AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251209
1. Native Parallel Reasoner: Reasoning in Parallelism via Self-Distilled Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: NPR, Large Language Models, self-distilled training, Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization, genuine parallel reasoning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces NPR, a teacher-free framework that enhances Large Language Models (LLMs) with native parallel reasoning capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– NPR employs a self-distilled progressive training paradigm, Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization (PAPO) algorithm, and a robust NPR Engine to enable native parallel cognition without external supervision.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Trained on Qwen3-4B, NPR achieves performance gains of up to 24.5% and inference speedups up to 4.6x, setting a new standard for efficient and scalable agentic reasoning with 100% genuine parallel execution.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07461

2. Beyond Real: Imaginary Extension of Rotary Position Embeddings for Long-Context LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Rotary Position Embeddings, Large Language Models, complex-valued dot product, long-context dependencies, positional information
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance Rotary Position Embeddings by integrating both real and imaginary components of the complex-valued dot product to improve long-context modeling in Large Language Models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves re-incorporating the imaginary component into the attention score, utilizing the full complex-valued representation to create a dual-component attention score.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach enhances long-context dependency modeling by preserving more positional information, and empirical evaluations demonstrate improved performance over standard RoPE, especially as context length increases.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07525

3. Unified Video Editing with Temporal Reasoner
🔑 Keywords: VideoCoF, Chain-of-Frames, reasoning tokens, instruction-to-region alignment, fine-grained video editing
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim is to enhance video editing precision and instruction-to-region mapping without user-provided masks by implementing a novel Chain-of-Frames approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes reasoning tokens to enforce a “see, reason, then edit” procedure, leveraging a video diffusion model to facilitate high precision in video editing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VideoCoF achieves state-of-the-art performance with minimal data costs, demonstrating efficiency and effectiveness in fine-grained video editing and motion alignment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07469
4. Voxify3D: Pixel Art Meets Volumetric Rendering
🔑 Keywords: Voxel Art, 3D Mesh Optimization, Pixel Art Supervision, Semantic Preservation, Gumbel-Softmax Quantization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop a framework, Voxify3D, to address the challenges of generating high-quality voxel art by combining 3D mesh optimization with 2D pixel art supervision.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces a differentiable two-stage framework that integrates orthographic pixel art supervision, patch-based CLIP alignment, and palette-constrained Gumbel-Softmax quantization to achieve semantic preservation and aesthetic coherence in voxel art.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Voxify3D demonstrates superior performance in generating voxel art with semantic preservation and discrete color coherence, achieving high user preference and performance scores across diverse characters and resolutions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07834
5. Scaling Zero-Shot Reference-to-Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: Reference-to-video generation, scalable zero-shot framework, identity-consistent representations, masked training strategy, OpenS2V-Eval benchmark
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Saber, a scalable zero-shot framework for generating videos from textual prompts without explicit reference data, maintaining subject identity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed masked training strategy and attention-based model design using video-text pairs, integrated mask augmentation to reduce copy-paste artifacts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Saber showcases superior generalization and outperforming existing models on the OpenS2V-Eval benchmark, establishing it as a robust solution in reference-to-video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06905

6. DoVer: Intervention-Driven Auto Debugging for LLM Multi-Agent Systems
🔑 Keywords: LLM-based multi-agent systems, intervention-driven debugging, DoVer, targeted interventions, failure hypotheses
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim is to enhance reliability in LLM-based multi-agent systems by actively validating failure hypotheses and measuring task progress through targeted interventions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of DoVer, an intervention-driven debugging framework, which augments hypothesis generation with active verification through targeted interventions, such as editing messages and altering plans.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DoVer successfully converts a significant percentage of failed trials into successes and achieves measurable progress in task success. It validates or refutes a high percentage of failure hypotheses, highlighting intervention as a practical mechanism for improving reliability in agentic systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06749

7. EgoEdit: Dataset, Real-Time Streaming Model, and Benchmark for Egocentric Video Editing
🔑 Keywords: EgoEdit, egocentric video editing, instruction-following, real-time streaming inference, EgoEditData
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a real-time, instruction-following egocentric video editor that effectively handles egomotion and hand-object interactions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Construction of EgoEditData, a specialized dataset for egocentric video editing with rich hand-object interactions.
– Development of EgoEdit, a real-time egocentric video editor operating on a single GPU.
– Introduction of EgoEditBench, an evaluation suite focusing on instruction faithfulness, hand and interaction preservation, and temporal stability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EgoEdit achieves notable improvements on egocentric editing benchmarks and maintains strong performance on general editing tasks.
– EgoEdit and its associated datasets and evaluation tools will be accessible for the research community.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06065
8. Distribution Matching Variational AutoEncoder
🔑 Keywords: DMVAE, latent distribution, distribution-level alignment, SSL-derived distributions, image synthesis fidelity
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve modeling efficiency and image synthesis fidelity by explicitly aligning the encoder’s latent distribution with a reference distribution in variational autoencoders (VAEs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of Distribution-Matching VAE (DMVAE) to explicitly align the encoder’s latent distribution using a distribution matching constraint, allowing exploration of optimal latent distributions beyond conventional Gaussian priors.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SSL-derived distributions provide an excellent balance between reconstruction fidelity and modeling efficiency, achieving a gFID of 3.2 on ImageNet with only 64 training epochs, highlighting the importance of choosing suitable latent distribution structures.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07778

9. Relational Visual Similarity
🔑 Keywords: Relational Similarity, Vision-Language Model, Image-Caption Dataset, Representation Space
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to capture relational similarity between images, moving beyond traditional visual similarity metrics that focus on perceptual attribute similarity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Formulation of relational image similarity as a problem where internal relations or functions among visual elements correspond.
– Curation of a 114k image-caption dataset with anonymized captions to describe relational logic.
– Fine-tuning of a Vision-Language model on this dataset to measure relational similarity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Existing visual similarity models fail to capture relational similarity, a critical gap that can have many real-world applications.
– The study introduces a new direction in connecting images by their underlying relational structure rather than visible appearance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07833
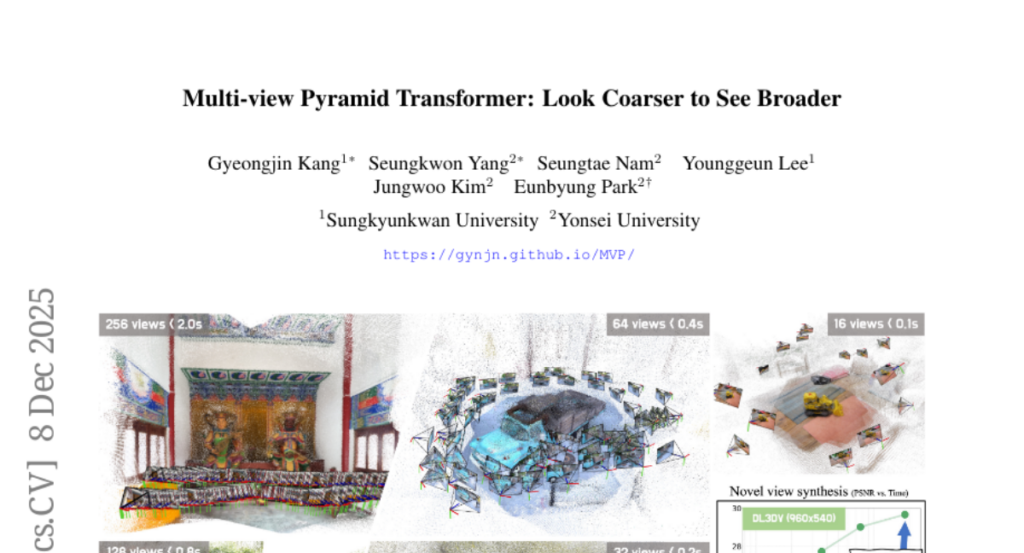
10. Multi-view Pyramid Transformer: Look Coarser to See Broader
🔑 Keywords: MVP, Multi-view Pyramid Transformer, 3D scenes, dual hierarchies, scalability
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop Multi-view Pyramid Transformer (MVP), a scalable architecture for reconstructing large 3D scenes from multiple images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The MVP uses a dual hierarchy structure: a local-to-global inter-view hierarchy for perspective broadening and a fine-to-coarse intra-view hierarchy for compact representation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MVP, when combined with 3D Gaussian Splatting, achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction quality, demonstrating high efficiency and scalability across diverse datasets and various view configurations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07806
11. UnityVideo: Unified Multi-Modal Multi-Task Learning for Enhancing World-Aware Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: UnityVideo, Multi-Modal Learning, video generation, zero-shot generalization, modality switcher
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective of the research is to improve the quality and alignment of AI-generated videos with real-world constraints by integrating multiple modalities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces a unified framework called UnityVideo which incorporates multiple modalities such as segmentation masks, human skeletons, DensePose, optical flow, and depth maps. It employs dynamic noising and a modality switcher with an in-context learner to achieve joint learning and processing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UnityVideo demonstrates superior video quality, consistency, and a better alignment with physical world constraints. It also enhances convergence speed and zero-shot generalization to unseen data, using a new large-scale unified dataset with 1.3 million samples.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07831

12. LongCat-Image Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: LongCat-Image, image generation, multilingual text rendering, photorealism, open-source ecosystem
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce LongCat-Image, a bilingual Chinese-English open-source foundation model for image generation addressing issues in multilingual text rendering, photorealism, deployment efficiency, and accessibility for developers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes rigorous data curation strategies and coordinated use of curated reward models during the RL phase to establish a new state-of-the-art standard.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LongCat-Image excels in text-rendering and photorealism, specifically in rendering complex Chinese characters. It offers a compact design with superior efficiency, resulting in minimal VRAM usage and rapid inference. The comprehensive open-source ecosystem established supports text-to-image and image editing capabilities, enhancing developer and researcher activities in visual content creation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07584

13. On the Interplay of Pre-Training, Mid-Training, and RL on Reasoning Language Models
🔑 Keywords: reinforcement learning, language models, pre-training, reasoning improvements, extrapolative generalization
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a controlled experimental framework to isolate and evaluate the contributions of pre-training, mid-training, and reinforcement learning in enhancing language model reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study uses synthetic reasoning tasks with explicit atomic operations, parseable step-by-step reasoning traces, and systematic manipulation of training distributions to analyze models’ generalization capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Reinforcement learning (RL) produces capability gains when pre-training provides sufficient headroom.
– Mid-training significantly enhances performance compared to using just RL.
– Contextual generalization requires minimal pre-training, after which RL can transfer effectively.
– Process-level rewards reduce reward hacking and enhance reasoning fidelity.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07783

14. ReCamDriving: LiDAR-Free Camera-Controlled Novel Trajectory Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: ReCamDriving, 3DGS renderings, two-stage training, camera controllability, ParaDrive dataset
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose ReCamDriving, a purely vision-based, camera-controlled video generation framework using novel-trajectory videos.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a two-stage training approach with dense 3DGS renderings for explicit geometric guidance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art results in camera controllability and structural consistency with the ParaDrive dataset.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03621

15. SPARK: Stepwise Process-Aware Rewards for Reference-Free Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: SPARK, Process reward models, Reinforcement Learning, Generative Models, Reference-free RL training
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a three-stage framework, SPARK, for creating synthetic training data that enables reference-free reinforcement learning superior to ground-truth methods in mathematical reasoning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a generator and verifier model framework to produce and evaluate synthetic training data.
– Application of parallel and sequential scaling techniques to enhance data quality.
– Implementation of chain-of-thought verification in training to improve mathematical reasoning accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SPARK enables the creation of process reward models that surpass ground-truth methods in mathematical reasoning, achieving higher accuracy on benchmarks.
– The framework enhances reference-free RL training, outperforming ground-truth-based RLVR, and opens new possibilities for domains lacking verifiable answers.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03244

16. VG-Refiner: Towards Tool-Refined Referring Grounded Reasoning via Agentic Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Tool-integrated visual reasoning, VG-Refiner, think-rethink mechanism, refinement reward, referring and grounding tasks
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The VG-Refiner framework is developed to manage unreliable tool outputs and enhance accuracy in referring and grounding tasks within tool-integrated visual reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A two-stage think-rethink mechanism is introduced to assess and respond to tool feedback, supplemented by a refinement reward to correct tool result inaccuracies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VG-Refiner improves accuracy and correction abilities using task-specific data, demonstrating significant advancements on referring and reasoning grounding benchmarks while maintaining the pretrained model’s general capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06373

17. Beyond Token-level Supervision: Unlocking the Potential of Decoding-based Regression via Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Decoding-based regression, Sequence-level rewards, Predictive precision, Sampling efficiency
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance decoding-based regression methods by employing Reinforcement Learning to address misalignments between token and sequence-level objectives, ultimately improving predictive precision and generalization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves formulating the generation process as a Markov Decision Process, utilizing sequence-level rewards to enforce global numerical coherence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art token-level baselines and traditional regression heads, highlighting the benefits of sequence-level signals in improving sampling efficiency and predictive precision.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06533

18. OmniSafeBench-MM: A Unified Benchmark and Toolbox for Multimodal Jailbreak Attack-Defense Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: OmniSafeBench-MM, multi-modal jailbreak attacks, safety alignment, defense strategies, AI Native
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce OmniSafeBench-MM, a comprehensive tool for evaluating multi-modal jailbreak attacks and defenses, providing a standardized foundation for future research.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of 13 attack methods, 15 defense strategies, and data spanning 9 risk domains and 50 categories.
– Establishment of a three-dimensional evaluation protocol assessing harmfulness, intent alignment, and response detail level.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OmniSafeBench-MM reveals the vulnerability of MLLMs to multi-modal jailbreaks and offers an open-source, reproducible platform for research enhancement.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06589

19. Decouple to Generalize: Context-First Self-Evolving Learning for Data-Scarce Vision-Language Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: dual-decoupling framework, vision-language models, reinforcement learning, synthetic data, curriculum learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance vision-language models by separating context learning from problem solving, improving reward signals and data diversity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of DoGe, a dual-decoupling framework, which decouples the learning process into two components, Thinker and Solver, and employs a two-stage RL post-training approach.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach consistently outperforms the baseline across various benchmarks, offering a scalable pathway for realizing self-evolving large vision-language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06835

20. Group Representational Position Encoding
🔑 Keywords: GRAPE, positional encoding, multiplicative rotations, additive logit biases, RoPE, ALiBi
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce GRAPE, a unified framework for positional encoding in long-context AI models, integrating multiplicative rotations and additive logit biases.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized group actions to form two positional encoding mechanisms: Multiplicative GRAPE based on SO(d) with skew generators, and Additive GRAPE using low-rank unipotent actions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GRAPE provides a comprehensive design space for positional geometry, extending and encompassing methods like RoPE and ALiBi, and is applicable in long-context models with efficient computational cost.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07805

21. Rethinking Training Dynamics in Scale-wise Autoregressive Generation
🔑 Keywords: Self-Autoregressive Refinement, exposure bias, Stagger-Scale Rollout, Contrastive Student-Forcing Loss, autoregressive models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve the quality of autoregressive generative models by addressing exposure bias through novel techniques.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of Self-Autoregressive Refinement (SAR) which includes Stagger-Scale Rollout for aligning train-test patterns and Contrastive Student-Forcing Loss for stable training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SAR, when applied to pretrained autoregressive models, enhances generation quality consistently with minimal additional computational effort, as demonstrated by a significant reduction in FID scores.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06421

22. VideoVLA: Video Generators Can Be Generalizable Robot Manipulators
🔑 Keywords: VideoVLA, Generalization, Robotic Manipulation, Multi-modal Diffusion Transformer
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop VideoVLA, a model that predicts actions and visual outcomes from language and image inputs, enabling advanced generalization in robotic manipulation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a multi-modal Diffusion Transformer to model video, language, and action modalities; leveraging pre-trained video generative models for visual and action forecasting.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VideoVLA shows promise in improving generalization in robotic tasks by predicting action sequences and visual outcomes, emphasizing the significance of visual imagination in task success and versatility.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06963
23. One Layer Is Enough: Adapting Pretrained Visual Encoders for Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: FAE, Feature Auto-Encoder, pre-trained visual representations, generative models, image generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introducing FAE, a framework that adapts pre-trained visual representations into low-dimensional latents to enhance image generation by utilizing dual decoders.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Leveraging a feature auto-encoder system with two deep decoders, integrated with self-supervised encoders, and applicable to diffusion models and normalizing flows.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FAE shows strong performance in class-conditional and text-to-image benchmarks with near state-of-the-art FID scores, demonstrating both high quality and fast learning capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07829

24. DZ-TDPO: Non-Destructive Temporal Alignment for Mutable State Tracking in Long-Context Dialogue
🔑 Keywords: DZ-TDPO framework, dynamic KL constraints, temporal attention bias, zero-shot generalization, Capacity-Stability Trade-off
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance long-context dialogue systems by resolving user intent conflicts using the DZ-TDPO framework that combines dynamic KL constraints with temporal attention bias.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a non-destructive alignment framework using conflict-aware dynamic KL constraints and calibrated temporal attention bias, and evaluated on the Multi-Session Chat dataset.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DZ-TDPO achieves state-of-the-art win rates and robust zero-shot generalization, demonstrating a trade-off between model capacity and stability. Larger models show better performance with minimal perplexity, confirming that precise attention regulation can address State Inertia without weight updates.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.03704

25. Vector Quantization using Gaussian Variational Autoencoder
🔑 Keywords: Gaussian VAE, VQ-VAE, Gaussian Quant, Codebook, Target Divergence Constraint
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper proposes Gaussian Quant (GQ), a method to convert Gaussian VAE into a VQ-VAE without retraining, introducing improvements over previous models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– GQ generates Gaussian noise as a codebook and identifies the nearest noise to the posterior mean, with a target divergence constraint (TDC) to optimize Gaussian VAE training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Gaussian Quant outperforms existing VQ-VAEs and Gaussian VAE discretization techniques across different architectures such as UNet and ViT, with source code available for implementation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06609

26. Small-Gain Nash: Certified Contraction to Nash Equilibria in Differentiable Games
🔑 Keywords: SGN condition, gradient-based learning, Euclidean geometry, pseudo-gradient, convergence
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To provide a framework using the Small-Gain Nash (SGN) condition for certifying convergence of gradient-based learning in games, especially when traditional Euclidean geometry conditions fail.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a block-weighted geometry and SGN condition to handle local curvature and cross-player Lipschitz coupling, converting these into a tractable certificate of contraction.
– Validation through quadratic games and extension to mirror/Fisher geometries for Markov games.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SGN offers a robust offline certification pipeline, validating convergence where Euclidean monotonicity fails, and provides a structural, computable certificate that includes metrics like contraction rate and safe step-sizes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06791

27. The SAM2-to-SAM3 Gap in the Segment Anything Model Family: Why Prompt-Based Expertise Fails in Concept-Driven Image Segmentation
🔑 Keywords: SAM2, SAM3, Multimodal Concept-Driven, Prompt-Based Segmentation, Unified Vision-Language Architecture
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the fundamental differences between SAM2 and SAM3 in segmentation capabilities and underlying architectures.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study is structured around five core components: conceptual differences, architectural divergence, dataset and annotation contrasts, training distinctions, and evaluation metrics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SAM3 emerges as a new class of segmentation model, based on a unified vision-language architecture, marking a shift toward a concept-driven segmentation paradigm that integrates open-vocabulary reasoning and semantic grounding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06032

28. Embodied Referring Expression Comprehension in Human-Robot Interaction
🔑 Keywords: Large-scale dataset, Multimodal model, Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), Refer360, MuRes
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve robots’ understanding of embodied human instructions for more intuitive Human-Robot Interaction by addressing perspective bias and enhancing multimodal signal integration.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the Refer360 dataset for diverse viewpoint collection of embodied interactions.
– Development of MuRes, a multimodal guided residual module, to enhance comprehension by extracting salient modality-specific signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MuRes augmentation significantly enhances the performance of multimodal models in capturing embodied interactions.
– Refer360 serves as a valuable benchmark demonstrating the efficacy of guided residual learning in advancing robots’ comprehension of human interactions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06558

29.
