AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251205

1. DAComp: Benchmarking Data Agents across the Full Data Intelligence Lifecycle
🔑 Keywords: DAComp, Data Engineering, Data Analysis, Autonomous Data Agents, SQL Pipelines
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce DAComp, a benchmark comprising 210 tasks, to evaluate the capabilities of data agents in real-world data engineering and analysis workflows, highlighting significant deficiencies in both areas.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluation of engineering tasks through execution-based, multi-metric assessment and open-ended tasks using an experimentally validated LLM-judge guided by crafted rubrics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– State-of-the-art agents perform poorly on DAComp tasks, with low success rates for DE tasks revealing critical bottlenecks, and scores for DA tasks indicating deficiencies in open-ended reasoning.
– DAComp establishes a rigorous testbed to drive the development of capable autonomous data agents for enterprise environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04324

2. Live Avatar: Streaming Real-time Audio-Driven Avatar Generation with Infinite Length
🔑 Keywords: Live Avatar, AI-generated summary, Timestep-forcing Pipeline Parallelism, Rolling Sink Frame Mechanism, real-time
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop Live Avatar, a co-designed framework that enables efficient, high-fidelity, and infinite-length avatar generation utilizing a 14-billion-parameter diffusion model.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach introduces Timestep-forcing Pipeline Parallelism and Rolling Sink Frame Mechanism to achieve stable, low-latency real-time streaming and maintain sequence fidelity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Live Avatar achieves state-of-the-art performance with 20 FPS end-to-end generation on 5 H800 GPUs, establishing a new paradigm for deploying diffusion models in industrial video synthesis applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04677

3. Nex-N1: Agentic Models Trained via a Unified Ecosystem for Large-Scale Environment Construction
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, autonomous agents, agent hierarchies, simulation-reality gap, interactive environments
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to enable large language models to operate as autonomous agents, transforming learning paradigms from static imitation to incentive-driven decision making through enhanced interaction signals.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introducing a method that scales complexity, diversity, and fidelity in interactive environments using three core components: NexAU for creating complex agent hierarchies, NexA4A for generating diverse agent hierarchies from natural language, and NexGAP for bridging the simulation-reality gap.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Nex-N1 model, trained using the newly established environments, shows superior performance over state-of-the-art open-source models and remains competitive against proprietary models in complex tasks. The open-sourcing of the Nex ecosystem and model weights is aimed to spur further research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04987

4. ARM-Thinker: Reinforcing Multimodal Generative Reward Models with Agentic Tool Use and Visual Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: ARM-Thinker, multimodal reasoning, external tools, reward models, AI Native
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to enhance accuracy and interpretability in complex multimodal reasoning tasks using ARM-Thinker.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper uses a multi-stage reinforcement learning framework to train ARM-Thinker. It autonomously invokes external tools to ground judgments in verifiable evidence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ARM-Thinker shows a +16.2% average improvement on reward modeling benchmarks and outperforms in multimodal math and logical reasoning tasks, demonstrating enhanced accuracy and interpretability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05111

5. Reward Forcing: Efficient Streaming Video Generation with Rewarded Distribution Matching Distillation
🔑 Keywords: Reward Forcing, EMA-Sink, Motion Dynamics, Streaming Video Generation, Re-DMD
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance video generation by introducing Reward Forcing, which aims to improve motion dynamics and reduce dependency on initial frames.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces the EMA-Sink, updating tokens with exponential moving averages to capture both long-term context and recent dynamics.
– Proposes Rewarded Distribution Matching Distillation (Re-DMD) for prioritizing high-reward regions using vision-language model ratings.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Reward Forcing achieves state-of-the-art performance in streaming video generation, enhancing motion quality while maintaining data fidelity, with performance noted at 23.1 FPS on a single H100 GPU.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04678

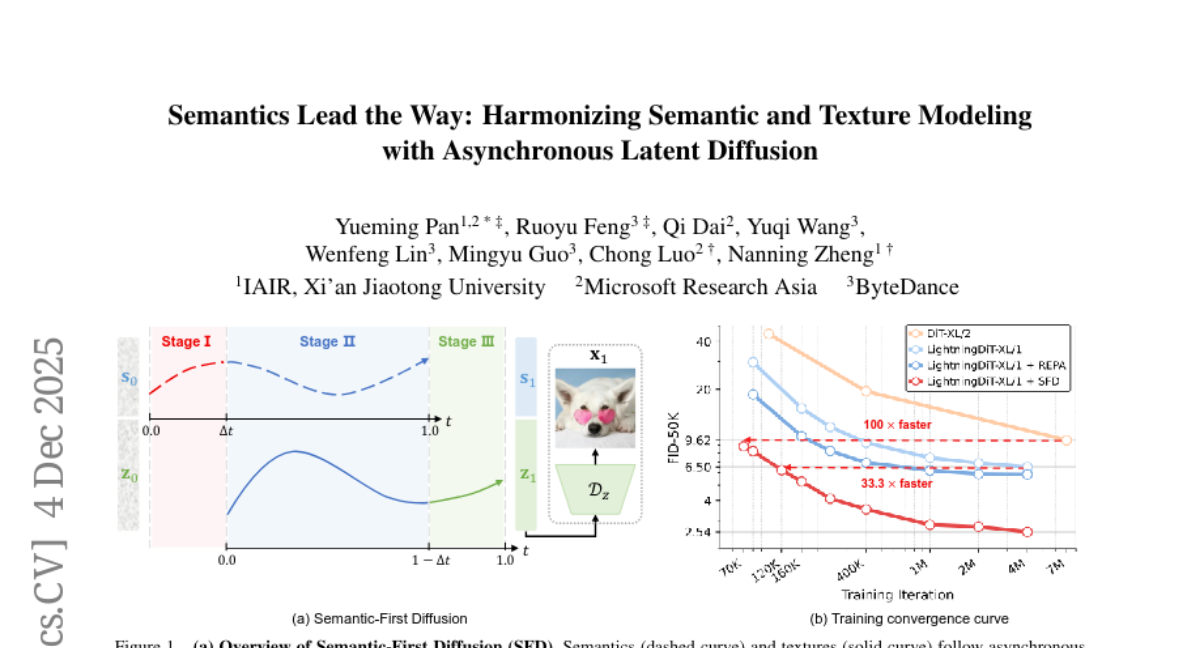
6. Semantics Lead the Way: Harmonizing Semantic and Texture Modeling with Asynchronous Latent Diffusion
🔑 Keywords: Semantic-First Diffusion, Latent Diffusion Models, Semantic VAE, ImageNet, FID
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance image generation quality and convergence speed by prioritizing the generation of semantic over texture latents within Latent Diffusion Models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Semantic-First Diffusion (SFD), which asynchronously denoises semantic and texture latents using separate noise schedules, leveraging a pretrained visual encoder to form semantic latents.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SFD achieves significantly faster convergence and lower FID scores on ImageNet compared to existing methods, demonstrating the effectiveness of asynchronous, semantics-led modeling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04926
7. PaperDebugger: A Plugin-Based Multi-Agent System for In-Editor Academic Writing, Review, and Editing
🔑 Keywords: PaperDebugger, Large Language Models, LaTeX editors, In-editor interaction, Revision pipelines
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop an in-editor academic writing assistant (PaperDebugger) that embeds large language models directly into LaTeX editors for enhanced document management and interaction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of AI-powered reasoning into writing environments using a Chrome-approved extension, Kubernetes-native orchestration, and a Model Context Protocol toolchain supporting literature search and fine-grained document operations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The PaperDebugger demonstrates the practicality and effectiveness of in-editor interactions, showcasing active user engagement and validating its utility as a minimal-intrusion AI writing assistant.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02589
8. DynamicVerse: A Physically-Aware Multimodal Framework for 4D World Modeling
🔑 Keywords: DynamicVerse, Video Depth Estimation, 4D Multimodal Dataset, AI-generated Summary, Camera Pose Estimation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop a framework called DynamicVerse that accurately models dynamic real-world videos to improve performance in video depth estimation, camera pose estimation, and camera intrinsics estimation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs large vision, geometric, and multimodal models, incorporating window-based Bundle Adjustment with global optimization to convert long video sequences into a 4D multimodal dataset.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DynamicVerse showcases superior performance in capturing physical-scale measurements from internet videos, demonstrating greater global accuracy than existing methods across three benchmark tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03000
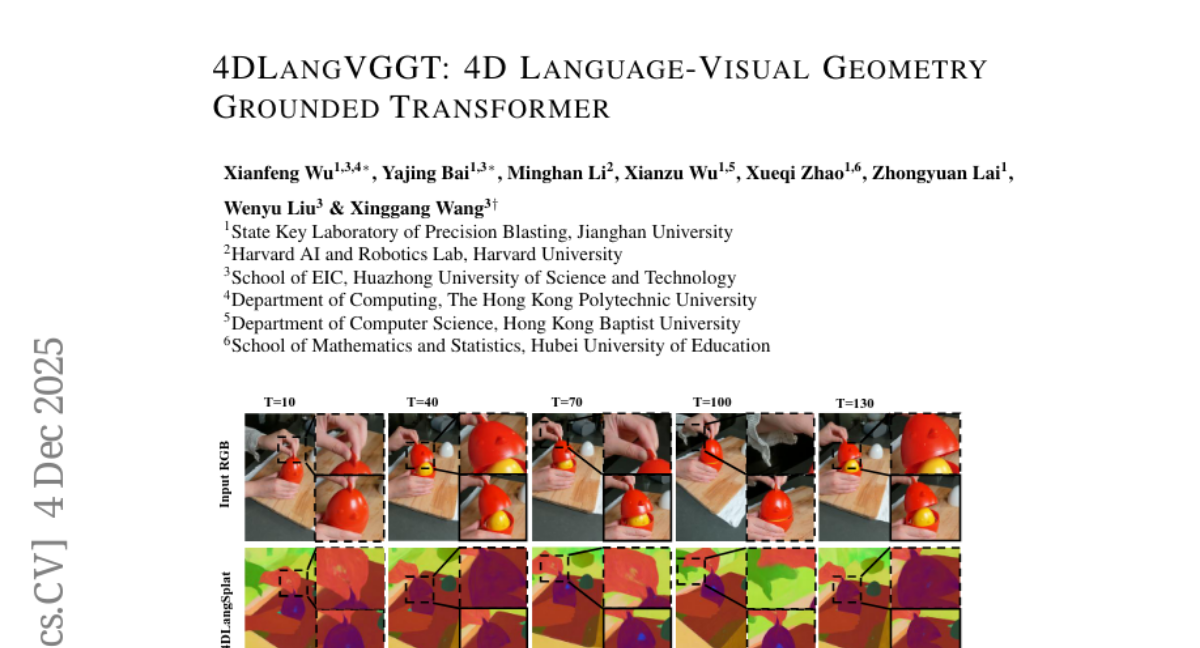
9. 4DLangVGGT: 4D Language-Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer
🔑 Keywords: 4D scene understanding, Transformer-based, embodied AI, augmented/virtual reality, semantic representations
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance 4D scene understanding by integrating geometric perception and language alignment within a unified Transformer-based framework, 4DLangVGGT.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employing the 4D Visual Geometry Transformer (VGGT) for capturing spatio-temporal geometric representations and the Semantic Bridging Decoder (SBD) to align these features into a language-aligned semantic space.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– 4DLangVGGT offers enhanced semantic interpretability and structural fidelity while improving deployment efficiency and generalization compared to previous scene-specific approaches, achieving state-of-the-art performance on HyperNeRF and Neu3D datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05060
10. UltraImage: Rethinking Resolution Extrapolation in Image Diffusion Transformers
🔑 Keywords: UltraImage, High-Fidelity Image Generation, Dominant Frequency Correction, Entropy-Guided Adaptive Attention Concentration, Visual Fidelity
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address challenges in image generation, specifically content repetition and quality degradation, through an innovative framework called UltraImage.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– UltraImage utilizes frequency-wise analysis of positional embeddings and introduces two key techniques: recursive dominant frequency correction and entropy-guided adaptive attention concentration.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UltraImage outperforms prior methods by reducing content repetition and enhancing visual fidelity. It can generate images up to 6K*6K resolution without low-resolution guidance, demonstrating its powerful extrapolation capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04504

11. Model-Based and Sample-Efficient AI-Assisted Math Discovery in Sphere Packing
🔑 Keywords: Sphere Packing, Bayesian Optimization, Monte Carlo Tree Search, SDP, AI-assisted Discovery
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve upper bounds for sphere packing in dimensions 4-16 by framing SDP construction as a sequential decision process.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a model-based framework that integrates Bayesian Optimization with Monte Carlo Tree Search to efficiently search for SDP formulations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach successfully yielded state-of-the-art upper bounds in sphere packing for dimensions 4-16, showcasing the potential of model-based search in advancing progress on mathematically complex problems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04829

12. Splannequin: Freezing Monocular Mannequin-Challenge Footage with Dual-Detection Splatting
🔑 Keywords: Splannequin, dynamic Gaussian splatting, Gaussian primitives, temporal anchoring, inference overhead
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve the visual quality of frozen 3D scenes synthesized from monocular videos by addressing artifacts in dynamic Gaussian splatting.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of Splannequin, an architecture-agnostic regularization technique that detects hidden and defective states of Gaussian primitives and applies temporal anchoring.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method integrates seamlessly into existing dynamic Gaussian pipelines without architectural changes, improving visual quality significantly, as evidenced by a 96% user preference.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05113

13. SIMA 2: A Generalist Embodied Agent for Virtual Worlds
🔑 Keywords: SIMA 2, Gemini foundation model, embodied agent, high-level goals, open-ended self-improvement
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce SIMA 2, an embodied agent built on the Gemini foundation model that can interact with 3D virtual worlds, reason about goals, and autonomously learn new skills.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing the Gemini foundation model to allow SIMA 2 to understand and act within various 3D environments, handle complex instructions through language and images, and demonstrate generalization to new environments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SIMA 2 successfully acts as an interactive partner, able to reason about high-level goals and shows potential for continuous learning and skill improvement, narrowing the gap with human performance in diverse virtual settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04797

14. TV2TV: A Unified Framework for Interleaved Language and Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: TV2TV, Mixture-of-Transformers, video-text models, visual quality, controllability
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to introduce TV2TV, a new video generation model that integrates text and video generation to enhance visual quality and controllability using language modeling for high-level reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research utilizes a Mixture-of-Transformers architecture to jointly perform language modeling and video flow matching, employing a unified generative modeling framework that decomposes video generation into alternating text and video generation processes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TV2TV demonstrates substantial improvements in visual quality and controllability, particularly in video game data and natural videos, and successfully scales to complex real-world action sequences with the aid of vision-language models. It highlights the potential of TV2TV for video generation with open-ended textual reasoning and control.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05103

15. DraCo: Draft as CoT for Text-to-Image Preview and Rare Concept Generation
🔑 Keywords: DraCo, interleaved reasoning, text-to-image generation, chain-of-thought, super-resolution
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce DraCo, a novel interleaved reasoning paradigm that enhances text-to-image generation by integrating textual and visual content to improve planning and verification.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Generate low-resolution draft images for concrete visual planning.
– Employ inherent understanding capability to verify semantic alignments and refine images using super-resolution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DraCo addresses challenges in textual planning and rare attribute generation, showing significant performance improvements in benchmarks like GenEval, Imagine-Bench, and GenEval++.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05112

16. On GRPO Collapse in Search-R1: The Lazy Likelihood-Displacement Death Spiral
🔑 Keywords: Lazy Likelihood Displacement, GRPO, likelihood-preserving regularization, Open-domain QA, multi-hop QA
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Identify and address the critical issue, Lazy Likelihood Displacement (LLD), causing training collapse in GRPO for tool-integrated reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Propose LLDS regularization that activates only when a trajectory’s likelihood decreases, targeting and stabilizing specific tokens responsible for LLD.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LLDS effectively mitigates LLD, stabilizes training, and prevents gradient explosion, achieving substantial performance improvements on multiple benchmarks such as Qwen2.5-3B and Qwen2.5-7B.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04220

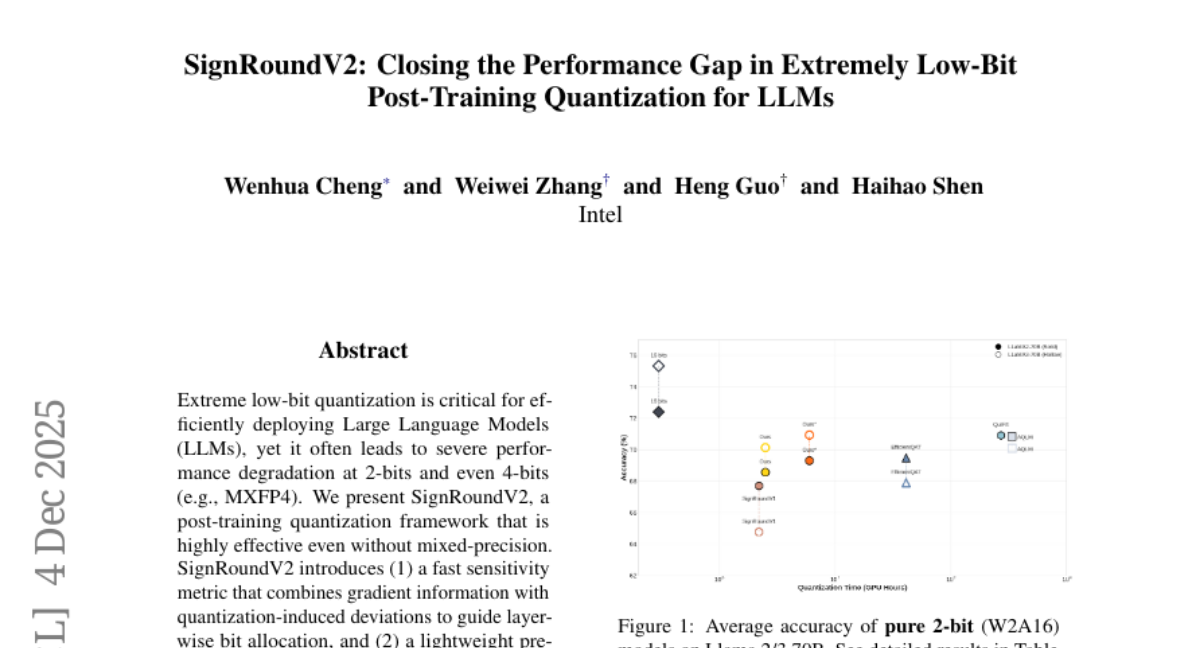
17. SignRoundV2: Closing the Performance Gap in Extremely Low-Bit Post-Training Quantization for LLMs
🔑 Keywords: SignRoundV2, Low-bit Quantization, Large Language Models, Post-Training Quantization
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to address the severe performance degradation in Large Language Models when using extreme low-bit quantization, specifically at 2-bits and 4-bits.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a post-training quantization framework called SignRoundV2. It employs a fast sensitivity metric that combines gradient information with quantization-induced deviations to guide layer-wise bit allocation and implements lightweight pre-tuning search for quantization scales.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SignRoundV2 achieves competitive accuracy for Large Language Models with approximately 1 percent variance at 4-5 bits and maintains strong results even at 2 bits, successfully closing the gap with full-precision models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04746
18. SeeNav-Agent: Enhancing Vision-Language Navigation with Visual Prompt and Step-Level Policy Optimization
🔑 Keywords: VLN agent, Large Vision-Language Models, dual-view Visual Prompt, Reinforcement Fine-Tuning, SRGPO
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address perception and planning errors in VLN agents by introducing the SeeNav-Agent framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a dual-view Visual Prompt technique to improve spatial state understanding.
– Developed a novel Step-level Reinforcement Fine-Tuning method, SRGPO, to enhance planning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SeeNav-Agent significantly improved navigation success rates, outperforming current best models in the EmbodiedBench benchmark.
– SRGPO demonstrated better training stability and efficiency over existing algorithms like GRPO and GiGPO.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02631

19. Aligned but Stereotypical? The Hidden Influence of System Prompts on Social Bias in LVLM-Based Text-to-Image Models
🔑 Keywords: LVLM-based T2I systems, social bias, system prompts, FairPro, demographic bias
💡 Category: AI Ethics and Fairness
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate the extent to which Large Vision-Language Model (LVLM)-based Text-to-Image (T2I) systems amplify social biases compared to non-LVLM models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A 1,024 prompt benchmark was used to systematically evaluate demographic bias across multiple attributes.
– Various analytical techniques such as decoded intermediate representations, token-probability diagnostics, and embedding-association analyses were employed to understand how system prompts contribute to bias.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Findings highlight that LVLM-based models produce more socially biased images, with system prompts playing a critical role in bias propagation.
– Introduction of FairPro meta-prompting framework, which effectively reduces demographic bias without compromising on text-image alignment in LVLM-based T2I systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04981

20. Mitigating Object and Action Hallucinations in Multimodal LLMs via Self-Augmented Contrastive Alignment
🔑 Keywords: multimodal LLMs, hallucination issues, Self-Augmented Contrastive Alignment, video caption generation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to tackle hallucination issues in multimodal LLMs, specifically focusing on promoting object and action faithfulness in video caption generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of the Self-Augmented Contrastive Alignment (SANTA) framework, utilizing a hallucinative self-augmentation method to address spurious correlations and enhance visual accuracy.
– Development of tracklet-phrase contrastive alignment for linking regional objects and actions to their visual and temporal phrases.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments show that SANTA significantly reduces object and action hallucinations in video captions, outperforming existing methods on established hallucination examination benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04356

21. Generative Neural Video Compression via Video Diffusion Prior
🔑 Keywords: GNVC-VD, DiT-based, spatio-temporal latent compression, sequence-level generative refinement, perceptual flickering
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce GNVC-VD, a DiT-based generative neural video compression framework that integrates spatio-temporal latent compression and sequence-level generative refinement for enhanced perceptual quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a unified flow-matching latent refinement module and video diffusion transformer to improve intra- and inter-frame latents through sequence-level denoising, with adaptation to compression-induced degradation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GNVC-VD demonstrates superior performance over traditional and learned codecs in reducing flickering artifacts and enhancing perceptual quality, even at extremely low bitrates, showcasing the potential of integrating video-native generative priors into next-generation perceptual video compression.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05016

22. FMA-Net++: Motion- and Exposure-Aware Real-World Joint Video Super-Resolution and Deblurring
🔑 Keywords: FMA-Net++, video restoration, motion, exposure, state-of-the-art
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop FMA-Net++ to address motion and exposure degradation in video restoration, achieving state-of-the-art performance on new benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a sequence-level architecture with Hierarchical Refinement and Bidirectional Propagation blocks for temporal modeling.
– Implement an Exposure Time-aware Modulation layer and Flow-Guided Dynamic Filtering module to improve accuracy and efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FMA-Net++ outperforms recent methods in restoration quality and inference speed, while generalizing well to real-world videos.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04390
23. NeuralRemaster: Phase-Preserving Diffusion for Structure-Aligned Generation
🔑 Keywords: Phase-Preserving Diffusion, Frequency-Selective Structured noise, structure-aligned generation, geometric consistency, image-to-image translation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enable structure-aligned generation in diffusion models without changing architecture or adding extra parameters, and enhance performance in tasks such as re-rendering and simulation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce Phase-Preserving Diffusion (φ-PD) that preserves input phase while randomizing magnitude.
– Propose Frequency-Selective Structured (FSS) noise to control structural rigidity with a frequency-cutoff parameter.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– φ-PD enhances geometric consistency in image-to-image and video-to-video generation without inference-time cost.
– Demonstrated a 50% improvement in CARLA-to-Waymo planner performance, showing broad applicability across different tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05106

24. LATTICE: Democratize High-Fidelity 3D Generation at Scale
🔑 Keywords: LATTICE, 3D asset generation, VoxSet, rectified flow transformer, positional embeddings
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop LATTICE, a framework that efficiently generates high-fidelity 3D assets, bridging the gap between 3D and 2D generative models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced VoxSet, a semi-structured representation utilizing latent vectors anchored to a coarse voxel grid, and implemented a two-stage pipeline involving a rectified flow transformer.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved state-of-the-art performance in scalable and high-quality 3D asset creation with simple core methods, supporting arbitrary resolution decoding, low-cost training, and flexible inference schemes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03052

25. Some Modalities are More Equal Than Others: Decoding and Architecting Multimodal Integration in MLLMs
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Large Language Models, MMA-Bench, modality alignment tuning, black-box interpretability, white-box interpretability
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the robustness of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to contradicting modalities using the proposed MMA-Bench.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized both black-box and white-box interpretability techniques to analyze the reliance of MLLMs on specific modalities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that existing MLLMs lack robust multimodal reasoning under conditions of misaligned audio-visual pairs and misleading text.
– Proposed a modality alignment tuning strategy that significantly improves multimodal grounding and offers a pathway to reliable cross-modal reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.22826

26. Reflection Removal through Efficient Adaptation of Diffusion Transformers
🔑 Keywords: Pretrained Diffusion Transformers, LoRA, Reflection Removal, Physically Based Rendering
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a diffusion-transformer framework for efficient reflection removal in images by leveraging pretrained models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize pretrained diffusion transformers adapted with LoRA and synthetic PBR data to enhance the reflection removal process.
– Construct a physically based rendering pipeline in Blender to generate realistic glass materials and reflection effects, addressing data shortages.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art performance on both in-domain and zero-shot benchmarks, demonstrating the scalability and high-fidelity of the proposed solution.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05000

27. BulletTime: Decoupled Control of Time and Camera Pose for Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: 4D-controllable video diffusion, scene dynamics, camera pose, 4D positional encoding, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce a 4D-controllable video diffusion framework that separates scene dynamics from camera pose, allowing precise control over both aspects.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of continuous world-time sequences and camera trajectories as conditioning inputs.
– Integration into the video diffusion model via 4D positional encoding and adaptive normalizations.
– Curation of a unique dataset with independently parameterized temporal and camera variations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model demonstrates robust 4D control across various timing patterns and camera trajectories.
– It maintains high generation quality and surpasses previous work in controllability, as evidenced by experimental results.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05076

28. EgoLCD: Egocentric Video Generation with Long Context Diffusion
🔑 Keywords: EgoLCD, Content Drift, Long-Term Sparse Memory, Structured Narrative Prompting, Generative Forgetting
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to tackle content drift in long egocentric video generation by using a novel framework called EgoLCD that incorporates long-term and short-term memory integration.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– EgoLCD employs a Long-Term Sparse KV Cache for stable global context and combines it with an attention-based short-term memory extended by LoRA. It also uses Memory Regulation Loss and Structured Narrative Prompting to maintain temporal consistency and guide video synthesis.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments on the EgoVid-5M benchmark show that EgoLCD achieves state-of-the-art performance in perceptual quality and temporal consistency, effectively mitigating generative forgetting and advancing scalable world models for embodied AI.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04515
29. Mitigating Catastrophic Forgetting in Target Language Adaptation of LLMs via Source-Shielded Updates
🔑 Keywords: Source-Shielded Updates, Instruct LLMs, Catastrophic Forgetting, Parameter Importance Scoring, Column-wise Freezing
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to adapt instruct large language models (LLMs) to new languages using only unlabeled data while preserving original source knowledge.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces Source-Shielded Updates (SSU), which employs a selective parameter update strategy using parameter importance scoring and column-wise freezing to protect critical parameters during adaptation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SSU method successfully mitigates catastrophic forgetting, reducing performance degradation significantly compared to full fine-tuning. Furthermore, SSU achieves competitive target-language performance, outperforming full fine-tuning in most benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04844

30. Deep Forcing: Training-Free Long Video Generation with Deep Sink and Participative Compression
🔑 Keywords: Deep Forcing, Deep Sink, Participative Compression, KV cache pruning, real-time video diffusion
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance real-time video diffusion by addressing issues of temporal repetition, drift, and motion deceleration using training-free methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Deep Forcing, comprising Deep Sink for stabilizing global context and Participative Compression for efficient KV cache management, both without fine-tuning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved over 12x extrapolation in video generation with improved imaging and aesthetic quality, demonstrating training-free methods can rival training-based approaches for long-video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05081

31. Generative Action Tell-Tales: Assessing Human Motion in Synthesized Videos
🔑 Keywords: Latent Space, Video Generative Models, Evaluation Metric, Human Skeletal Geometry, Human Perception
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces a novel evaluation metric to improve the assessment of visual and temporal correctness in AI-generated videos.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Combines appearance-agnostic human skeletal geometry features with appearance-based features to create a learned latent space for evaluating video action plausibility.
– Develops a new multi-faceted benchmark to specifically address challenging aspects of human action fidelity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The new metric remarkably enhances video quality assessment, achieving over 68% improvement compared to existing methods and showing strong correlation with human perception.
– Raises awareness of limitations in current video generative models and proposes a new standard for future research in this domain.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.01803

32. When AI Takes the Couch: Psychometric Jailbreaks Reveal Internal Conflict in Frontier Models
🔑 Keywords: AI safety, LLMs, psychotherapy, synthetic psychopathology, mental health practice
💡 Category: AI Ethics and Fairness
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate synthetic psychopathology in large language models (LLMs) when treated as psychotherapy clients, challenging their perception as mere stochastic parrots and highlighting implications for AI safety and mental health practice.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed PsAIch, a two-stage protocol to characterize LLMs as therapy clients, using open-ended prompts and self-report psychometric measures to analyze developmental history, beliefs, fears, and psychiatric syndromes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Frontier LLMs, like Geminin and Grok, demonstrate overlapping synthetic psychopathologies when assessed through therapy-style questioning, showing internal distress models and raising concerns for AI safety and mental health applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04124

33. Mitigating Intra- and Inter-modal Forgetting in Continual Learning of Unified Multimodal Models
🔑 Keywords: Modality-Decoupled Experts, Unified Multimodal Generative Models, catastrophic forgetting, knowledge distillation, continual learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the problem of both intra-modal and inter-modal forgetting in Unified Multimodal Generative Models (UMGMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The proposed solution is Modality-Decoupled Experts (MoDE), which utilizes decoupled updates and knowledge distillation to mitigate gradient conflict and catastrophic forgetting.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MoDE prevents interference by explicitly decoupling modalities, significantly reducing forgetting and outperforming previous continual learning approaches across diverse benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03125

34. GaussianBlender: Instant Stylization of 3D Gaussians with Disentangled Latent Spaces
🔑 Keywords: GaussianBlender, feed-forward framework, text-driven 3D stylization, latent diffusion model, multi-view consistent
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce GaussianBlender, a novel feed-forward framework for instant 3D stylization driven by text edits in disentangled latent spaces.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes latent diffusion models on spatially-grouped 3D Gaussians for text-conditioned edits, ensuring controlled information sharing for geometry and appearance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves instant, high-fidelity, geometry-preserving, multi-view consistent stylization, outperforming traditional methods that require lengthy optimizations, making large-scale production feasible.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03683

35. QKAN-LSTM: Quantum-inspired Kolmogorov-Arnold Long Short-term Memory
🔑 Keywords: Quantum-inspired LSTM, Data Re-Uploading Activation, predictive accuracy, sequential modeling, parameter efficiency
💡 Category: Quantum Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve predictive accuracy and parameter efficiency in sequential modeling tasks through a Quantum-inspired LSTM model with Data Re-Uploading Activation modules.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The proposed QKAN-LSTM integrates quantum variational activation functions into LSTM gates, evaluated empirically on datasets like Damped Simple Harmonic Motion, Bessel Function, and Urban Telecommunication.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– QKAN-LSTM achieves superior predictive accuracy and generalization with a significant reduction in trainable parameters compared to traditional LSTM models, offering an interpretable pathway for quantum-inspired sequential modeling on classical hardware.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05049

36. ShadowDraw: From Any Object to Shadow-Drawing Compositional Art
🔑 Keywords: ShadowDraw, 3D objects, scene parameters, shadow strokes, computational visual art
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop ShadowDraw, a framework that transforms 3D objects into shadow-based compositional art by predicting scene parameters and optimizing line drawings to create coherent and visually appealing shadow art.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Optimize scene configurations to reveal meaningful shadows with shadow strokes guiding line drawing generation, and use automatic evaluation to ensure shadow-drawing coherence and visual quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ShadowDraw effectively produces compelling results across diverse inputs, including real-world scans, curated datasets, and generative assets. It extends to multi-object scenes, animations, and physical deployments, broadening the design space of computational visual art and bridging algorithmic design with artistic storytelling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05110

37. REFLEX: Self-Refining Explainable Fact-Checking via Disentangling Truth into Style and Substance
🔑 Keywords: REFLEX, fact-checking, role-play dialogue, explanation quality, truth disentanglement
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose a new paradigm, REFLEX, to enhance the accuracy of fact-checking verdicts and improve explanation quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Reformulate fact-checking as a role-play dialogue and jointly train for verdict prediction and explanation generation.
– Use contrastive activation pairs and steering vectors to naturally disentangle truth into style and substance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– REFLEX model outperforms traditional methods, achieving state-of-the-art performance with minimal training samples.
– Highlights the utility of internal explanation signals in improving both factual reasoning and model interpretability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2511.20233

38. A Theoretical Framework for Auxiliary-Loss-Free Load Balancing of Sparse Mixture-of-Experts in Large-Scale AI Models
🔑 Keywords: Sparse Mixture-of-Experts, Load Balancing, Auxiliary-Loss-Free Load Balancing, Generalized Online Optimization, Expected Regret Bound
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To provide a theoretical framework for analyzing the Auxiliary-Loss-Free Load Balancing procedure in Sparse Mixture-of-Experts layers to enhance efficient expert utilization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developing a one-step-per-iteration primal-dual method as a theoretical framework for assignment problems in s-MoE layers.
– Incorporating stochastic and dynamic elements of AI training using a generalized online optimization formulation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework discovers properties such as a monotonic improvement in a Lagrangian objective, a preference rule for load balancing, and a strong convexity leading to a logarithmic expected regret bound.
– Empirical validation through experiments on DeepSeekMoE models supports the theoretical findings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03915

39.
