AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260102

1. Improving Multi-step RAG with Hypergraph-based Memory for Long-Context Complex Relational Modeling
🔑 Keywords: Retrieval-Augmented Generation, LLMs, Hypergraph-Based Memory, Complex Reasoning, Global Understanding
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces HGMem, a hypergraph-based memory mechanism designed to enhance multi-step retrieval-augmented generation by transforming memory from static storage to a dynamic, expressive structure.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Memory is represented using a hypergraph whose hyperedges form distinct memory units, enabling higher-order interactions for complex reasoning and global comprehension.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HGMem consistently improves multi-step RAG, outperforming baseline systems across diverse tasks through enhanced representational capacity and integrated knowledge structures.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23959

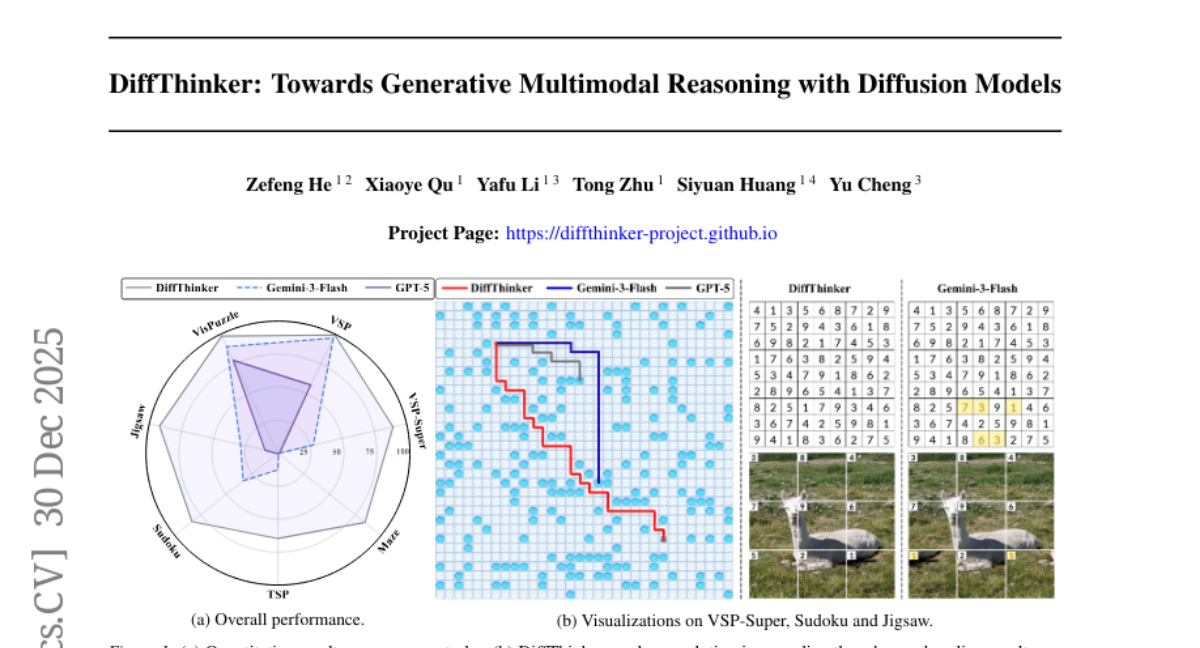
2. DiffThinker: Towards Generative Multimodal Reasoning with Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Large Language Models, Generative Multimodal Reasoning, DiffThinker, Vision-Centric Tasks
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to establish a new Generative Multimodal Reasoning paradigm by introducing DiffThinker, focusing on improving reasoning in vision-centric tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A diffusion-based reasoning framework called DiffThinker is introduced, which reformulates multimodal reasoning as a generative image-to-image task.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DiffThinker significantly outperforms existing models in four domains: sequential planning, combinatorial optimization, constraint satisfaction, and spatial configuration, demonstrating the potential of generative multimodal reasoning for vision-centric tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24165
3. FlowBlending: Stage-Aware Multi-Model Sampling for Fast and High-Fidelity Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: Model Capacity, FlowBlending, Sampling Strategy, Inference Speedup, AI Systems and Tools
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study investigates the role of model capacity across different timesteps in achieving efficient model sampling and proposes FlowBlending as a novel approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A new stage-aware multi-model sampling strategy is introduced, utilizing both large and small models at different stages, along with criteria for determining stage boundaries based on a velocity-divergence analysis.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FlowBlending significantly enhances inference speed by up to 1.65x and reduces FLOPs by 57.35%, without losing model performance, and is also compatible with existing sampling-acceleration techniques for additional speed enhancements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24724

4. TESO Tabu Enhanced Simulation Optimization for Noisy Black Box Problems
🔑 Keywords: Simulation optimization, Tabu-Enhanced Simulation Optimization, Metaheuristic framework, Adaptive search, Memory-based strategy
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a novel metaheuristic framework, TESO, to address challenges in simulation optimization such as noisy evaluations and complex search landscapes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a Tabu List and Elite Memory to achieve a balance between exploration and exploitation, enhanced by memory components and an aspiration criterion.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TESO shows improved performance in queue optimization problems compared to benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness and reliability of its memory components.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24007
5.

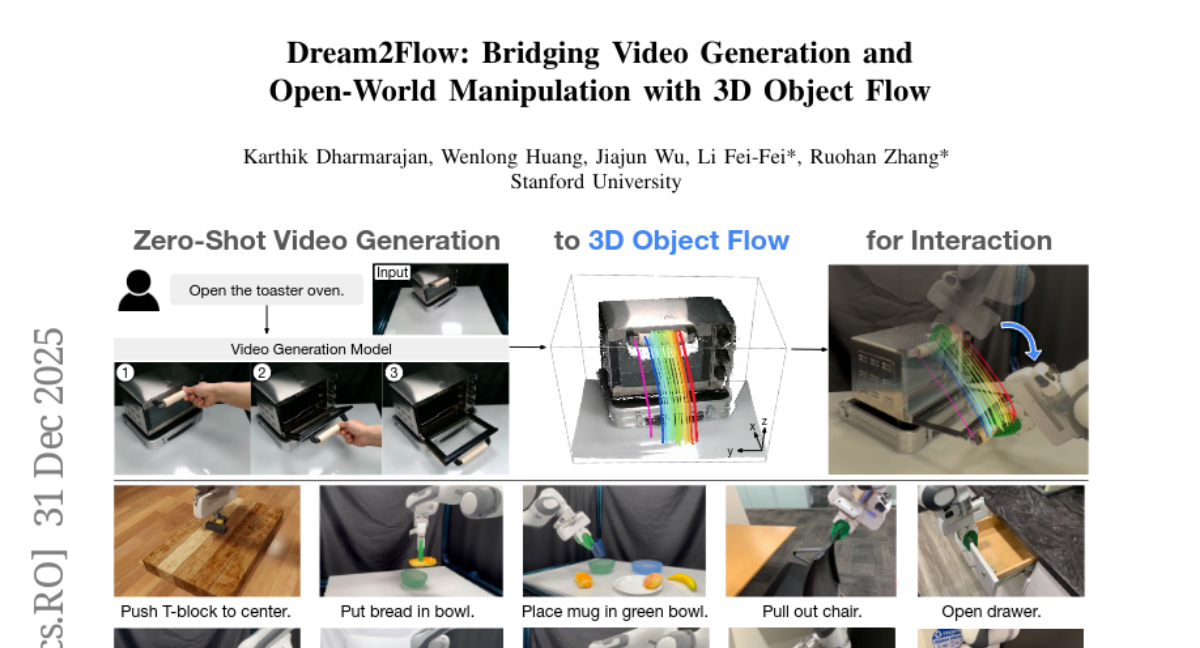
6. Dream2Flow: Bridging Video Generation and Open-World Manipulation with 3D Object Flow
🔑 Keywords: Generative video modeling, Robotic control, 3D object flow, Zero-shot guidance, Open-world manipulation
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to bridge video generation and robotic control using 3D object flow as an intermediate representation, enabling zero-shot manipulation of diverse object categories.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors introduce Dream2Flow, which reconstructs 3D object motions from generated videos and formulates manipulation as object trajectory tracking using trajectory optimization or reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Dream2Flow effectively translates synthesized object motions into executable commands, demonstrating 3D object flow as a versatile interface adaptable for open-world robotic manipulation, proven through simulations and real-world experiments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24766
7. On the Role of Discreteness in Diffusion LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion models, Language generation, Parallel decoding, Iterative refinement, Multi-token dependencies
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– This paper revisits diffusion language modeling by analyzing the diffusion process and outlining critical properties distinguishing diffusion mechanics from language-specific needs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors categorize approaches into continuous diffusion in embedding space and discrete diffusion over tokens and analyze recent large diffusion language models to identify central issues.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study highlights two central issues: uniform corruption does not respect information distribution, and token-wise marginal training fails to capture multi-token dependencies, advocating for more coherent diffusion language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22630

8. Dynamic Large Concept Models: Latent Reasoning in an Adaptive Semantic Space
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Dynamic Large Concept Models, Hierarchical Compression, Compression-Aware Scaling Law
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the computational efficiency of Large Language Models (LLMs) by introducing Dynamic Large Concept Models (DLCM) which allocate computation based on semantic significance rather than uniform token processing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a hierarchical language modeling framework that learns semantic boundaries to shift computation from tokens to a concept space, along with introducing a compression-aware scaling law.
– Implementation of a decoupled μP parametrization to stabilize training and support hyperparameter transfer under varied computational regimes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DLCM effectively reallocates computational resources, leading to a +2.69% improvement in performance across 12 zero-shot benchmarks, optimizing computation under a fixed budget of inference FLOPs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24617