AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20251230
1. Coupling Experts and Routers in Mixture-of-Experts via an Auxiliary Loss
🔑 Keywords: Mixture-of-Experts, expert-router coupling, internal activations, expert specialization
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the lack of explicit constraints in Mixture-of-Experts models by introducing ERC loss to enhance model performance and computational efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce ERC loss, a lightweight auxiliary loss, applying constraints on internal activations and using expert-specific proxy tokens.
– Conduct pre-training on MoE-LLMs with extensive analysis across trillions of tokens.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ERC loss improves model performance by monitoring and aligning router decisions with expert capabilities, providing efficient and scalable expert specialization during training.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23447

2. Yume-1.5: A Text-Controlled Interactive World Generation Model
🔑 Keywords: diffusion models, real-time performance, text-controlled generation, interactive worlds, framework
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address challenges in generating interactive and explorable worlds using diffusion models, focusing on enhancing real-time performance and enabling text-controlled generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a novel framework, \method, designed to generate realistic and continuous worlds from a single image or text prompt.
– The framework consists of three key components: long-video generation with context compression and linear attention, real-time streaming using bidirectional attention distillation, and an enhanced text embedding scheme for text-controlled world event generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method successfully overcomes previous limitations related to parameter sizes, inference step duration, and historical context growth, offering a viable solution for real-time, text-controlled interactive world generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22096
3. Diffusion Knows Transparency: Repurposing Video Diffusion for Transparent Object Depth and Normal Estimation
🔑 Keywords: Transparent objects, Video diffusion models, TransPhy3D, DKT, Zero-shot SOTA
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the perception of transparent objects by leveraging modern video diffusion models to synthesize and predict depth and normals in transparent and reflective scenes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Creation of TransPhy3D, a synthetic video dataset, coupled with Blender/Cycles rendering for RGB, depth, and normals.
– Use of video-to-video translation for depth using lightweight LoRA adapters within a video diffusion model.
– Co-training with existing datasets to ensure temporally consistent predictions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The developed model, DKT, sets new zero-shot SOTA benchmarks on both real and synthetic video datasets concerning transparency.
– Achieves improved accuracy and temporal consistency in scenarios involving translucent and reflective surfaces, outperforming previous depth estimators.
– Demonstrates that generative video priors can be effectively adapted for robust perception in realistic manipulation tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23705

4. Dream-VL & Dream-VLA: Open Vision-Language and Vision-Language-Action Models with Diffusion Language Model Backbone
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion-based VLM, Dream-VL, Dream-VLA, Vision-Language-Action, Parallel Generation
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to construct Vision-Language Models upon diffusion-based large language models to overcome limitations seen in autoregressive Large Vision-Language Models, enhancing efficacy in visual planning and dynamic robotic control.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of Dream-VL, a diffusion-based Vision-Language Model, and Dream-VLA, a Vision-Language-Action model, developed through continuous pre-training on open robotic datasets. The models utilize a bidirectional diffusion backbone suited for action chunking and parallel generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Dream-VLA exhibited superior performance with significant success rates in various environments, outperforming leading models and showcasing faster convergence in fine-tuning. The release of Dream-VL and Dream-VLA encourages further community research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22615

5. GRAN-TED: Generating Robust, Aligned, and Nuanced Text Embedding for Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: text encoder, TED-6K, GRAN-TED, visual synthesis, diffusion models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address challenges in developing efficient and effective text encoders for text-to-image and text-to-video diffusion models by introducing the GRAN-TED paradigm and the TED-6K benchmark.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced TED-6K, a text-only benchmark for efficient and robust assessment of encoder quality.
– Developed a two-stage training paradigm for improved text encoder performance, involving fine-tuning on a Multimodal Large Language Model and a layer-wise weighting method.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The GRAN-TED encoder achieves state-of-the-art performance on the TED-6K benchmark and leads to significant improvements in text-to-image and text-to-video generation.
– TED-6K allows for approximately 750 times faster evaluation compared to training a diffusion model from scratch.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.15560

6. Web World Models
🔑 Keywords: Web World Models, large language models, latent state, structured exploration
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Web World Models (WWMs) that merge web frameworks and large language models to create controllable, open-ended environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented world state and “physics” using web code; used large language models for context and narratives; constructed various applications like an infinite travel atlas and fictional galaxy explorers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified design principles, such as separating code-defined rules from model-driven imagination, to demonstrate that web stacks can be scalable substrates for world models, balancing control and open-ended possibilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23676

7. OmniAgent: Audio-Guided Active Perception Agent for Omnimodal Audio-Video Understanding
🔑 Keywords: OmniAgent, multimodal alignment, audio-guided perception, state-of-the-art performance
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce OmniAgent, an audio-guided agent aimed at improving fine-grained audio-visual reasoning and addressing multimodal alignment challenges.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a novel coarse-to-fine audio-guided perception paradigm to dynamically orchestrate specialized tools, focusing perceptual attention on task-relevant cues.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OmniAgent achieves significant performance improvements, outperforming leading models by 10% – 20% accuracy on audio-video understanding benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23646

8. Training AI Co-Scientists Using Rubric Rewards
🔑 Keywords: AI co-scientists, research plan generation, reinforcement learning, cross-domain generalization, Qwen3-30B-A3B
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the capability of AI co-scientists in generating effective research plans that adhere to specific aims and constraints.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Leveraged existing research papers to create a scalable training corpus and trained language models using reinforcement learning with self-grading to improve research plan generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The finetuned Qwen3-30B-A3B model generates preferred research plans for 70% of research goals and approves 84% of grading rubrics. It shows 12-22% improvements and significant cross-domain efficacy, including in medical research contexts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23707

9. Nested Browser-Use Learning for Agentic Information Seeking
🔑 Keywords: Information-seeking agents, Browser interaction, Deep web
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance the capabilities of Information-seeking agents by introducing a novel framework called Nested Browser-Use Learning (NestBrowse) to improve interaction control, separate from page exploration.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– NestBrowse employs a minimal and complete browser-action framework using a nested structure to allow effective deep-web information acquisition.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Empirical results on deep Information-seeking benchmarks demonstrate the clear practical benefits of NestBrowse, highlighting its efficiency and flexibility.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23647

10. SurgWorld: Learning Surgical Robot Policies from Videos via World Modeling
🔑 Keywords: Surgical robotics, Vision Language Action (VLA) models, Synthetic data, AI Native, Autonomous surgical skill
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to overcome the limitation of data scarcity in achieving fully autonomous surgical robots by utilizing large-scale Vision Language Action models and synthetic data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed SurgWorld, a world model for surgical physical AI, using the Surgical Action Text Alignment (SATA) dataset to produce varied and realistic synthetic surgical videos.
– Implemented an inverse dynamics model to infer pseudokinematics from these synthetic videos, creating paired video action data for training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that surgical VLA policy models trained with augmented data from SurgWorld outperformed those trained solely on real demonstrations, offering a scalable approach to developing efficient and generalizable surgical robot policies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23162

11. Robo-Dopamine: General Process Reward Modeling for High-Precision Robotic Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Reward Functions, Dopamine-Reward, Policy-Invariant Reward Shaping
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address challenges in reinforcement learning for robotics by designing effective reward functions using Dopamine-Reward, a novel approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves learning a general-purpose, step-aware process reward model called General Reward Model (GRM) using a large dataset and techniques like Step-wise Reward Discretization and Multi-Perspective Reward Fusion.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed Dopamine-RL framework demonstrates significant improvements in policy learning efficiency and accuracy in reward assessment, achieving high success rates with minimal training times in various simulated and real-world tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23703

12. An Information Theoretic Perspective on Agentic System Design
🔑 Keywords: Agentic language model, Multi-LM architectures, Compressor-Predictor systems, Information-theoretic framework
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the design concerns of compressor-predictor systems in Agentic language model systems by introducing an information-theoretic framework to quantify compression quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs a mutual information estimator to assess the compression quality independently of specific tasks and conducts an empirical analysis across five datasets and three model families.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Findings indicate that larger compressors are more accurate and token-efficient than smaller ones, leading to improved performance. Scaling compressors proves more beneficial compared to scaling predictors, significantly enhancing cost efficiency in practical applications like “Deep Research.”
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.21720

13. Bridging Your Imagination with Audio-Video Generation via a Unified Director
🔑 Keywords: Mixture-of-Transformers, script drafting, keyframe consistency, AI-generated films, UniMAGE
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to unify script drafting and keyframe generation into a single AI framework to enable non-experts to create coherent video scripts and consistent keyframes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of the Mixture-of-Transformers architecture with a novel “interleaving, then disentangling” training approach, including Interleaved Concept Learning and Disentangled Expert Learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The UniMAGE model surpasses other open-source models in generating logically coherent video scripts and visually consistent keyframe images.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23222

14. KernelEvolve: Scaling Agentic Kernel Coding for Heterogeneous AI Accelerators at Meta
🔑 Keywords: DLRM, KernelEvolve, heterogeneous hardware, AI accelerators, PyTorch
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address system challenges in DLRM by creating a fast and efficient training and inference framework, focusing on model architecture diversity, kernel primitive diversity, and hardware heterogeneity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed KernelEvolve, a framework that automates kernel generation and optimization by using multiple programming abstractions and a graph-based search process, adaptable to different hardware architectures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– KernelEvolve achieves a 100% correctness rate on the KernelBench suite and PyTorch ATen operators, significantly reducing development time and improving performance across various production use cases and heterogeneous AI systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23236

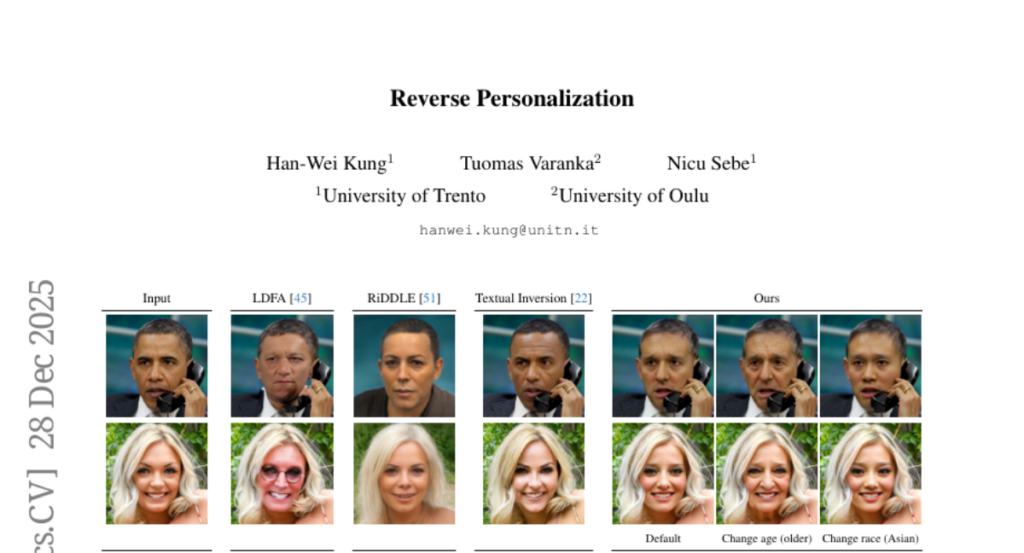
15. Reverse Personalization
🔑 Keywords: reverse personalization framework, conditional diffusion inversion, attribute-controllable face anonymization, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces a reverse personalization framework for face anonymization, focusing on balancing identity removal and image quality while allowing control over facial attributes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– It uses conditional diffusion inversion to manipulate images directly without text prompts and introduces an identity-guided conditioning branch to generalize beyond the model’s training data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method achieves a state-of-the-art balance in preserving attributes and image quality while effectively removing identities, offering a significant improvement over previous methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22984
16. Self-Evaluation Unlocks Any-Step Text-to-Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: Self-Evaluating Model, text-to-image generation, self-evaluation mechanism, few-step generation, unified framework
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Self-E, a novel text-to-image generation model trained from scratch, which supports any-step inference.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a self-evaluation mechanism to dynamically self-teach and combines local learning with self-driven global matching, differentiating from traditional diffusion or distillation-based models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Self-E demonstrates high-quality performance even at low step counts and is competitive with state-of-the-art models, showcasing improvements in both ultra-fast few-step and high-quality long-trajectory sampling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22374
17.

18. Shape of Thought: When Distribution Matters More than Correctness in Reasoning Tasks
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-Thought (CoT), Synthetic Datasets, Language Model, Reasoning Tasks
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the potential of improving language models’ reasoning capabilities through training on synthetic datasets of chain-of-thought traces, even when these are incorrect.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted experiments using synthetic datasets versus human-annotated datasets.
– Tested hypotheses by paraphrasing human-annotated traces to match the model’s distribution and introducing flawed CoT traces.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Synthetic datasets closer to the model’s language distribution can enhance reasoning performance better than human-annotated datasets.
– The presence of partially correct reasoning in incorrect traces offers valuable learning potential for models.
– Correct answers are not always indicative of a sound reasoning process.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22255

19. Introducing TrGLUE and SentiTurca: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Turkish General Language Understanding and Sentiment Analysis
🔑 Keywords: TrGLUE, SentiTurca, Natural Language Understanding, transformers, benchmarks
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces TrGLUE, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating natural language understanding (NLU) tasks in the Turkish language, addressing the gap in existing resources for Turkish NLU.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research involves creating Turkish-native corpora and using a semi-automated pipeline that integrates LLM-based annotation and human validation to ensure linguistic naturalness and minimize translation artifacts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The establishment of TrGLUE aims to provide a robust evaluation framework for Turkish NLU, empowering researchers with resources and insights into creating high-quality semi-automated datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22100

20. Knot Forcing: Taming Autoregressive Video Diffusion Models for Real-time Infinite Interactive Portrait Animation
🔑 Keywords: Real-time portrait animation, Temporal coherence, Visual fidelity, Interactive applications, Streaming framework
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to create a novel streaming framework for real-time portrait animation that ensures high visual fidelity, temporal coherence, ultra-low latency, and responsive control, suitable for applications like virtual assistants and live avatars.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a three-part framework called Knot Forcing, which includes: (1) a chunk-wise generation strategy with global identity preservation and sliding window attention, (2) a temporal knot module for smooth transitions between video chunks, and (3) a “running ahead” mechanism to maintain long-term semantic coherence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Knot Forcing achieved high-fidelity, temporally consistent real-time portrait animation with strong visual stability, even on consumer-grade GPUs, overcoming challenges like error accumulation and motion discontinuities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.21734

21. ProGuard: Towards Proactive Multimodal Safeguard
🔑 Keywords: Generative models, ProGuard, Multimodal safety, Reinforcement learning, Out-of-distribution
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study proposes ProGuard, a proactive vision-language guard to identify and describe out-of-distribution safety risks in generative models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– ProGuard utilizes a modality-balanced dataset of 87K samples for training through reinforcement learning, focusing on consistent moderation across text, image, and text-image inputs. The model is further enhanced by introducing an OOD safety category inference task and employs a synonym-bank-based similarity reward.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ProGuard matches closed-source large models on binary safety classification and significantly outperforms existing open-source models in categorizing unsafe content, enhancing OOD risk detection by 52.6% and description by 64.8%.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23573
22. Quantile Rendering: Efficiently Embedding High-dimensional Feature on 3D Gaussian Splatting
🔑 Keywords: Open-vocabulary segmentation, 3D Gaussian Splatting, Quantile Rendering, 3D neural network
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Quantile Rendering (Q-Render) to efficiently handle high-dimensional features for Open-vocabulary segmentation in 3D.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop Q-Render, a novel strategy that sparsely samples 3D Gaussians with dominant influence, and integrate it into a Gaussian Splatting Network (GS-Net) for predicting Gaussian features.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Q-Render and GS-Net outperform existing methods, enabling real-time rendering with significant speedup (~43.7x) on 512-D feature maps.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.20927

23. Monadic Context Engineering
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Monadic Context Engineering, AI agents, Functors, Monads
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Monadic Context Engineering (MCE) as a novel architectural paradigm designed to improve the construction of autonomous agents through the use of algebraic structures like Functors, Applicative Functors, and Monads.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MCE is applied to agent workflows, leveraging algebraic properties to manage complex tasks such as state propagation, error handling, and asynchronous execution. The paper demonstrates how Monads and Monad Transformers facilitate robust sequential and parallel processing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study concludes that MCE allows for the building of complex, resilient, and efficient AI agents by composing simple, verifiable components, and extends the framework to describe Meta-Agents that dynamically orchestrate sub-agent workflows through metaprogramming.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22431

24. YOLO-Master: MOE-Accelerated with Specialized Transformers for Enhanced Real-time Detection
🔑 Keywords: Real-Time Object Detection, YOLO-Master, Adaptive Computation, Sparse Mixture-of-Experts
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– This study aimed to enhance Real-Time Object Detection by addressing the inefficiencies in current YOLO-like architectures through dynamic resource allocation based on scene complexity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors introduced YOLO-Master, employing an Efficient Sparse Mixture-of-Experts block with a lightweight dynamic routing network to allocate computational resources adaptively for each input.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– YOLO-Master demonstrated superior detection performance, achieving 42.4% AP with 1.62ms latency on MS COCO, making it 0.8% more accurate and 17.8% faster than YOLOv13-N.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23273

25. VL-LN Bench: Towards Long-horizon Goal-oriented Navigation with Active Dialogs
🔑 Keywords: Dialog-Enabled Navigation, Interactive Learning, Vision Language-Language Navigation, oracle, dialog-augmented trajectories
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a new benchmark for dialog-enabled navigation tasks to enhance the real-world applicability of embodied agents by resolving ambiguous instructions through active dialog.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed the Interactive Instance Object Navigation (IION) task, allowing agents to use natural language dialogues with an oracle while navigating.
– Presented the Vision Language-Language Navigation (VL-LN) benchmark with a large-scale dataset and evaluation protocol to train and assess dialog-enabled navigation models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated significant improvements in navigation models equipped with dialog capabilities over baselines, proving the effectiveness of VL-LN for advancing dialog-enabled embodied navigation research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22342
26. Video-BrowseComp: Benchmarking Agentic Video Research on Open Web
🔑 Keywords: Modal gap, Autonomous agents, Proactive video reasoning, Temporal visual evidence, Metadata-sparse domains
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the gap in modality by presenting a benchmark for proactive, open-web video reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Video-BrowseComp, a benchmark with 210 questions, requiring navigation of video timelines and verification against external claims.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current models, like GPT-5.1 (w/ Search), show limited performance with only 15.24% accuracy, indicating reliance on textual proxies and challenges in metadata-sparse, dynamic video environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23044

27. DiRL: An Efficient Post-Training Framework for Diffusion Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Language Models, DiRL, Reinforcement Learning, Math Performance
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce an efficient post-training framework, DiRL, for optimizing Diffusion Language Models with enhanced performance in complex reasoning tasks, particularly mathematics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a framework combining FlexAttention-accelerated blockwise training with LMDeploy-optimized inference, facilitating two-stage post-training (Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning).
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed DiRL framework and its unbiased Group Relative Policy Optimization (DiPO) achieve state-of-the-art math performance among diffusion models, surpassing comparable models in the Qwen2.5 series on several benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22234

28. Act2Goal: From World Model To General Goal-conditioned Policy
🔑 Keywords: goal-conditioned visual world model, Multi-Scale Temporal Hashing, end-to-end cross-attention, hindsight goal relabeling, LoRA-based finetuning
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main objective is to achieve robust long-horizon robotic manipulation through structured planning and adaptive execution using a goal-conditioned visual world model integrated with multi-scale temporal control.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Act2Goal employs a goal-conditioned visual world model that generates intermediate visual states for long-horizon tasks.
– Multi-Scale Temporal Hashing (MSTH) is used to decompose trajectories into dense proximal frames for fine control and sparse distal frames for task consistency.
– Techniques like end-to-end cross-attention and hindsight goal relabeling with LoRA-based finetuning are utilized for enhanced adaptability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Act2Goal demonstrates a significant improvement in success rates from 30% to 90% on complex tasks without external supervision, displaying strong zero-shot generalization to new conditions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23541

29. SpotEdit: Selective Region Editing in Diffusion Transformers
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Transformer, Image Editing, SpotEdit, Computational Efficiency, Contextual Coherence
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to optimize image editing by addressing the inefficiency in current methods that modify all image regions uniformly, questioning the necessity of regenerating unchanged areas.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The proposed framework, SpotEdit, integrates two components: SpotSelector, which leverages perceptual similarity to identify and skip stable regions, and SpotFusion, which uses dynamic fusion to blend features while maintaining contextual coherence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SpotEdit enhances image editing by reducing unnecessary computations and preserving the fidelity of unmodified regions, hence achieving more efficient and precise modifications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22323

30. Stream-DiffVSR: Low-Latency Streamable Video Super-Resolution via Auto-Regressive Diffusion
🔑 Keywords: Video Super-Resolution, Diffusion-Based Methods, Online Deployment, Low Latency
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop Stream-DiffVSR, a causally conditioned diffusion framework that enhances efficiency and reduces latency for online video super-resolution (VSR) applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a four-step distilled denoiser, Auto-regressive Temporal Guidance (ARTG) to provide motion-aligned cues, and a Temporal Processor Module (TPM) to maintain temporal coherence in video processing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Stream-DiffVSR processes 720p frames significantly faster than previous methods, with latency reduced from over 4600 seconds to 0.328 seconds on an RTX4090 GPU. It achieves the lowest latency reported for diffusion-based VSR, making it suitable for low-latency online deployment, while improving perceptual quality over the state-of-the-art.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23709
31. SmartSnap: Proactive Evidence Seeking for Self-Verifying Agents
🔑 Keywords: Agentic Reinforcement Learning, Self-Verifying Agent, LLM-as-a-Judge, SmartSnap
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address scalability issues in agentic reinforcement learning by introducing a proactive self-verification approach for autonomous agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of the SmartSnap paradigm that enables agents to perform self-verification using curated snapshots and leverage 3C Principles (Completeness, Conciseness, Creativity) for task accomplishment validation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SmartSnap paradigm enhances scalability and performance of LLM-driven agents, achieving significant gains in model performance against established agent models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22322

32. LiveTalk: Real-Time Multimodal Interactive Video Diffusion via Improved On-Policy Distillation
🔑 Keywords: Real-time video generation, Multimodal Conditioning, On-policy distillation, Human-AI interaction, Audio language models
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve real-time video generation with diffusion techniques by addressing challenges in multimodal (text, image, audio) conditioning for interactive systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of an enhanced distillation approach focusing on quality condition inputs, initialization, and optimized scheduling in on-policy optimization to reduce latency and maintain quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method achieves visual quality comparable to full-step models with significantly reduced inference cost and latency (20x decrease), enabling effective real-time human-AI interaction through the LiveTalk system, surpassing existing models in coherence and quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23576