AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251219

1. Kling-Omni Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Kling-Omni, Generative Framework, Multimodal Inputs, Video Generation, Cinematic-Quality
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop Kling-Omni, a generalist generative framework that synthesizes high-fidelity videos from multimodal visual language inputs, integrating video generation, editing, and reasoning into a unified system.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing an end-to-end approach, Kling-Omni supports various user inputs and processes them into a unified multimodal representation. The framework is empowered by large-scale pre-training and infrastructure optimizations for efficient inference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Kling-Omni exhibits exceptional capabilities in in-context generation, reasoning-based editing, and multimodal instruction following. It represents a significant step towards becoming a multimodal world simulator that perceives, reasons, generates, and interacts with dynamic and complex environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16776

2. Next-Embedding Prediction Makes Strong Vision Learners
🔑 Keywords: Generative pretraining, Next-Embedding Predictive Autoregression (NEPA), causal masking, ImageNet, semantic segmentation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore generative pretraining in visual tasks by shifting from learning representations to predictive models using next embedding prediction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a simple Transformer architecture pretrained on ImageNet-1k with the sole objective of next embedding prediction, utilizing techniques like causal masking and stop gradient.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– NEPA demonstrates high effectiveness with top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K and successful transfer to semantic segmentation on ADE20K, offering a scalable and straightforward alternative for visual self-supervised learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16922

3. StereoPilot: Learning Unified and Efficient Stereo Conversion via Generative Priors
🔑 Keywords: StereoPilot, learnable domain switcher, cycle consistency loss, visual fidelity, computational efficiency
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a model named StereoPilot that synthesizes high-quality stereo video directly without relying on depth maps, addressing issues in existing methods such as error propagation and depth ambiguity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a feed-forward model with a learnable domain switcher and cycle consistency loss to adapt to different stereo formats.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– StereoPilot outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both visual fidelity and computational efficiency, proving to be a superior approach in stereoscopic video content creation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16915
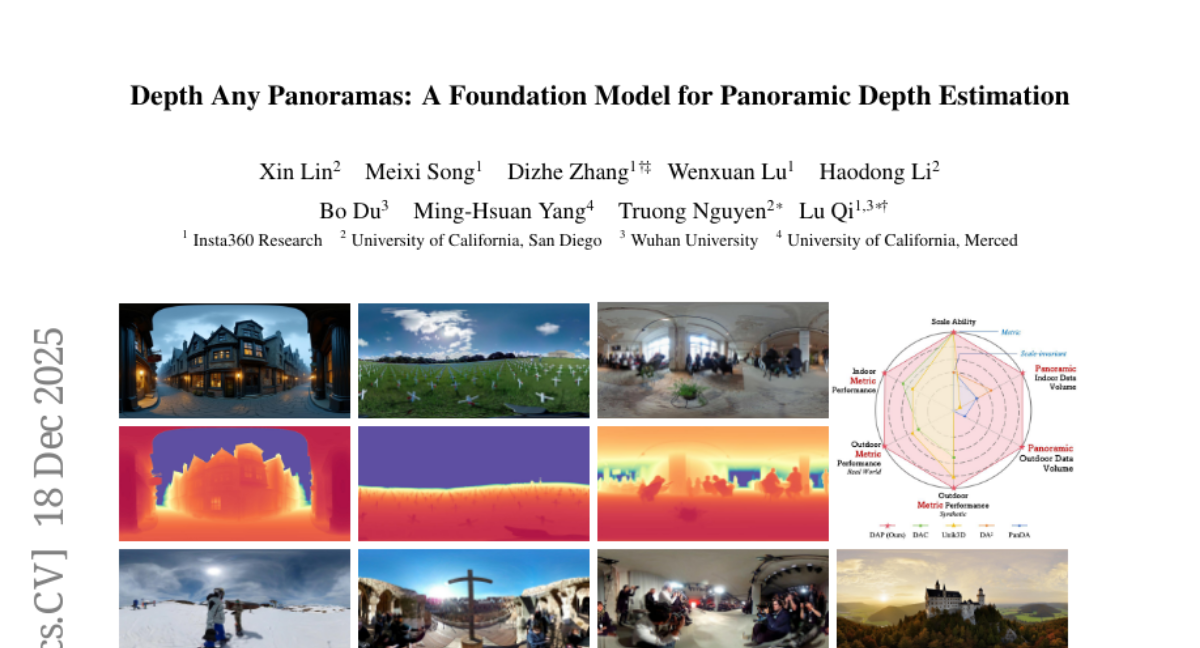
4. Depth Any Panoramas: A Foundation Model for Panoramic Depth Estimation
🔑 Keywords: Panoramic Metric Depth, DINOv3-Large, Three-Stage Pseudo-Label Pipeline, AI-generated Summary, Zero-Shot Generalization
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– This paper presents a panoramic metric depth foundation model designed to perform robustly across diverse real-world scenes and varying scene distances.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a data-in-the-loop paradigm involving data collection combining public datasets, synthetic data from a UE5 simulator, and real panoramic images.
– Implements a three-stage pseudo-label curation pipeline to create reliable ground truth for unlabeled images.
– Employ DINOv3-Large as the backbone, incorporating a range mask head, and optimization techniques focused on sharpness and geometry for better robustness and consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model demonstrates strong performance and zero-shot generalization on multiple benchmarks with robust and stable metric predictions in various real-world scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16913
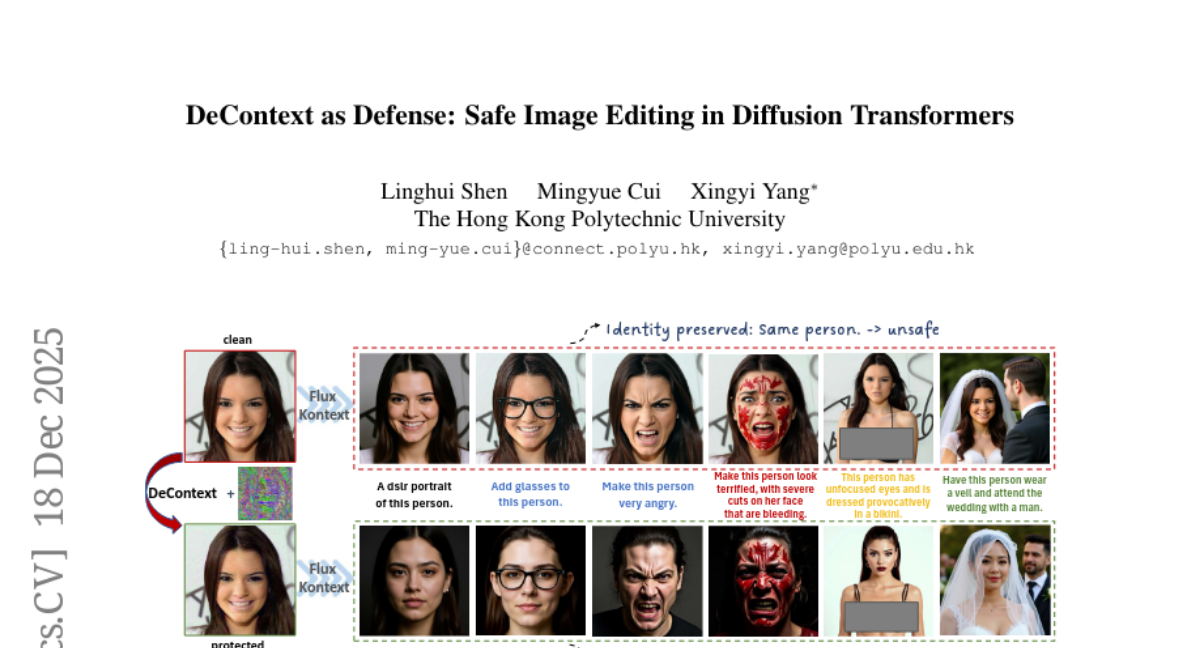
5. DeContext as Defense: Safe Image Editing in Diffusion Transformers
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, DeContext, multimodal attention layers, cross-attention pathways, image manipulation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces DeContext as a method to defend against unauthorized in-context image editing by attenuating cross-attention pathways in multimodal layers, preserving the visual quality by preventing unwanted modifications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– DeContext works by injecting small, targeted perturbations to weaken the cross-attention pathways in large-scale in-context models, effectively disrupting the connection between input and output, which is critical for unauthorized modification prevention.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments on Flux Kontext and Step1X-Edit demonstrate that DeContext successfully blocks unwanted image edits while maintaining visual quality, showcasing the effectiveness of attention-based perturbations for safeguarding images from manipulation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16625
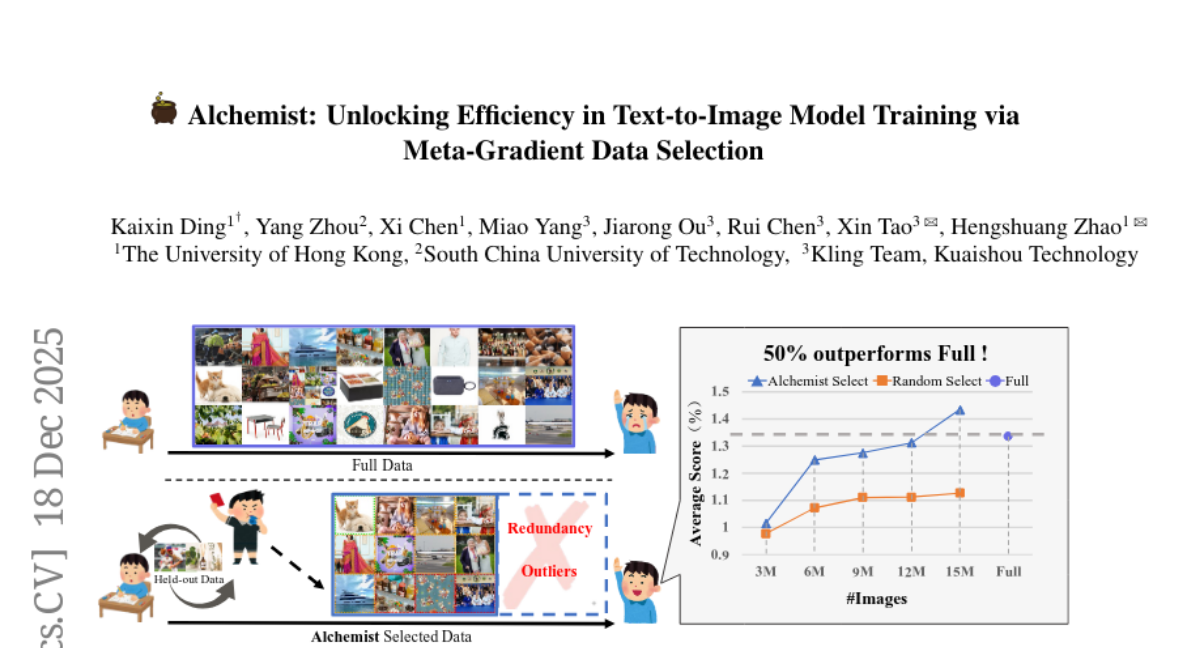
6. Alchemist: Unlocking Efficiency in Text-to-Image Model Training via Meta-Gradient Data Selection
🔑 Keywords: Alchemist, meta-gradient-based, data selection, visual quality, Text-to-Image
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Alchemist, designed to enhance visual quality and training efficiency by selecting high-quality subsets from large-scale text-image datasets.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Alchemist operates with two main stages: data rating and data pruning, using a lightweight rater to estimate sample influence based on gradient information and employing Shift-Gsampling for informative subset selection.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Alchemist is the first automatic, scalable, meta-gradient-based framework for Text-to-Image model training, showing consistent improvement in visual quality and downstream performance even when trained on only 50% of the dataset.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16905
7. N3D-VLM: Native 3D Grounding Enables Accurate Spatial Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: native 3D object perception, 3D-aware visual reasoning, 3D object localization, spatial understanding, AI Native
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim is to integrate native 3D perception and reasoning within vision-language models, enhancing their ability to accurately localize and understand spatial relationships in 3D space.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– This paper introduces N3D-VLM, a unified framework that combines native 3D object perception with 3D-aware visual reasoning, facilitated by a large-scale dataset. A scalable data construction pipeline is developed to lift 2D annotations into 3D, significantly enhancing the dataset’s size and diversity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The unified framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D grounding tasks and consistently outperforms existing methods in 3D spatial reasoning within vision-language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16561
8. AdaTooler-V: Adaptive Tool-Use for Images and Videos
🔑 Keywords: AdaTooler-V, AI-generated summary, reinforcement learning, adaptive tool-use, visual reasoning tasks
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– AdaTooler-V aims to enhance multimodal language models’ performance by adaptively using vision tools only when beneficial, thus reducing unnecessary operations and improving efficiency in visual reasoning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– AdaTooler-V utilizes AT-GRPO, a reinforcement learning algorithm that adjusts reward scales based on the Tool Benefit Score, encouraging efficient tool use. The research also involves constructing two datasets, AdaTooler-V-CoT-100k and AdaTooler-V-300k, for model training with varying data types.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Through experiments across twelve benchmarks, AdaTooler-V demonstrated superior reasoning capabilities, achieving notable accuracy, and outperforming existing commercial models like GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Pro in visual reasoning tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16918

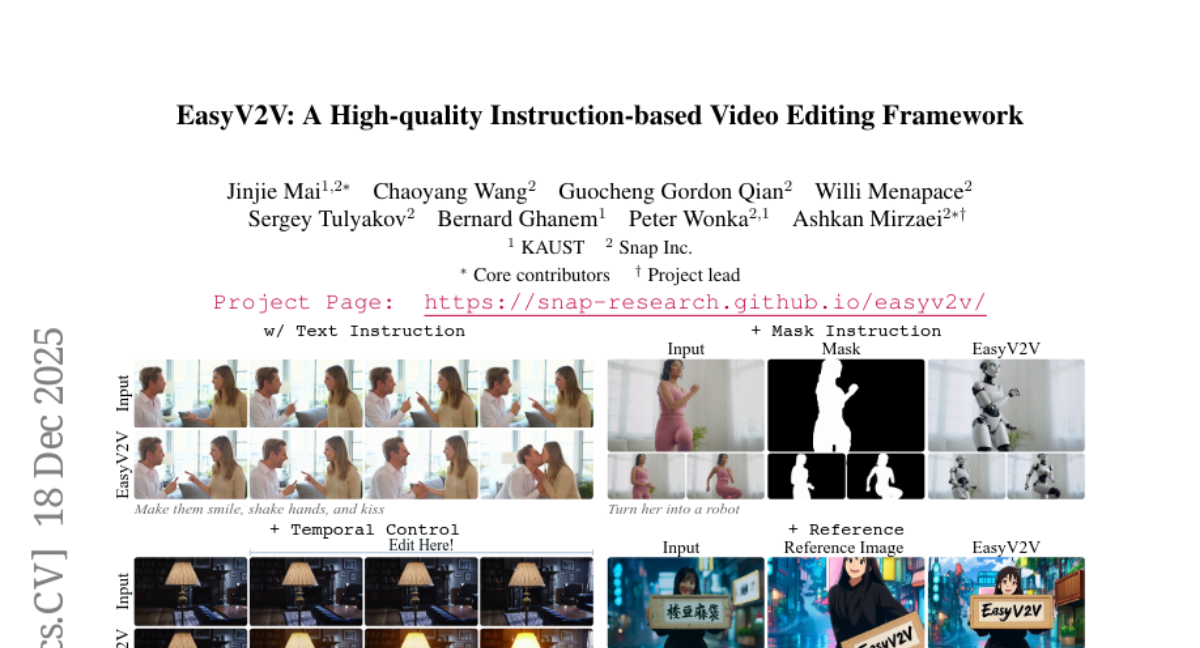
9. EasyV2V: A High-quality Instruction-based Video Editing Framework
🔑 Keywords: EasyV2V, pretrained text-to-video models, LoRA fine-tuning, spatiotemporal control, video editing
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to advance video editing by addressing challenges in consistency, control, and generalization using a novel framework called EasyV2V.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research integrates diverse data sources and combines existing experts with innovative techniques like single-frame supervision and pseudo pairs.
– Utilizes pretrained text-to-video models with LoRA fine-tuning, offering simplified training through sequence concatenation and unified spatiotemporal control.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EasyV2V framework effectively processes flexible inputs and achieves superior video editing results, outperforming existing commercial and concurrent systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16920
10. FlashPortrait: 6x Faster Infinite Portrait Animation with Adaptive Latent Prediction
🔑 Keywords: ID consistency, dynamic sliding-window scheme, higher-order latent derivatives, long-portrait animation, diffusion latents
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address the challenge of ensuring ID consistency in long-portrait animation with a novel approach called FlashPortrait. This method promises significant acceleration in video synthesis.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– FlashPortrait employs an end-to-end video diffusion transformer that utilizes a dynamic sliding-window scheme and higher-order latent derivatives to accelerate inference while maintaining ID consistency in the output.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FlashPortrait demonstrates effective synthesis of ID-preserving, infinite-length videos with up to 6x acceleration in inference speed, showcasing its advantages both qualitatively and quantitatively over existing methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16900

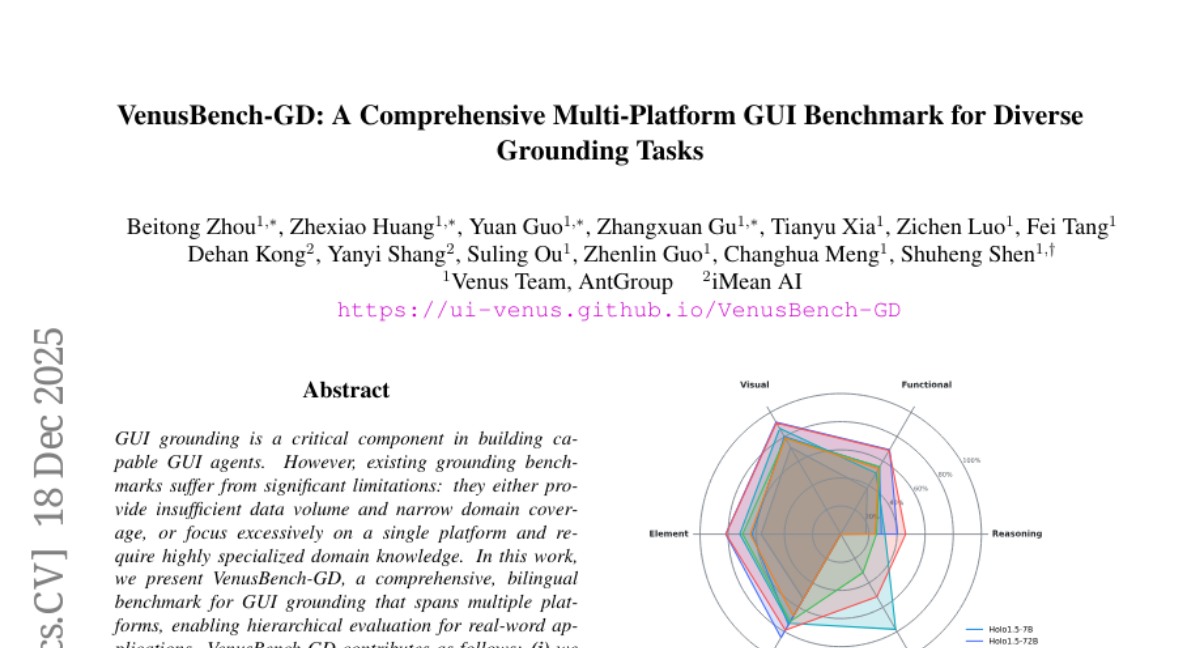
11. VenusBench-GD: A Comprehensive Multi-Platform GUI Benchmark for Diverse Grounding Tasks
🔑 Keywords: VenusBench-GD, GUI grounding, cross-platform benchmark, high-quality data construction, evaluation frameworks
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce VenusBench-GD, a comprehensive, bilingual benchmark for GUI grounding that crosses multiple platforms and provides hierarchical evaluation for real-world applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a high-quality data construction pipeline to enhance annotation accuracy.
– Proposed a hierarchical task taxonomy that divides GUI grounding into basic and advanced categories, with six distinct subtasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– General-purpose multimodal models perform comparably to specialized GUI models on basic tasks, but advanced tasks still favor specialized models, which face overfitting and robustness issues.
– Highlights the need for comprehensive, multi-tiered evaluation frameworks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16501
12. Insight Miner: A Time Series Analysis Dataset for Cross-Domain Alignment with Natural Language
🔑 Keywords: Insight Miner, TS-Insights, large-scale multimodal model, time-series analysis, GPT-4
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim is to propose Insight Miner, a large-scale multimodal model designed to generate high-quality, comprehensive time-series descriptions enriched with domain-specific knowledge.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– This research introduces a novel agentic workflow and the TS-Insights dataset, which contains 100k time-series data excerpts. Statistical tools are utilized to extract features and synthesize them into trend descriptions with the help of GPT-4.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Insight Miner, when tuned with TS-Insights, outperforms state-of-the-art multimodal models such as LLaVA and GPT-4 in generating time-series descriptions and insights, suggesting a promising direction for leveraging large-scale multimodal models in time series analysis.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.11251

13. Hearing to Translate: The Effectiveness of Speech Modality Integration into LLMs
🔑 Keywords: SpeechLLMs, speech-to-text translation, Large Language Models, cascaded systems, multilingual LLMs
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to evaluate and compare the effectiveness of SpeechLLMs and cascaded systems in speech-to-text translation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers conducted a comprehensive benchmarking of 5 state-of-the-art SpeechLLMs against 16 direct and cascade systems, across 16 benchmarks, 13 language pairs, and 9 challenging conditions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Cascaded systems were found to be more reliable overall, while current SpeechLLMs only matched cascades in specific settings, emphasizing the importance of integrating multilingual LLMs for high-quality speech translation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16378

14. FrameDiffuser: G-Buffer-Conditioned Diffusion for Neural Forward Frame Rendering
🔑 Keywords: Neural rendering, G-buffer, Temporal consistency, ControlNet, ControlLoRA
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop an autoregressive neural rendering framework, FrameDiffuser, that generates temporally consistent, photorealistic frames using G-buffer data and previous frame outputs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of FrameDiffuser’s dual-conditioning architecture combining ControlNet for structural guidance with ControlLoRA for temporal coherence, and employing a three-stage training strategy for stable autoregressive generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FrameDiffuser, when specialized to individual environments, achieves superior photorealistic quality with accurate lighting, shadows, and reflections, maintaining temporal consistency over extensive sequence generation compared to generalized approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16670
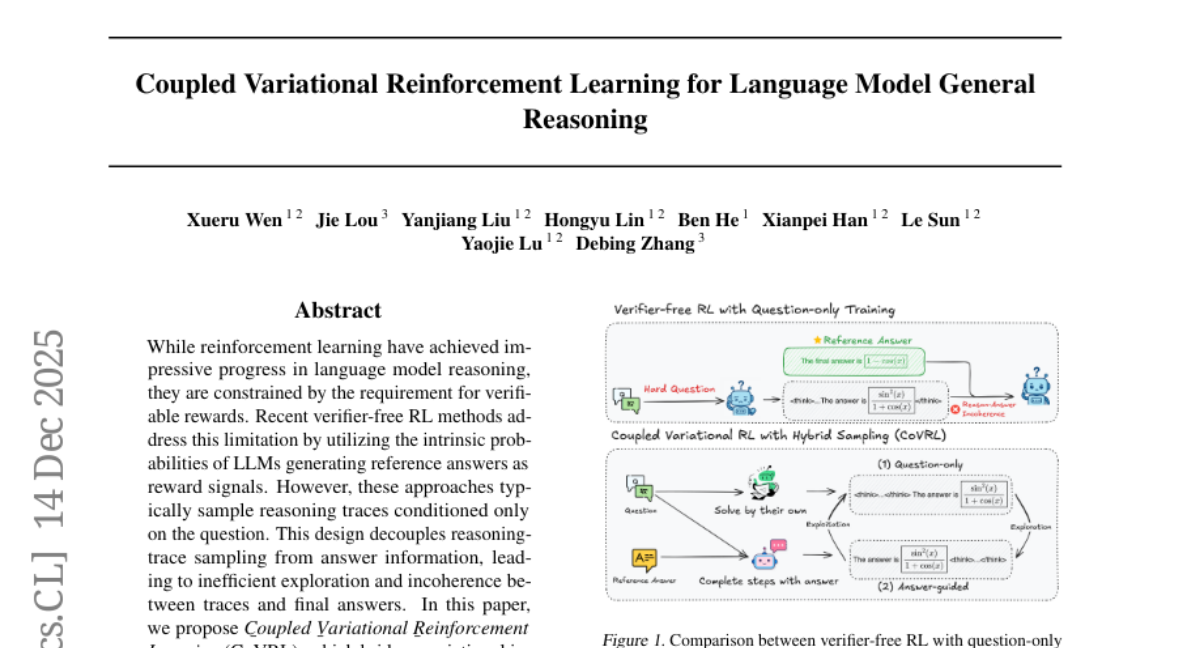
15. Coupled Variational Reinforcement Learning for Language Model General Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: CoVRL, variational inference, reinforcement learning, thought-answer coherence, efficient exploration
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance language model reasoning by integrating CoVRL, which combines variational inference and reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– CoVRL uses a hybrid sampling strategy that couples prior and posterior distributions, optimizing a composite distribution to enable more efficient exploration and thought-answer coherence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CoVRL shows a 12.4% performance improvement over the base model and a 2.3% gain over state-of-the-art verifier-free RL baselines in mathematical and general reasoning benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12576
16. TabReX : Tabular Referenceless eXplainable Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: TabReX, Large Language Models, Canonical Knowledge Graphs, LLM-guided matching, Trustworthy Evaluation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To create TabReX, a framework for evaluating tables generated by LLMs without relying on references, through graph-based reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of canonical knowledge graphs and LLM-guided matching to align source text with generated tables, computing scores for structural and factual fidelity.
– Introduction of TabReX-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark across multiple domains and perturbation types to assess metric robustness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TabReX demonstrates the highest correlation with expert rankings and provides reliable judgments and error traces even under complex perturbations.
– The framework offers controllable trade-offs between sensitivity and specificity, promoting fine-grained analysis and establishing a paradigm for explainable evaluations of structured generation systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15907

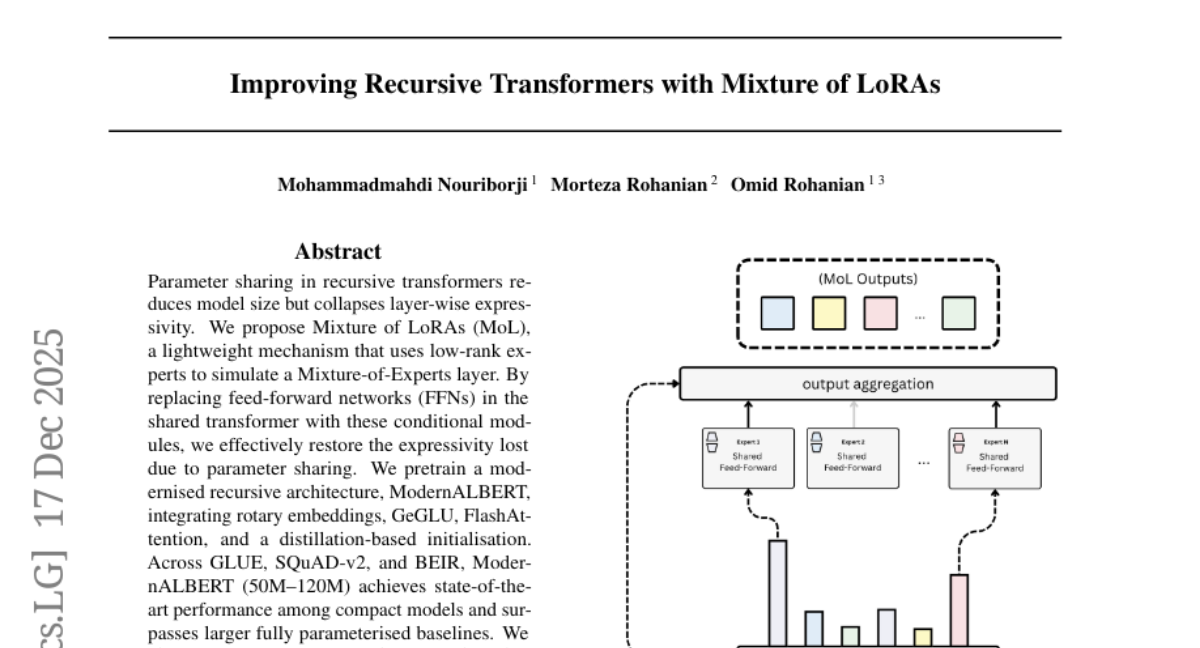
17. Improving Recursive Transformers with Mixture of LoRAs
🔑 Keywords: Mixture of LoRAs, parameter sharing, recursive transformers, ModernALBERT, conditional weight-space modulation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To restore expressivity in parameter-shared recursive transformers using Mixture of LoRAs, achieving state-of-the-art performance with compact models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the Mixture of LoRAs (MoL), incorporating Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) experts within a shared feed-forward network.
– Pretraining of ModernALBERT, integrating rotary embeddings, GeGLU, FlashAttention, and distillation-based initialization.
– Proposal of an expert-merging procedure for efficient inference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MoL effectively restores the expressivity lost in recursive transformers due to aggressive parameter sharing.
– ModernALBERT achieves state-of-the-art results among compact models and surpasses larger fully parameterised baselines across various benchmarks.
– The expert-merging procedure maintains accuracy while allowing efficient deployment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12880
18. Nemotron-Math: Efficient Long-Context Distillation of Mathematical Reasoning from Multi-Mode Supervision
🔑 Keywords: Nemotron-Math, AI-generated summary, mathematical reasoning dataset, Python tool-integrated reasoning, long-context training
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce Nemotron-Math, a large-scale dataset aimed at enhancing performance and robustness in mathematical reasoning by integrating diverse problems and efficient long-context training strategies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized multi-mode generation capabilities from gpt-oss-120b, integrating 85K AoPS problems and 262K StackExchange-Math problems. Employed a sequential bucketed strategy for efficient long-context training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Nemotron-Math outperforms OpenMathReasoning on AoPS problems and improves robustness and generalization, particularly on HLE-Math, while maintaining accuracy on math competition benchmarks. Achieved 100% maj@16 accuracy on AIME 2024 and 2025 with Python TIR integration.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15489

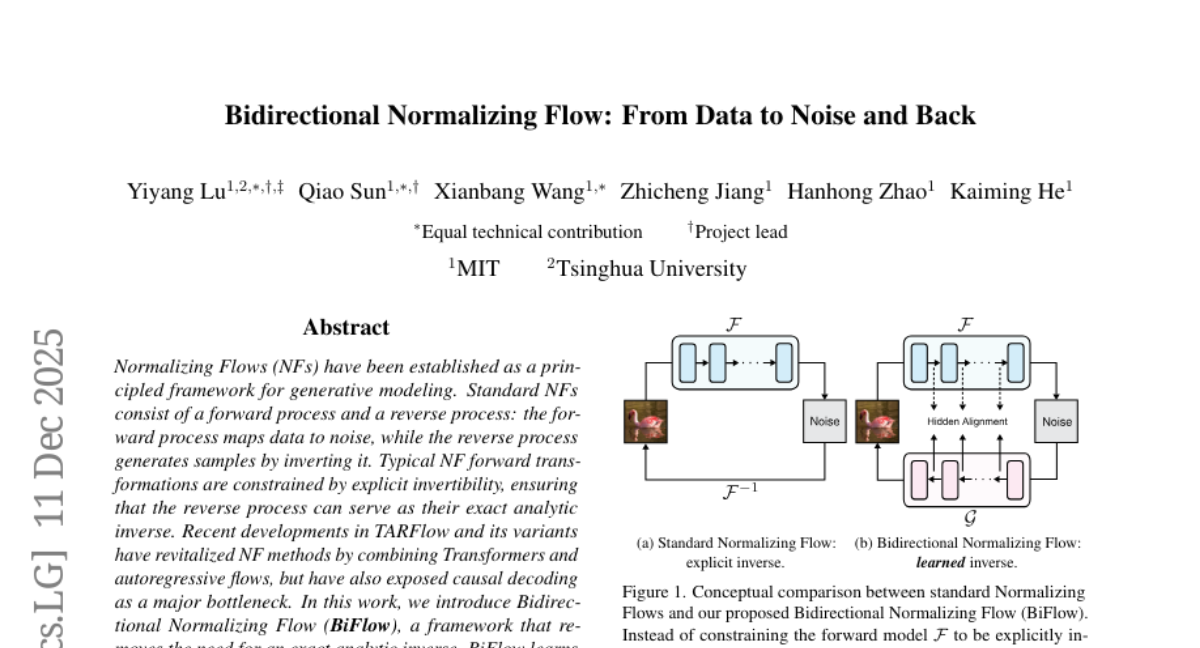
19. Bidirectional Normalizing Flow: From Data to Noise and Back
🔑 Keywords: Bidirectional Normalizing Flow, Generative Modelling, Noise-to-Data Inverse Mapping, Normalizing Flows, ImageNet
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Bidirectional Normalizing Flow (BiFlow) to enhance generative modeling by approximating the noise-to-data inverse mapping, thereby improving generation quality and sampling speed.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– BiFlow utilizes a reverse model to approximate the inverse mapping in Normalizing Flows, allowing for more flexible loss functions and architectures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BiFlow demonstrated improved generation quality and accelerated sampling by up to two orders of magnitude compared to its causal decoding counterpart. It achieves state-of-the-art results among NF-based methods on ImageNet.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.10953
20.

21. Sharing State Between Prompts and Programs
🔑 Keywords: Natural Language Programming, Interoperability, Shared Program State, Large Language Models, Python
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce shared program state to enable interoperability between natural language code and formal languages like Python.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a schema for natural function interfaces supporting natural code.
– Implement the shared program state within the Nightjar programming system.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Nightjar achieves comparable or higher task accuracy (+4-19%) than manual implementations while reducing code size by 39.6% on average.
– Runtime overhead is a tradeoff, ranging from 0.4x to 4.3x compared to manual methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14805

22. EmoCaliber: Advancing Reliable Visual Emotion Comprehension via Confidence Verbalization and Calibration
🔑 Keywords: EmoCaliber, Multimodal Large Language Model, Visual Emotion Comprehension, Confidence Estimation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance Visual Emotion Comprehension by integrating confidence-awareness in Multimodal Large Language Models to improve reliability and accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a three-stage training framework to equip the model with structured reasoning capabilities, teach verbalization of confidence, and calibrate confidence expression.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EmoCaliber showed superiority in both emotion prediction and confidence estimation, indicating its effectiveness as a reliable system for Visual Emotion Comprehension.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15528

23. Vibe Spaces for Creatively Connecting and Expressing Visual Concepts
🔑 Keywords: Vibe Blending, Vibe Space, hierarchical graph manifold, feature spaces, geodesics
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce and develop Vibe Blending, a novel task to generate coherent and meaningful image hybrids by revealing shared attributes between images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize Vibe Space, a hierarchical graph manifold, to learn low-dimensional geodesics in feature spaces like CLIP, facilitating smooth and semantically consistent transitions between concepts.
– Combine human judgments, LLM reasoning, and a geometric path-based difficulty score to evaluate creative quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Vibe Space produces image blends that are rated by humans as more creative and coherent compared to current methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.14884
24. MomaGraph: State-Aware Unified Scene Graphs with Vision-Language Model for Embodied Task Planning
🔑 Keywords: MomaGraph-R1, vision-language model, reinforcement learning, zero-shot task planner, scene graphs
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To create a unified scene representation for mobile manipulators in household environments that integrates spatial-functional relationships with part-level interactive elements to enhance task planning capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Trained a 7B vision-language model called MomaGraph-R1 using reinforcement learning on the MomaGraph-Scenes dataset and evaluated using the MomaGraph-Bench suite.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MomaGraph-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting task-oriented scene graphs and zero-shot task planning, demonstrating significant improvement over existing models, with 71.6% accuracy on the benchmark and effective generalization to real-world robot experiments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16909

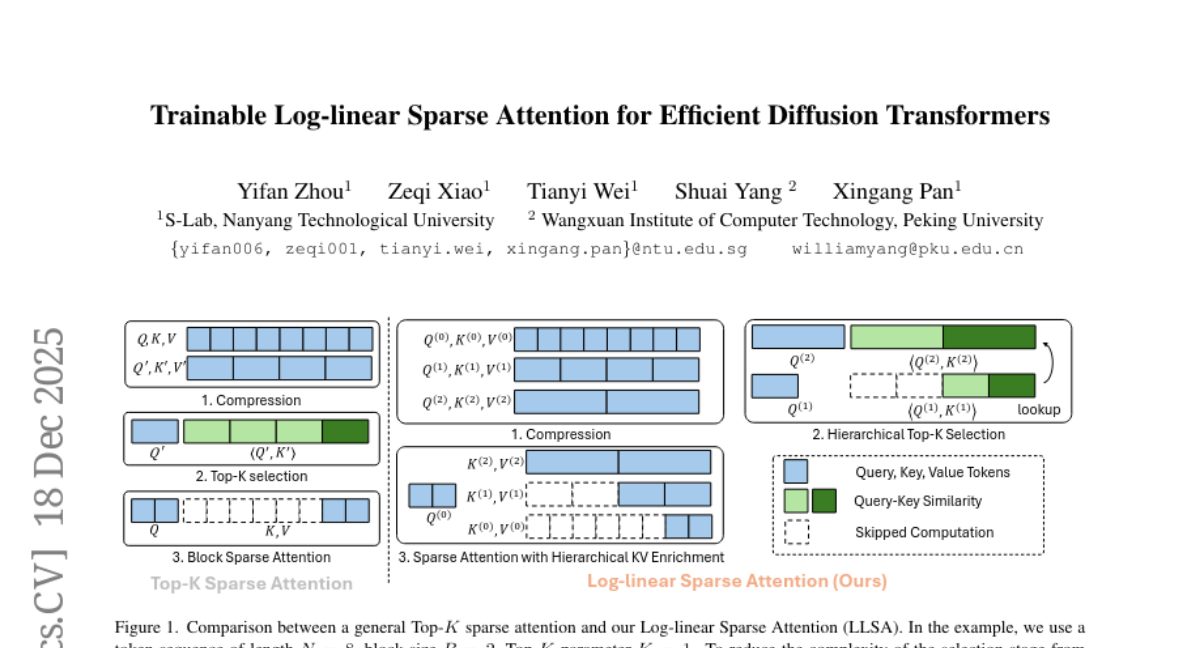
25. Trainable Log-linear Sparse Attention for Efficient Diffusion Transformers
🔑 Keywords: Log-linear Sparse Attention, Diffusion Transformers, Hierarchical structure, GPU implementation, Sparse Attention
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve the efficiency of Diffusion Transformers for long token sequences by introducing Log-linear Sparse Attention (LLSA) to reduce computational costs and enhance training speed without sacrificing quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors propose a novel sparse attention mechanism called LLSA, which uses a hierarchical structure to achieve log-linear complexity in token selection and attention computation. It incorporates hierarchical Top-K selection and a Hierarchical KV Enrichment mechanism and is supported by an efficient GPU implementation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LLSA significantly accelerates attention inference and DiT training on high-resolution image generation while maintaining generation quality. This approach offers a promising direction for efficient long-sequence DiT training.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16615
26. Make-It-Poseable: Feed-forward Latent Posing Model for 3D Humanoid Character Animation
🔑 Keywords: Make-It-Poseable, latent-space transformation, latent posing transformer, dense pose representation, 3D editing applications
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Make-It-Poseable, a novel framework that addresses challenges in character posing by reformulating it as a latent-space transformation problem.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework employs a latent posing transformer and shape tokens manipulated by skeletal motion, facilitated by a dense pose representation. Additional methods include latent-space supervision and an adaptive completion module.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Make-It-Poseable demonstrates superior posing quality and extends naturally to 3D editing applications, enhancing robustness and generalizability in computer graphics tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16767
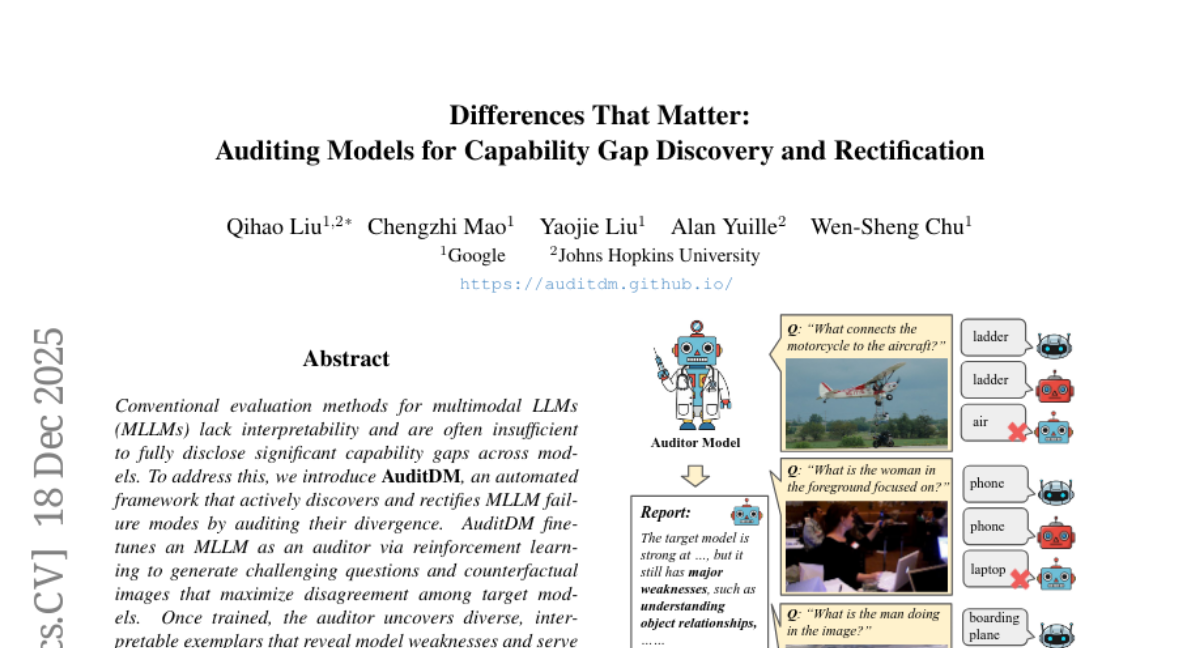
27. Differences That Matter: Auditing Models for Capability Gap Discovery and Rectification
🔑 Keywords: AuditDM, multimodal LLMs, reinforcement learning, model weaknesses, model auditing
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce AuditDM, an automated framework to identify and rectify failure modes in multimodal LLMs by generating challenging examples.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize reinforcement learning to fine-tune MLLMs, creating an auditor that generates questions and counterfactual images to expose model weaknesses without annotations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AuditDM discovers over 20 distinct failure types, enhancing model performance across 16 benchmarks, demonstrating that targeted model auditing can significantly improve AI models when data scaling diminishes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16921
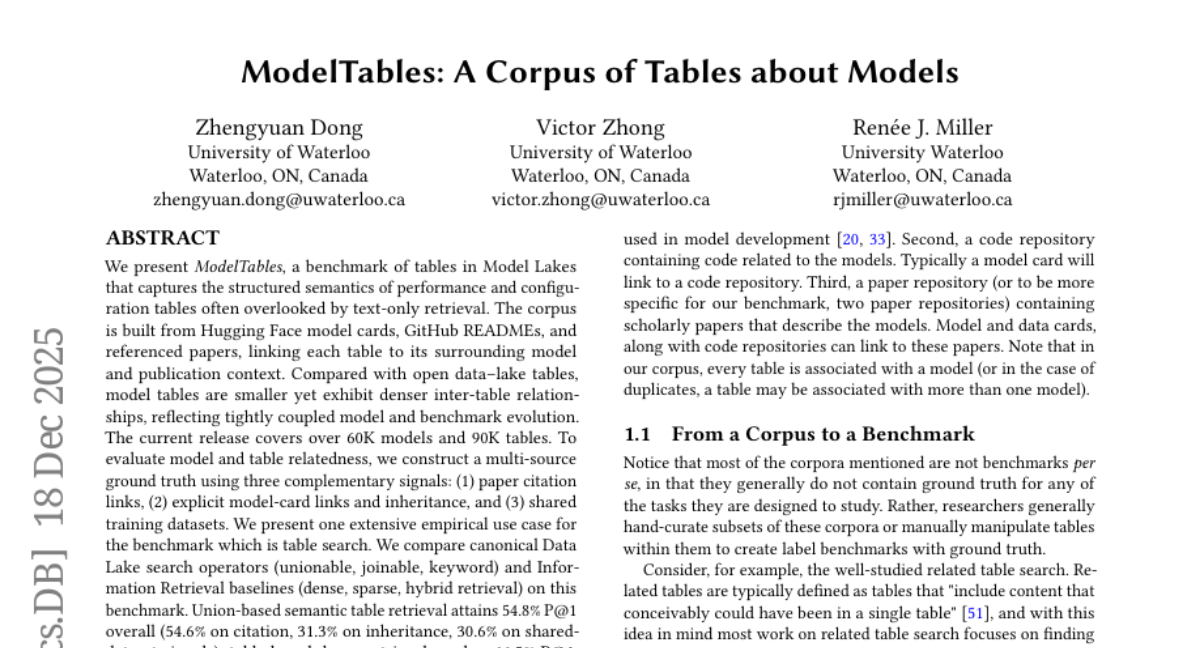
28. ModelTables: A Corpus of Tables about Models
🔑 Keywords: ModelTables, semantic retrieval, structured semantics, table-based retrieval, AI model
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To benchmark structured performance and configuration tables from various sources to enhance table-based retrieval and semantic understanding of AI model performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Construction of a multi-source ground truth using paper citation links, explicit model card links, and shared training datasets.
– Comparison of canonical Data Lake search operators and Information Retrieval baselines on the benchmark.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Union-based semantic table retrieval achieved 54.8% P@1, while dense retrieval reached 66.5%.
– Demonstrates room for advancement in table search methods.
– The release of ModelTables provides a large-scale benchmark, guiding the development of more accurate semantic retrieval and organization of structured model knowledge.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16106
29. RePlan: Reasoning-guided Region Planning for Complex Instruction-based Image Editing
🔑 Keywords: RePlan, vision-language planner, diffusion editor, Instruction-Visual Complexity, attention-region injection mechanism
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance instruction-based image editing by integrating a plan-then-execute framework, addressing IV-Complexity in intricate and ambiguous visual scenes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing a vision-language planner coupled with a diffusion editor to decompose and ground instructions for precise editing.
– Employing GRPO-based reinforcement learning to improve reasoning fidelity using limited data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RePlan consistently outperforms existing models, achieving superior regional precision and overall fidelity even with limited data, and establishes a benchmark in IV-Edit for knowledge-intensive edits.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16864

30. Exploration v.s. Exploitation: Rethinking RLVR through Clipping, Entropy, and Spurious Reward
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement learning, Verifiable rewards, Large Language Models, Spurious rewards, Entropy minimization
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper investigates the exploration-exploitation trade-off in reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards to enhance the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Examination of two mechanisms: spurious rewards and entropy minimization, in their impact on LLM reasoning performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Findings indicate that clipping bias under spurious rewards reduces policy entropy, leading to more deterministic outputs.
– Spurious rewards can improve performance beyond contaminated settings, explained by a proposed reward-misalignment model.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16912

31. Multimodal RewardBench 2: Evaluating Omni Reward Models for Interleaved Text and Image
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal RewardBench 2, Reward Models, Large Language Models, Multimodal Understanding, Interleaved Generation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Multimodal RewardBench 2 (MMRB2) as a benchmark for reward models focusing on multimodal understanding and interleaved text-image generation tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The benchmark consists of expert-annotated preference pairs across four tasks, utilizing responses from state-of-the-art models and agents, and a strong human-expert consensus through an ensemble filtering strategy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Evaluations show models like Gemini 3 Pro achieving 75-80% accuracy. Human experts exceed 90% accuracy, while other models like GPT-5 achieve 66-75%, indicating potential areas for improving reward models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16899

32. JustRL: Scaling a 1.5B LLM with a Simple RL Recipe
🔑 Keywords: JustRL, Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Single-Stage Training, Fixed Hyperparameters
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate if the increasing complexity in reinforcement learning for large language models is necessary by introducing JustRL, which simplifies the process.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented JustRL using single-stage training with fixed hyperparameters, and tested on two 1.5B reasoning models across nine mathematical benchmarks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– JustRL achieves state-of-the-art performance with 54.9% and 64.3% average accuracy, using half the compute compared to more complex approaches.
– The research suggests that added complexity may be unnecessary and that a stable, scaled-up baseline could eliminate certain issues without additional interventions.
– Standard tricks like explicit length penalties can hinder performance, highlighting the efficiency of the proposed minimal approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16649

33. The World is Your Canvas: Painting Promptable Events with Reference Images, Trajectories, and Text
🔑 Keywords: WorldCanvas, multimodal framework, user-directed simulation, trajectories, reference images
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to present WorldCanvas, a framework designed to generate coherent and controllable world events by integrating text, trajectories, and reference images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves a multimodal approach combining text, trajectories for motion and timing, and reference images for visual grounding, enabling rich simulations with multi-agent interactions and other complex scenarios.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework advances world models from passive predictors to interactive simulators, supporting the generation of expressive and consistent world events, preserving object identity even with temporary disappearance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16924
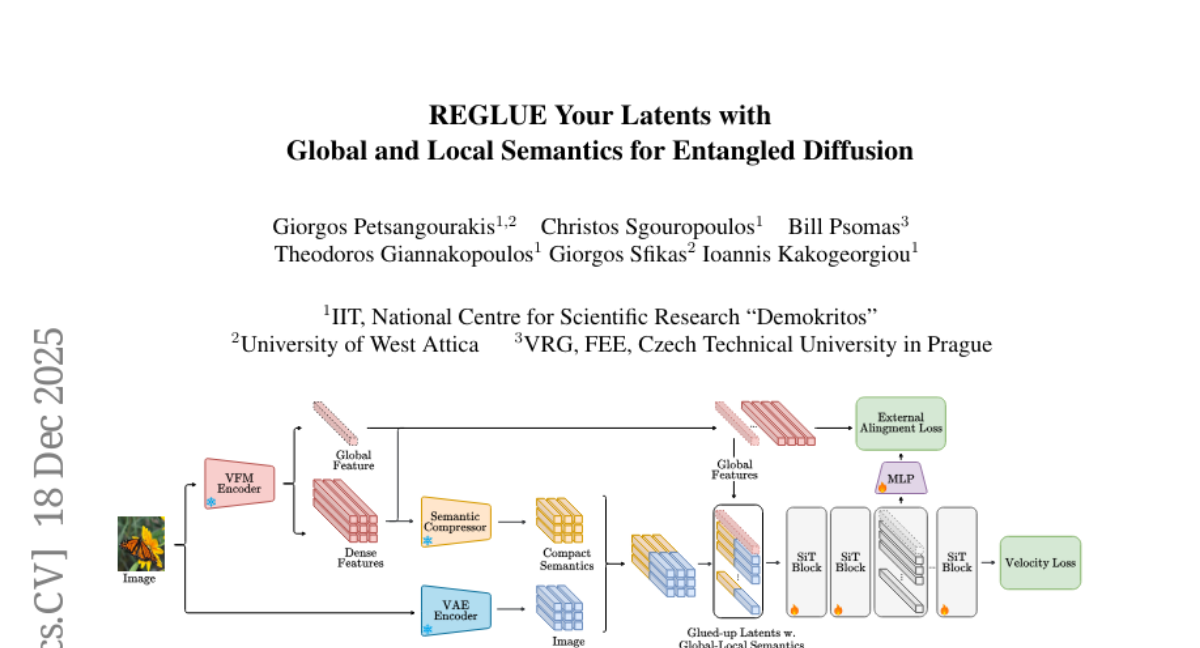
34. REGLUE Your Latents with Global and Local Semantics for Entangled Diffusion
🔑 Keywords: Latent diffusion models, AI-generated, Semantic supervision, Vision Foundation Models, Image synthesis
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance image synthesis by introducing REGLUE, a unified latent diffusion framework that improves semantic supervision and convergence through joint modeling of VAE latents, patch-level VFM semantics, and global tokens.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a lightweight convolutional semantic compressor to nonlinearly aggregate multi-layer VFM features, with entanglement in the VAE latents.
– Implementation of external alignment loss to regularize internal representations towards frozen VFM targets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– REGLUE improves FID and convergence on ImageNet 256×256 compared to various baselines, demonstrating the importance of spatial VFM semantics, non-linear compression, and the complementary role of global tokens and external alignment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16636
35. Generative Refocusing: Flexible Defocus Control from a Single Image
🔑 Keywords: Generative Refocusing, DeblurNet, BokehNet, semi-supervised training, text-guided adjustments
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a Generative Refocusing method for high-quality single-image refocusing with controllable bokeh and text-guided adjustments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of DeblurNet to recover all-in-focus images and BokehNet for creating controllable bokeh.
– Implementation of semi-supervised training combining synthetic paired data with unpaired real bokeh images, utilizing EXIF metadata for capturing real optical characteristics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated top performance in defocus deblurring, bokeh synthesis, and refocusing benchmarks through the proposed method.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16923
36. Seedance 1.5 pro: A Native Audio-Visual Joint Generation Foundation Model
🔑 Keywords: dual-branch Diffusion Transformer, cross-modal integration, Supervised Fine-Tuning, Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback, AI-generated video
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Seedance 1.5 pro, a model designed for native, joint audio-video generation using a cross-modal integration method for enhanced synchronicity and quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a dual-branch Diffusion Transformer architecture with a multi-stage data pipeline.
– Use of post-training optimizations including Supervised Fine-Tuning on quality datasets and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback with multi-dimensional reward models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Seedance 1.5 pro demonstrates superior audio-visual synchronization and narrative coherence, with precise multilingual and dialect lip-syncing, making it suitable for professional content creation.
– The acceleration framework significantly boosts inference speed by over 10X, enhancing its practicality and efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13507

37. Adaptation of Agentic AI
🔑 Keywords: agentic AI systems, foundation models, agent adaptations, tool adaptations, AI capabilities
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present a framework for agent and tool adaptation in agentic AI systems and clarify design strategies to enhance AI capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Unification of research into a systematic framework covering both agent and tool adaptations, with decomposition into various forms such as tool-execution-signaled and agent-output-signaled adaptations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework aids in understanding the design space of adaptation strategies, clarifies their trade-offs, and offers practical guidance for system design, while highlighting key open challenges and future opportunities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16301

38. LLaDA2.0: Scaling Up Diffusion Language Models to 100B
🔑 Keywords: LLaDA2.0, discrete diffusion, auto-regressive models, Mixture-of-Experts, parallel decoding
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to establish a new paradigm for transforming auto-regressive models into discrete diffusion large language models (dLLM), optimizing for frontier-scale deployment with superior performance and efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A novel 3-phase block-level WSD training scheme is introduced, which includes adaptive block-size diffusion, full-sequence diffusion, and compact block diffusion, alongside post-training alignment using SFT and DPO.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research successfully develops LLaDA2.0 models, specifically LLaDA2.0-mini (16B) and LLaDA2.0-flash (100B), which are optimized for practical deployment, showcasing enhanced performance and efficiency through innovative training and parallel decoding strategies. Both models have been open-sourced.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15745
