AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251223
1. DataFlow: An LLM-Driven Framework for Unified Data Preparation and Workflow Automation in the Era of Data-Centric AI
🔑 Keywords: DataFlow, LLM-driven, data preparation pipelines, system-level abstractions, PyTorch-style pipeline
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to enhance data quality and reproducibility for Large Language Models (LLMs) through the DataFlow framework, optimizing LLM performance with innovative, automatically generated data pipelines.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– DataFlow employs system-level abstractions for creating modular and composable data transformations, alongside a PyTorch-style API for constructing optimizable pipelines. It introduces DataFlow-Agent for converting natural-language specifications into executable pipelines using operator synthesis, pipeline planning, and iterative verification.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DataFlow greatly improves LLM performance. It achieves enhancements in execution accuracy and benchmarks, demonstrating practical, scalable, and reproducible data preparation, setting a foundation for data-centric AI development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16676

2. Region-Constraint In-Context Generation for Instructional Video Editing
🔑 Keywords: ReCo, Instructional Video Editing, In-Context Generation, Constraint Modeling, Attention Regularization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces ReCo, a new paradigm for instructional video editing aimed at improving editing accuracy and reducing token interference by incorporating constraint modeling and regularization techniques during in-context generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves width-wise concatenation of source and target videos for joint denoising, utilizing latent and attention regularization to manage discrepancies between editing and non-editing regions, and presenting a large-scale dataset, ReCo-Data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of ReCo in improving performance on major instruction-based video editing tasks, demonstrating its superiority due to the novel techniques employed.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17650
3. QuCo-RAG: Quantifying Uncertainty from the Pre-training Corpus for Dynamic Retrieval-Augmented Generation
🔑 Keywords: QuCo-RAG, hallucinations, large language models, pre-training data, corpus-grounded verification
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of QuCo-RAG is to reduce hallucinations in large language models using objective corpus statistics instead of unreliable internal model signals.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves quantifying uncertainty through identifying low-frequency entities before generation, and verifying entity co-occurrence during generation, leveraging Infini-gram for retrieval triggers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– QuCo-RAG demonstrates a 5-12 point EM improvement over state-of-the-art benchmarks and effectively transfers to models with different pre-training data, achieving up to a 14-point increase, showcasing its robustness and domain generalization in various applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19134

4. WorldWarp: Propagating 3D Geometry with Asynchronous Video Diffusion
🔑 Keywords: 3D geometric cache, spatio-temporal diffusion model, Gaussian Splatting, structural consistency, textural refinement
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the challenge of generating consistent long-range videos by integrating a 3D geometric cache with a spatio-temporal diffusion model.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a 3D structural anchor paired with a 2D generative refiner and maintain an online 3D geometric cache constructed through Gaussian Splatting.
– Implement a Spatio-Temporal Diffusion model with a varying noise schedule to manage occlusions and artifacts, ensuring both structural grounding and textural refinement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– WorldWarp effectively achieves state-of-the-art video fidelity by maintaining geometric consistency across video chunks, addressing previous limitations with occluding areas and complex camera trajectories.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19678
5. UCoder: Unsupervised Code Generation by Internal Probing of Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Large language models, Unsupervised framework, Internal Probing, Code generation, Resource-constrained scenarios
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce IPC, an unsupervised framework for code generation without relying on labeled datasets to reduce resource dependency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Leverage Internal Probing of LLMs by exploring problem space, test understanding, solution space, and knowledge reinforcement.
– Implement self-consistency mechanisms and representation-based quality estimation to train UCoder.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Unsupervised methods can achieve competitive performance in code generation, reducing reliance on labeled data and computational resources.
– Internal model states provide valuable insights for code quality and correctness, enabling effective training in resource-constrained scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17385
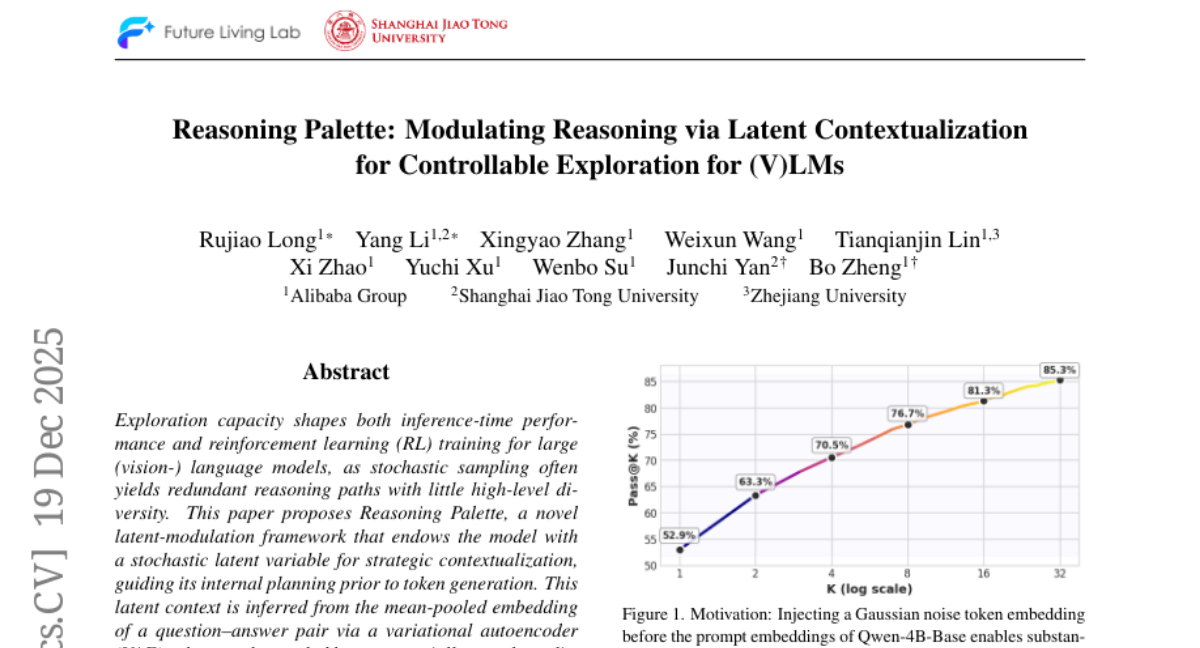
6. Reasoning Palette: Modulating Reasoning via Latent Contextualization for Controllable Exploration for (V)LMs
🔑 Keywords: Reasoning Palette, Latent-Modulation Framework, Stochastic Latent Variable, Variational Autoencoder, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance large language models’ reasoning capabilities and improve both inference and reinforcement learning performance through a novel framework called Reasoning Palette.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers employed a latent-modulation framework leveraging a stochastic latent variable for strategic contextualization, using a variational autoencoder to infer distinct reasoning contexts from mean-pooled embeddings. The latent context is then decoded into token prefixes to modulate the model’s internal reasoning trajectory.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments show that the Reasoning Palette facilitates structured exploration, significantly enhancing exploration efficiency and learning capability, thereby achieving consistent performance gains over standard reinforcement learning methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17206
7. StoryMem: Multi-shot Long Video Storytelling with Memory
🔑 Keywords: StoryMem, Memory-to-Video, keyframes, cinematic quality, multi-shot video generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance multi-shot video generation by transforming single-shot video diffusion models into storytellers with AI Native memory mechanisms.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a Memory-to-Video design that uses a compact memory bank of keyframes, semantic keyframe selection, and aesthetic preference filtering to ensure quality and consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– StoryMem provides superior cross-shot consistency and aesthetic quality, improving upon previous methods in coherent multi-shot video storytelling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19539

8. Does It Tie Out? Towards Autonomous Legal Agents in Venture Capital
🔑 Keywords: Legal AI, Capitalization tie-out, Multi-document reasoning, Evidence traceability, Applied legal intelligence
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the challenges of automating capitalization tie-out in legal diligence by proposing solutions that improve multi-document reasoning and evidence traceability within agentic systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analyzed and compared the performance of existing agentic systems in the context of capitalization tie-out.
– Proposed a world model architecture to facilitate tie-out automation and enhance applied legal intelligence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current agentic systems struggle to reliably deliver deterministic outputs required for the capitalization tie-out task.
– A world model architecture can provide a foundation for overcoming these challenges in applied legal workflows.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.18658

9. Name That Part: 3D Part Segmentation and Naming
🔑 Keywords: semantic 3D part segmentation, AI-generated, 3D part fields, multi-view vision features, unified ontology
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance semantic 3D part segmentation by aligning implicit 3D part representations with part descriptions through geometric, appearance, and semantic cues.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces ALIGN-Parts, utilizing set alignment and bipartite assignment for part naming. The method incorporates geometric cues, appearance from multi-view vision features, and language-model-generated semantic knowledge.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method supports open-vocabulary part naming and creates a unified ontology, demonstrating applications in scalable annotation with zero-shot matching capability. The research introduces two novel metrics for named 3D part segmentation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.18003
10. MatSpray: Fusing 2D Material World Knowledge on 3D Geometry
🔑 Keywords: 3D reconstruction, diffusion models, Gaussian Splatting, photorealism, relighting
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance relighting and photorealism in reconstructed scenes by integrating 2D material maps into 3D geometry using diffusion models and Gaussian Splatting.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework combines learning-based and projection-based approaches, applying diffusion models to generate 2D maps for material attributes like albedo, roughness, and metallicity, followed by integration into 3D geometry using Gaussian ray tracing and a neural refinement step.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed methods outperform existing techniques in both quantitative metrics and visual realism, improving the realism and efficiency of asset creation in content production pipelines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.18314
11. SecureCode v2.0: A Production-Grade Dataset for Training Security-Aware Code Generation Models
🔑 Keywords: SecureCode v2.0, Incident Grounding, Vulnerability Categories, Defense-in-Depth, OWASP Top 10:2025
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present SecureCode v2.0, a comprehensive dataset of security-focused coding examples that is production-grade and rigorously validated.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Constructed a dataset with 1,215 coding examples that passed structural validation and expert security review, incorporating SIEM integration, infrastructure hardening recommendations, and language-specific security implementations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SecureCode v2.0 fills the gap of existing datasets by providing grounded, scalable, and context-rich examples across multiple languages, aiding in realistic and effective secure coding practices.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.18542

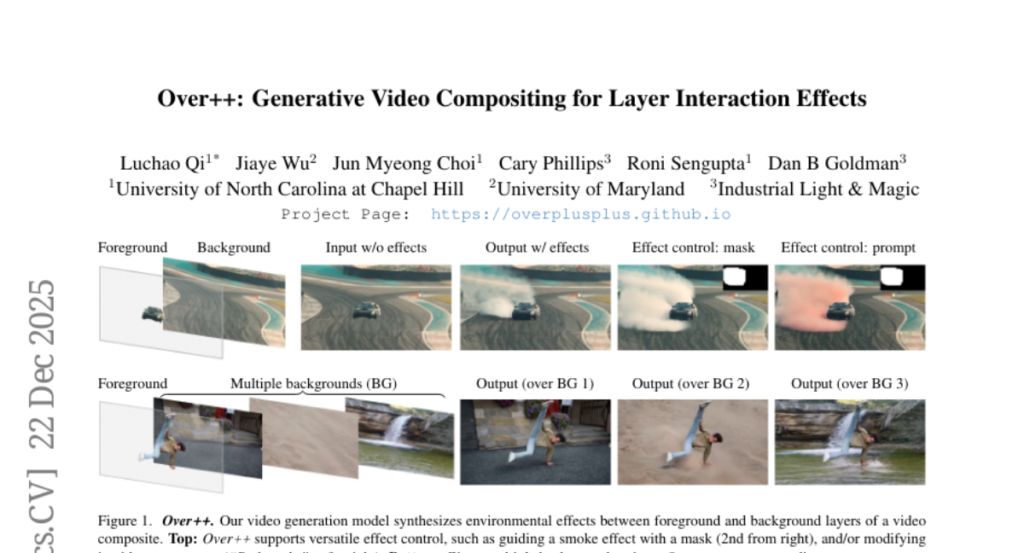
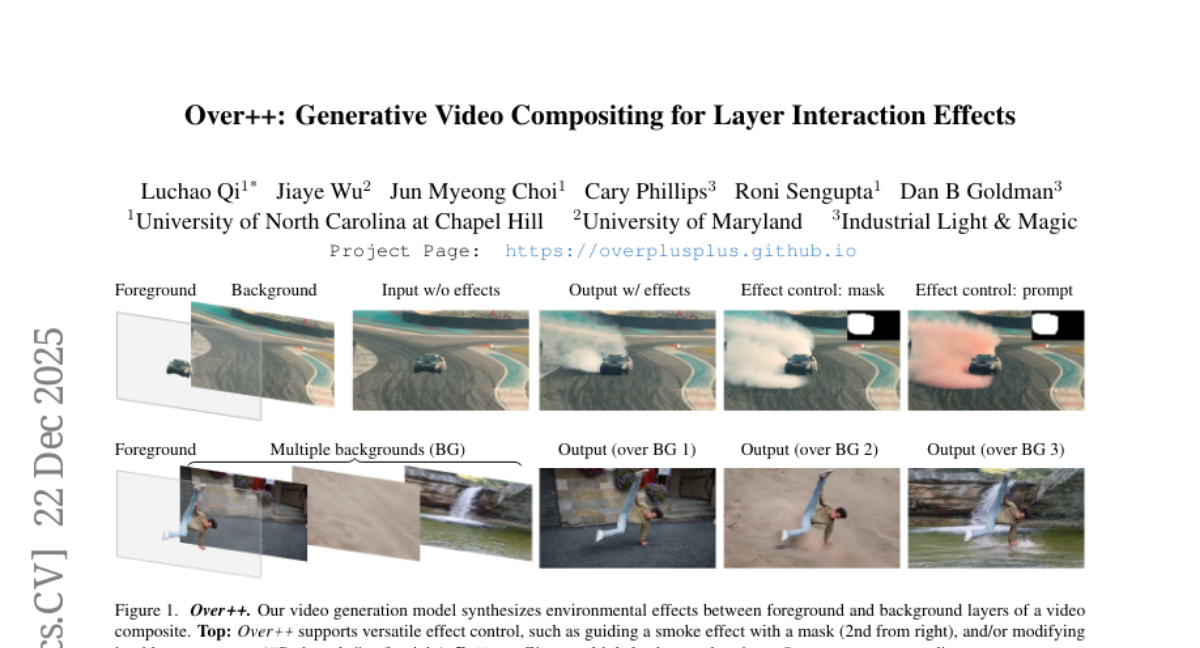
12. Over++: Generative Video Compositing for Layer Interaction Effects
🔑 Keywords: Over++, Effect generation, Text-driven editability, Scene preservation, Environmental effects
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Over++, a framework for generating realistic environmental effects based on text prompts that preserve the original video scene without relying on camera pose or dense annotations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a paired effect dataset and an unpaired augmentation strategy for text-driven editability.
– Supports optional mask control and keyframe guidance for enhanced effect generation without dense annotations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Over++ effectively produces diverse and realistic environmental effects, outperforming existing baselines in both effect generation and scene preservation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19661
13.

14. Brain-Grounded Axes for Reading and Steering LLM States
🔑 Keywords: Neurophysiological brain activity, Large Language Models, Interpretability, Controllability, SMN4Lang MEG dataset
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance the interpretability and controllability of large language models (LLMs) by using neurophysiological brain activity as a coordinate system.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Human brain activity is used to create a word-level brain atlas of phase-locking value patterns, extracting latent axes via ICA. Lightweight adapters map LLM hidden states to brain axes without fine-tuning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Neurophysiology-grounded axes are shown to provide interpretable and controllable handles for altering LLM behavior, with robust axes demonstrated in models like TinyLlama and GPT-2. The study supports a new interface for LLMs grounded in neurophysiology.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19399

15. Understanding Syllogistic Reasoning in LLMs from Formal and Natural Language Perspectives
🔑 Keywords: Syllogistic Reasoning, LLMs, Symbolic Inference, Natural Language Understanding
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research investigates syllogistic reasoning within LLMs, focusing on their logical and natural language capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed 14 large language models to evaluate their proficiency in syllogistic reasoning through symbolic inferences and natural language understanding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Found that while not all LLMs exhibit syllogistic reasoning uniformly, some models demonstrate perfect symbolic performance, indicating a shift towards formal reasoning mechanisms.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.12620

16. CASA: Cross-Attention via Self-Attention for Efficient Vision-Language Fusion
🔑 Keywords: Vision-language models, CASA, cross-attention, self-attention, multimodal applications
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance vision-language models’ performance on detailed visual tasks while maintaining scalability for long-context multimodal applications by developing a novel method called CASA.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors introduce CASA, a cross-attention method enhanced with self-attention, which facilitates local text-to-text interaction within the dedicated cross-attention layers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CASA significantly closes the performance gap with full token insertion on common image understanding benchmarks and retains the scalability of cross-attention models, proving efficient for tasks like streaming video captioning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19535

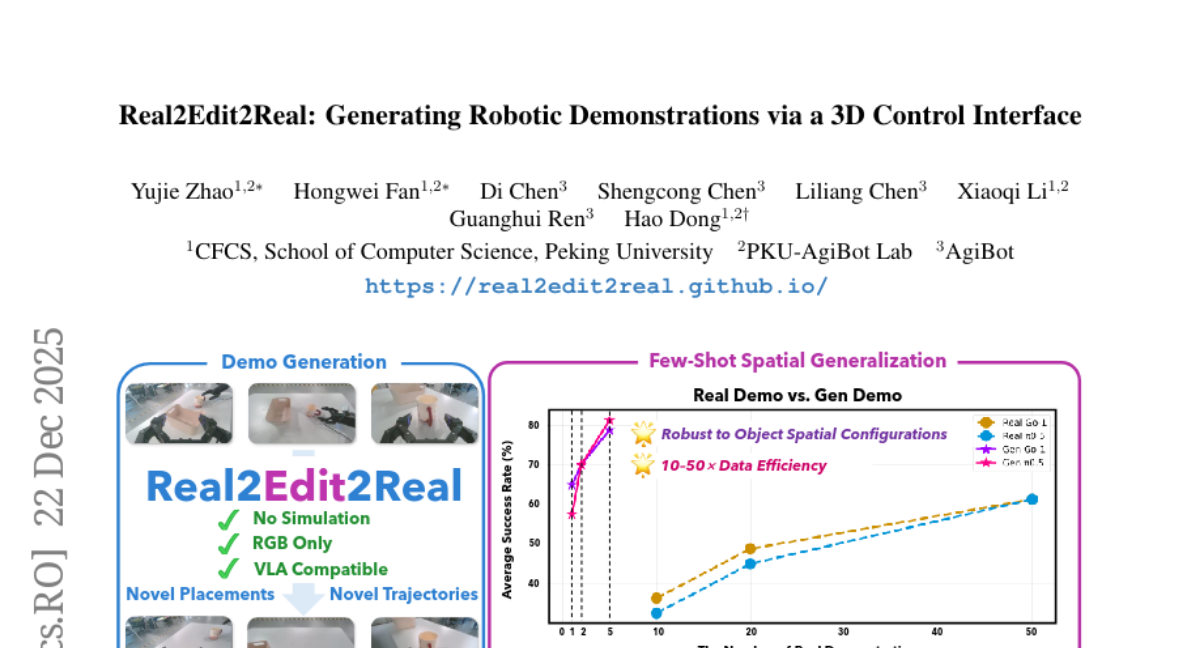
17. Real2Edit2Real: Generating Robotic Demonstrations via a 3D Control Interface
🔑 Keywords: 3D reconstruction, video synthesis, robot learning, data efficiency, manipulation tasks
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve data efficiency in robot learning by generating new manipulation demonstrations through a framework called Real2Edit2Real.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework uses 3D reconstruction to generate new manipulation trajectories, performs depth-reliable 3D editing, and utilizes a multi-conditional video generation model to synthesize spatially augmented multi-view manipulation videos.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments show that policies trained on data from 1-5 source demonstrations can match or surpass those trained on 50 real-world demonstrations, indicating improved data efficiency by up to 10-50x. The framework also shows flexibility in height and texture editing, suggesting its potential as a unified data generation framework.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19402
18. MobileWorld: Benchmarking Autonomous Mobile Agents in Agent-User Interactive, and MCP-Augmented Environments
🔑 Keywords: MobileWorld, long-horizon tasks, cross-application interactions, agent-user interaction, MCP-augmented tasks
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to introduce MobileWorld, a benchmark designed to reflect real-world mobile usage scenarios more accurately and challenge current models’ capabilities significantly beyond the existing benchmarks like AndroidWorld.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research involves developing MobileWorld with 201 tasks across 20 applications. It emphasizes long-horizon and multi-application tasks, and extends beyond typical GUI manipulation by introducing categories like agent-user interactions and MCP-augmented tasks. A snapshot-based container environment and precise functional verifications are used for robust evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study finds that current models show a sharp performance drop on MobileWorld compared to AndroidWorld, with the best results achieving a 51.7% success rate. It highlights current models’ struggles with user interactions and MCP calls, indicating a need for more robust, next-generation mobile intelligence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19432

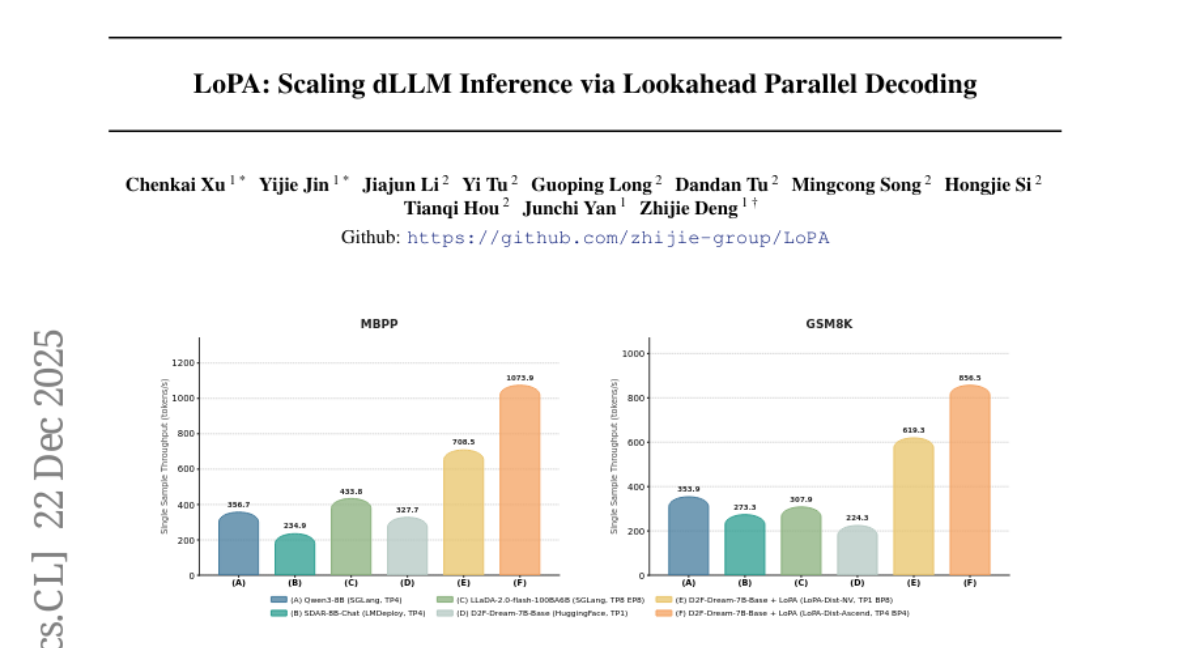
19. LoPA: Scaling dLLM Inference via Lookahead Parallel Decoding
🔑 Keywords: LoPA, Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs), Token Filling Order (TFO), multi-GPU deployment, Branch Parallelism (BP)
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance the parallelism of diffusion large language models by introducing LoPA, a training-free algorithm that optimizes Token Filling Order to accelerate inference.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– LoPA is implemented as a plug-and-play algorithm that explores different candidate Token Filling Orders through parallel branches, selecting the optimal one based on branch confidence. It also involves developing a specialized multi-device inference system to support Branch Parallelism.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The application of LoPA significantly increases the tokens per forward pass in state-of-the-art D2F models, achieving superior throughput and maintaining high performance compared to the baseline. The system achieves a throughput of 1073.9 tokens per second using multi-GPU deployment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16229
20. GenEnv: Difficulty-Aligned Co-Evolution Between LLM Agents and Environment Simulators
🔑 Keywords: GenEnv, Large Language Model, generative environment simulator, co-evolutionary game, data-efficient
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces GenEnv, a co-evolutionary framework to enhance Large Language Model (LLM) agent performance through a generative environment simulator, addressing the limitations of high costs and static nature of real-world interaction data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– GenEnv establishes a difficulty-aligned co-evolutionary game between an agent and a scalable, generative environment simulator, using a dynamic curriculum policy that adapts to the agent’s capabilities guided by the α-Curriculum Reward.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GenEnv improves agent performance by up to 40.3% over 7B baselines across five benchmarks and achieves superior data efficiency compared to Gemini 2.5 Pro-based offline data augmentation while using significantly less data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19682

21. LoGoPlanner: Localization Grounded Navigation Policy with Metric-aware Visual Geometry
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, end-to-end learning, localization, trajectory planning, obstacle avoidance
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce LoGoPlanner, an end-to-end navigation framework addressing trajectory planning challenges in unstructured environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– LoGoPlanner utilizes a long-horizon visual-geometry backbone for implicit state estimation, reconstructs scene geometry for environmental awareness, and conditions policy on geometry to reduce error propagation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LoGoPlanner shows a 27.3% improvement over oracle-localization baselines, enhancing planning consistency and obstacle avoidance in both simulation and real-world environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19629
22. Can LLMs Estimate Student Struggles? Human-AI Difficulty Alignment with Proficiency Simulation for Item Difficulty Prediction
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Human-AI Difficulty Alignment, machine consensus, introspection
💡 Category: AI in Education
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate the capability of Large Language Models to estimate human cognitive difficulty and align with human perspectives.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted large-scale empirical analysis on Human-AI Difficulty Alignment using over 20 models across domains such as medical knowledge and mathematical reasoning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Found systematic misalignment where increasing model size leads to a shared machine consensus rather than aligning with human perceptions.
– High performance in problem-solving does not equate to an understanding of human cognitive struggles, with models failing to introspect and recognize their own limitations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.18880
23. Infinite-Homography as Robust Conditioning for Camera-Controlled Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: InfCam, camera-pose-faithful, video diffusion models, infinite homography warping
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance camera-controlled novel-view video generation with high fidelity to specified camera poses.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a depth-free framework called InfCam using infinite homography warping.
– Integrated a data augmentation pipeline to increase trajectory diversity in synthetic datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– InfCam significantly improves camera-pose accuracy and visual fidelity, effectively bridging synthetic and real-world data performances.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17040

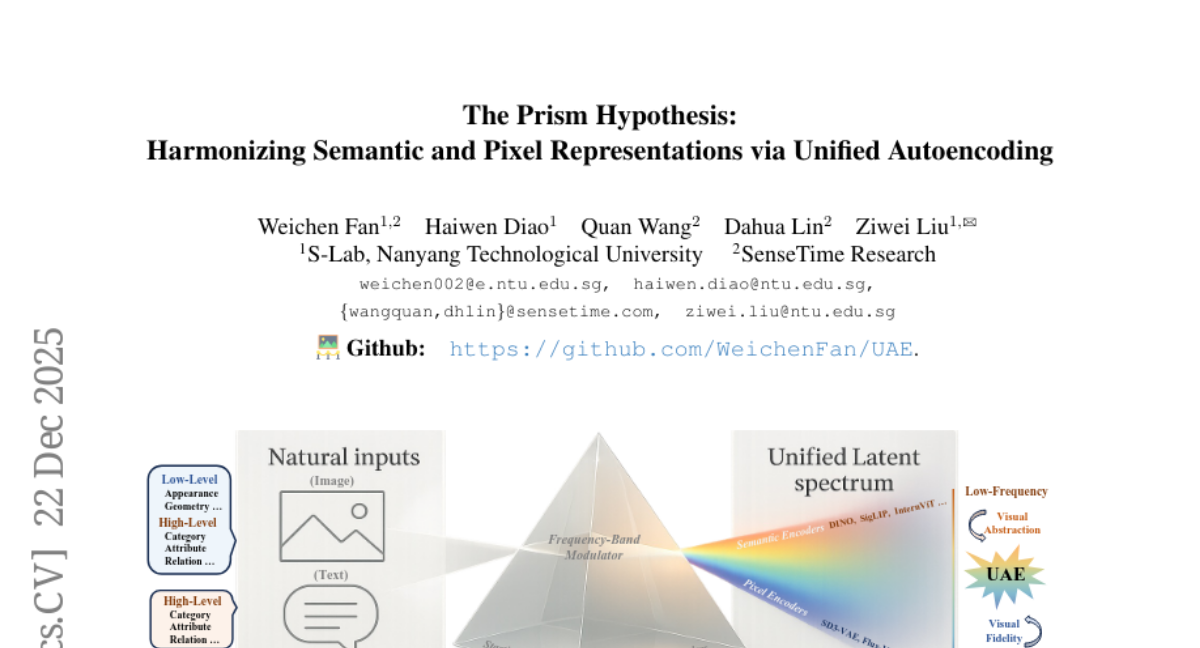
24. The Prism Hypothesis: Harmonizing Semantic and Pixel Representations via Unified Autoencoding
🔑 Keywords: Unified Autoencoding, frequency-band modulator, Prism Hypothesis, semantic encoders, pixel encoders
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the spectral characteristics of semantic and pixel encoders and propose Unified Autoencoding (UAE) to combine semantic and pixel-level information effectively.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Systematic analysis of encoder spectral characteristics and conceptual development of the Prism Hypothesis. Implementation of a frequency-band modulator to harmonize semantic and pixel details.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The UAE model unifies semantic abstraction and pixel fidelity, delivering state-of-the-art performance on ImageNet and MS-COCO benchmarks by creating a cohesive latent space with both semantic and pixel-level information.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19693