AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251217

1. MMGR: Multi-Modal Generative Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: MMGR, generative reasoning, perceptual quality, causality, spatial planning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces MMGR as a new evaluation framework to assess the reasoning abilities of video and image generative models across multiple reasoning domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study uses MMGR to evaluate models based on five reasoning abilities: Physical, Logical, 3D Spatial, 2D Spatial, and Temporal, applying it to diverse domains such as Abstract Reasoning, Embodied Navigation, and Physical Commonsense.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Key limitations in current video and image models were identified, including an overreliance on perceptual data and weak global consistency. MMGR benchmarks highlight significant performance gaps, with models showing better performance on Physical Commonsense tasks, but struggling with Abstract Reasoning and long-horizon spatial planning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14691

2. Video Reality Test: Can AI-Generated ASMR Videos fool VLMs and Humans?
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated videos, ASMR, perceptual realism, audio-visual consistency, real-fake discrimination
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to evaluate the realism and detection capability of AI-generated ASMR videos, focusing on their ability to deceive both Visual Language Models (VLMs) and humans, highlighting challenges in perceptual fidelity and audio-visual consistency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a benchmark suite called Video Reality Test, leveraging ASMR-sourced video-audio content, and employed an adversarial creator-reviewer protocol in which video generation models are tested against VLM reviewers for their ability to identify fakeness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research finds that even top-performing models like Veo3.1-Fast can deceive most VLMs, with significant lower accuracy compared to human experts. Additional audio enhances real-fake discrimination, yet superficial cues can still mislead models, exposing limitations in current models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13281
3. WorldPlay: Towards Long-Term Geometric Consistency for Real-Time Interactive World Modeling
🔑 Keywords: WorldPlay, Dual Action Representation, Reconstituted Context Memory, Context Forcing
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop WorldPlay, a streaming video diffusion model that enables real-time, interactive world modeling with long-term geometric consistency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Dual Action Representation for robust action control.
– Utilized Reconstituted Context Memory for dynamic context rebuilding and temporal reframing to address memory attenuation.
– Developed Context Forcing, a novel distillation method for aligning memory contexts between teacher and student models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– WorldPlay generates 720p streaming video at 24 FPS with superior consistency and generalization across diverse scenes, outperforming existing techniques in long-term geometric consistency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14614
4. Scone: Bridging Composition and Distinction in Subject-Driven Image Generation via Unified Understanding-Generation Modeling
🔑 Keywords: Composition, Distinction, Semantic Alignment, Attention-based Masking, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to introduce Scone, a unified method for integrating composition and distinction in subject-driven image generation, addressing limitations in identifying and generating the correct subject in complex visual settings.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Scone uses a two-stage training scheme that first focuses on learning composition, and then enhances distinction through semantic alignment and attention-based masking. Additionally, SconeEval is introduced as a benchmark to evaluate both composition and distinction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments demonstrate that Scone surpasses existing open-source models in both composition and distinction tasks, using two benchmarks to validate its effectiveness. The model, benchmark, and training data are made available on GitHub.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12675

5. RoboTracer: Mastering Spatial Trace with Reasoning in Vision-Language Models for Robotics
🔑 Keywords: RoboTracer, 3D-aware VLM, TraceSpatial, universal spatial encoder, reinforcement fine-tuning
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop RoboTracer, a 3D-aware visual language model aimed at enhancing spatial tracing capabilities for robots by addressing challenges in multi-step metric-grounded reasoning and complex spatial referring.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a universal spatial encoder in combination with a regression-supervised decoder for enhanced scale awareness during supervised fine-tuning.
– Implementation of reinforcement fine-tuning with metric-sensitive process rewards to improve multi-step metric-grounded reasoning.
– Introduction of TraceSpatial, a large-scale dataset, and TraceSpatial-Bench as a benchmarking platform.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RoboTracer achieves state-of-the-art performance in spatial understanding, measuring, and referring, with a success rate of 79.1%.
– It significantly outperforms existing models, such as Gemini-2.5-Pro, on the TraceSpatial-Bench, with a 36% accuracy increase.
– The model’s versatility is highlighted by its integration capabilities with various control policies for executing dynamic tasks using different robot types across real-world scenes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13660
6. OpenDataArena: A Fair and Open Arena for Benchmarking Post-Training Dataset Value
🔑 Keywords: OpenDataArena, Large Language Models, Data-Centric AI, unified training-evaluation pipeline, multi-dimensional scoring framework
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To create OpenDataArena (ODA), an open platform that benchmarks post-training datasets for Large Language Models to enhance data understanding and reproducibility.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a unified training-evaluation pipeline, a multi-dimensional scoring framework, an interactive data lineage explorer, and open-source tools to conduct over 600 training runs and process 40 million data points.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Discovered trade-offs between data complexity and task performance, identified redundancy in benchmarks, and mapped genealogical relationships in datasets, promoting a shift to principled Data-Centric AI practices.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14051

7. Reveal Hidden Pitfalls and Navigate Next Generation of Vector Similarity Search from Task-Centric Views
🔑 Keywords: Vector Similarity Search, AI-Generated Summary, Information Loss Funnel, Embedding Loss, Metric Misuse
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate Vector Similarity Search methods in real-world contexts and identify key sources of performance degradation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A holistic benchmark suite named Iceberg is introduced, which involves eight diverse datasets and benchmarks 13 state-of-the-art VSS methods. The study focuses on performance metrics across practical applications.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Iceberg reveals the Information Loss Funnel with three main sources of performance degradation: Embedding Loss, Metric Misuse, and Data Distribution Sensitivity. It provides a task-centric evaluation, re-ranking traditional methods based on application-level metrics and offering practitioner guidance through a decision tree.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12980
8. Vector Prism: Animating Vector Graphics by Stratifying Semantic Structure
🔑 Keywords: SVG Animation, Vision-Language Models, Semantic Structure, Statistical Aggregation, Semantic Recovery
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a framework that aggregates weak predictions to recover the semantic structure needed for reliable SVG animation, improving the interactions between Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and vector graphics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize statistical aggregation of multiple weak part predictions to reorganize SVGs into semantic groups, allowing VLMs to produce animations with greater coherence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework significantly enhances the robustness of SVG animation and supports more interpretable interactions between VLMs and vector graphics by focusing on semantic recovery as a key step.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14336

9. ShowTable: Unlocking Creative Table Visualization with Collaborative Reflection and Refinement
🔑 Keywords: ShowTable, MLLMs, Diffusion Models, Creative Table Visualization, Multi-Modal Reasoning
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce and address the task of creative table visualization, requiring generation of infographics from data tables with high fidelity and aesthetic appeal.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop ShowTable, a pipeline combining MLLMs and diffusion models using a progressive self-correcting process.
– Implement three automated data construction pipelines to train different modules of the model.
– Create TableVisBench, a benchmark with 800 instances across 5 dimensions to evaluate performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ShowTable pipeline significantly outperforms existing baselines, demonstrating effective multi-modal reasoning, generation, and error correction capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13303

10. RecGPT-V2 Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Hierarchical Multi-Agent System, Hybrid Representation Inference, Meta-Prompting, constrained reinforcement learning, Agent-as-a-Judge
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance recommender systems by integrating multiple advanced AI techniques, addressing limitations in previous models like RecGPT-V1.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a Hierarchical Multi-Agent System for intent reasoning and cognitive efficiency.
– Utilization of Hybrid Representation Inference to reduce resource consumption and improve recall.
– Development of a Meta-Prompting framework for increased explanation diversity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RecGPT-V2 significantly improves system metrics like CTR, IPV, TV, and NER, confirming the technical feasibility and commercial viability of deploying large language models in recommendation systems on a large scale.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14503

11. MemFlow: Flowing Adaptive Memory for Consistent and Efficient Long Video Narratives
🔑 Keywords: MemFlow, memory bank, narrative coherence, historical frames, streaming video generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the challenge of maintaining content consistency in long-context streaming video generation by dynamically updating a memory bank.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementing a system, MemFlow, that retrieves the most relevant historical frames for each video chunk using a text prompt to ensure narrative coherence and efficient generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MemFlow achieves outstanding long-context consistency and generation efficiency with minimal computational burden, maintaining compatibility with any streaming video generation model with KV cache.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14699
12. Feedforward 3D Editing via Text-Steerable Image-to-3D
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated 3D assets, text steerability, ControlNet, flow-matching training, Direct Preference Optimization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Steer3D aims to enable text-based editing of AI-generated 3D assets to make them easily editable for real applications like design, AR/VR, and robotics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method includes adapting ControlNet for image-to-3D generation using flow-matching training and Direct Preference Optimization, allowing for text steerability directly in the forward pass.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Compared to other methods, Steer3D follows language instructions more accurately, maintains better consistency with the original 3D asset, and demonstrates significantly faster performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13678
13. Differentiable Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, AI-generated summary, Differentiable Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning, Meta-Optimizer, Reward Functions
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance agent performance across various domains by evolving reward functions in reinforcement learning through a bilevel differentiable approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces Differentiable Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning (DERL), a bilevel framework utilizing a Meta-Optimizer to evolve structured reward functions. This approach captures the causal relationship between reward structure and task performance, making it differentiable and capable of approximating the meta-gradient of task success.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DERL shows state-of-the-art performance in robotic (ALFWorld) and scientific simulation (ScienceWorld) domains, outperforming heuristic-based methods, especially in out-of-distribution scenarios. The study demonstrates that DERL successfully captures intricate task structures, facilitating self-improving agent alignment without human interference.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13399

14. Nemotron-Cascade: Scaling Cascaded Reinforcement Learning for General-Purpose Reasoning Models
🔑 Keywords: Cascade RL, Reinforcement Learning, General-Purpose Reasoning Models, AI-generated summary, Domain-wise RL
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop general-purpose reasoning models using Cascade RL, improving performance across multiple benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors propose a new method called Cascaded Domain-wise Reinforcement Learning, which simplifies engineering complexity and overcomes variability issues in traditional approaches, leveraging RLHF for better model alignment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research demonstrates that Cascade RL can significantly outperform teacher models, as shown in competitions and benchmarks like LiveCodeBench and the International Olympiad in Informatics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13607
15. Olmo 3
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, language models, long-context reasoning, knowledge recall, instruction following
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduction of Olmo 3, a fully-open language model family focused on enhancing capabilities in long-context reasoning and various applications like function calling, coding, and instruction following.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Comprehensive model development process including every stage, checkpoint, data point, and dependency to ensure transparency and reproducibility in creating these models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Olmo 3 Think 32B is highlighted as the most robust fully-open thinking model to date, excelling in areas such as general chat and knowledge recall.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13961
16. VersatileFFN: Achieving Parameter Efficiency in LLMs via Adaptive Wide-and-Deep Reuse
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, VersatileFFN, dual-process theory, memory efficiency, parameter reuse
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to introduce VersatileFFN, a novel feed-forward network designed to address memory costs while enhancing the architectural capacity of Large Language Models (LLMs) through efficient parameter reuse.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– VersatileFFN leverages two adaptive pathways: a width-versatile path mimicking sparse expert routing without additional parameters and a depth-versatile path applying recursive FFN for complex token processing. A difficulty-aware gating mechanism balances these pathways dynamically.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results across various benchmarks and model scales demonstrate that VersatileFFN effectively enhances model performance by utilizing computation instead of memory for capacity expansion. The approach offers a practical solution for memory-efficient model scaling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14531

17. SS4D: Native 4D Generative Model via Structured Spacetime Latents
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, 4D generative model, monocular video, temporal coherence, structural consistency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research focuses on synthesizing dynamic 3D objects from monocular video using a native 4D generative model, achieving high fidelity, temporal coherence, and structural consistency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach builds on pre-trained single-image-to-3D models to maintain spatial consistency and introduces temporal layers to ensure temporal coherence. It employs factorized 4D convolutions and temporal downsampling for efficient training on long video sequences.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method presents a robust and efficient technique for synthesizing 3D objects from video, overcoming challenges like data scarcity and occlusion through a carefully designed training strategy.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14284
18. A4-Agent: An Agentic Framework for Zero-Shot Affordance Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: A4-Agent, Affordance prediction, Zero-shot framework, Vision-language models, Generative models
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose A4-Agent, a training-free framework that decouples affordance prediction into three stages to enhance generalization and performance in real-world settings.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Coordinate specialized foundation models at test time through a three-stage pipeline involving Dreamer (using generative models), Thinker (utilizing large vision-language models), and Spotter (orchestrating vision foundation models).
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The zero-shot framework significantly outperforms state-of-the-art supervised methods across multiple benchmarks and demonstrates robust generalization to real-world environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14442

19. Sparse-LaViDa: Sparse Multimodal Discrete Diffusion Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Sparse-LaViDa, Masked Discrete Diffusion Models, inference speed, register tokens, attention mask
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Sparse-LaViDa aims to enhance the inference speed of Masked Discrete Diffusion Models by dynamically truncating unnecessary masked tokens while maintaining quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of Sparse-LaViDa, utilizing specialized register tokens for compact token representation and an attention mask that reflects the truncated process during training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Sparse-LaViDa achieves up to a 2x speedup in tasks like text-to-image generation, image editing, and mathematical reasoning, maintaining high generation quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14008
20. Spherical Leech Quantization for Visual Tokenization and Generation
🔑 Keywords: Lattice Coding, Non-parametric Quantization, Leech Lattice, Compression, Auto-regressive Image Generation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present a unified formulation of different non-parametric quantization methods using lattice coding, particularly focusing on improving image tokenization, compression, and generation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Explored various lattice structures, including random lattices, generalized Fibonacci lattices, and densest sphere packing lattices, identifying the Spherical Leech Quantization (Λ_{24}-SQ) for its benefits in symmetry and distribution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Spherical Leech Quantization method achieved superior reconstruction quality and efficiency over existing methods like BSQ, enhancing both image tokenization and auto-regressive image generation frameworks, while requiring fewer bits.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14697

21. Janus: Disaggregating Attention and Experts for Scalable MoE Inference
🔑 Keywords: Mixture-of-Experts, Janus, GPU sub-clusters, adaptive two-phase communication, lightweight scheduler
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address the scalability and resource inefficiency issues in Large Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model inference by proposing a novel inference system named Janus.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Janus disaggregates attention and expert modules onto separate GPU sub-clusters, allowing independent scaling.
– Utilizes an adaptive two-phase communication scheme for efficient data exchange.
– Employs a lightweight scheduler implemented as a GPU kernel to balance activated experts across GPUs with minimal overhead.
– Performs fine-grained resource management for dynamic expert placement and resource scaling.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Janus significantly enhances per-GPU throughput by up to 3.9 times compared to existing systems, while meeting per-token latency requirements, thus proving its efficiency and scalability over state-of-the-art methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13525

22. Efficient-DLM: From Autoregressive to Diffusion Language Models, and Beyond in Speed
🔑 Keywords: AR-to-dLM conversion, Diffusion language models, Attention patterns, Token masking, Continuous pretraining
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study investigates AR-to-dLM conversion to transform pretrained autoregressive models into efficient diffusion language models (dLMs) that enhance speed and maintain task accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Identified limitations in existing AR-to-dLM methods and proposed refined techniques such as continuous pretraining with block-wise attention patterns and position-dependent token masking strategies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed methods led to the Efficient-DLM family, which outperforms state-of-the-art autoregressive models and dLMs in both accuracy and throughput.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14067

23. Zoom-Zero: Reinforced Coarse-to-Fine Video Understanding via Temporal Zoom-in
🔑 Keywords: Zoom-Zero, temporal grounding, Group Relative Policy Optimization, visual verification
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance grounded video question answering by improving both temporal grounding and answer accuracy through a novel coarse-to-fine framework called Zoom-Zero.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a “zoom-in accuracy reward” for validating temporal grounding predictions and facilitating fine-grained visual verification.
– Implements “token-selective credit assignment” to attribute rewards to tokens responsible for temporal localization or answer generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Zoom-Zero framework improves temporal grounding by 5.2% on the NExT-GQA benchmark and 4.6% on the ReXTime benchmark, while enhancing average answer accuracy by 2.4%.
– Benefits long-form video understanding during inference with a 6.4% improvement on long-video benchmarks, preserving critical visual details without compromising global context.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14273

24. TAT: Task-Adaptive Transformer for All-in-One Medical Image Restoration
🔑 Keywords: Medical image restoration, Task-adaptive Transformer, Task interference, Task imbalance
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve medical image restoration by developing a task-adaptive Transformer framework that addresses task interference and imbalance to achieve state-of-the-art performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study proposes a novel framework with two key strategies: task-adaptive weight generation to eliminate potential gradient conflicts and task-adaptive loss balancing to adjust loss weights based on task-specific learning difficulties.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed TAT framework demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in PET synthesis, CT denoising, and MRI super-resolution, highlighting its effectiveness in both task-specific and All-in-One settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14550

25. EVOLVE-VLA: Test-Time Training from Environment Feedback for Vision-Language-Action Models
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action, test-time training, autonomous feedback, cross-task generalization, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop EVOLVE-VLA, a framework enabling Vision-Language-Action models to continuously adapt and improve through environmental interaction with minimal task-specific demonstrations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a learned progress estimator to provide dense feedback.
– Designed mechanisms such as accumulative progress estimation and progressive horizon extension to manage noisy signals during adaptation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EVOLVE-VLA achieved significant performance improvements and generalization, such as a +8.6% gain on long-horizon tasks and +22.0% in 1-shot learning, along with a 20.8% success rate on unseen tasks without task-specific demonstrations.
– Emerged capabilities include error recovery and development of novel strategies, showcasing its potential beyond static imitation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14666

26. CRISP: Contact-Guided Real2Sim from Monocular Video with Planar Scene Primitives
🔑 Keywords: CRISP, reinforcement learning, planar primitives, motion tracking, real-to-sim applications
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to recover simulatable human motion and scene geometry from monocular video, significantly enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of simulation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of planar primitive fitting and reinforcement learning to achieve clean and simulation-ready geometry and improved motion tracking.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The CRISP method dramatically reduces motion tracking failure rates and increases simulation throughput, showing promise for applications in robotics and AR/VR.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14696
27. RePo: Language Models with Context Re-Positioning
🔑 Keywords: RePo, In-context learning, Cognitive Load Theory, extraneous cognitive load, attention allocation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces RePo, a novel context re-positioning mechanism in LLMs aimed at reducing extraneous cognitive load and enhancing performance in noisy and long-context tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a differentiable module within RePo for assigning token positions based on contextual dependencies, trained continually on the OLMo-2 1B backbone.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RePo significantly boosts performance in tasks with noisy and longer contexts while maintaining efficiency in short-context tasks by allocating higher attention to relevant, distant information and capturing context structure in dense, non-linear spaces.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14391
28. UAGLNet: Uncertainty-Aggregated Global-Local Fusion Network with Cooperative CNN-Transformer for Building Extraction
🔑 Keywords: Building extraction, hybrid CNN, transformer layers, global-local feature integration, Uncertainty-Aggregated Decoder
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to tackle the challenges of building extraction from remote sensing images by enhancing the integration of global and local features using a new network architecture.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper introduces the Uncertainty-Aggregated Global-Local Fusion Network (UAGLNet), which integrates a hybrid CNN and transformer cooperative encoder, intermediate interaction block, and an Uncertainty-Aggregated Decoder to handle feature integration and segmentation ambiguity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in building extraction, with experiments highlighting the superior performance of UAGLNet in accurately interpreting remote sensing images.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12941

29. TraPO: A Semi-Supervised Reinforcement Learning Framework for Boosting LLM Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: semi-supervised reinforcement learning, verifiable rewards, AI-generated summary, TraPO, mathematical reasoning benchmarks
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research investigates a novel semi-supervised reinforcement learning approach that leverages a small labeled dataset to enhance training efficiency and accuracy on mathematical reasoning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study proposes an innovative policy optimization algorithm, TraPO, which identifies reliable unlabeled samples through learning trajectory similarity with labeled ones, improving training stability and efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TraPO demonstrated remarkable data efficiency and strong generalization on mathematical reasoning benchmarks and out-of-distribution tasks, achieving superior performance compared to both unsupervised methods with more data and fully supervised models with fewer labeled samples.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13106

30. Comparative Analysis of LLM Abliteration Methods: A Cross-Architecture Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: AI Safety, large language models, abliteration techniques, Bayesian-optimized abliteration, mathematical reasoning capabilities
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate the effectiveness of four abliteration tools in removing refusal representations from large language models while preserving capability and minimizing distribution shift.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluated four abliteration tools (Heretic, DECCP, ErisForge, FailSpy) across sixteen instruction-tuned models using quantitative metrics and model compatibility assessments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Single-pass methods showed superior capability preservation on benchmarked models.
– Bayesian-optimized abliteration created variable distribution shifts with model-dependent impacts.
– Mathematical reasoning capabilities exhibit the highest sensitivity to abliteration interventions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13655

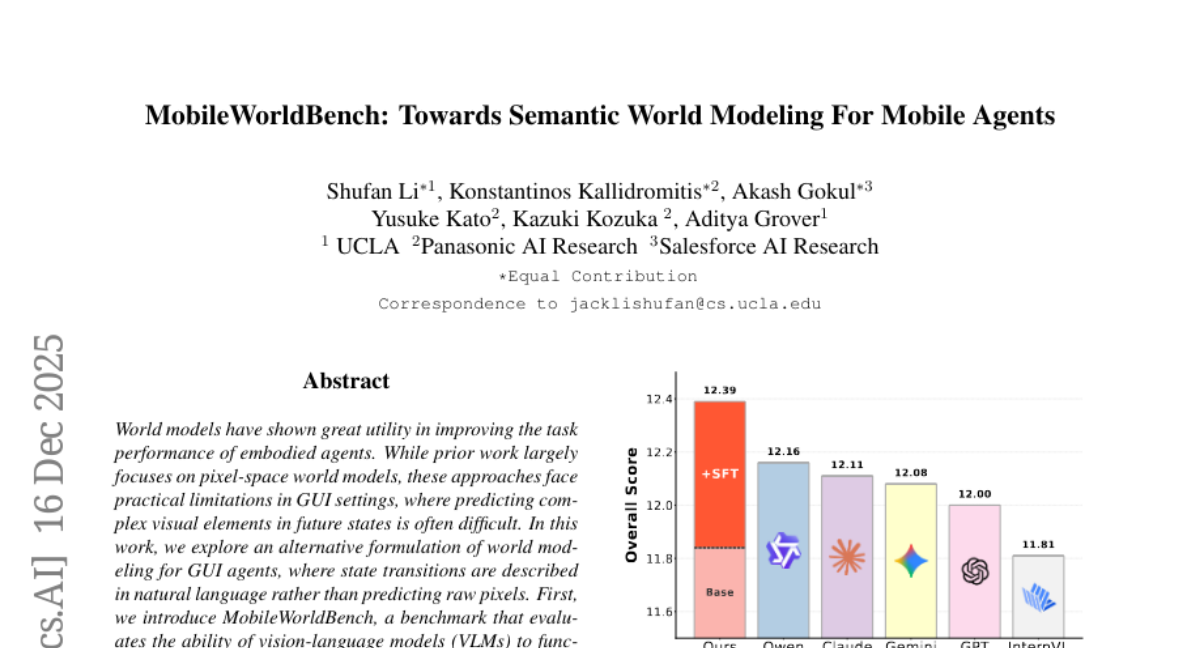
31. MobileWorldBench: Towards Semantic World Modeling For Mobile Agents
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Models, World Models, GUI Agents, Semantic World Models, Task Success Rates
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to improve the task success rates of mobile GUI agents by utilizing semantic world models instead of traditional pixel-based predictions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced MobileWorldBench, a benchmark to evaluate vision-language models for GUI agents.
– Released MobileWorld, a comprehensive dataset with 1.4 million samples to enhance world modeling capabilities of vision-language models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that integrating vision-language model world models into mobile agents’ planning frameworks can significantly enhance task success rates.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14014
32. JMMMU-Pro: Image-based Japanese Multi-discipline Multimodal Understanding Benchmark via Vibe Benchmark Construction
🔑 Keywords: JMMMU-Pro, Vibe Benchmark Construction, visual-textual understanding, LMMs, image generative model
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to introduce JMMMU-Pro, a Japanese multi-discipline multimodal benchmark, enhancing the evaluation tool for assessing the Japanese capabilities of large multimodal models (LMMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes Vibe Benchmark Construction, a method leveraging image generative models like Nano Banana Pro, to produce and verify candidate visual questions with integrated visual-textual understanding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results indicate significant challenges for open-source LMMs with JMMMU-Pro, highlighting its value as a benchmark and providing a guideline for future image-based VQA benchmark development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14620

33. ContextAnyone: Context-Aware Diffusion for Character-Consistent Text-to-Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: ContextAnyone, diffusion framework, DiT-based diffusion backbone, Emphasize-Attention module, Gap-RoPE positional embedding
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address the challenge of maintaining consistent character identities in text-to-video (T2V) generation by preserving contextual cues such as hairstyle, outfit, and body shape.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A novel context-aware diffusion framework, ContextAnyone, is proposed, utilizing a DiT-based diffusion backbone and an Emphasize-Attention module to integrate reference information, prevent identity drift, and stabilize temporal modeling with Gap-RoPE positional embeddings.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ContextAnyone outperforms existing methods in identity consistency and visual quality, effectively generating coherent and context-preserving character videos across diverse motions and scenes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.07328

34. CoSPlan: Corrective Sequential Planning via Scene Graph Incremental Updates
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Models, Sequential Planning, Error Detection, Scene Graph Incremental updates, Corrective Sequential Planning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve the performance of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in error-prone, vision-based sequential planning tasks by introducing intermediate reasoning steps.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a Corrective Sequential Planning Benchmark (CoSPlan) to evaluate VLMs in tasks like maze navigation, block rearrangement, image reconstruction, and object reorganization. Proposed a novel method, Scene Graph Incremental updates (SGI), to help VLMs reason about sequences better.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The use of Scene Graph Incremental updates (SGI) yields a 5.2% average performance improvement for VLMs, enhancing their reliability in corrective sequential planning and generalizing to traditional planning tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10342

35. MeViS: A Multi-Modal Dataset for Referring Motion Expression Video Segmentation
🔑 Keywords: MeViS, motion expression-guided video understanding, AI-generated, RVOS, LMPM++
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce MeViS, a large-scale multi-modal dataset for exploring motion expression-guided video segmentation and understanding, focusing on tracking and segmenting target objects in complex videos based on motion descriptions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Benchmark 15 existing methods over 4 tasks supported by MeViS, which include RVOS, AVOS, RMOT, and video captioning methods for RMEG task.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Highlight the limitations of current methods in addressing motion expression-guided video understanding, and propose LMPM++ achieving state-of-the-art results in RVOS/AVOS/RMOT, facilitating the development of algorithms for complex video scenes. The dataset and code are publicly accessible.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10945

36. Hierarchical Dataset Selection for High-Quality Data Sharing
🔑 Keywords: Dataset Selection, DaSH, Resource Constraints, Multi-Source Learning
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance model performance by selecting entire datasets rather than individual samples, optimizing utility under resource constraints.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of Dataset Selection via Hierarchies (DaSH), which evaluates and selects datasets based on utility at both dataset and group levels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DaSH significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, with up to 26.2% increase in accuracy, and demonstrates robustness in low-resource settings, making it apt for scalable and adaptive multi-source learning workflows.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10952

37. Unveiling User Perceptions in the Generative AI Era: A Sentiment-Driven Evaluation of AI Educational Apps’ Role in Digital Transformation of e-Teaching
🔑 Keywords: AI educational apps, Generative AI, Sentiment analysis, Personalization, Ethics
💡 Category: AI in Education
🌟 Research Objective:
– To assess user perceptions and the efficacy of top AI educational apps through sentiment analysis.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Used RoBERTa for binary sentiment classification, GPT-4o for key point extraction, and GPT-5 for synthesizing themes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– User reviews showed predominantly positive sentiments, especially for homework helpers due to their accuracy and speed.
– Language and LMS apps experienced challenges due to instability and limited features.
– The study highlights AI’s potential in democratizing education and proposes a future ecosystem using hybrid AI-human models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11934

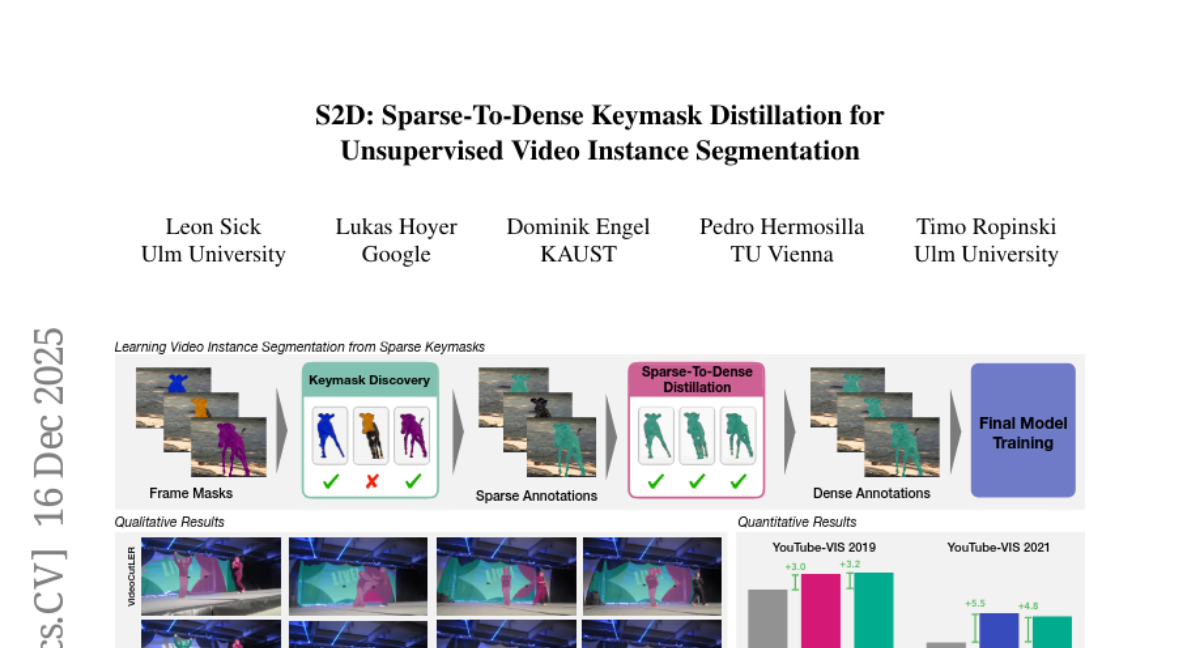
38. S2D: Sparse-To-Dense Keymask Distillation for Unsupervised Video Instance Segmentation
🔑 Keywords: Unsupervised video instance segmentation, real video data, deep motion priors, keymasks, Sparse-To-Dense Distillation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose an unsupervised video instance segmentation model trained exclusively on real video data to establish temporal coherence and improve motion modeling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized unsupervised instance segmentation masks on video frames and leveraged keymasks with deep motion priors.
– Introduced a Sparse-To-Dense Distillation approach aided by Temporal DropLoss for mask propagation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed model, trained on dense label sets derived from sparse pseudo-annotations, outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in video instance segmentation benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14440
39.
