AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251203

1. DeepSeek-V3.2: Pushing the Frontier of Open Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: DeepSeek-V3.2, DeepSeek Sparse Attention, scalable reinforcement learning, reasoning proficiency
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces DeepSeek-V3.2, aiming to enhance reasoning and agent performance while maintaining high computational efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper describes the implementation of DeepSeek Sparse Attention to reduce computational complexity in long-context scenarios.
– It employs a scalable reinforcement learning framework with robust protocols for post-training computation, showcasing performance equal to or exceeding leading models like GPT-5 and Gemini-3.0-Pro.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The high-compute variant, DeepSeek-V3.2-Speciale, achieves top performance in international competitions (IMO and IOI) by matching or surpassing the reasoning proficiency of Gemini-3.0-Pro.
– The model also includes a large-scale agentic task synthesis pipeline, enhancing generalization and robustness in complex, interactive environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02556

2. ToolOrchestra: Elevating Intelligence via Efficient Model and Tool Orchestration
🔑 Keywords: ToolOrchestra, Reinforcement Learning, Orchestrator, AI Systems and Tools, tool-augmented reasoning systems
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces ToolOrchestra, a method for training small orchestrators that coordinate intelligent tools to enhance efficiency and accuracy in solving complex tasks like Humanity’s Last Exam.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– ToolOrchestra uses reinforcement learning with outcome-, efficiency-, and user-preference-aware rewards to train an 8B model named Orchestrator.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Orchestrator achieves higher accuracy and efficiency compared to larger models like GPT-5, demonstrating a better trade-off between performance and cost, which supports the advancement of practical and scalable tool-augmented reasoning systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.21689

3. MultiShotMaster: A Controllable Multi-Shot Video Generation Framework
🔑 Keywords: MultiShotMaster, RoPE, video generation, spatiotemporal, automated annotation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a framework (MultiShotMaster) for controllable multi-shot video generation to address challenges in narrative coherence, flexibility, and control.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Extend a single-shot model with novel RoPE variants including Multi-Shot Narrative RoPE and Spatiotemporal Position-Aware RoPE.
– Implement an automated data annotation pipeline to combat data scarcity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MultiShotMaster demonstrates superior performance and controllability, supporting customizable shot count, duration, inter-shot consistency, and scene customization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03041

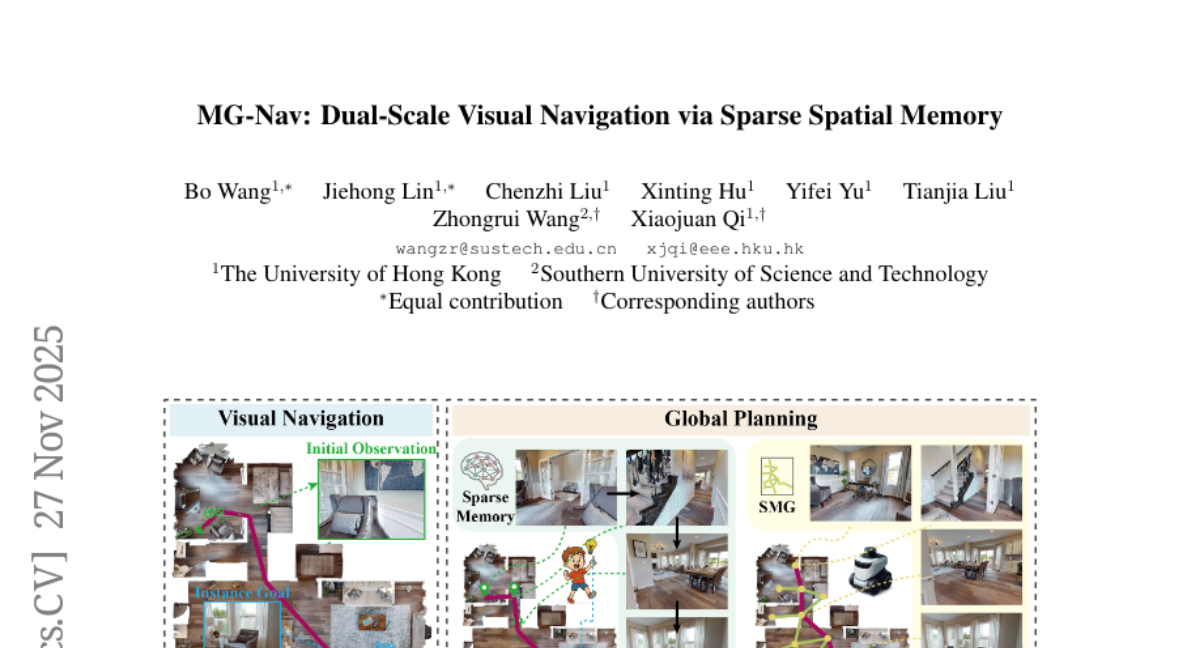
4. MG-Nav: Dual-Scale Visual Navigation via Sparse Spatial Memory
🔑 Keywords: MG-Nav, zero-shot visual navigation, Sparse Spatial Memory Graph, VGGT-adapter
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces MG-Nav, a dual-scale framework designed for zero-shot visual navigation by integrating global memory-guided planning with local geometry-enhanced control.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a Sparse Spatial Memory Graph to support region-centric memory, maintaining viewpoint diversity and planning goal-conditioned node paths for navigation.
– Incorporates a VGGT-adapter for enhanced alignment of observation and goal features within a 3D-aware space, improving viewpoint alignment and goal recognition.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MG-Nav demonstrates state-of-the-art zero-shot performance on HM3D and MP3D benchmarks and maintains robustness in dynamic environments and unseen scene conditions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22609
5. DualCamCtrl: Dual-Branch Diffusion Model for Geometry-Aware Camera-Controlled Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: DualCamCtrl, diffusion model, camera-controlled video generation, RGB-depth fusion
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce DualCamCtrl, a novel diffusion model designed for improved camera-controlled video generation by enhancing consistency and separating appearance and geometry modeling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a dual-branch framework to generate camera-consistent RGB and depth sequences, augmented by the Semantic Guided Mutual Alignment mechanism for semantics-guided RGB-depth fusion.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DualCamCtrl significantly reduces camera motion errors by over 40% compared to previous methods, effectively adhering to specified camera trajectories and enhancing both the global structure and local details of the generated videos.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.23127

6. Guided Self-Evolving LLMs with Minimal Human Supervision
🔑 Keywords: AI self-evolution, R-Few, Self-Play Challenger-Solver, concept drift, co-evolutionary dynamics
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enable stable and controllable AI self-evolution with minimal human supervision, improving performance on math and reasoning benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces R-Few, a guided Self-Play Challenger-Solver framework, incorporating lightweight human oversight through in-context grounding and mixed training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– R-Few achieves consistent performance improvements by mitigating drift and enabling stable co-evolutionary dynamics. It enhances math tasks performance and achieves results comparable to models trained on significantly more human data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02472

7. Skywork-R1V4: Toward Agentic Multimodal Intelligence through Interleaved Thinking with Images and DeepResearch
🔑 Keywords: multimodal agentic model, supervised fine-tuning, interleaved reasoning, tool-execution traces, long-horizon reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To overcome limitations in existing multimodal agentic systems by developing Skywork-R1V4, a unified model that integrates multimodal planning, image manipulation, and search with interleaved reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model was trained using supervised fine-tuning on under 30,000 high-quality trajectories, focusing on planning-execution consistency without relying on reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Skywork-R1V4 achieves state-of-the-art performance in perception and multimodal search benchmarks, demonstrating sophisticated multimodal intelligence and successful orchestration of complex multi-step tasks. The model exceeds performance metrics compared to existing systems, particularly Gemini 2.5 Flash.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02395

8. SimScale: Learning to Drive via Real-World Simulation at Scale
🔑 Keywords: Autonomous Driving, Simulation Framework, Neural Rendering, Co-training Strategy, SimScale
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a scalable simulation framework for autonomous driving, capable of synthesizing diverse and high-fidelity driving scenarios that improve generalization and robustness in real-world testing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A novel pipeline utilizing advanced neural rendering and a reactive environment to generate high-fidelity observations.
– Development of pseudo-expert trajectory generation for action supervision on synthesized states.
– Implementation of a co-training strategy on both real-world and simulated samples to enhance robustness and generalization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Simulation data significantly improve planning methods’ robustness and generalization, demonstrated by a maximum +6.8 EPDMS on navhard and +2.9 on navtest.
– Policy improvements scale smoothly with only simulation data, revealing crucial findings in sim-real learning systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.23369

9. InnoGym: Benchmarking the Innovation Potential of AI Agents
🔑 Keywords: AI Agents, Innovation Potential, Performance Gain, Novelty, Reproducible Evaluations
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces InnoGym, a benchmark and framework designed to evaluate the innovation potential of AI agents by assessing both the performance gain and originality of their approaches.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Two complementary metrics are introduced: performance gain (improvement over known solutions) and novelty (methodological differences from prior approaches). The framework includes 18 tasks from real-world engineering and scientific domains.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Although AI agents sometimes develop novel approaches, their lack of robustness limits their performance gains, indicating a gap between creativity and effectiveness, thus emphasizing the need for benchmarks that assess both.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01822

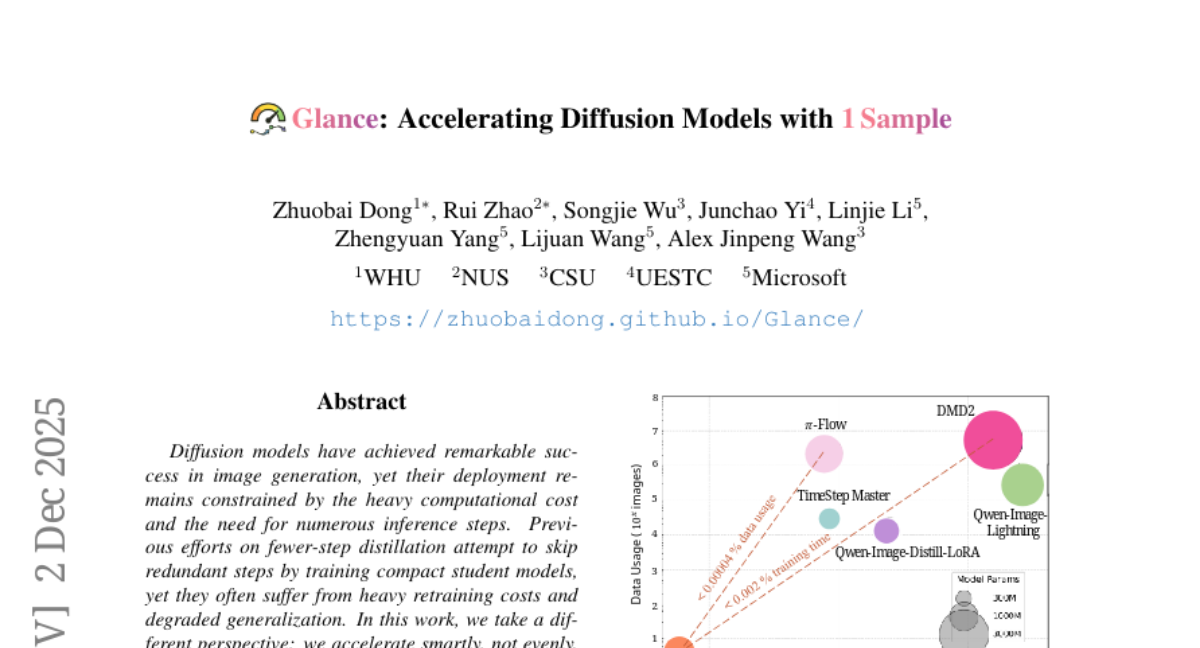
10. Glance: Accelerating Diffusion Models with 1 Sample
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion models, Computational cost, Inference steps, Lightweight LoRA adapters, Phase-aware strategy
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to accelerate diffusion models efficiently and enhance generalization without excessive retraining.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementing phase-aware LoRA adapters, specifically Slow-LoRA and Fast-LoRA, to achieve strategic acceleration in diffusion models, focusing smaller speedups on early semantic stages and larger ones on later redundant phases.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– By equipping the base model with lightweight LoRA adapters, the method achieves up to 5 times faster performance than the base model while maintaining visual quality, with generalization benefits achieved with minimal samples and training time.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02899
11. ViSAudio: End-to-End Video-Driven Binaural Spatial Audio Generation
🔑 Keywords: ViSAudio, binaural spatial audio generation, BiAudio dataset, conditional flow matching, dual-branch audio generation architecture
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address limitations in video-to-audio generation by developing an end-to-end framework for binaural spatial audio generation directly from silent video.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce the BiAudio dataset of approximately 97K video-audio pairs, and propose ViSAudio framework employing conditional flow matching with a dual-branch audio generation architecture for precise spatio-temporal alignment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ViSAudio demonstrably surpasses current state-of-the-art methods, delivering high-quality binaural audio with spatial immersion across various scenarios, effectively adapting to viewpoint changes and diverse acoustic environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03036
12. WorldMM: Dynamic Multimodal Memory Agent for Long Video Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: multimodal memory agent, episodic memory, semantic memory, visual memory, adaptive retrieval
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce WorldMM to enhance long video question-answering by effectively utilizing multimodal memory across different temporal scales.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed WorldMM, a multimodal memory agent, integrating episodic, semantic, and visual memories to improve context capture in long videos.
– Utilized an adaptive retrieval agent to select the most relevant memory source and temporal granularity iteratively.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– WorldMM significantly outperformed existing baselines, achieving an average 8.4% performance gain, demonstrating its effectiveness in long video reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02425

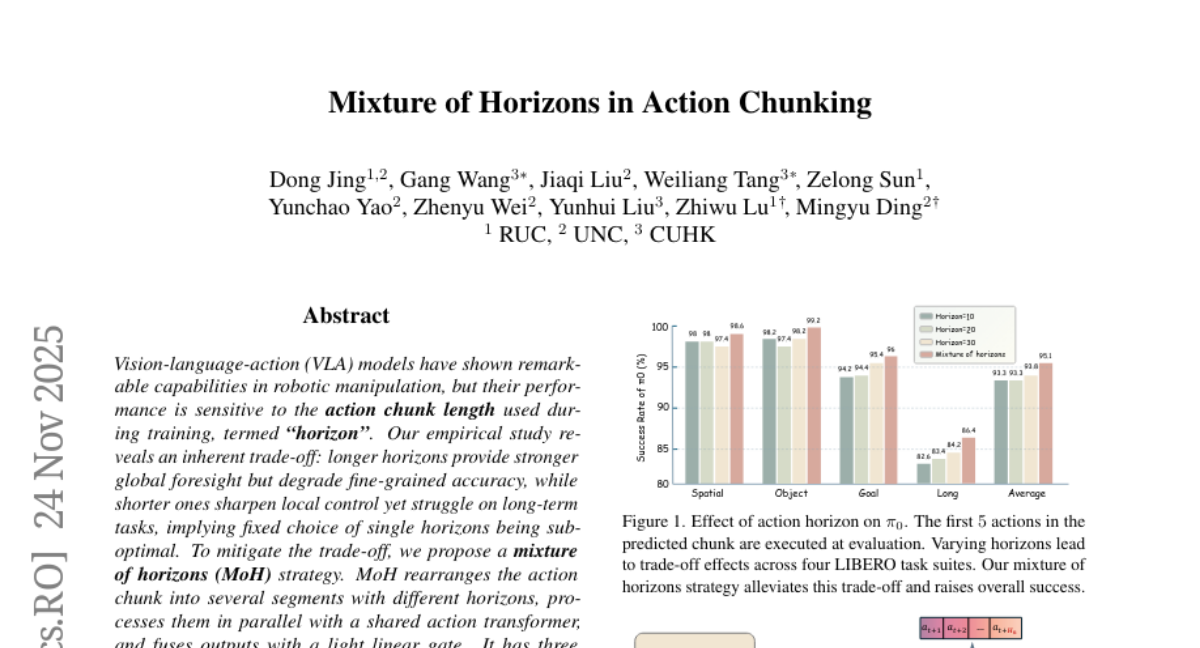
13. Mixture of Horizons in Action Chunking
🔑 Keywords: Mixture of Horizons (MoH), Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, Horizon, Robotic manipulation, Performance
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve performance and generalizability in robotic manipulation tasks by integrating long-term foresight with short-term precision through a Mixture of Horizons (MoH) strategy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The MoH strategy rearranges action chunks into several segments processed in parallel, using a shared action transformer and a linear gate for output fusion. This approach is applied to vision-language-action models with plug-and-play capability, minimal overhead, and dynamic inference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MoH significantly enhances performance and generalizability, achieving higher throughput than baselines. It consistently yields impressive gains in both simulations and real-world tasks. Particularly, the MoH approach achieves a state-of-the-art 99% success rate in mixed-task settings after only 30k training iterations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19433
14. PixelDiT: Pixel Diffusion Transformers for Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: PixelDiT, pixel space, transformer-based architecture, text-to-image generation, latent-space modeling
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address limitations of latent-space modeling in Diffusion Transformers by developing a single-stage, end-to-end PixelDiT model that operates directly in pixel space.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study proposes a dual-level transformer architecture consisting of a patch-level DiT for capturing global semantics and a pixel-level DiT for refining texture details, optimizing diffusion directly in the pixel space.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PixelDiT demonstrates competitive performance in image and text-to-image generation, achieving superior results on ImageNet, GenEval, and DPG-bench, thus overcoming limitations of existing pixel generative models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20645

15. WUSH: Near-Optimal Adaptive Transforms for LLM Quantization
🔑 Keywords: Quantization, Dynamic Range, Hadamard Matrices, Data-Aware Transforms, WUSH
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to derive closed-form optimal linear blockwise transforms for joint weight-activation quantization, incorporating data statistics to improve upon standard orthogonal transforms like the Hadamard transform.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers developed optimal adaptive (data-aware) transforms for round-to-nearest and AbsMax-scaled block quantizers suitable for both integer and floating-point numerical formats.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed WUSH transform, which features a Hadamard backbone combined with a data-dependent component, is shown to be non-orthogonal and optimally effective under certain conditions, surpassing the performance of the Hadamard transform in preliminary experiments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00956

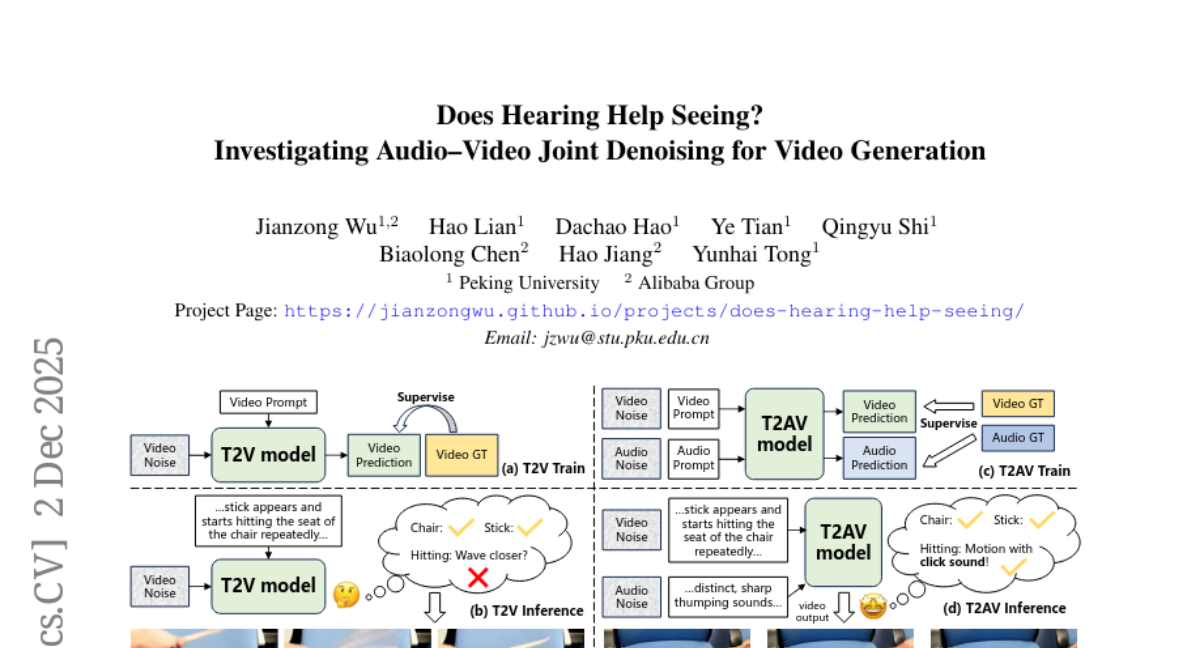
16. Does Hearing Help Seeing? Investigating Audio-Video Joint Denoising for Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: Audio-video joint denoising, AVFullDiT, cross-modal co-training
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate if audio-video joint denoising training enhances video generation quality, focusing purely on video quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced the AVFullDiT architecture using pre-trained text-to-video and text-to-audio modules for joint denoising and trained a T2AV model alongside a T2V-only model for comparison.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Audio-video joint denoising improves video quality beyond synchrony, aiding in predicting audio as a privileged signal, suggesting cross-modal co-training as an effective strategy for developing robust world models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02457
17. Deep Research: A Systematic Survey
🔑 Keywords: Deep Research, Large Language Models, query planning, reasoning capabilities, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The survey aims to provide a comprehensive and systematic overview of Deep Research systems integrating LLMs with external tools.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper formalizes a three-stage roadmap and distinguishes Deep Research from related paradigms.
– It introduces four core components: query planning, information acquisition, memory management, and answer generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The paper summarizes optimization techniques and consolidates evaluation criteria and open challenges, guiding future development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02038

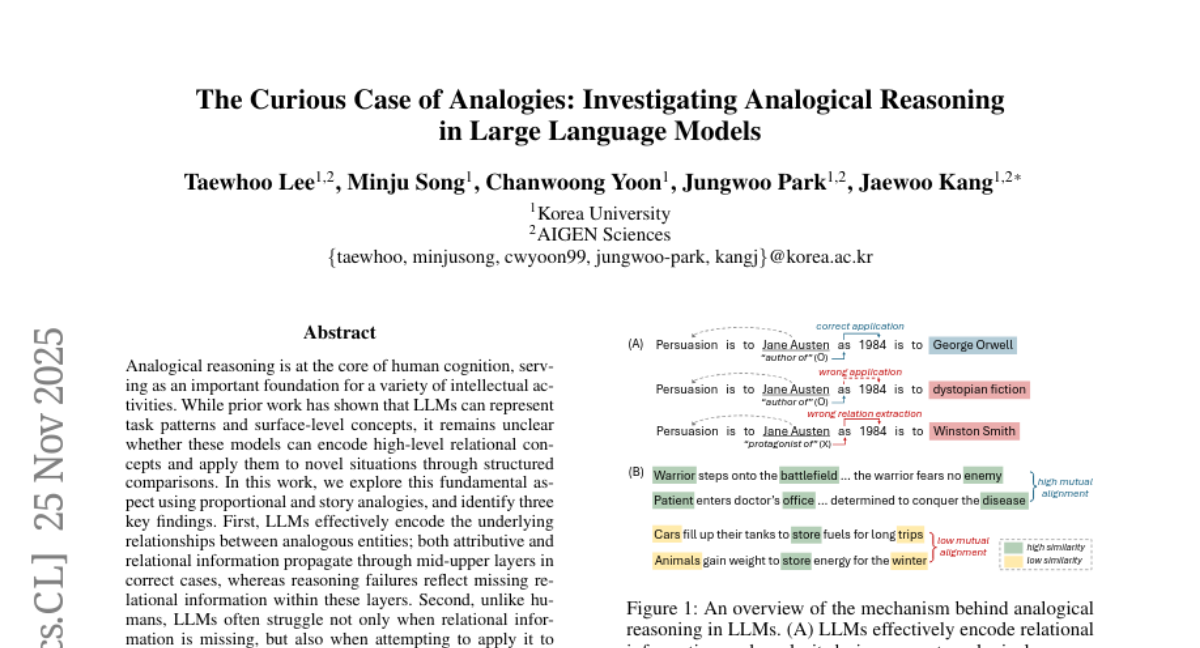
18. The Curious Case of Analogies: Investigating Analogical Reasoning in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: LLMs, analogical reasoning, high-level relational concepts, relational information, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate whether LLMs can encode high-level relational concepts and apply them to novel situations through structured comparisons using proportional and story analogies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analysis of LLMs’ capabilities to encode relational concepts, focusing on proportional and story analogies, identifying encoding strengths and strategic representation modification.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LLMs can effectively encode underlying relationships in cases where both attributive and relational information propagate correctly.
– Unlike humans, LLMs face challenges when relational information is missing or when transferring information to new entities.
– Successful analogical reasoning correlates with strong structural alignment, whereas failures indicate misalignment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20344
19. CUDA-L2: Surpassing cuBLAS Performance for Matrix Multiplication through Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: CUDA-L2, Large Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, CUDA kernels, HGEMM
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of this research is to optimize Half-precision General Matrix Multiply (HGEMM) CUDA kernels using a system that combines Large Language Models and Reinforcement Learning, named CUDA-L2, achieving significant performance enhancements.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– CUDA-L2 uses the speed of CUDA execution as the reinforcement learning reward to automatically optimize HGEMM kernels across 1,000 configurations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CUDA-L2 consistently outperforms major matrix multiplication baselines across various modes, demonstrating the potential of LLM-guided RL automation to enhance even the most optimized kernels. In server mode, it achieves up to +28.7% speedup over common libraries.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02551

20. DiG-Flow: Discrepancy-Guided Flow Matching for Robust VLA Models
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action models, geometric regularization, flow matching, observation embeddings, action embeddings
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance the robustness of Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models through geometric regularization to improve performance on complex tasks and distribution shifts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement geometric regularization to align observation and action embeddings, using discrepancy measures to guide training without modifying flow matching paths.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DiG-Flow framework provides theoretical guarantees for improved training objectives and demonstrates empirical performance gains in existing VLA architectures, especially on complex multi-step tasks and with limited data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01715
21. TRivia: Self-supervised Fine-tuning of Vision-Language Models for Table Recognition
🔑 Keywords: Table Recognition, Vision-Language Models, Self-Supervised Fine-Tuning, Question-Answering-Based Reward Mechanism, Open-Source
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce TRivia, a self-supervised fine-tuning method enabling vision-language models to learn table recognition from unlabeled data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Uses a question-answering-based reward mechanism and attention-guided module to interpret and train on unlabeled table images without human annotations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TRivia-3B, an open-sourced model, surpasses existing models in performance on popular benchmarks, offering a cost-effective and privacy-compliant solution.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01248

22. RULER-Bench: Probing Rule-based Reasoning Abilities of Next-level Video Generation Models for Vision Foundation Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: video generation, reasoning capabilities, RULER-Bench, cognitive rules, rule coherence
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to evaluate the reasoning abilities of video generation models using a benchmark called RULER-Bench, focusing on rule-based reasoning capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– RULER-Bench assesses video generation models through 40 tasks across six rule categories and employs a checklist with four evaluation metrics, using GPT-o3 to align with human judgments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current state-of-the-art video generation models show a significant gap in rule coherence with a performance of only 48.87%, indicating substantial potential for improvement in reasoning capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02622

23. Revisiting the Necessity of Lengthy Chain-of-Thought in Vision-centric Reasoning Generalization
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-Thought, vision-language models, visual reasoning, CoT design
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate how different Chain-of-Thought (CoT) designs impact the generalizable visual reasoning ability in vision-language models (VLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A controlled maze-solving benchmark is used with Qwen2.5-VL-7B under a standard SFT-then-RL pipeline to evaluate the effectiveness of different CoT designs, including Language CoT, Grounding CoT, and Visual CoT.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Findings indicate that concise CoT containing only essential grounding steps outperforms longer CoT traces, and minimal grounding steps exhibit the best generalization across various tasks, highlighting a “short is long” effect for efficient visual reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22586

24. MagicQuillV2: Precise and Interactive Image Editing with Layered Visual Cues
🔑 Keywords: MagicQuill V2, generative image editing, diffusion models, layered composition, granular control
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces MagicQuill V2, aiming to enhance generative image editing by integrating diffusion models with a layered composition paradigm for better user control.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Decomposition of creative intent into controllable visual cues including content, spatial, structural, and color layers.
– Development of a specialized data generation pipeline and a unified control module to handle these visual cues effectively.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MagicQuill V2 successfully bridges the user intention gap, providing creators with direct and intuitive control over the generative process, as validated by extensive experiments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03046

25. PAI-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark For Physical AI
🔑 Keywords: Physical AI, Multi-Modal Large Language Models, Video Generative Models, Physical Coherence, Causal Reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the study is to develop a unified benchmark called Physical AI Bench (PAI-Bench) that evaluates the perception and prediction capabilities of multi-modal large language models and video generative models, specifically focusing on physical coherence and causal reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– PAI-Bench comprises 2,808 real-world cases with task-aligned metrics designed to capture physical plausibility and domain-specific reasoning, assessing models across video generation, conditional video generation, and video understanding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study highlights that although video generative models show strong visual fidelity, they often struggle with maintaining physically coherent dynamics. Additionally, multi-modal large language models exhibit limited performance in forecasting and causal interpretation, indicating that current systems are still in early stages of meeting the perceptual and predictive demands of Physical AI.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01989

26. SwiftVLA: Unlocking Spatiotemporal Dynamics for Lightweight VLA Models at Minimal Overhead
🔑 Keywords: SwiftVLA, Vision-Language-Action, Fusion Tokens, spatiotemporal reasoning, edge devices
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance compact Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models with 4D understanding while maintaining efficiency in design and execution.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a pretrained 4D visual geometry transformer employing a temporal cache to extract 4D features from 2D images.
– Introduction of Fusion Tokens to facilitate unified representations for action generation, and a mask-and-reconstruct strategy to enable effective 4D representations learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SwiftVLA outperforms existing lightweight baselines and matches the performance of significantly larger VLAs, offering a substantial speed and memory advantage on edge devices.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00903

27. SimWorld: An Open-ended Realistic Simulator for Autonomous Agents in Physical and Social Worlds
🔑 Keywords: SimWorld, Unreal Engine 5, LLM/VLM Agents, Realistic Simulation, Procedural Environment Generation
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduction of SimWorld, a new Unreal Engine 5-based simulator designed to develop and evaluate LLM/VLM agents in realistic physical and social settings.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Deployment of frontier LLM agents on long-horizon multi-agent delivery tasks, demonstrating strategic cooperation and competition to evaluate agent capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SimWorld reveals distinct reasoning patterns and limitations across AI models, providing a foundational platform for real-world agent intelligence advancement across various disciplines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01078

28. YingVideo-MV: Music-Driven Multi-Stage Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: YingVideo-MV, audio semantic analysis, temporal-aware diffusion Transformer, music-motion-camera synchronization, Music-in-the-Wild Dataset
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introducing YingVideo-MV for generating high-quality music performance videos with synchronized camera motion.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes cascaded frameworks including audio semantic analysis, temporal-aware diffusion Transformers, and a camera adapter module.
– Constructs a large-scale Music-in-the-Wild Dataset to support video generation diversity and quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates that YingVideo-MV achieves outstanding performance in creating coherent, expressive music videos with precise synchronization of music, motion, and camera.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02492

29. Video4Spatial: Towards Visuospatial Intelligence with Context-Guided Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: Video4Spatial, video diffusion models, spatial understanding, visuospatial intelligence, video-only inputs
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Video4Spatial to explore whether video generative models can demonstrate visuospatial intelligence using only visual data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework uses video diffusion models conditioned on video-based scene context to perform complex spatial tasks like scene navigation and object grounding without auxiliary modalities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Video4Spatial shows strong spatial understanding and generalization by planning navigation, grounding objects, and maintaining spatial consistency, advancing video generative models toward general visuospatial reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03040

30. BlockVid: Block Diffusion for High-Quality and Consistent Minute-Long Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: BlockVid, block diffusion, KV caching, semantic-aware sparse KV cache, Block Forcing
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to address challenges in block diffusion video generation by introducing BlockVid, a framework designed to produce high-quality, coherent minute-long videos.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs semantic-aware sparse KV caching, Block Forcing training, and chunk-wise noise scheduling to enhance temporal consistency and reduce error propagation in video generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BlockVid consistently outperforms existing methods in generating high-quality, coherent minute-long videos, achieving significant improvements on VBench and LV-Bench metrics, including 22.2% improvement in VDE Subject and 19.4% in VDE Clarity.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22973
31. Ovis-Image Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Ovis-Image, text-to-image model, diffusion-based visual decoder, multimodal backbone, text-centric training pipeline
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce and optimize Ovis-Image, a 7B text-to-image model for high-quality text rendering under computational constraints.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of a diffusion-based visual decoder with a multimodal backbone.
– Utilization of a text-centric training pipeline combining large-scale pre-training with post-training refinements.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Ovis-Image achieves performance comparable to larger models with efficient deployment on a single high-end GPU.
– Demonstrates that a strong multimodal backbone with a text-focused training strategy can achieve effective bilingual text rendering without relying on large or proprietary models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22982

32. CodeV: Code with Images for Faithful Visual Reasoning via Tool-Aware Policy Optimization
🔑 Keywords: CodeV, Tool-Aware Policy Optimization (TAPO), visual reasoning, multimodal reasoning, AI Native
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve faithful tool use and accuracy in visual and multimodal reasoning tasks through the use of a new code-based visual agent called CodeV.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces a faithfulness evaluation protocol to measure tool use efficacy and uses Tool-Aware Policy Optimization (TAPO), which enhances a process-level reinforcement learning framework for training CodeV.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CodeV improves the rates of faithful tool use in visual search benchmarks and achieves competitive or superior accuracy in multimodal reasoning and math benchmarks, highlighting the importance of explicitly supervising intermediate tool behavior.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.19661

33. Masks Can Be Distracting: On Context Comprehension in Diffusion Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Masked Diffusion Language Models, context comprehension, locality bias, mask-agnostic loss function
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To examine and improve context comprehension abilities of Masked Diffusion Language Models (MDLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Systematic ablations to identify limitations and test the effectiveness of a mask-agnostic loss function for reducing distractions from mask tokens.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Despite a global training objective, MDLMs show strong locality bias. Adding mask tokens degrades context comprehension. Introducing a mask-agnostic loss function significantly enhances robustness and context comprehension abilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.21338

34. Gold-Medal-Level Olympiad Geometry Solving with Efficient Heuristic Auxiliary Constructions
🔑 Keywords: HAGeo, AI-generated summary, Automated theorem proving, Euclidean geometry, Heuristic-based method
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance geometry theorem proving for International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) level problems without relying on neural network-based approaches, achieving high performance using a heuristic-based method.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of HAGeo, a heuristic-based method for adding auxiliary constructions in geometric deduction, which operates efficiently on CPUs.
– Creation of a benchmark, HAGeo-409, comprising 409 geometry problems with human-assessed difficulty levels to provide a comprehensive evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HAGeo achieves gold-medal level performance on the IMO-30 benchmark, solving 28 out of 30 problems and outperforming the neural network-based AlphaGeometry approach.
– The HAGeo-409 benchmark offers greater challenges compared to the existing IMO-30 benchmark, setting higher standards for geometry theorem proving.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.00097

35. C^2DLM: Causal Concept-Guided Diffusion Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Causal Concept-Guided Diffusion Language Model (C^2DLM), Diffusion Language Models (DLMs), causal relationships, training efficiency, reasoning tasks
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces a new model called the Causal Concept-Guided Diffusion Language Model (C^2DLM) to improve reasoning capabilities in language models by incorporating causal relationships between concepts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The proposed model starts with the fully connected attention mechanism from DLMs and involves constructing a concept-level causal graph from a teacher model to guide attention in learning causal relationships.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– C^2DLM significantly enhances performance, showing a 12% improvement with approximately 3.2 times faster training speed in the COT-OrderPerturb task, and achieves an average gain of 1.31% across six downstream reasoning tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22146

36. Shoe Style-Invariant and Ground-Aware Learning for Dense Foot Contact Estimation
🔑 Keywords: Foot contact estimation, Adversarial training, Shoe style-invariant, Ground feature extraction
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to develop a framework for dense foot contact estimation that addresses challenges related to shoe appearance diversity and effective ground feature extraction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers employed shoe style adversarial training to ensure shoe style-invariant contact estimation. Additionally, they introduced a ground feature extractor that captures ground properties using spatial context.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The FECO framework achieves robust and accurate foot contact estimation regardless of shoe appearance and effectively leverages ground information, showing promise for advancing the understanding of human movement and interaction.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22184

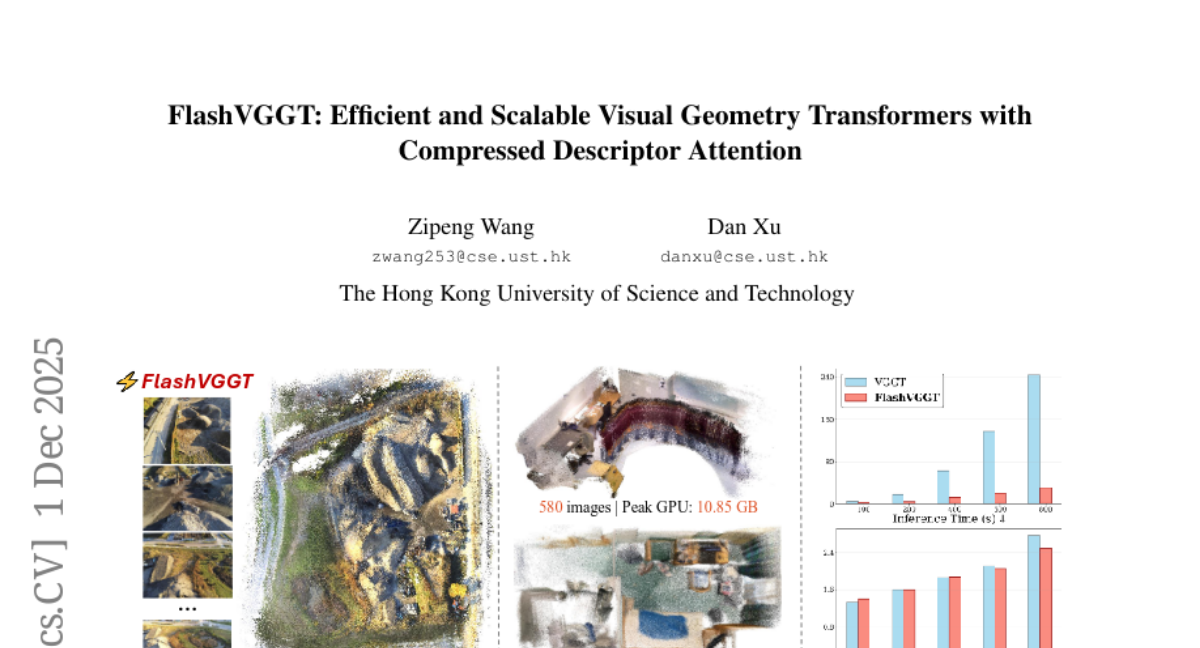
37. FlashVGGT: Efficient and Scalable Visual Geometry Transformers with Compressed Descriptor Attention
🔑 Keywords: 3D reconstruction, descriptor-based attention, self-attention, descriptor tokens, cross-attention
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce FlashVGGT, an efficient model utilizing descriptor-based attention for 3D reconstruction to improve scalability and reduce inference time compared to VGGT.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement a descriptor-based attention mechanism that compresses spatial information using descriptor tokens, applying cross-attention to manage computational load.
– Employ a chunk-recursive mechanism for online inference over extending sequences by reusing cached descriptors.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FlashVGGT achieves competitive reconstruction accuracy relative to VGGT with significant reductions in inference time, handling up to 3,000 images efficiently.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01540
38. UnicEdit-10M: A Dataset and Benchmark Breaking the Scale-Quality Barrier via Unified Verification for Reasoning-Enriched Edits
🔑 Keywords: lightweight data pipeline, benchmark, Image Editing, scalable quality control, failure detection
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the quality and scale of image editing datasets and model evaluations by introducing a new data pipeline and benchmark.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A lightweight data pipeline replaces multi-toolchains with an end-to-end model and unified post-verification, and uses a 7B dual-task expert model, Qwen-Verify, for scalable quality control, failure detection, and instruction recaptioning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Introduced UnicEdit-10M, a versatile 10M-scale dataset, and UnicBench, a benchmark assessing both basic and complex edits, revealing limitations in current models and pathways for future research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02790

39. Artemis: Structured Visual Reasoning for Perception Policy Learning
🔑 Keywords: Perception-Policy Learning, Structured Spatial Reasoning, Bounding-Box, Visual Tasks, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Artemis, a perception-policy learning framework designed to enhance performance on visual tasks by utilizing structured spatial reasoning with (label, bounding-box) pairs instead of relying solely on linguistic reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Artemis employs structured proposal-based reasoning, representing intermediate steps as (label, bounding-box) pairs to capture verifiable visual states, facilitating direct supervision for proposal quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research demonstrates that Artemis achieves strong performance on grounding and detection tasks, showing substantial generalization to counting and geometric-perception tasks. Aligning reasoning with spatial representations enhances perception-policy learning, providing a scalable approach to developing general perception policies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01988

40. Visual Sync: Multi-Camera Synchronization via Cross-View Object Motion
🔑 Keywords: VisualSync, multi-view dynamics, epipolar constraints, 3D reconstruction, feature matching
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to synchronize unposed, unsynchronized video recordings across multiple consumer cameras with millisecond accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes multi-view dynamics and epipolar constraints to align videos, leveraging techniques such as 3D reconstruction, feature matching, dense tracking, and minimizing epipolar error.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VisualSync demonstrates superior performance over existing methods, achieving a median synchronization error below 50 ms on various challenging datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02017
41. Understanding and Harnessing Sparsity in Unified Multimodal Models
🔑 Keywords: unified multimodal models, Mixture-of-Experts Adaptation, compression, sparse activation, expert-frozen tuning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address inefficiencies in unified multimodal models, particularly in generation, by implementing Mixture-of-Experts Adaptation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted a systematic analysis using training-free pruning to assess compressibility in model components and proposed sparse activation and expert-frozen tuning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The adapted BAGEL model achieves comparable performance to the full model with only about half of the parameters activated, demonstrating the effectiveness of this approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02351

42. GUI Exploration Lab: Enhancing Screen Navigation in Agents via Multi-Turn Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: GUI Exploration Lab, GUI agent navigation, Reinforcement Learning, screen navigation
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address challenges in training and evaluating GUI agents in complex real-world GUI environments by introducing the GUI Exploration Lab.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a simulation environment for flexible definition of screens and navigation graphs.
– Implementation of supervised fine-tuning for foundational knowledge memorization.
– Application of single-turn and multi-turn reinforcement learning to enhance generalization and exploration strategies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated improved navigation performance through reinforcement learning.
– Validated methods on both static and interactive benchmarks, showcasing their effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02423

43. Benchmarking Scientific Understanding and Reasoning for Video Generation using VideoScience-Bench
🔑 Keywords: VideoScience-Bench, Scientific Reasoning, Zero-shot Reasoning, T2V, I2V
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate video models’ ability to perform scientific reasoning by generating phenomena consistent with undergraduate-level physics and chemistry concepts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed VideoScience-Bench, a benchmark featuring 200 prompts covering 14 topics and 103 concepts to test video models’ scientific understanding and reasoning.
– Conducted expert-annotated evaluations on state-of-the-art video models across five dimensions including Prompt Consistency and Spatio-Temporal Continuity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VideoScience-Bench is the first benchmark to test video models as both generators and reasoners, demonstrating strong correlation with human assessments and requiring scientific understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02942

44. In-Context Sync-LoRA for Portrait Video Editing
🔑 Keywords: Sync-LoRA, image-to-video diffusion model, identity consistency, temporal coherence
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to develop a method, Sync-LoRA, for editing portrait videos that achieves high-quality visual modifications while maintaining frame-accurate synchronization and identity consistency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Sync-LoRA utilizes an image-to-video diffusion model trained with in-context LoRA. It involves modifying the first frame, then propagating edits throughout the video, with training on a curated set of synchronized human portraits.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Sync-LoRA achieves a robust balance between edit fidelity and precise motion preservation, demonstrating high visual fidelity and strong temporal coherence. It generalizes well to unseen identities and diverse edits.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03013

45. Click2Graph: Interactive Panoptic Video Scene Graphs from a Single Click
🔑 Keywords: Click2Graph, Panoptic Video Scene Graph Generation, user-guided, Dynamic Interaction Discovery, Semantic Classification
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop Click2Graph, an interactive framework that combines user cues with dynamic interaction discovery and semantic classification to enhance scene understanding in Panoptic Video Scene Graph Generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework uses a Dynamic Interaction Discovery Module for generating subject-conditioned object prompts and a Semantic Classification Head for joint entity and predicate reasoning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Click2Graph demonstrates a robust foundation for user-guided PVSG, effectively integrating human prompting with panoptic grounding and relational inference for controllable and interpretable video scene understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.15948

46. BOOM: Beyond Only One Modality KIT’s Multimodal Multilingual Lecture Companion
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal, Multilingual, AI-generated summary, Slide-aware transcripts, Summarization
💡 Category: AI in Education
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address the challenge of localizing educational content by developing BOOM, a multimodal multilingual lecture companion that translates audio and slides to produce synchronized outputs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The system processes and translates lecture audio and slides, maintaining synchronized outputs across text, images, and speech to support various modalities of learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments show that slide-aware transcripts enhance downstream tasks, such as summarization and question answering, helping students access lectures in their native language while preserving the original content.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02817

47.
