physics-grounded post-training framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework employs verifiable rewards using measurable proxies like optical flow for velocity and high-level appearance features for mass, applying Newtonian kinematic constraints and a mass conservation reward for improved motion quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– NewtonRewards enhances physical plausibility, motion smoothness, and temporal coherence across various motion primitives, and maintains performance across different conditions, indicating a scalable approach to physics-aware video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00425

7. The Consistency Critic: Correcting Inconsistencies in Generated Images via Reference-Guided Attentive Alignment
🔑 Keywords: ImageCritic, reference-guided post-editing, attention alignment loss, detail encoder
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address image generation inconsistencies by implementing a reference-guided post-editing approach, introducing ImageCritic.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a dataset of reference-degraded-target triplets with VLM-based selection and explicit degradation.
– Develop an attention alignment loss and a detail encoder to fix inconsistencies in AI-generated images.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments indicate that ImageCritic significantly improves the consistency of fine-grained details in various customized image generation scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20614

8. Infinity-RoPE: Action-Controllable Infinite Video Generation Emerges From Autoregressive Self-Rollout
🔑 Keywords: $\infty$-RoPE, autoregressive video diffusion models, Block-Relativistic RoPE, KV Flush, RoPE Cut
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To overcome the limitations in autoregressive video diffusion models by introducing a new inference-time framework, $\infty$-RoPE.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement Block-Relativistic RoPE to eliminate fixed temporal positions, enabling continuous video generation.
– Use KV Flush to maintain fine-grained action control for immediate prompt responsiveness.
– Apply RoPE Cut to allow controlled discontinuities for cinematic transitions within a single generation stream.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– $\infty$-RoPE enables infinite-horizon, controllable, and cinematic video diffusion without retraining, consistently surpassing previous models in VBench scores.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20649
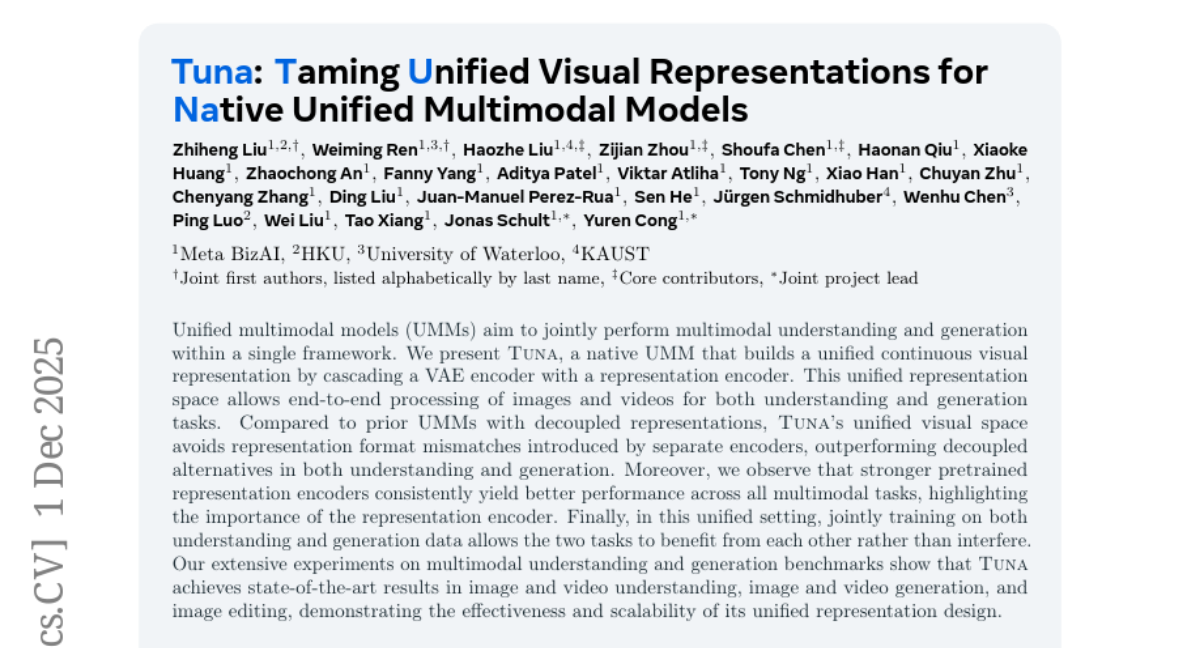
9. TUNA: Taming Unified Visual Representations for Native Unified Multimodal Models
🔑 Keywords: TUNA, Unified Multimodal Models, VAE Encoder, Multimodal Understanding, Representation Encoder
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– TUNA aims to achieve end-to-end multimodal understanding and generation within a unified framework, outperforming decoupled models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– TUNA employs a cascaded VAE and representation encoder to construct a continuous visual representation space for processing images and videos jointly for both understanding and generation tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TUNA’s unified representation space enhances performance by avoiding format mismatches and benefits from stronger pretrained representation encoders, achieving state-of-the-art results in multimodal tasks including image and video understanding, generation, and editing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02014
10. LFM2 Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Liquid Foundation Models, hardware-in-the-loop architecture search, multimodal applications, memory-efficient inference, edge applications
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study presents the LFM2 family of Liquid Foundation Models designed for efficient on-device deployment, accommodating multimodal tasks with high efficiency and performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of hardware-in-the-loop architecture search to create a compact hybrid backbone.
– A three-stage training pipeline involving tempered decoupled Top-K knowledge distillation and other advanced training techniques.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LFM2 models, spanning from 350M to 8.3B parameters, demonstrate strong performance across benchmarks like IFEval and GSM8K.
– Various variants, such as LFM2-VL, LFM2-Audio, and LFM2-ColBERT, show competitive results for vision-language tasks, real-time speech interactions, and multilingual retrieval, respectively, with available deployment packages facilitating practical edge applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.23404

11. Wikontic: Constructing Wikidata-Aligned, Ontology-Aware Knowledge Graphs with Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Knowledge graphs, AI-generated summary, candidate triplets, Wikidata, state-of-the-art
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Wikontic, a multi-stage pipeline designed to construct ontology-consistent knowledge graphs from open-domain text with high information retention and efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The pipeline involves extracting candidate triplets with qualifiers, enforcing type and relation constraints based on Wikidata, and normalizing entities to minimize duplication, creating compact and well-connected knowledge graphs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Wikontic achieves notable performance with a 96% correct answer rate in generated triplets on the MuSiQue dataset and comparable F1 scores on HotpotQA and MuSiQue datasets, surpassing several baselines. It also demonstrates state-of-the-art information retention on the MINE-1 benchmark and is more efficient at build time compared to existing methods like AriGraph and GraphRAG.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00590

12. Rectifying LLM Thought from Lens of Optimization
🔑 Keywords: RePro, LLM reasoning, long chain-of-thought, reinforcement learning, surrogate objective function
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance Large Language Models’ (LLMs) reasoning capabilities by refining the optimization process of chain-of-thought prompting through a novel process-level reward mechanism, RePro.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– RePro introduces a surrogate objective function with a dual scoring mechanism to quantify the intensity and stability of the optimization process in chain-of-thought reasoning. This approach is integrated into reinforcement learning pipelines with verifiable rewards.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experimentation across various reinforcement learning algorithms and LLMs indicates that RePro significantly improves reasoning performance and reduces suboptimal reasoning behaviors, as tested on platforms encompassing mathematics, science, and coding benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01925

13. Flash-DMD: Towards High-Fidelity Few-Step Image Generation with Efficient Distillation and Joint Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Flash-DMD, Timestep-aware distillation, Reinforcement Learning, Generative Models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Flash-DMD to accelerate and stabilize the training of generative diffusion models while maintaining high generation quality and reducing computational cost.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Propose an efficient timestep-aware distillation strategy to reduce training cost.
– Develop a joint training scheme combining reinforcement learning with distillation to enhance model stability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Flash-DMD enables faster convergence and achieves state-of-the-art generation quality in few-step sampling.
– The framework outperforms existing methods in visual quality, human preference, and text-image alignment metrics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20549

14. VLASH: Real-Time VLAs via Future-State-Aware Asynchronous Inference
🔑 Keywords: asynchronous inference, Vision-Language-Action models, action stability, reaction latency, high-precision tasks
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce VLASH, an asynchronous inference framework designed to enhance the speed and accuracy of Vision-Language-Action models for robotic tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement asynchronous inference to allow simultaneous action execution and inference without additional overhead or architectural changes.
– Address the temporal misalignment by estimating future execution-time states to improve action stability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VLASH achieves significant speedups of up to 2.03x and reduces reaction latency up to 17.4x compared to synchronous inference while maintaining full accuracy.
– Enables advanced robotic tasks like playing ping-pong and whack-a-mole, which are challenging for synchronous inference.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01031
15. GR-RL: Going Dexterous and Precise for Long-Horizon Robotic Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: GR-RL, Reinforcement Learning, Vision-Language-Action, Dexterous Manipulation, Long-Horizon Reasoning
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a framework, GR-RL, that transforms a generalist Vision-Language-Action policy into a specialist for long-horizon dexterous manipulation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a multi-stage training pipeline that filters, augments, and refines human demonstrations using reinforcement learning.
– Implemented morphological symmetry augmentation for improved generalization.
– Used offline and online reinforcement learning to strengthen the model’s alignment and precision.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GR-RL achieved a high success rate in complex tasks such as threading shoelaces, showing proficiency in long-horizon reasoning and millimeter-level precision.
– This work marks a step forward in enabling generalist robot foundation models to become reliable specialists in real-world applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01801
16. InternVideo-Next: Towards General Video Foundation Models without Video-Text Supervision
🔑 Keywords: InternVideo-Next, Encoder-Predictor-Decoder, video representation learning, semantic abstraction, shortcut learning
💡 Category: Video Representation Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a state-of-the-art video representation learning model using a novel Encoder-Predictor-Decoder framework, which combines pixel-level fidelity with high-level semantics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The use of a two-stage pretraining scheme comprising a conditional diffusion decoder to enhance semantics and convergence, and learning world knowledge to mitigate shortcut learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– InternVideo-Next achieves state-of-the-art results across benchmarks using public, unlabeled videos, offering a scalable approach for general video representation learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01342

17. Flow Straighter and Faster: Efficient One-Step Generative Modeling via MeanFlow on Rectified Trajectories
🔑 Keywords: Rectified MeanFlow, Flow-based generative models, mean velocity field, one-step sampling, truncation heuristic
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve sample quality and training efficiency in flow-based generative models using a framework called Rectified MeanFlow.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a framework that models the mean velocity field with a single reflow step and a truncation heuristic to reduce residual curvature.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Rectified MeanFlow outperforms prior methods in both sample quality and training efficiency, demonstrated through experiments on ImageNet at various resolutions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.23342

18. SpeContext: Enabling Efficient Long-context Reasoning with Speculative Context Sparsity in LLMs
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, distilled language model, long-context reasoning, cloud and edge environments, retrieval algorithms
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop an algorithm using a distilled language model (DLM) for efficient long-context reasoning in cloud and edge environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Uses a lightweight retrieval head based on head-level attention weights, asynchronous prefetch dataflow via elastic loading strategy, and an adaptive memory management system for maximized GPU memory utilization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SpeContext significantly enhances throughput, achieving up to 24.89x improvement in the cloud and 10.06x speedup at the edge, with minimal accuracy loss compared to existing frameworks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00722

19. Accelerating Streaming Video Large Language Models via Hierarchical Token Compression
🔑 Keywords: Streaming Video Large Language Models, Vision Transformer, Token Compression, STC-Cacher, STC-Pruner
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to optimize Streaming Video Large Language Models (VideoLLMs) by reducing the ViT encoding and LLM pre-filling latency, using a novel framework called Streaming Token Compression (STC).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The STC framework employs token caching and pruning through two main components: STC-Cacher and STC-Pruner. These techniques aim to reduce overhead by reusing features from similar frames and compressing visual token sequences to retain salient information.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments demonstrate that the STC framework significantly reduces ViT encoding and LLM pre-filling latency by 24.5% and 45.3% respectively, while maintaining up to 99% accuracy in video understanding tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00891

20. Where Culture Fades: Revealing the Cultural Gap in Text-to-Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: Text-to-image Models, Cultural Consistency, Semantic Alignment, Culture-related Representations
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– This study aims to improve cultural consistency in multilingual text-to-image models without compromising image fidelity and diversity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A comprehensive analysis was conducted on multilingual T2I models to identify cultural biases.
– A probing method that focuses on localizing culture-sensitive signals to specific neurons and layers was proposed.
– Two alignment strategies were introduced: inference-time cultural activation and layer-targeted cultural enhancement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed strategies demonstrated consistent improvements over strong baselines in maintaining cultural consistency while preserving image fidelity and diversity, as validated through experiments on the CultureBench.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.17282

21. SCALE: Selective Resource Allocation for Overcoming Performance Bottlenecks in Mathematical Test-time Scaling
🔑 Keywords: SCALE, large language models, computational resources, problem decomposition, difficulty assessment
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce SCALE, a framework that selectively allocates computational resources based on sub-problem difficulty to enhance mathematical reasoning in large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– SCALE operates in four stages: problem decomposition, difficulty assessment, selective processing mode assignment, and sequential execution with context propagation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SCALE achieves significant accuracy improvements of up to 13.75 percentage points and reduces computational costs by 33%-53% compared to uniform scaling baselines, effectively addressing the limitations of current test-time compute scaling approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00466

22. PromptBridge: Cross-Model Prompt Transfer for Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: PromptBridge, Model Drifting, Large Language Models, cross-model prompt mapping, Model-Adaptive Reflective Prompt Evolution
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce PromptBridge as a framework to facilitate prompt transfer between different LLMs without needing re-optimization, addressing the model drifting challenge.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Use Model-Adaptive Reflective Prompt Evolution (MAP-RPE) for iterative reflective refinement and quantitative evaluation.
– Develop a cross-model prompt mapping to enable transfer of optimized prompts between models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PromptBridge significantly improves downstream accuracy and reduces migration effort across both single-agent and multi-agent settings, making it a promising solution for maintaining prompt effectiveness in the evolving model landscape.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01420
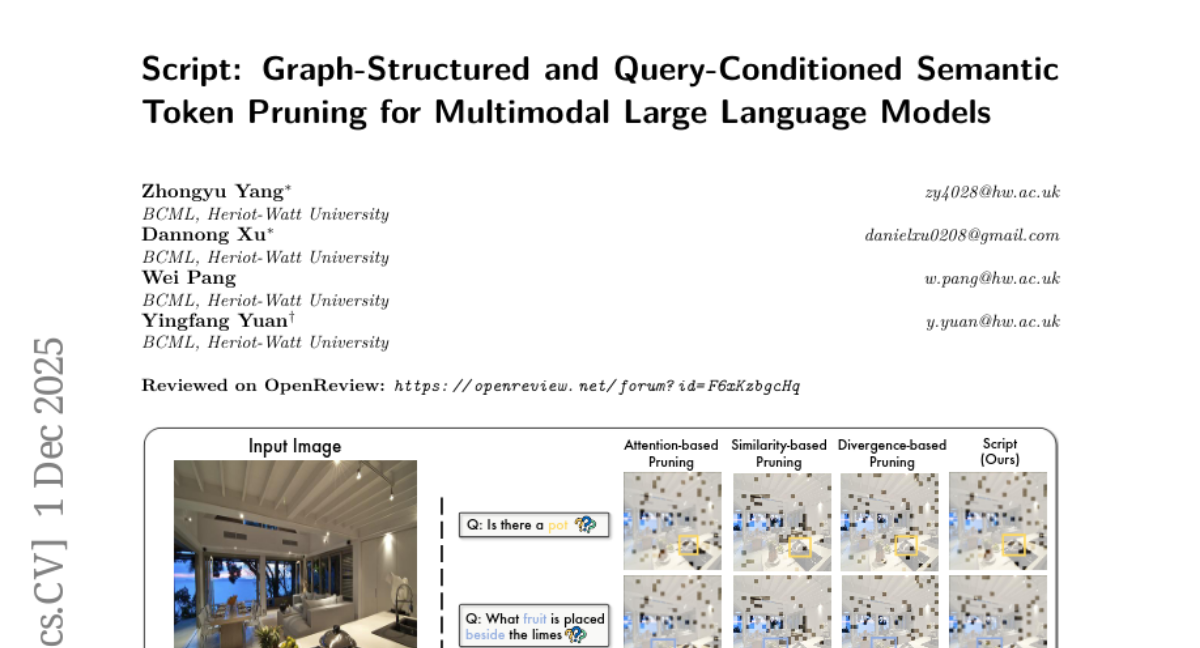
23. Script: Graph-Structured and Query-Conditioned Semantic Token Pruning for Multimodal Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Token pruning, Graph-structured pruning, Query-conditioned semantic pruning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve efficiency and accuracy in multimodal large language models by removing redundant and irrelevant visual tokens without requiring retraining.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented Script, a plug-and-play token pruning method, which includes two modules: a graph-structured pruning module and a query-conditioned semantic pruning module.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Script enhances model efficiency and predictive accuracy on multimodal tasks. It outperforms existing pruning methods, achieving up to 6.8x prefill speedup and 10x FLOP reduction while retaining 96.88% of the original performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01949
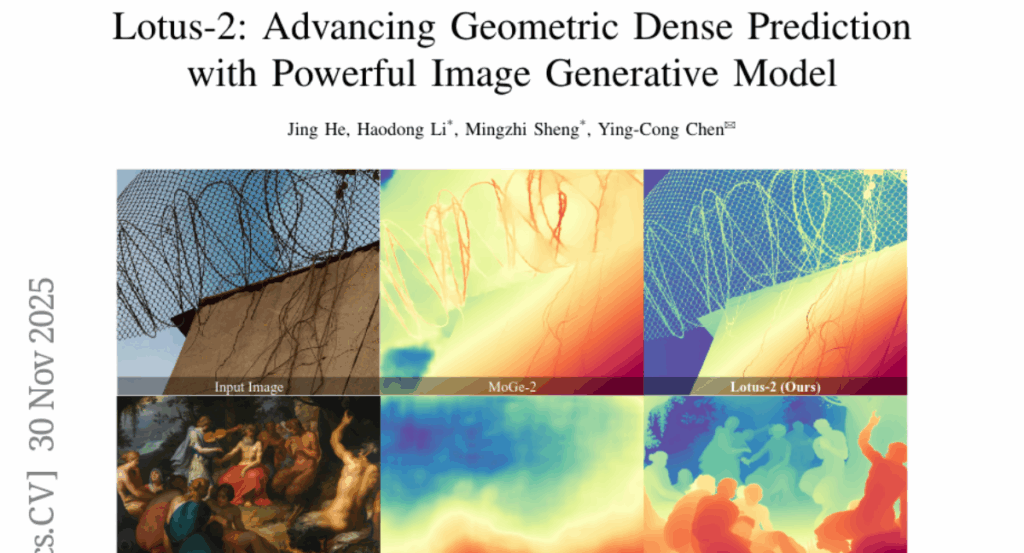
24. Lotus-2: Advancing Geometric Dense Prediction with Powerful Image Generative Model
🔑 Keywords: Lotus-2, diffusion models, deterministic framework, monocular depth estimation, surface normal prediction
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop Lotus-2, a two-stage deterministic framework for achieving high-quality geometric inference, specifically in monocular depth estimation and surface normal prediction, using diffusion models’ world priors.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– In the first stage, a core predictor employs a single-step deterministic formulation using a clean-data objective and a lightweight local continuity module to generate globally coherent structures.
– In the second stage, a detail sharpener performs constrained multi-step rectified-flow refinement to enhance fine-grained geometry through noise-free deterministic flow matching.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Lotus-2 achieves state-of-the-art results in monocular depth estimation and competitive surface normal prediction with limited training data, demonstrating the potential of diffusion models as deterministic world priors for advanced geometric reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01030

25. StreamGaze: Gaze-Guided Temporal Reasoning and Proactive Understanding in Streaming Videos
🔑 Keywords: StreamGaze, MLLMs, gaze signals, temporal reasoning, proactive reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to evaluate how effectively Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) utilize gaze signals for temporal and proactive reasoning in streaming video contexts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a benchmark named StreamGaze which includes tasks that incorporate gaze-guided past, present, and proactive tasks.
– Introduction of a gaze-video QA generation pipeline that aligns egocentric videos with gaze trajectories using fixation extraction and scanpath construction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Significant performance gaps were identified between MLLMs and human performance in gaze-based temporal reasoning, intention modeling, and proactive prediction.
– The study provides insights into the limitations of current MLLMs and suggests necessary future model enhancements by offering detailed analyses of gaze-prompting strategies and reasoning behaviors.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01707

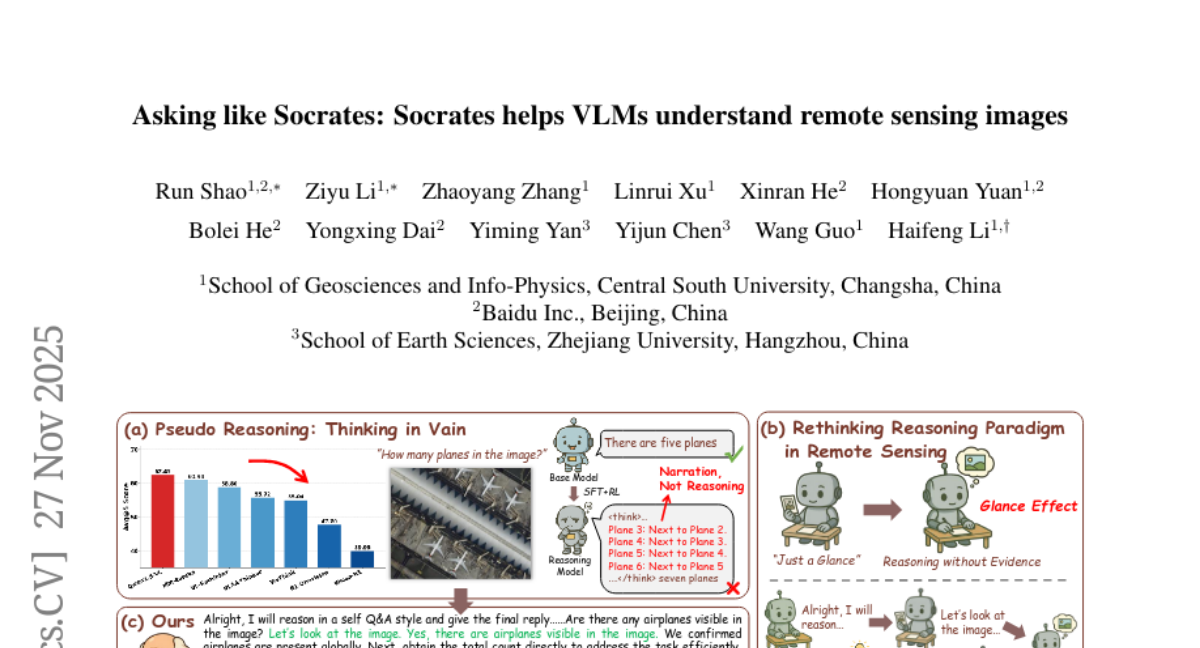
26. Asking like Socrates: Socrates helps VLMs understand remote sensing images
🔑 Keywords: RS-EoT, Remote Sensing, AI Native, Iterative Visual Evidence-Seeking, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance reasoning in remote sensing tasks by introducing the RS-EoT framework, diminishing pseudo reasoning through a language-driven, iterative visual evidence-seeking approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a self-play multi-agent system called SocraticAgent and a two-stage progressive reinforcement learning strategy to improve RS-EoT capabilities and generalize understanding in RS VQA scenarios.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RS-EoT demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on RS VQA benchmarks, effectively addressing the Glance Effect and enabling genuine evidence-grounded reasoning in remote sensing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22396
27. ORION: Teaching Language Models to Reason Efficiently in the Language of Thought
🔑 Keywords: ORION models, Mentalese, Reinforcement Learning, Efficiency, Compression
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance reasoning efficiency and cost-effectiveness by using ORION models that compress reasoning steps into ultra-compressed tokens.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces a reinforcement learning method named SHORTER LENGTH PREFERENCE OPTIMIZATION (SLPO) to reward concise reasoning solutions.
– Models are trained to use a symbolic, compositional language called Mentalese to enable compact reasoning styles.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ORION models achieve significant token reduction, reduced inference latency, and lower training costs while maintaining high accuracy across standard benchmarks.
– They outperform existing models, such as Claude and ChatGPT-4o, in accuracy and compression, demonstrating potential steps toward human-like cognitive efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22891

28. POLARIS: Projection-Orthogonal Least Squares for Robust and Adaptive Inversion in Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: POLARIS, diffusion models, noise approximation errors, image inversion, guidance scale
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance the quality and accuracy of image editing and restoration by minimizing noise approximation errors in the image inversion process.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– POLARIS, a novel approach based on diffusion models, reformulates inversion from an error-compensation problem into an error-origin problem. It treats the guidance scale as a step-wise variable and uses a mathematically grounded formula to minimize inversion error at each step.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– POLARIS improves inversion latent quality significantly with minimal code changes and mitigates noise approximation errors with negligible performance overhead, thus enhancing the accuracy of downstream tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00369

29. Learning Eigenstructures of Unstructured Data Manifolds
🔑 Keywords: spectral basis, unstructured data, geometry processing, Laplacian operator, unsupervised method
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a novel deep learning framework for learning spectral bases directly from unstructured data, eliminating the need for traditional operator selection and eigendecomposition.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework utilizes optimal-approximation theory to train a network, minimizing reconstruction error by decomposing an implicit approximation operator across chosen probe functions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method provides a data-driven alternative for geometry processing by retrieving spectral bases and eigenvalues without assumptions on meshing or manifold dimensionality, effectively scaling across datasets of arbitrary dimensions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01103

30. HiconAgent: History Context-aware Policy Optimization for GUI Agents
🔑 Keywords: HiconAgent, HCPO, GUI navigation, Dynamic Context Sampling, Anchor-guided History Compression
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal of the research is to enhance the performance of GUI agents in navigation tasks by efficiently utilizing historical context, reducing computational costs without compromising decision-making capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces HiconAgent, a GUI agent trained with History Context-aware Policy Optimization (HCPO), which incorporates Dynamic Context Sampling (DCS) and Anchor-guided History Compression (AHC) to optimize history usage during both sampling and policy updates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HiconAgent demonstrates strong performance on GUI navigation benchmarks, achieving a significant improvement in grounding accuracy and step success rate, along with substantial computational speedup and FLOPs reduction compared to existing models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01763

31. Agentic Policy Optimization via Instruction-Policy Co-Evolution
🔑 Keywords: Instruction-Policy co-evolution, dynamic component, reinforcement learning loop, large language models, strategic reasoning paths
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces INSPO, a novel framework designed to dynamically optimize instructions within the reinforcement learning loop to enhance performance in multi-turn retrieval and reasoning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– INSPO integrates instruction optimization as a dynamic element of the reinforcement learning process. It maintains a dynamic population of candidate instructions, applying reward signals and on-policy reflection to evolve more effective strategies through an LLM-based optimizer.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments demonstrate that INSPO significantly outperforms static instruction-based methods, discovering innovative instructions and achieving high performance with minimal computational overhead.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01945

32. WiseEdit: Benchmarking Cognition- and Creativity-Informed Image Editing
🔑 Keywords: WiseEdit, Cognition-Informed, Creativity-Informed, Image Editing, Knowledge Representation
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce WiseEdit, a comprehensive benchmark to evaluate cognition- and creativity-informed image editing models across three cognitive stages: Awareness, Interpretation, and Imagination.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Decompose image editing into tasks assessing declarative, procedural, and metacognitive knowledge, along with 1,220 test cases to evaluate model capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– WiseEdit highlights the limitations of existing state-of-the-art image editing models in handling knowledge-based reasoning and creative composition, with public availability of the benchmark and resources enhancing evaluation transparency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00387

33. Seeing the Wind from a Falling Leaf
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, inverse graphics framework, force representations, physics-based video generation, object geometry
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to recover invisible physical forces from video observations, such as estimating a wind field by observing falling leaves.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes an end-to-end differentiable inverse graphics framework to model object geometry, physical properties, and interactions directly from videos, enabling the recovery of force representations through backpropagation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method successfully infers plausible force fields from both synthetic and real-world video scenarios and demonstrates potential applications in physics-based video generation and editing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00762
34. Generalist Large Language Models Outperform Clinical Tools on Medical Benchmarks
🔑 Keywords: Generalist LLMs, Clinical AI Assistants, AI Evaluation, Clinical Decision Support
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To compare the performance of specialized clinical AI assistants with general-purpose LLMs in a clinical setting.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a 1,000-item mini-benchmark combining MedQA and HealthBench tasks to evaluate two clinical AI systems and three state-of-the-art generalist LLMs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Generalist LLMs consistently outperformed clinical AI tools, with GPT-5 achieving the highest scores, highlighting the deficits in existing clinical AI tools and the need for independent and transparent evaluations before their deployment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01191

35. ChronosObserver: Taming 4D World with Hyperspace Diffusion Sampling
🔑 Keywords: ChronosObserver, 3D-consistent, high-fidelity, multi-view videos, World State Hyperspace
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a training-free method for generating high-fidelity, 3D-consistent, time-synchronized multi-view videos, addressing the limitations of existing camera-controlled video generation models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce World State Hyperspace for representing 4D world spatiotemporal constraints.
– Utilize Hyperspace Guided Sampling to synchronize diffusion sampling trajectories across multiple views.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ChronosObserver is shown to generate high-fidelity and 3D-consistent time-synchronized multi-view videos without the need for training or fine-tuning in diffusion models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01481

36. The Art of Scaling Test-Time Compute for Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Test-time scaling, large language models, inference, compute budget, reasoning datasets
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to systematically evaluate test-time scaling strategies in large language models under identical conditions, investigating the effects of model type, problem difficulty, and compute budget on performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted a large-scale study using over thirty billion tokens generated from eight open-source large language models, ranging from 7B to 235B parameters, across four reasoning datasets to compare test-time scaling strategies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– No single test-time scaling strategy consistently outperforms others; reasoning models show distinct patterns based on problem difficulty and trace length, classifying into short-horizon and long-horizon categories; the optimal performance for a model type scales with the compute budget. A practical guide is provided for selecting suitable strategies based on these factors.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02008

37. IndicParam: Benchmark to evaluate LLMs on low-resource Indic Languages
🔑 Keywords: IndicParam, low-resource languages, LLMs, cross-lingual transfer, multiple-choice questions
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim of the study is to evaluate large language models (LLMs) on their performance in multiple-choice questions across 11 Indic languages, with a focus on identifying limitations in cross-lingual transfer and grammatical proficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– IndicParam, a human-curated benchmark with over 13,000 questions, was developed and used to test 19 LLMs. The dataset includes a variety of low and extremely low-resource languages and utilizes different question formats to assess the models’ capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Top-performing LLMs like GPT-5 achieved only 45.0% average accuracy, highlighting significant challenges in handling low-resource Indic languages. The study provides crucial insights into cross-lingual transfer limitations and establishes a demanding benchmark for evaluating LLM capabilities in these languages.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00333

38. DreamingComics: A Story Visualization Pipeline via Subject and Layout Customized Generation using Video Models
🔑 Keywords: DreamingComics, diffusion-transformer model, region-aware positional encoding, character consistency, style similarity
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance story visualization by improving layout control, character consistency, and style similarity through the introduction of DreamingComics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a diffusion-transformer model with spatiotemporal priors.
– Introduction of RegionalRoPE for layout-based position control.
– Integration of an LLM-based layout generator for comic-style layouts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved a 29.2% increase in character consistency and a 36.2% increase in style similarity compared to previous methods.
– Demonstrated high spatial accuracy in layout control.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01686

39. CauSight: Learning to Supersense for Visual Causal Discovery
🔑 Keywords: CauSight, Visual Causal Discovery, Visual Causal Graph dataset, Tree-of-Causal-Thought, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces CauSight, a novel vision-language model designed to perform visual causal discovery by inferring cause-and-effect relationships in images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research utilizes a dataset named Visual Causal Graph (VCG-32K) as a foundation for training.
– It integrates Tree-of-Causal-Thought for synthesizing reasoning trajectories and employs reinforcement learning with a causal reward to enhance reasoning policies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CauSight significantly outperforms GPT-4.1 in visual causal discovery tasks, achieving a performance boost of over threefold (21% absolute gain).
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01827

40. OpenREAD: Reinforced Open-Ended Reasoing for End-to-End Autonomous Driving with LLM-as-Critic
🔑 Keywords: OpenREAD, Reinforcement Fine-Tuning, Autonomous Driving, Vision-Language Model, Reasoning
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The development of OpenREAD, an autonomous driving framework, to enhance both reasoning and planning through end-to-end reinforcement fine-tuning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed two-stage fine-tuning strategies, specifically leveraging supervised fine-tuning followed by reinforcement fine-tuning.
– Constructed large-scale Chain-of-Thought annotations and utilized the Qwen3 large language model as a critic in reward modeling.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OpenREAD significantly improves upstream and downstream task performance, achieving state-of-the-art results in reasoning and planning benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01830

41. Structured Extraction from Business Process Diagrams Using Vision-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: BPMN, Vision-Language Models, OCR, Image Extraction
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To extract structured JSON representations of BPMN diagrams directly from images without source model files or textual annotations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A pipeline utilizing Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and incorporating optical character recognition (OCR) for textual enrichment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach enables robust component extraction when source files are unavailable, showing performance improvements in several VLMs with OCR text enrichment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22448

42. OmniFusion: Simultaneous Multilingual Multimodal Translations via Modular Fusion
🔑 Keywords: multimodal translation, OmniFusion, AI Native, translation LLMs
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop an effective multimodal translation system that seamlessly integrates pretrained multimodal foundation models with translation large language models for simultaneous and improved translation quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of a novel fusion strategy that connects hidden states from multiple layers of a pretrained multimodal foundation model to a translation large language model, enabling joint end-to-end training for speech and image translation tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OmniFusion significantly reduces latency in simultaneous speech translation compared to cascaded pipelines and enhances overall translation quality by effectively leveraging both audio and visual inputs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00234

43. Doppler-Enhanced Deep Learning: Improving Thyroid Nodule Segmentation with YOLOv5 Instance Segmentation
🔑 Keywords: YOLOv5, ultrasound images, thyroid nodules, instance segmentation, doppler images
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance thyroid nodule segmentation accuracy in ultrasound images using YOLOv5 algorithms, particularly by incorporating doppler images for real-time clinical diagnostics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluation of multiple variants of YOLOv5 (Nano, Small, Medium, Large, XLarge) on two dataset versions, comparing performance with and without doppler images.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The YOLOv5-Large algorithm achieved the highest performance with notable improvements by including doppler images, proving their potential to significantly enhance segmentation accuracy and support automated diagnostic systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00639

44. MEGConformer: Conformer-Based MEG Decoder for Robust Speech and Phoneme Classification
🔑 Keywords: Conformer, MEG, Speech Detection, Phoneme Classification, SpecAugment
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aimed to develop Conformer-based decoders for handling two primary MEG tasks: Speech Detection and Phoneme Classification.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers adapted a compact Conformer model to raw 306-channel MEG signals, employing techniques such as task-specific augmentations, a lightweight convolutional projection layer, and class weighting.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed systems achieved significant performance, scoring 88.9% for Speech Detection and 65.8% for Phoneme Classification, surpassing baseline models and ranking in the top-10 of the LibriBrain 2025 PNPL competition.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01443

45. Generative Video Motion Editing with 3D Point Tracks
🔑 Keywords: Video-to-Video (V2V), 3D point tracks, Joint Camera/Object Manipulation, Spatiotemporal Coherence, Occlusions
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Present a track-conditioned V2V framework to enable precise joint editing of camera and object motion, maintaining spatiotemporal coherence despite occlusions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize 3D point tracks paired with source videos to train a video generation model in two stages on synthetic and real data, allowing for precise motion control and handling of occlusions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method facilitates diverse motion edits, including joint camera/object manipulation, motion transfer, and non-rigid deformation, enhancing creative possibilities in video editing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02015
46.
