AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260101

1. mHC: Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections
🔑 Keywords: Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections, Residual Connection, Identity Mapping Property, Scalability, Infrastructure Optimization
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To stabilize and scale residual connection architectures by restoring the identity mapping properties through manifold projection and infrastructure optimization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections as a general framework to project the residual connection space onto a specific manifold.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections are effective for training at scale, showing tangible performance improvements and superior scalability in empirical experiments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24880
2. Let It Flow: Agentic Crafting on Rock and Roll, Building the ROME Model within an Open Agentic Learning Ecosystem
🔑 Keywords: Agentic Learning Ecosystem (ALE), Post-Training Optimization, Sandbox Environments, Policy Alignment
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the Agentic Learning Ecosystem (ALE) to enhance long-horizon training stability and performance for real-world agent development.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop ALE with three components: ROLL for weight optimization, ROCK as a sandbox environment manager, and iFlow CLI for context engineering.
– Use data composition protocols and the Interaction-based Policy Alignment (IPA) algorithm.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ROME, developed within ALE, shows strong performance in benchmarks like SWE-bench Verified and Terminal Bench, demonstrating the effectiveness of the ALE infrastructure.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24873

3. A unified framework for detecting point and collective anomalies in operating system logs via collaborative transformers
🔑 Keywords: CoLog, log anomaly detection, collaborative transformers, multi-head impressed attention, modality adaptation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop CoLog, a framework for high-precision detection of point and collective anomalies across diverse log modalities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize collaborative transformers and multi-head impressed attention to encode interactions among modalities with a modality adaptation layer to handle heterogeneity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CoLog achieves superior performance over state-of-the-art methods, with a mean precision of 99.63%, a mean recall of 99.59%, and a mean F1 score of 99.61% across seven benchmark datasets, emphasizing its applicability in cybersecurity and system monitoring.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23380

4. PhyGDPO: Physics-Aware Groupwise Direct Preference Optimization for Physically Consistent Text-to-Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: Text-to-Video, VLM, Physics-Augmented, Video Generation, PhyGDPO
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve text-to-video generation by ensuring that synthesized videos adhere to physical laws.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced PhyAugPipe to construct a large-scale dataset for training.
– Developed the PhyGDPO framework for holistic preference optimization with physics-guided rewards.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method significantly surpasses existing open-source methods, showing enhanced performance on PhyGenBench and VideoPhy2 datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24551

5. GR-Dexter Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Vision-language-action models, Bimanual dexterous-hand, Teleoperation, Generalization
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce GR-Dexter, a holistic framework for VLA-based generalist manipulation on a bimanual dexterous-hand robot.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Combines a compact 21-DoF robotic hand design with a bimanual teleoperation system for data collection and a training recipe leveraging teleoperated robot trajectories with multimodal datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GR-Dexter demonstrated strong in-domain performance and robustness to unseen objects and instructions in real-world evaluations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24210
6. SpaceTimePilot: Generative Rendering of Dynamic Scenes Across Space and Time
🔑 Keywords: SpaceTimePilot, video diffusion model, space-time disentanglement, temporal-warping training, synthetic dataset
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a video diffusion model, SpaceTimePilot, for independent control of spatial viewpoint and temporal motion in video generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a time-embedding mechanism and temporal-warping training, supplemented with the CamxTime dataset to achieve precise space-time disentanglement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SpaceTimePilot demonstrates effective control over space-time in video rendering, showing improved performance on both real-world and synthetic data compared to prior models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.25075
7. Forging Spatial Intelligence: A Roadmap of Multi-Modal Data Pre-Training for Autonomous Systems
🔑 Keywords: Spatial Intelligence, Multi-Modal Learning, Foundation Models, 3D Object Detection, Model Scalability
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to develop a comprehensive framework for multi-modal pre-training to enhance Spatial Intelligence from diverse onboard sensor data, such as those from self-driving vehicles and drones.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study dissects foundational sensor characteristics and learning strategies, evaluates platform-specific datasets, and integrates textual inputs and occupancy representations for open-world perception and planning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The paper formulates a unified taxonomy for pre-training paradigms, identifies bottlenecks like computational efficiency and scalability, and proposes a roadmap for creating general-purpose multi-modal foundation models suitable for real-world applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24385

8. Geometry-Aware Optimization for Respiratory Sound Classification: Enhancing Sensitivity with SAM-Optimized Audio Spectrogram Transformers
🔑 Keywords: Respiratory sound classification, Audio Spectrogram Transformer, Sharpness-Aware Minimization, Class imbalance, Clinical screening
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance respiratory sound classification on constrained datasets like ICBHI 2017 using an optimized framework for Audio Spectrogram Transformer with Sharpness-Aware Minimization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces a framework that integrates Audio Spectrogram Transformer (AST) with Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) and utilizes a weighted sampling strategy for effective handling of class imbalance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method achieved a state-of-the-art score of 68.10% on ICBHI 2017, surpassing CNN and hybrid models, and demonstrated improved sensitivity crucial for reliable clinical screening, validating the learning of robust features using t-SNE and attention maps.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22564

9. Guiding a Diffusion Transformer with the Internal Dynamics of Itself
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion model, Internal Guidance (IG), Generative Models, Classifier Free Guidance (CFG), ImageNet
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the generation quality of diffusion models by introducing a novel guidance strategy called Internal Guidance (IG).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed IG by adding auxiliary supervision on intermediate layers during training.
– Examined the outputs of intermediate and deep layers during the sampling process.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– IG significantly improves training efficiency and generation quality.
– Achieved state-of-the-art FID scores on ImageNet 256×256, notably FID=1.19 with LightningDiT-XL/1+IG combined with CFG.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24176

10. JavisGPT: A Unified Multi-modal LLM for Sounding-Video Comprehension and Generation
🔑 Keywords: JavisGPT, Multi-Modal Learning, Audio-Video Comprehension, Multimodal Instructions, AI Native
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces JavisGPT, a unified multimodal large language model designed for joint audio-video comprehension and generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model employs a concise encoder-LLM-decoder architecture with a SyncFusion module for spatio-temporal audio-video fusion and synchrony-aware queries.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– JavisGPT surpasses existing multimodal large language models, especially in complex and temporally synchronized settings, proven by extensive experiments on comprehension and generation benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22905

11.

12. Valori: A Deterministic Memory Substrate for AI Systems
🔑 Keywords: deterministic AI memory, fixed-point arithmetic, non-determinism, replayable state machine, trustworthy AI
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To establish a deterministic AI memory system that ensures bit-identical results across platforms, addressing non-determinism in vector embeddings and similarity search.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Valori, a deterministic AI memory substrate, is presented, using fixed-point arithmetic (Q16.16) to replace floating-point memory operations and model memory as a replayable state machine.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study demonstrates that deterministic memory is crucial for trustworthy AI systems and provides an open-source implementation to ensure consistency across different hardware architectures.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22280
13. Factorized Learning for Temporally Grounded Video-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: video-language models, temporal grounding, textual response, factorized learning, evidence tokens
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to decouple video understanding tasks, specifically temporal grounding and textual response, to achieve precise event-level perception with a clear logical hierarchy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of D^2VLM framework that separates learning tasks while maintaining dependency. It uses a “grounding then answering” paradigm with evidence tokens for enhanced event-level visual semantics.
– Development of a novel factorized preference optimization (FPO) algorithm, incorporating probabilistic temporal grounding to improve preference learning for tasks.
– Creation of a synthetic dataset to support factorized preference learning with explicit temporal grounding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments demonstrate that the proposed methods lead to clear advantages in various video understanding tasks, substantiating the efficacy of the factorized learning approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24097

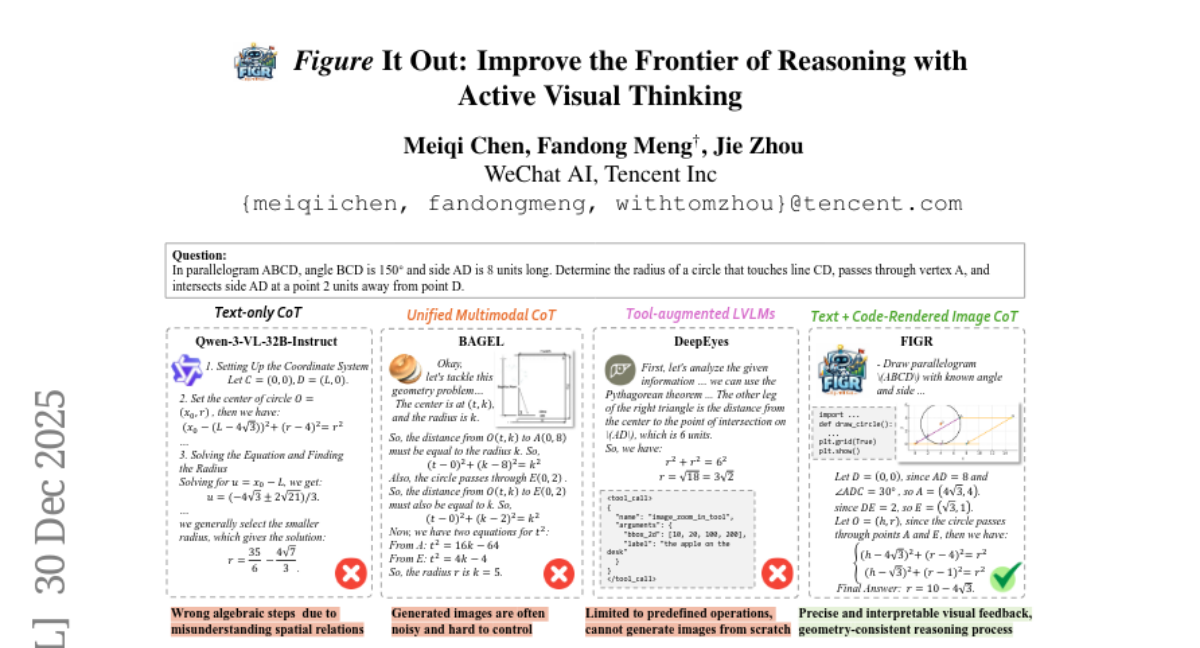
14. Figure It Out: Improving the Frontier of Reasoning with Active Visual Thinking
🔑 Keywords: complex reasoning, visual thinking, reinforcement learning, multimodal reasoning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce FIGR to enhance multi-turn reasoning with visual thinking in complex reasoning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– FIGR uses end-to-end reinforcement learning to integrate visual representations during problem solving and regulate visual reasoning adaptively.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FIGR significantly improves reasoning performance over text-only models, outperforming baselines by 13.12% on AIME 2025 and 11.00% on BeyondAIME, demonstrating enhanced stability and reliability in complex reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24297
15. BEDA: Belief Estimation as Probabilistic Constraints for Performing Strategic Dialogue Acts
🔑 Keywords: BEDA, belief estimation, probabilistic constraints, Adversarial, Alignment
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to improve strategic dialogue by using probabilistic constraints on belief estimation, introducing formalized adversarial and alignment acts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers developed a framework named BEDA, which includes a belief estimator and a conditional generator to execute dialogue acts based on inferred beliefs across various task settings.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BEDA outperforms baseline models significantly in different settings, achieving higher success rates and optimal outcomes in adversarial, cooperative, and negotiation scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24885

16. Pretraining Frame Preservation in Autoregressive Video Memory Compression
🔑 Keywords: neural network, video compression, high-frequency details, pretrained models, autoregressive video models
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The goal is to develop PFP, a neural network structure, for compressing long videos into short contexts while preserving high-frequency details at arbitrary temporal positions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach includes explicit pretraining objectives aimed at maintaining perceptual details. The neural network can compress a 20-second video into a context of approximately 5k length, enabling random frame retrieval with preserved appearances.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Pretrained models can be fine-tuned as memory encoders for autoregressive video models, allowing for long history memory with low context cost and acceptable fidelity loss. The framework is evaluated with different settings to discuss potential trade-offs in neural architecture designs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23851

17. Fantastic Reasoning Behaviors and Where to Find Them: Unsupervised Discovery of the Reasoning Process
🔑 Keywords: Sparse auto-encoders, Reasoning behaviors, Large language models, Unsupervised latent discovery
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to uncover and control interpretable reasoning behaviors within large language models through an unsupervised framework leveraging sparse auto-encoders.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors propose a method called RISE (Reasoning behavior Interpretability via Sparse auto-Encoder) that identifies reasoning vectors in activation space, using chain-of-thought traces and step-level activations to train sparse auto-encoders.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study finds that reasoning behaviors are separable in decoder space and can be controlled via interventions on specific vectors, revealing potential for unsupervised latent discovery to interpret and steer reasoning in large models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23988

18. AI Meets Brain: Memory Systems from Cognitive Neuroscience to Autonomous Agents
🔑 Keywords: Memory, LLM-driven agents, Cognitive neuroscience, Memory security, Skill acquisition
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To systematically synthesize interdisciplinary knowledge connecting cognitive neuroscience insights with LLM-driven agents for improved memory workflows in autonomous agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Elucidation of memory definitions and functions from cognitive neuroscience to LLMs and autonomous agents.
– Comparative analysis of memory taxonomy and storage mechanisms.
– Review of benchmarks for evaluating agent memory, and exploration of memory security from attack and defense perspectives.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Bridging interdisciplinary gaps, and envisioning future research in multimodal memory systems and skill acquisition for autonomous agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23343

19. Scaling Open-Ended Reasoning to Predict the Future
🔑 Keywords: Language Models, Forecasting, Reinforcement Learning, Open Source
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance language models’ predictive capabilities on open-ended forecasting questions using a scalable dataset derived from global news events.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed OpenForesight dataset and trained the Qwen3 models, incorporating an offline news corpus and improved reward function for reinforcement learning to prevent future information leakage.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The smaller model, OpenForecaster 8B, matches larger proprietary models in performance, showing improved accuracy, calibration, and consistency in predictions. All models, code, and data are open-sourced to promote accessibility in language model forecasting research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.25070

20. GaMO: Geometry-aware Multi-view Diffusion Outpainting for Sparse-View 3D Reconstruction
🔑 Keywords: GaMO, Geometry-aware Multi-view Outpainter, 3D reconstruction, zero-shot, multi-view outpainting
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance sparse-view 3D reconstruction by using geometry-aware multi-view outpainting to improve scene coverage and consistency with reduced computational cost.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes multi-view conditioning and geometry-aware denoising in a zero-shot manner for processing, without the need for training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction quality with significantly less computational time, surpassing previous diffusion-based methods in PSNR and LPIPS metrics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.25073
21. Youtu-LLM: Unlocking the Native Agentic Potential for Lightweight Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Youtu-LLM, Computational Efficiency, Agentic Intelligence, Planning and Reasoning, Lightweight Models
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Youtu-LLM, a lightweight language model designed to combine high computational efficiency with strong agentic intelligence for enhanced planning and reasoning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Youtu-LLM employs a Compact Architecture with Long-Context Support to handle long-horizon tasks and utilize a “Commonsense-STEM-Agent” training curriculum to progressively enhance cognitive abilities.
– Scalable agentic mid-training is employed through diverse data construction schemes, enabling the model to synthesize rich trajectories in domains like math, coding, and tool use.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Youtu-LLM sets a new state-of-the-art for sub-2B language models, achieving competitive performance on general benchmarks and significantly surpassing existing baselines on agent-specific tasks, showcasing the potential of lightweight models equipped with agentic capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24618
