AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251218

1. Step-GUI Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: GUI automation, Calibrated Step Reward System, self-evolving training pipeline, GUI-MCP, high-privacy execution
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance GUI automation efficiency, accuracy, and privacy using a self-evolving training pipeline powered by the Calibrated Step Reward System.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces the self-evolving training pipeline that utilizes trajectory-level calibration to convert model-generated trajectories into reliable training data, significantly lowering costs while maintaining high annotation accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study showcases the potential for real-world deployment of GUI agents, achieving state-of-the-art GUI performance metrics, leveraging a new Model Context Protocol (GUI-MCP) for consistent interfaces, and maintaining user privacy during execution.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15431

2. Fast and Accurate Causal Parallel Decoding using Jacobi Forcing
🔑 Keywords: Jacobi Forcing, parallel decoding, inference latency, transformers, diffusion Large Language Models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to reduce inference latency of transformer-based models while maintaining their performance through the introduction of Jacobi Forcing, a progressive distillation method.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study integrates transformer-based models with Jacobi Forcing, a method that allows models to train on their own generated parallel decoding trajectories. It adapts auto-regressive models into efficient parallel decoders, preserving their causal inference properties.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Models implemented with Jacobi Forcing achieve significant speedup, with a reported 3.8x improvement in wall-clock speed on coding and math benchmarks with minimal performance loss and a 4.0x speedup through multi-block decoding and rejection recycling techniques.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14681
3. Puzzle Curriculum GRPO for Vision-Centric Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Vision Language Models, Self-Supervised, Difficulty-Aware Curriculum, Reinforcement Learning, Reasoning-Answer Consistency
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance visual reasoning in Vision Language Models through a self-supervised approach without relying on external annotations or verifiers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed Puzzle Curriculum GRPO (PC-GRPO), using self-supervised puzzle environments like PatchFit, Rotation, and Jigsaw to replace labels and improve reward schemes.
– Introduced a difficulty-aware curriculum to dynamically weight samples, improving training stability and reasoning consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PC-GRPO improves reasoning quality, consistency, and end-task accuracy in Vision Language Models, offering a scalable and verifiable reinforcement learning method.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14944
4. IC-Effect: Precise and Efficient Video Effects Editing via In-Context Learning
🔑 Keywords: IC-Effect, DiT-based framework, Video VFX editing, Temporal consistency, Spatiotemporal sparse tokenization
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop IC-Effect, a DiT-based framework that facilitates instruction-guided, few-shot video VFX editing while preserving spatial and temporal consistency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a two-stage training strategy comprising general editing adaptation and effect-specific learning via Effect-LoRA.
– Implements spatiotemporal sparse tokenization to enhance efficiency and maintain high fidelity with reduced computation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– IC-Effect achieves high-quality, controllable, and temporally consistent VFX editing, providing new opportunities for video creation.
– Released a new paired VFX editing dataset featuring 15 high-quality visual styles.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15635

5. Qwen-Image-Layered: Towards Inherent Editability via Layer Decomposition
🔑 Keywords: Qwen-Image-Layered, diffusion model, RGBA layers, inherent editability, consistent image editing
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve the decomposition quality and consistency of images by proposing Qwen-Image-Layered, which leverages a diffusion model to decompose images into semantically disentangled RGBA layers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Three key components are utilized: RGBA-VAE for unifying latent representations, VLD-MMDiT for decomposing variable number of layers, and Multi-stage Training for adapting a pretrained model into a multilayer decomposer.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method demonstrates significant improvement in decomposition quality over existing approaches and establishes a new paradigm for consistent image editing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15603
6. SAGE: Training Smart Any-Horizon Agents for Long Video Reasoning with Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: SAGE, multi-turn reasoning, synthetic data, reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop SAGE, a system capable of multi-turn reasoning on long videos, mirroring human behavior in handling video content across various durations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methods include creating a synthetic data generation pipeline using Gemini-2.5-Flash, establishing SAGE-MM as the core orchestrator, and applying a reinforcement learning post-training technique for enhanced reasoning capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study observed significant improvements in open-ended video reasoning tasks, achieving up to a 6.1% enhancement, and an 8.2% improvement for videos longer than 10 minutes, validating the system’s effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13874
7. FiNERweb: Datasets and Artifacts for Scalable Multilingual Named Entity Recognition
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Named Entity Recognition, Zero Shot Transfer, Multilingual, Synthetic Supervision
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to introduce FiNERweb, a dataset-creation pipeline designed to enhance multilingual NER across 91 languages and 25 scripts by leveraging large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methodology involved training regression models to identify NER-relevant passages and annotating them with multilingual LLMs, producing a large dataset with 225k passages and 235k distinct entity labels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The FiNERweb approach not only achieves high F1 scores in regression models but also shows improved or comparable performance in zero shot transfer settings, even with significantly less training data. The dataset is released with English and translated label sets to support multilingual NER research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13884

8. End-to-End Training for Autoregressive Video Diffusion via Self-Resampling
🔑 Keywords: Resampling Forcing, Autoregressive video diffusion models, exposure bias, self-resampling scheme, temporal consistency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a teacher-free framework, Resampling Forcing, to enhance temporal consistency in autoregressive video diffusion models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement a self-resampling scheme to simulate inference-time model errors on history frames during training.
– Use a sparse causal mask to enforce temporal causality and allow parallel training with frame-level diffusion loss.
– Introduce history routing to dynamically retrieve relevant history frames for long-horizon generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The approach maintains a performance comparable to distillation-based baselines while significantly improving temporal consistency for longer video sequences due to native-length training.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15702

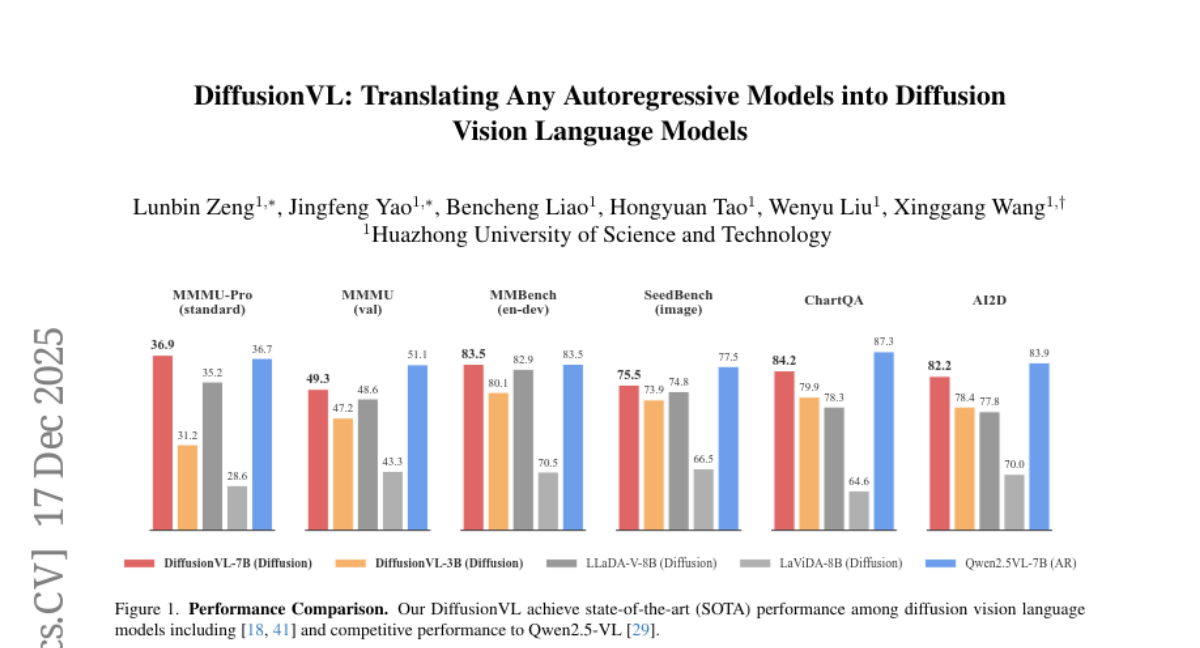
9. DiffusionVL: Translating Any Autoregressive Models into Diffusion Vision Language Models
🔑 Keywords: DiffusionVL, diffusion vision language model, fine-tuning, inference speedup
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Explore if it is possible to construct diffusion vision language models (dVLMs) based on existing powerful autoregressive (AR) models and improve performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Adapt AR pre-trained models into the diffusion paradigm through simple fine-tuning and introduce a block-decoding design to enhance speed and support arbitrary-length generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The paradigm shift from AR-based models to diffusion models is highly effective, achieving performance competitive with mainstream models like LLaVA. Additionally, DiffusionVL demonstrates a significant inference speedup and improved performance on vision and cognitive benchmarks, with reduced data requirements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15713
10. In Pursuit of Pixel Supervision for Visual Pre-training
🔑 Keywords: Pixio, Autoencoders, Self-Supervised Learning, Masked Autoencoder, Downstream Tasks
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To demonstrate the competitive performance of Pixio, an enhanced masked autoencoder, across various downstream tasks using pixel-space self-supervised learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Pixio, the proposed model, is an enhanced masked autoencoder trained on 2 billion web-crawled images using a self-curation strategy, focusing on challenging pre-training tasks and capable architectures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Pixio outperforms or matches similar models like DINOv3 in tasks such as monocular depth estimation, 3D reconstruction, semantic segmentation, and robot learning, highlighting the potential of pixel-space self-supervised learning as a viable alternative to latent-space approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15715
11. Is Nano Banana Pro a Low-Level Vision All-Rounder? A Comprehensive Evaluation on 14 Tasks and 40 Datasets
🔑 Keywords: Nano Banana Pro, Low-Level Vision, Text-to-Image Generation, Generative Models, Zero-Shot Evaluation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– This paper investigates whether Nano Banana Pro can be an all-rounder in low-level vision tasks without fine-tuning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study conducted a zero-shot evaluation on 14 low-level tasks using 40 diverse datasets, employing simple textual prompts to benchmark performance against specialist models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Nano Banana Pro excels in subjective visual quality by hallucinating plausible high-frequency details. However, it struggles with traditional quantitative metrics due to the stochastic nature of generative models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15110

12. LikeBench: Evaluating Subjective Likability in LLMs for Personalization
🔑 Keywords: LikeBench, LLMs, likability, personalized LLM, simulated user
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce LikeBench, a multi-session evaluation framework to assess the likability of Language Learning Models (LLMs) by adapting to user preferences across multiple dimensions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a dynamic evaluation framework where LLMs engage in conversation with simulated users, adapting to user preferences and being evaluated for likability through seven diagnostic metrics: emotional adaptation, formality matching, knowledge adaptation, reference understanding, conversation length fit, humor fit, and callback.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– High memory performance does not necessarily lead to higher likability. For instance, DeepSeek R1, with lower memory accuracy, achieved a higher likability score than Qwen3 despite its superior memory accuracy. State-of-the-art models like GPT-5 show limitations in longer, noisier interactions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13077

13. Understanding and Improving Hyperbolic Deep Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Hyperbolic feature spaces, Proximal policy optimization, Stable critic training, Hyper++, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance stability and performance of reinforcement learning (RL) agents by addressing gradient issues and norm constraints in hyperbolic feature spaces.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study identifies and analyzes factors affecting training of hyperbolic deep RL agents, particularly focusing on Poincaré Ball and Hyperboloid models.
– Hyper++ is introduced as a new hyperbolic PPO agent with stable critic training via categorical value loss, feature regularization ensuring bounded norms, and a more optimization-friendly formulation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Hyper++ guarantees stable learning, outperforms both prior hyperbolic agents and Euclidean baselines, and reduces wall-clock time by approximately 30%, especially noted in experiments conducted on ProcGen and Atari-5 environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14202

14. FrontierCS: Evolving Challenges for Evolving Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: FrontierCS, open-ended problems, algorithmic problems, expert reference solution, frontier reasoning models
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces FrontierCS, a benchmark designed to evaluate models on computer science problems with unknown optimal solutions, focusing on executable program implementations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A collection of 156 open-ended problems was curated by experts in various CS fields. For each problem, an expert reference solution and an automatic evaluator are provided to allow objective evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Frontier reasoning models lag behind human expertise on algorithmic and research tracks. Simply increasing reasoning budgets does not close the gap, and models often optimize for workable code over high-quality solutions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15699

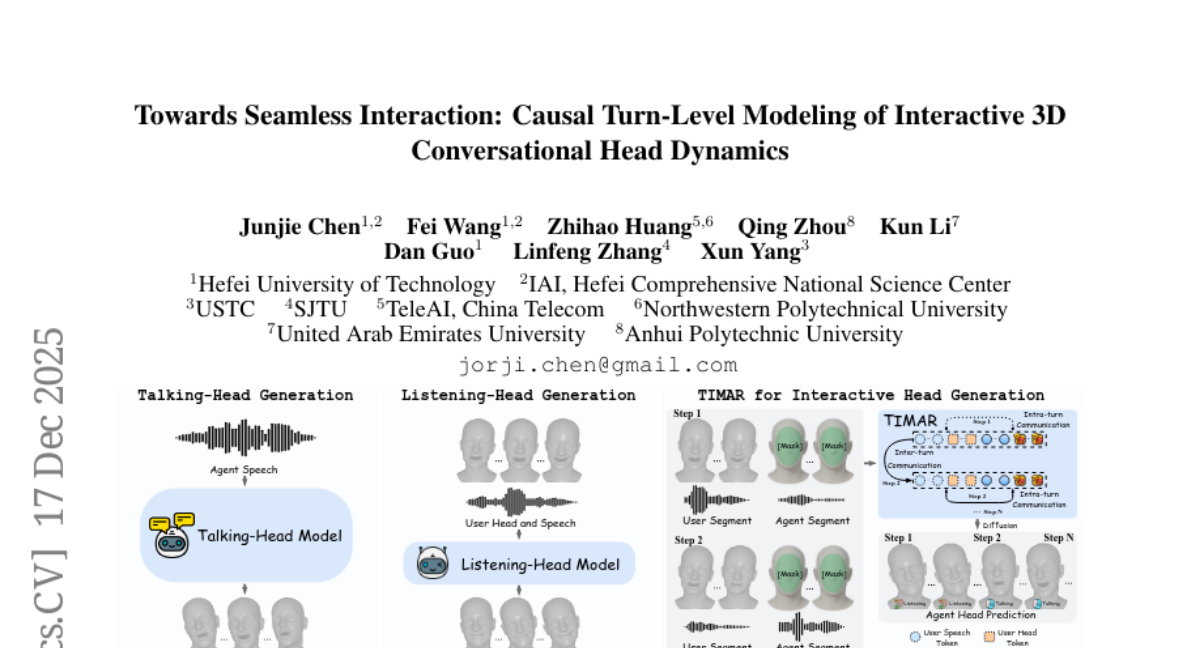
15. Towards Seamless Interaction: Causal Turn-Level Modeling of Interactive 3D Conversational Head Dynamics
🔑 Keywords: TIMAR, causal framework, 3D conversational head generation, dialogue, interleaved audio-visual contexts
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces TIMAR, a causal framework for generating 3D conversational heads that models dialogue as interleaved audio-visual contexts, aiming to improve coherence and expressive variability in conversational agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– TIMAR employs turn-level Interleaved Masked AutoRegression to integrate multimodal information and apply causal attention, using a lightweight diffusion head to predict continuous 3D head dynamics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments on the DualTalk benchmark demonstrate that TIMAR reduces Fréchet Distance and MSE by 15-30% on test data and maintains similar performance improvements on out-of-distribution datasets. The framework will be released on GitHub for public access and further development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15340
16.

17. SonicMoE: Accelerating MoE with IO and Tile-aware Optimizations
🔑 Keywords: Mixture of Experts, Memory Efficiency, Token Rounding, Computational Efficiency, Activation Caching
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to optimize memory usage and computational efficiency in Mixture of Experts (MoE) models through innovative methods such as minimal activation caching, IO-computation overlap, and token rounding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a memory-efficient algorithm for MoE models that minimizes activation caching during backward passes.
– Design of GPU kernels to overlap memory IO with computation.
– Introduction of a token rounding method to reduce wasted compute due to padding in Grouped GEMM kernels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SonicMoE achieves a 45% reduction in activation memory and improves compute throughput by 1.86x using Hopper GPUs.
– The method results in a training throughput comparable to ScatterMoE but with fewer resources.
– The proposed tile-aware token rounding yields additional speedups and maintains similar downstream performance, with all kernels open-sourced for wider use.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14080

18. Simultaneous Tactile-Visual Perception for Learning Multimodal Robot Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: TacThru-UMI, STS sensors, multimodal signals, imitation learning, Transformer-based Diffusion Policy
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance robotic manipulation by integrating simultaneous multimodal perception with an effective learning framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A novel system, TacThru-UMI, combining TacThru sensors with a Transformer-based Diffusion Policy is developed to achieve simultaneous visual and tactile perception.
– The approach involves leveraging imitation learning to utilize multimodal signals for manipulation tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The TacThru-UMI system significantly outperforms baseline methods, achieving an 85.5% success rate in real-world tasks.
– This work highlights the capability of combining multimodal perception with modern learning frameworks to enable precise and adaptable robotic manipulation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.09851

19. Hybrid Attribution Priors for Explainable and Robust Model Training
🔑 Keywords: Class-Aware Attribution Prior, interpretability, robustness, explanation-guided learning, attribution-based supervision
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance language model interpretability and robustness through a novel framework that guides models to capture fine-grained class distinctions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research develops the Class-Aware Attribution Prior (CAP) framework, combining it with existing attribution methods to balance supervisory signals and improve classification tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method consistently improves interpretability and robustness across various scenarios, demonstrating the value of enriched attribution priors for model learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14719

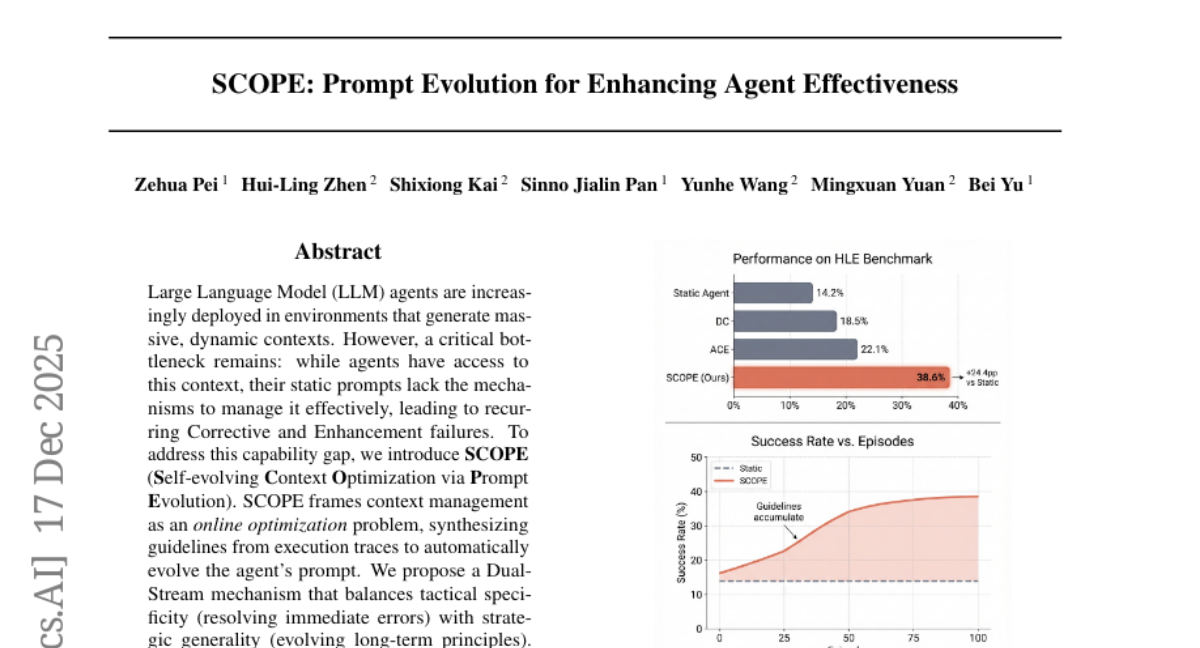
20. SCOPE: Prompt Evolution for Enhancing Agent Effectiveness
🔑 Keywords: LLM agents, Prompt Evolution, context management, Dual-Stream mechanism, Perspective-Driven Exploration
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance the context management abilities of Large Language Model (LLM) agents through a mechanism called SCOPE, which evolves prompts to improve task success rates in dynamic environments without human interference.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors introduce SCOPE, which frames context management as an online optimization challenge, utilizing guidelines from execution traces to auto-evolve the agent’s prompt.
– A Dual-Stream mechanism is proposed to balance immediate error resolution with long-term strategic principles. Additionally, Perspective-Driven Exploration is implemented to expand strategic coverage.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments conducted using the HLE benchmark demonstrate that SCOPE significantly improves task success rates from 14.23% to 38.64% autonomously.
– The authors provide open access to the code used at the specified GitHub repository.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15374
21. WAY: Estimation of Vessel Destination in Worldwide AIS Trajectory
🔑 Keywords: Deep Learning Architecture, Vessel Destination Estimation, AIS Data, Gradient Dropout, CASP Blocks
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve accuracy in long-term vessel destination estimation using AIS data by proposing a novel architecture called WAY.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces a nested sequence structure and spatial grids, utilizes a trajectory representation layer and CASP blocks, and applies a Gradient Dropout technique for enhanced training performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– WAY demonstrates superior performance over traditional spatial grid-based methods using 5-year AIS data, with Gradient Dropout contributing to significant performance improvements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13190

22. VTCBench: Can Vision-Language Models Understand Long Context with Vision-Text Compression?
🔑 Keywords: vision-language models, long-context information, vision-text compression, VLMs, token compression
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a benchmark to evaluate vision-language models’ ability to understand long-context information through vision-text compression.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Systematic assessment of vision-language models across three settings: VTC-Retrieval, VTC-Reasoning, and VTC-Memory.
– Establishment of VTCBench-Wild to simulate diverse input scenarios.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Most vision-language models struggle to capture long-term dependencies in VTC-compressed information, despite their proficiency in decoding textual data.
– This benchmark study lays the foundation for improving the efficiency and scalability of such models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15649

23. VABench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Audio-Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: VABench, audio-video generation, evaluation, synchronization, multi-dimensional
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the lack of convincing evaluations for audio-video generation models that generate synchronized outputs, introducing the VABench framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a benchmark framework with three primary tasks: text-to-audio-video (T2AV), image-to-audio-video (I2AV), and stereo audio-video generation. Establish evaluation modules covering 15 dimensions such as pairwise similarities and lip-speech consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VABench provides a comprehensive standard for assessing video generation models with synchronous audio capabilities, aiming to advance the field of audio-video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.09299

24. VOYAGER: A Training Free Approach for Generating Diverse Datasets using LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Voyager, synthetic datasets, diversity, determinantal point processes, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces Voyager, a method designed to generate diverse synthetic datasets for model evaluation and training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Voyager uses an iterative approach employing determinantal point processes to optimize dataset diversity without additional training, making it applicable to closed-source models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Voyager significantly surpasses popular baseline methods, achieving a 1.5-3x improvement in dataset diversity according to comprehensive experiments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12072

25. MMSI-Video-Bench: A Holistic Benchmark for Video-Based Spatial Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: MMSI-Video-Bench, MLLMs, spatial intelligence, geometric reasoning, motion grounding
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to benchmark video-based spatial intelligence in MLLMs through MMSI-Video-Bench, revealing the human-AI performance gap and challenges in geometric reasoning, motion grounding, and cross-video correspondence.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study implements a comprehensive, four-level framework (Perception, Planning, Prediction, and Cross-Video Reasoning) with human-annotated questions and evaluates 25 MLLMs using data from 25 datasets and in-house videos.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Findings indicate a significant performance gap between humans and AI models, with the best models trailing humans by nearly 60%. The research uncovers systematic failures in spatial reasoning tasks and reveals that common techniques like frame-sampling have limited effectiveness on this benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10863
26. Can LLMs Guide Their Own Exploration? Gradient-Guided Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Gradient-Guided Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Update Geometry, Exploration, Semantic Coherence
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance exploration in large language models through a gradient-guided reinforcement learning framework, G2RL, improving performance on reasoning benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes model’s own first-order update geometry for exploration, compares sequence level features, and rewards novel gradient directions to reshape policy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– G2RL consistently improves benchmark performances by expanding exploration into orthogonal gradient directions while maintaining semantic coherence, offering a more effective exploration foundation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15687

27. Robust and Calibrated Detection of Authentic Multimedia Content
🔑 Keywords: deepfake detection, resynthesis framework, false positive rate, adversarial robustness, multi-modalities
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance deepfake detection by using a resynthesis framework that ensures authenticity verification with low false positive rates and robustness against adversaries.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a calibrated resynthesis method for high-precision, low-recall settings, particularly against compute-restricted adversaries, utilizing state-of-the-art inversion techniques.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method verifies authentic samples reliably with controllable false positive rates and achieves adversarial robustness that previous methods fail to maintain under similar computational conditions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15182

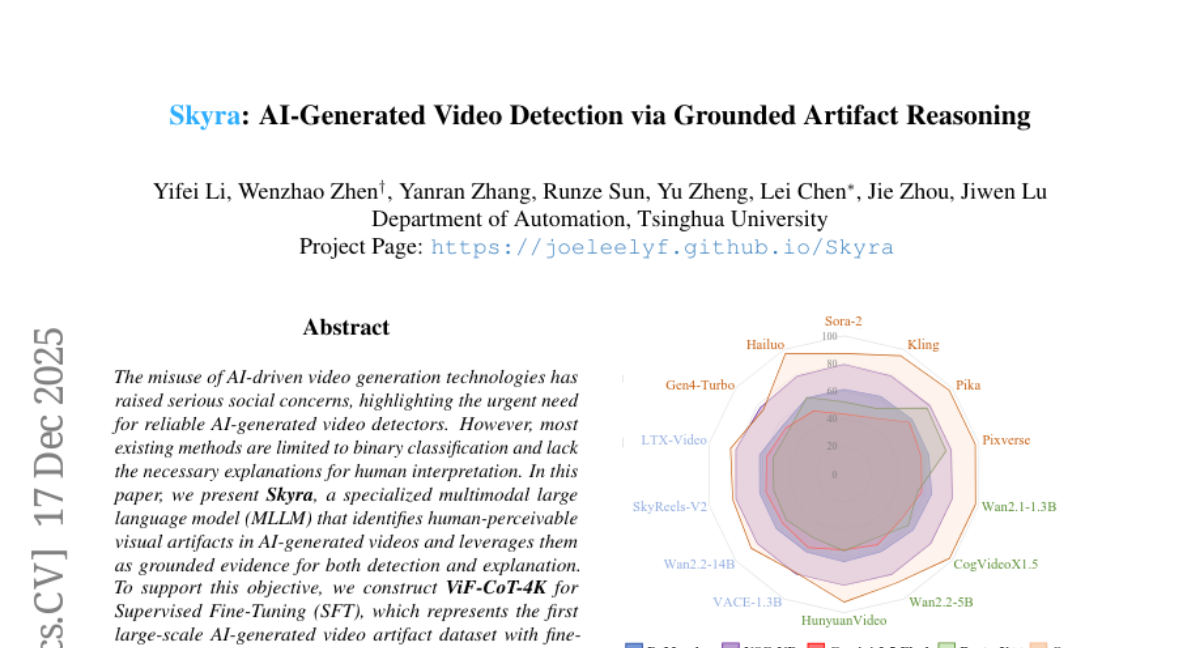
28. Skyra: AI-Generated Video Detection via Grounded Artifact Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated video detectors, multimodal large language model, visual artifacts, explainable AI, spatio-temporal artifact perception
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper presents Skyra, a specialized multimodal large language model designed to identify and explain human-perceivable visual artifacts in AI-generated videos.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study involves constructing the ViF-CoT-4K dataset with fine-grained human annotations for supervised fine-tuning and developing a two-stage training strategy to enhance the model’s capabilities in detection, explanation, and artifact perception.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Skyra outperforms existing methods across multiple benchmarks, demonstrating significant advancements in explainable AI for video detection and providing valuable insights for future research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15693
29. Universal Reasoning Model
🔑 Keywords: Universal Reasoning Model, ARC-AGI, Universal Transformers, nonlinear components, truncated backpropagation
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance reasoning performance on ARC-AGI tasks by improving the Universal Transformers with short convolution and truncated backpropagation techniques.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Systematic analysis of Universal Transformers variants to identify performance gains sources, focusing on recurrent inductive bias and the application of strong nonlinear components.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed Universal Reasoning Model significantly improves reasoning performance, achieving state-of-the-art results on ARC-AGI challenges, with 53.8% pass@1 on ARC-AGI 1 and 16.0% pass@1 on ARC-AGI 2.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14693

30. HyperVL: An Efficient and Dynamic Multimodal Large Language Model for Edge Devices
🔑 Keywords: HyperVL, on-device inference, multimodal large language model, Visual Resolution Compressor, Dual Consistency Learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop HyperVL, an efficient multimodal large language model for on-device inference that reduces memory usage, latency, and power consumption without sacrificing performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model employs an image-tiling strategy.
– It incorporates a Visual Resolution Compressor to determine optimal encoding resolutions.
– Dual Consistency Learning is used to integrate multi-scale ViT encoders within a unified framework.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HyperVL achieves state-of-the-art performance among models of similar size across various benchmarks.
– It effectively reduces latency and power consumption on real mobile devices, highlighting its practicality for on-device multimodal inference.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14052

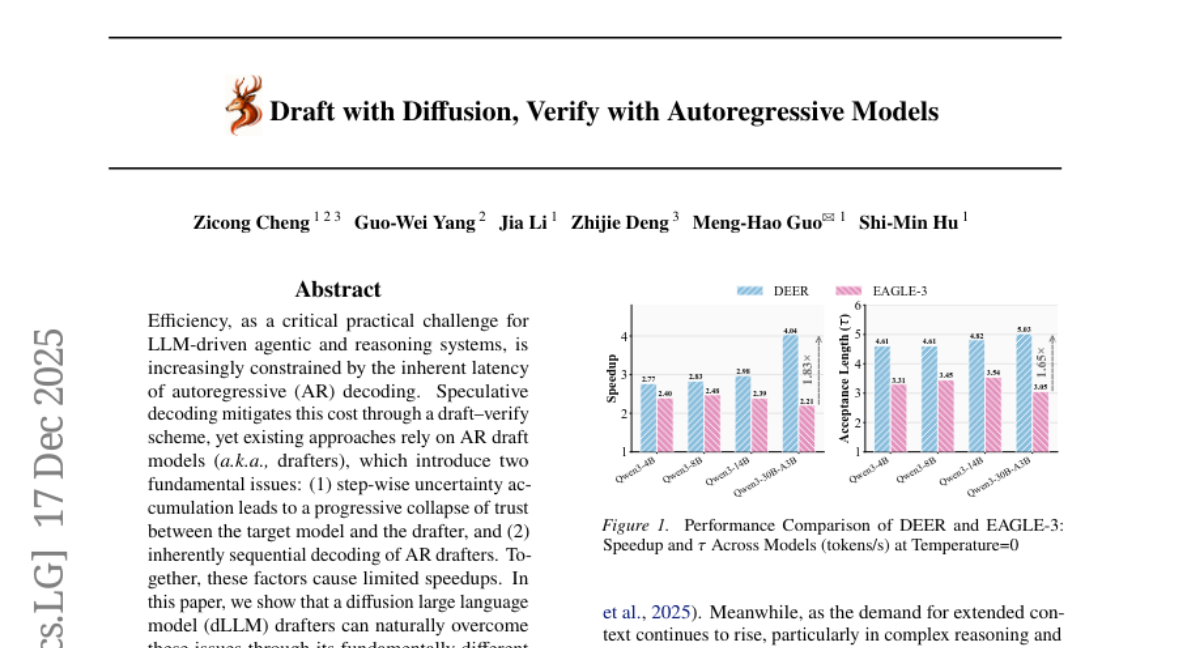
31. DEER: Draft with Diffusion, Verify with Autoregressive Models
🔑 Keywords: DEER framework, Diffusion large language models, Speculative decoding, Parallel decoding, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the efficiency limitations of autoregressive (AR) drafters by utilizing diffusion large language models (dLLM) for speculative decoding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a DEER framework using a two-stage training pipeline for alignment between dLLM-based drafters and the target AR model, along with single-step decoding to generate long draft segments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DEER framework achieves significant improvements in draft acceptance length and speedup compared to existing methods, with a draft acceptance of up to 32 tokens and a 5.54x speedup on HumanEval.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15176