AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251210

1. Wan-Move: Motion-controllable Video Generation via Latent Trajectory Guidance
🔑 Keywords: Motion Control, Video Generative Models, Dense Point Trajectories, Latent Space, Motion Guidance
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Present Wan-Move framework to enhance motion control in video generative models for high-quality and scalable video synthesis.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integrate motion-aware features into latent space by representing object motions with dense point trajectories, projecting them to produce a spatiotemporal feature map for improved motion accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Wan-Move outperforms existing models with precise motion control, validated by MoveBench experiments, and is available with open-source code and data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08765
2. Visionary: The World Model Carrier Built on WebGPU-Powered Gaussian Splatting Platform
🔑 Keywords: Visionary, Neural Rendering, 3D Gaussian Splatting, WebGPU, AI-generated
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Present Visionary, a web-native platform enabling real-time rendering of 3D Gaussian Splatting and meshes with efficient GPU-based inference.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize an efficient WebGPU renderer with per-frame ONNX inference for dynamic neural processing and a “click-to-run” browser experience.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Visionary achieves superior rendering efficiency, unifies inference and rendering in the browser, and lowers the barrier for reproduction, comparison, and deployment of 3D Gaussian Splatting-family methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08478
3. Preserving Source Video Realism: High-Fidelity Face Swapping for Cinematic Quality
🔑 Keywords: Video face swapping, AI-generated summary, Identity preservation, High-fidelity reconstruction
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance video face swapping by using keyframes and reference guidance to maintain identity and fidelity over long sequences.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs keyframes as conditioning signals coupled with video reference guidance, develops a paired face-swapping dataset named Face2Face, and reverses data pairs for reliable supervision.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method achieves state-of-the-art results in video face swapping, significantly reduces manual effort, and ensures seamless integration of the target identity with the source video’s expressions, lighting, and motion.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07951

4. OneStory: Coherent Multi-Shot Video Generation with Adaptive Memory
🔑 Keywords: Multi-shot video generation, Narrative coherence, Frame Selection module, Adaptive Conditioner, AI Native
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to overcome the limitations of existing multi-shot video generation by proposing OneStory, which models global cross-shot context to achieve coherent and scalable narrative generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced OneStory reformulating MSV as a next-shot generation task using autoregressive shot synthesis.
– Utilized a Frame Selection module and an Adaptive Conditioner to construct semantically relevant global memory and generate compact context.
– Curated a high-quality multi-shot dataset with referential captions, leveraging pretrained I2V models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OneStory achieves state-of-the-art narrative coherence across diverse scenes, enabling controllable and immersive long-form video storytelling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07802
5. ThreadWeaver: Adaptive Threading for Efficient Parallel Reasoning in Language Models
🔑 Keywords: ThreadWeaver, adaptive parallel reasoning, parallel trajectory generator, trie-based training-inference co-design, parallelization-aware reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces ThreadWeaver, a framework designed to achieve high accuracy in adaptive parallel reasoning while significantly reducing inference latency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a two-stage parallel trajectory generator for high-quality data with parallel annotations.
– Implements a trie-based training-inference co-design to enable parallel reasoning on standard autoregressive inference engines.
– Incorporates parallelization-aware reinforcement learning to balance accuracy and parallelization efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ThreadWeaver achieves accuracy comparable to sequential models while providing up to 1.53x speedup in token latency across challenging mathematical reasoning benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07843

6. Arbitrage: Efficient Reasoning via Advantage-Aware Speculation
🔑 Keywords: Arbitrage, Speculative Decoding, AI-generated summary, inference latency, step-level semantic verification
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve the efficiency of large language model inference by introducing Arbitrage, a dynamic routing framework, to optimize speculative decoding processes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework employs a lightweight router trained to predict when a target model would provide a better step in speculative generation, approximating an ideal Arbitrage Oracle for optimal efficiency-accuracy trade-offs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Arbitrage consistently outperforms traditional step-level Speculative Decoding systems, achieving significant reductions in inference latency while maintaining accuracy across multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05033

7. Boosting Unsupervised Video Instance Segmentation with Automatic Quality-Guided Self-Training
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, Video Instance Segmentation, unsupervised methods, quality-guided self-training, synthetic-to-real domain gap
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the challenges of Video Instance Segmentation (VIS) by bridging the synthetic-to-real domain gap using quality-guided self-training in an unsupervised framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– AutoQ-VIS is presented as a novel unsupervised framework that utilizes a closed-loop system for pseudo-label generation and automatic quality assessment, enabling progressive adaptation from synthetic videos to real videos.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance, achieving a 52.6 AP_{50} on the YouTubeVIS-2019 validation set, surpassing previous methods by 4.4% without requiring human annotations, showcasing the effectiveness of quality-aware self-training for unsupervised VIS.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06864

8. MIND-V: Hierarchical Video Generation for Long-Horizon Robotic Manipulation with RL-based Physical Alignment
🔑 Keywords: Semantic Reasoning, Domain-Invariant Representations, Physical Plausibility, AI Native, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective of this research is to develop MIND-V, a hierarchical framework capable of generating long-horizon robotic manipulation videos that are both physically plausible and logically coherent.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MIND-V integrates three core components inspired by cognitive science: a Semantic Reasoning Hub, a Behavioral Semantic Bridge, and a Motor Video Generator. It employs a test-time optimization strategy called Staged Visual Future Rollouts and a GRPO reinforcement learning post-training phase guided by a Physical Foresight Coherence reward.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MIND-V demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in generating long-horizon robotic manipulation videos, offering a scalable and controllable paradigm for embodied data synthesis, aligning generated videos with physical laws through an innovative reinforcement learning approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06628

9. See, Hear, and Understand: Benchmarking Audiovisual Human Speech Understanding in Multimodal Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: AV-SpeakerBench, Multimodal Large Language Models, Speaker-centric, Audiovisual Reasoning, Audiovisual Fusion
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce AV-SpeakerBench, a benchmark for evaluating speaker-centric audiovisual reasoning in videos to enhance audiovisual fusion in multimodal large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Created a benchmark with 3,212 multiple-choice questions focusing on speaker-centric audiovisual reasoning. It employs a speaker-centered formulation, fusion-grounded question design, and expert-curated annotations for accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Comprehensive evaluations reveal that the Gemini family outperforms open-source systems. Specifically, Gemini 2.5 Pro achieved the best results, with the significance attributed to advanced audiovisual fusion capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.02231

10. DeepCode: Open Agentic Coding
🔑 Keywords: DeepCode, document-to-codebase synthesis, information overload, autonomous scientific reproduction, retrieval-augmented generation
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address challenges in document-to-codebase synthesis with an autonomous framework, DeepCode, which optimizes information flow for superior performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– DeepCode implements channel optimization through operations like blueprint distillation, stateful code memory, retrieval-augmented generation, and closed-loop error correction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DeepCode achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming leading coding agents and surpassing human experts in key metrics, thus setting new standards for autonomous scientific reproduction.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07921
11. TreeGRPO: Tree-Advantage GRPO for Online RL Post-Training of Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: TreeGRPO, Reinforcement learning, training efficiency, denoising process, generative models
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance training efficiency for generative models by introducing TreeGRPO, which recasts the denoising process as a search tree.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a tree-structured approach to improve sample efficiency, perform fine-grained credit assignment, and enable amortized computation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TreeGRPO achieves 2.4 times faster training and establishes a superior Pareto frontier in efficiency-reward trade-off, outperforming GRPO baselines across various benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08153

12. From Next-Token to Next-Block: A Principled Adaptation Path for Diffusion LLMs
🔑 Keywords: autoregressive models, block-wise diffusion, parallel generation, NBDiff-7B, train-inference consistency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to adapt autoregressive models to block-wise diffusion to enable parallel generation while retaining pretrained knowledge, thus achieving superior performance in 7B-class diffusion language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a context-causal attention mask, an efficient parallel adaptation procedure, an auxiliary AR loss, and gradually increases the generation block size to ensure seamless integration with masked block-diffusion.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The adaptation from AR to block-diffusion showcases an effective and compute-efficient strategy alternative to training from scratch, exhibiting remarkable gains in general-knowledge, math, and code benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06776

13. Ground Slow, Move Fast: A Dual-System Foundation Model for Generalizable Vision-and-Language Navigation
🔑 Keywords: DualVLN, Vision-Language Navigation, Dual-System, Global Planner, Real-Time Control
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve vision-language navigation in dynamic environments by integrating high-level reasoning and low-level action execution.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of DualVLN, a dual-system model integrating a VLM-based global planner (System 2) and a multi-modal conditioning Diffusion Transformer policy (System 1).
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DualVLN achieves robust real-time control and long-horizon planning, outperforming prior methods in benchmarks and real-world tests by providing adaptive local decision-making in complex environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08186
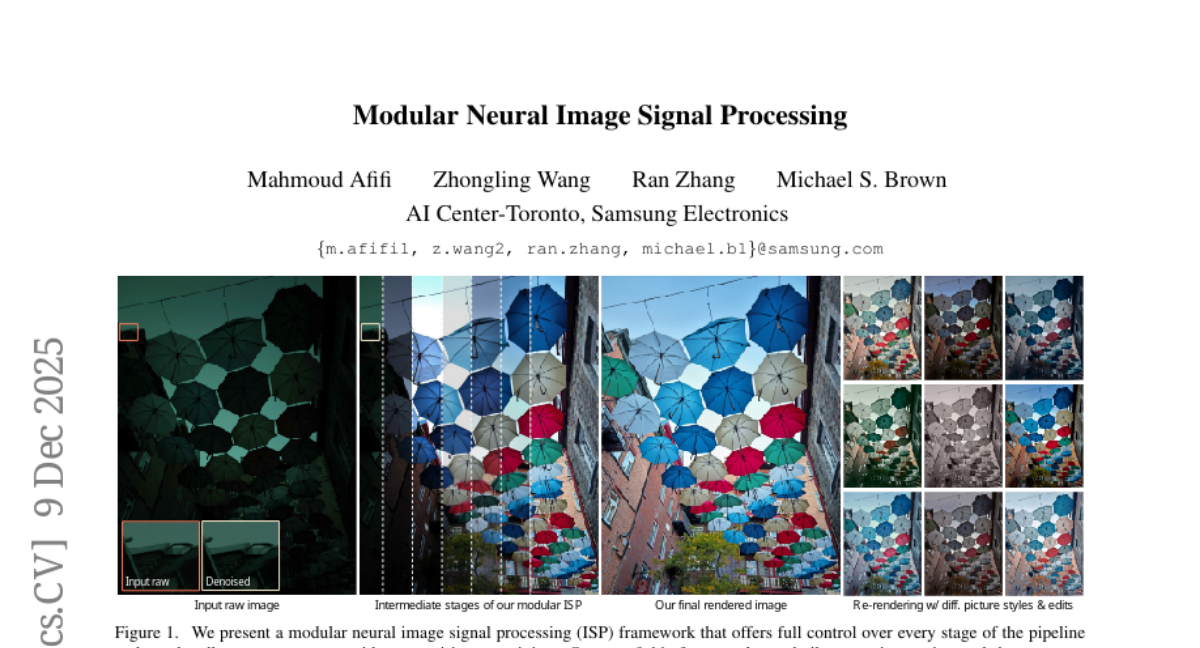
14. Modular Neural Image Signal Processing
🔑 Keywords: modular neural ISP, rendering accuracy, scalability, photo-editing tool, neural ISP
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce a modular neural ISP framework that enhances rendering accuracy, scalability, and flexibility for photo-editing operations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a user-interactive photo-editing tool utilizing the proposed modular framework, supporting diverse editing operations and styles.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework consistently delivers competitive results across multiple test sets, allowing high-quality rendering and unlimited post-editable re-rendering.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08564
15. Efficiently Reconstructing Dynamic Scenes One D4RT at a Time
🔑 Keywords: D4RT, Unified Transformer Architecture, 4D Reconstruction, Querying Mechanism, Computer Vision
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To efficiently reconstruct 4D scenes from video data using a unified transformer-based model.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a novel querying mechanism and a unified transformer architecture to infer depth, spatio-temporal correspondence, and full camera parameters without dense, per-frame decoding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed model, D4RT, sets a new standard in 4D reconstruction tasks, outperforming existing methods with its scalable and lightweight design.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08924

16. LYNX: Learning Dynamic Exits for Confidence-Controlled Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: LYNX, early-exit mechanism, hidden-state awareness, confidence-controlled stopping, reasoning cues
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research seeks to improve efficiency and accuracy in large reasoning models by implementing an early-exit mechanism named LYNX, which uses hidden-state awareness and confidence-controlled stopping decisions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– LYNX attaches exit decisions to naturally occurring reasoning cues during the model’s generation process. A lightweight probe is trained on hidden states with supervision from forced exits, and scores are wrapped in split conformal prediction for distribution-free control over premature exits.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The LYNX mechanism yields strong accuracy-efficiency tradeoffs across multiple benchmark datasets, achieving baseline or improved accuracy with substantial token savings. Compared to other early-exit methods, LYNX provides competitive or superior Pareto frontiers without additional inference proxies and allows user-tunable confidence guarantees.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.05325

17. Novel Deep Learning Architectures for Classification and Segmentation of Brain Tumors from MRI Images
🔑 Keywords: Brain tumor detection, AI in Healthcare, Deep Learning architectures, SAETCN, SAS-Net
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to accurately classify and segment brain tumors from MRI scans using novel AI-based architectures.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development and implementation of two deep learning models: SAETCN for tumor classification with 99.38% accuracy, and SAS-Net for tumor segmentation achieving 99.23% pixel accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed architectures demonstrate high accuracy, indicating their potential effectiveness in aiding early detection and improvement of treatment outcomes for brain tumors.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.06531

18. TrackingWorld: World-centric Monocular 3D Tracking of Almost All Pixels
🔑 Keywords: Monocular 3D tracking, AI-generated summary, dense 3D tracking, world-centric 3D coordinate system, optimization-based framework
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose TrackingWorld, a new pipeline for dense 3D tracking of pixels in a world-centric coordinate system, addressing limitations in existing monocular 3D tracking methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a tracking upsampler to convert sparse 2D tracks into dense 2D tracks.
– Applied an optimization-based framework to project dense 2D tracks into world-centric 3D trajectories by estimating camera poses and 3D coordinates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TrackingWorld achieves accurate and dense 3D tracking in a world-centric coordinate frame, as demonstrated by evaluations on synthetic and real-world datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08358
19. EcomBench: Towards Holistic Evaluation of Foundation Agents in E-commerce
🔑 Keywords: EcomBench, AI Native, Deep Information Retrieval, Multi-step Reasoning, Cross-source Knowledge Integration
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop EcomBench, a benchmark for evaluating agent performance in real-world e-commerce environments by focusing on practical applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of genuine user demands and expert curation to create a holistic and dynamic testbed in the e-commerce domain.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EcomBench provides a rigorous benchmark for assessing agents on deep information retrieval, multi-step reasoning, and cross-source knowledge integration in realistic e-commerce contexts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08868

20. Predicting Time-Dependent Flow Over Complex Geometries Using Operator Networks
🔑 Keywords: Deep Operator Network, signed distance field, CNN, predictive modeling, unsteady flow
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop a geometry-aware Deep Operator Network capable of predicting velocity fields for unsteady flows, offering a speedup over traditional CFD simulations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model utilizes a signed distance field trunk for geometry encoding and a CNN branch for capturing flow history, trained on high-fidelity simulations of various shapes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Deep Operator Network achieves significant speedup and maintains accuracy in near-term transients, though challenges remain in handling error accumulation for sharp-cornered geometries. The study also discusses practical mitigations and provides open-access resources for reproducibility.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04434

21. MemLoRA: Distilling Expert Adapters for On-Device Memory Systems
🔑 Keywords: Memory Adapters, MemLoRA, Multimodal Contexts, AI Native, Small Language Models
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces MemLoRA and MemLoRA-V to enhance small language and vision-language models with memory adapters for efficient local deployment and improved multimodal capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing knowledge distillation principles to train specialized memory adapters for specific operations like knowledge extraction, memory update, and memory-augmented generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MemLoRA shows significant performance improvements in text-based tasks, outperforming much larger baseline models on the LoCoMo benchmark. MemLoRA-V demonstrates substantial improvements in visual understanding, particularly in Visual Question Answering tasks, showcasing strong performance in multimodal contexts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.04763

22. SUCCESS-GS: Survey of Compactness and Compression for Efficient Static and Dynamic Gaussian Splatting
🔑 Keywords: Gaussian Splatting, real-time, high-fidelity, computational demands, dynamic scenes
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The survey aims to provide a unified overview of efficient 3D and 4D Gaussian Splatting techniques focusing on memory and computational efficiency while maintaining reconstruction quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The techniques are categorized into Parameter Compression and Restructuring Compression, summarizing the core ideas and trends within these methodologies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The paper discusses current limitations and suggests promising research directions for scalable, compact, and real-time Gaussian Splatting for both static and dynamic 3D scene representation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07197

23. SAM-Body4D: Training-Free 4D Human Body Mesh Recovery from Videos
🔑 Keywords: Human Mesh Recovery, Temporal Consistency, SAM-Body4D, Occlusion Robustness, Parallel Strategy
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance 3D human mesh recovery from videos by addressing temporal consistency and robustness against occlusions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementing a training-free framework, SAM-Body4D, that utilizes masklet generation and an Occlusion-Aware module.
– Utilizing promptable video segmentation for identity-consistent masklets and refining them for occlusion handling.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SAM-Body4D effectively improves temporal stability and robustness in complex video scenarios without the need for retraining.
– The framework demonstrates efficient multi-human inference using a padding-based parallel strategy.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08406

24. Terrain Diffusion: A Diffusion-Based Successor to Perlin Noise in Infinite, Real-Time Terrain Generation
🔑 Keywords: Terrain Diffusion, diffusion models, procedural noise, InfiniteDiffusion, seamless infinite extent
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Terrain Diffusion, an innovative AI-driven successor to Perlin noise, aimed at generating realistic, seamless, procedural worlds using diffusion models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs a novel algorithm called InfiniteDiffusion for infinite landscape generation, along with a hierarchical stack of diffusion models to couple planetary context with local detail.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The integration of these components establishes diffusion models as a practical foundation for creating procedural worlds, capable of synthesizing entire planets in a coherent and controllable manner.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08309

25. Same Content, Different Answers: Cross-Modal Inconsistency in MLLMs
🔑 Keywords: cross-modal inconsistency, multimodal large language models, embedding space, consistency score, modality gap
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces two benchmarks, REST and REST+, to evaluate cross-modal inconsistency in multimodal large language models (MLLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study assesses 15 MLLMs by providing samples with semantic information across image, text, and mixed modalities, measuring performance under different visual characteristics and modality conditions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study reveals significant variability in modality inconsistency among MLLMs, influenced by factors like text colour and resolution, with neither rendering text as images nor vice versa providing a complete solution.
– The consistency score correlates with the modality gap between text and images, providing insights into MLLM inconsistency mechanisms.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.08923
26.
