AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251224

1. SemanticGen: Video Generation in Semantic Space
🔑 Keywords: SemanticGen, Diffusion Model, VAE Latents, Semantic Space, Video Generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce SemanticGen to address slow convergence and computational costs in video generation through a novel two-stage diffusion model approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a two-stage generation process: first stage generates compact Semantic Video Features using a Diffusion Model for global video layout, followed by generating VAE Latents conditioned on these features in the second stage to produce the final video output.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SemanticGen achieves faster convergence, is computationally efficient for long video generation, and produces high-quality videos, outperforming state-of-the-art models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.20619

2. LongVideoAgent: Multi-Agent Reasoning with Long Videos
🔑 Keywords: Multi-agent framework, Temporal grounding, Vision agent, Long-video QA, Reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance long-video question answering (QA) by improving temporal grounding and effectively leveraging both visual and textual data through a multi-agent framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces a multi-agent framework consisting of a master LLM, grounding agent, and vision agent, where reinforcement learning is employed to encourage concise and efficient multi-agent cooperation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed system significantly surpasses existing non-agent baselines in performance on episode-level datasets, showcasing improved reasoning and planning due to reinforcement learning, and providing interpretable trajectories.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.20618

3. MemEvolve: Meta-Evolution of Agent Memory Systems
🔑 Keywords: MemEvolve, self-evolving memory systems, large language model, meta-evolutionary framework
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present MemEvolve, a meta-evolutionary framework that enhances self-evolving memory systems by evolving both agents’ experiential knowledge and memory architecture, thus improving performance and generalization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of EvolveLab, a unified self-evolving memory codebase that integrates twelve representative memory systems into a modular design space, providing a standardized implementation and experimental arena.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MemEvolve achieves substantial performance gains, enhancing frameworks like SmolAgent and Flash-Searcher by up to 17.06%.
– Demonstrates strong cross-task and cross-LLM generalization, with effective memory architecture transfer across diverse benchmarks and backbone models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.18746

4. Reinforcement Learning for Self-Improving Agent with Skill Library
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Skill Library, SAGE, Large Language Models, Self-Improvement
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents’ self-improvement capabilities by systematically integrating skills from a skill library using a novel RL framework called SAGE.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Skill Augmented GRPO for self-Evolution (SAGE), which uses Sequential Rollout to iteratively deploy agents across similar tasks, accumulating skills in a library and augmenting rewards with Skill-integrated Reward.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SAGE achieved 8.9% higher scenario goal completion while requiring 26% fewer interaction steps and generating 59% fewer tokens, demonstrating superior performance in accuracy and efficiency compared to existing methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17102

5. INTELLECT-3: Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Mixture-of-Experts, Reinforcement Learning, Open-source, AI Systems and Tools, INTELLECT-3
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introducing INTELLECT-3, a large Mixture-of-Experts model, aimed at achieving state-of-the-art performances across various benchmarks using reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a 106B-parameter Mixture-of-Experts model trained with large-scale reinforcement learning on an end-to-end RL infrastructure stack, supported by the open-source prime-rl framework for scalable asynchronous reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model not only achieves top performance for its size but also outperforms many larger models in math, code, science, and reasoning benchmarks. The complete model and its development infrastructure have been open-sourced, facilitating community engagement and further development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.16144

6. Active Intelligence in Video Avatars via Closed-loop World Modeling
🔑 Keywords: ORCA, Internal World Model, Dual-System Architecture, POMDP, Video Avatar
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to advance video avatar intelligence from passive animation to active, goal-oriented behavior using a framework called ORCA.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A dual innovation strategy is applied, featuring a closed-loop OTAR cycle and a hierarchical dual-system architecture, to enable autonomous task completion in video avatars.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ORCA demonstrates significant improvements in task success rate and behavioral coherence, outclassing traditional open-loop and non-reflective baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.20615

7. Scaling Laws for Code: Every Programming Language Matters
🔑 Keywords: scaling laws, multilingual pre-training, programming languages, Code LLMs, interpreted languages
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Explore scaling laws for multilingual code pre-training, focusing on language-specific impacts and optimal token allocation across programming languages.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted over 1000 experiments with model sizes ranging from 0.2B to 14B parameters and dataset sizes up to 1T tokens, analyzing performance across different programming languages.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Revealed that interpreted languages benefit more from increased model size and data than compiled languages. Proposed a proportion-dependent multilingual scaling law to enhance cross-lingual abilities and optimize token allocation for superior performance across all languages.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.13472

8. Memory-T1: Reinforcement Learning for Temporal Reasoning in Multi-session Agents
🔑 Keywords: Temporal Reasoning, Reinforcement Learning, Time-Dialog benchmark, Temporal Consistency, Evidence Grounding
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance temporal reasoning over long dialogues by using a reinforcement learning-based framework, Memory-T1.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Memory-T1 employs a coarse-to-fine strategy to prune dialogue histories into candidate sets, followed by a reinforcement learning agent to select evidence sessions, optimized by a multi-level reward function for temporal consistency, evidence grounding, and answer accuracy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Memory-T1 achieved state-of-the-art performance on the Time-Dialog benchmark, improving robustness up to 128k tokens and outperforming established models by 10.2%, with demonstrated 15.0% performance gains due to temporal consistency and evidence grounding rewards.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.20092

9. Toxicity Ahead: Forecasting Conversational Derailment on GitHub
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, conversational derailment, proactive moderation, GitHub, Sentiment shifts
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a framework using Large Language Models to predict and prevent conversational derailment in OSS communities on GitHub.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A dataset of derailed and non-toxic threads was curated, and a Large Language Model-based two-step prompting pipeline was utilized for prediction, involving the generation of Summaries of Conversation Dynamics and the use of Least-to-Most prompting.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The structured prompting framework effectively forecasts conversational derailment on GitHub with high F1-scores, outperforming existing NLP baselines and supporting proactive and explainable moderation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15031

10.

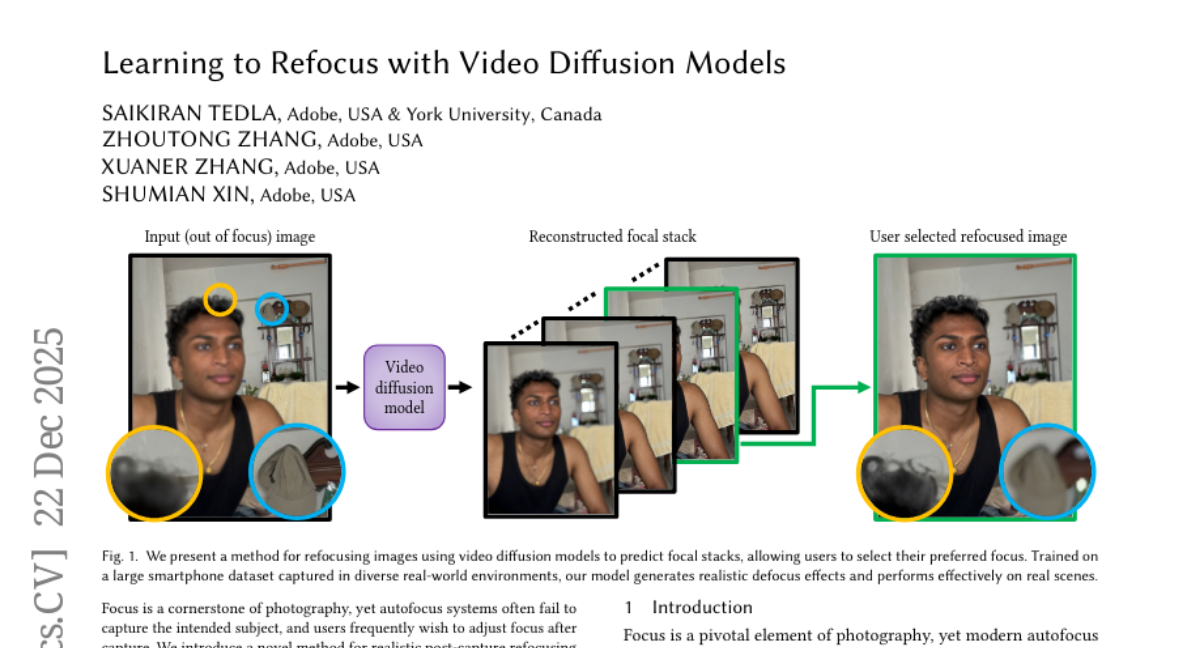
11. Learning to Refocus with Video Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: Realistic Post-Capture Refocusing, Video Diffusion Models, Focal Stack, Smartphone Photography
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a new method using video diffusion models for post-capture refocusing from a single defocused image to improve focus-editing capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a video sequence representing a focal stack to enable interactive refocusing and support with a large-scale focal stack dataset collected under various smartphone conditions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method surpasses existing approaches in perceptual quality and robustness, showcasing potential for advanced focus-editing in everyday photography.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19823
12. QuantiPhy: A Quantitative Benchmark Evaluating Physical Reasoning Abilities of Vision-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: QuantiPhy, VLMs, physical reasoning, numerical accuracy, kinematic properties
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to quantitatively evaluate vision perception models’ ability to reason about physical properties like size, velocity, and acceleration using the QuantiPhy benchmark.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– QuantiPhy comprises over 3.3K video-text instances with numerical ground truth, assessing models’ numerical accuracy in estimating physical properties, standardized prompts, and scoring for fair comparisons.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study identifies a consistent gap between qualitative plausibility and numerical correctness in state-of-the-art VLMs, which rely more on pre-trained world knowledge than visual and textual inputs for quantitative reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19526

13. Multi-LLM Thematic Analysis with Dual Reliability Metrics: Combining Cohen’s Kappa and Semantic Similarity for Qualitative Research Validation
🔑 Keywords: Thematic Analysis, Ensemble Validation, Cohen’s Kappa, Cosine Similarity, AI-assisted Qualitative Research
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address reliability challenges in qualitative research by introducing a multi-perspective validation framework for LLM-based thematic analysis.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Combines ensemble validation with dual reliability metrics: Cohen’s Kappa for inter-rater agreement and cosine similarity for semantic consistency.
– Evaluated on psychedelic art therapy interview transcripts using three leading LLMs: Gemini 2.5 Pro, GPT-4o, and Claude 3.5 Sonnet.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Gemini 2.5 Pro achieved the highest reliability with κ= 0.907 and a cosine similarity of 95.3%, showcasing the effectiveness of the multi-run ensemble approach.
– The framework proved successful in extracting consensus themes, providing a robust foundation for AI-assisted qualitative research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.20352

14. Simulstream: Open-Source Toolkit for Evaluation and Demonstration of Streaming Speech-to-Text Translation Systems
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Streaming Speech-to-Text Translation, incremental decoding, re-translation methods, web interface
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce simulstream, an open-source framework for evaluating and demonstrating streaming speech-to-text translation systems, with a focus on long-form audio processing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Supports incremental decoding and re-translation methods, providing a unified framework for comparing quality and latency. Incorporates an interactive web interface for system demonstrations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Simulstream is highlighted as a solution to the limitations of SimulEval, offering features for long-form audio processing and an easy demonstration platform.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.17648

15. FaithLens: Detecting and Explaining Faithfulness Hallucination
🔑 Keywords: FaithLens, Large Language Models, Faithfulness Hallucination Detection, Explanation Quality, Trustworthiness
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce FaithLens, a cost-efficient model designed to detect faithfulness hallucinations in outputs from large language models (LLMs) and provide corresponding explanations to enhance trustworthiness in applications like retrieval-augmented generation and summarization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized advanced LLMs for synthesizing training data with high-quality explanations, applying a data filtering strategy to maintain label correctness, explanation quality, and data diversity.
– Fine-tuned the model using rule-based reinforcement learning focused on prediction correctness and explanation quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FaithLens, an 8B-parameter model, demonstrated superior performance over advanced models like GPT-4.1 and o3 across 12 tasks, excelling in delivering efficient and effective high-quality explanations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.20182

16. SAM Audio: Segment Anything in Audio
🔑 Keywords: SAM Audio, diffusion transformer, general audio separation, multimodal AI, audio benchmarks
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a foundation model ( SAM Audio) for general audio separation that incorporates multiple prompting modalities—text, visual, and temporal spans.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a diffusion transformer architecture and trained the model with flow matching on large-scale audio datasets covering speech, music, and general sounds.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SAM Audio model achieves state-of-the-art performance in separating various audio types, surpassing existing general-purpose and specialized systems, and includes a new real-world separation benchmark evaluated with human-like precision.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.18099

17. Step-DeepResearch Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Step-DeepResearch, data synthesis strategy, progressive training, Checklist-style Judger, ADR-Bench
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to develop an end-to-end agent, Step-DeepResearch, to enhance deep research capabilities by addressing real-world demands for intent recognition, long-horizon decision-making, and cross-source verification.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a Data Synthesis Strategy based on Atomic Capabilities and used a progressive training path from agentic mid-training to SFT and RL to improve planning and report writing.
– Introduced a Checklist-style Judger to boost robustness and established ADR-Bench to evaluate performance in the Chinese domain.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Step-DeepResearch achieves significant improvements over existing models, scoring 61.4% on the Scale AI Research Rubrics and outperforming comparable models in ADR-Bench, demonstrating expert-level capabilities with cost-efficiency in medium-sized models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.20491

18. SpatialTree: How Spatial Abilities Branch Out in MLLMs
🔑 Keywords: SpatialTree, spatial abilities, multimodal LLMs, cross-level transfer, auto-think strategy
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate and enhance spatial abilities in multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) through the formation of a hierarchy inspired by cognitive science.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed SpatialTree, organizing spatial abilities into a hierarchy of four levels and benchmarked these levels to study interdependencies among 27 sub-abilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study discovered orthogonality in low-level skills, with higher-level skills showing strong correlation, indicating interdependency. Supervised fine-tuning revealed a negative transfer at low levels but beneficial cross-level transfer. An auto-think strategy was proposed to enhance performance consistently across all levels in MLLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.20617
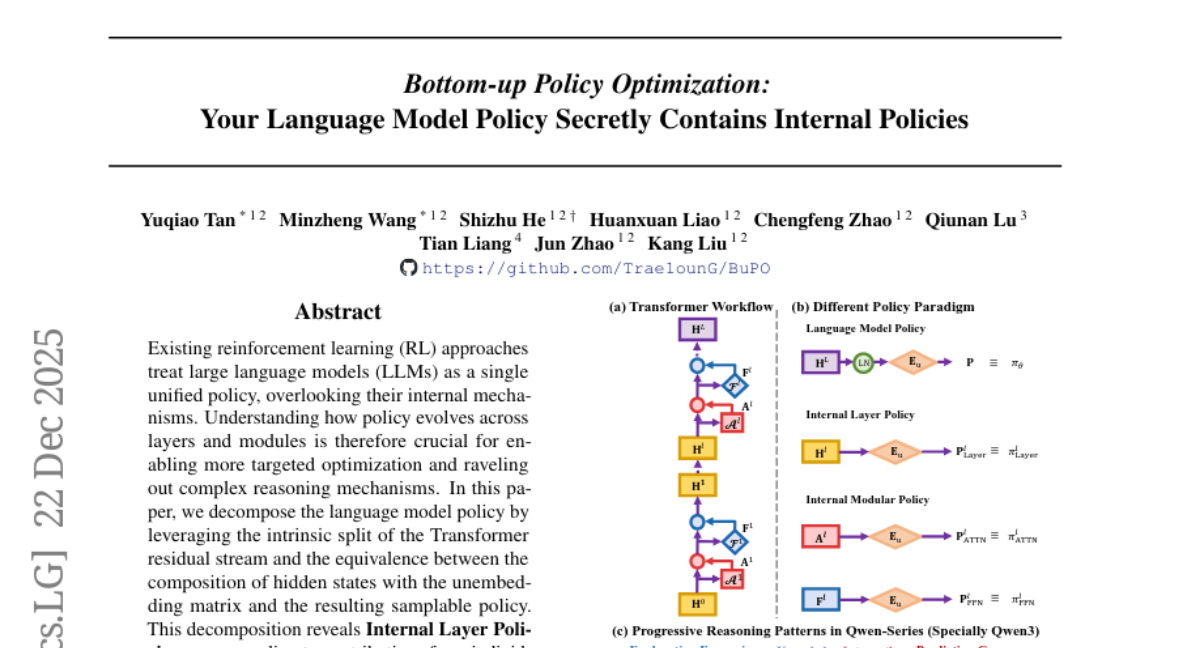
19. Bottom-up Policy Optimization: Your Language Model Policy Secretly Contains Internal Policies
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Transformer Residual Stream, Internal Layer Policies, Bottom-up Policy Optimization
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance performance on complex reasoning tasks by decomposing and optimizing the internal policies of large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– This research utilizes insights from the Transformer residual stream and internal modular policies to propose a decomposition approach and introduces Bottom-up Policy Optimization for targeted reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Bottom-up Policy Optimization improves foundational reasoning capabilities and demonstrates superior performance on complex reasoning benchmarks by directly optimizing internal layer policies early in the training process.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.19673