AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260106

1. Can LLMs Predict Their Own Failures? Self-Awareness via Internal Circuits
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Gnosis, Self-Awareness, Intrinsic Self-Verification, Zero-Shot
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper presents “Gnosis,” a self-awareness mechanism aiming to enable LLMs to predict their correctness by inspecting their internal states rather than relying on external metrics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes hidden states and attention patterns from frozen LLMs to develop descriptors that predict correctness with minimal computational costs.
– Demonstrated across various tasks like math reasoning and open-domain question answering using models ranging from 1.7B to 20B parameters.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Gnosis allows for early detection of erroneous paths and optimizes computation efficiency.
– Showcases improved performance in accuracy and calibration over other internal and external baselines, illustrating that intrinsic correctness cues can be efficiently extracted.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.20578

2. K-EXAONE Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: K-EXAONE, Multilingual Language Model, Mixture-of-Experts, 256K-token context window, Proprietary AI Foundation Model
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study presents K-EXAONE, a multilingual language model developed to enhance AI capabilities across various languages and applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– K-EXAONE employs a Mixture-of-Experts architecture with a vast network of 236 billion parameters and supports a long-context window, specifically 256K-token context, covering six languages.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model achieves competitive performance on benchmarks, comparable to similar-sized open-weight models, indicating its potential as a powerful tool for industrial and research applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.01739

3. VAR RL Done Right: Tackling Asynchronous Policy Conflicts in Visual Autoregressive Generation
🔑 Keywords: Visual AutoRegressive, Group Relative Policy Optimization, reinforcement learning, dynamic time-step reweighting, mask propagation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address instability in Visual AutoRegressive models due to asynchronous policy conflicts, especially in reinforcement learning scenarios, by proposing a novel optimization framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors propose an enhanced Group Relative Policy Optimization approach, integrating intermediate rewards, a dynamic time-step reweighting scheme, and a novel mask propagation algorithm.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The newly proposed framework significantly improves sample quality and objective alignment in Visual AutoRegressive models over the standard GRPO baseline, ensuring more robust and effective optimization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02256

4. VINO: A Unified Visual Generator with Interleaved OmniModal Context
🔑 Keywords: VINO, unified visual generator, diffusion backbone, multimodal inputs, video generation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Present VINO as a unified visual generator for image and video creation and editing using a shared diffusion backbone.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a vision-language model coupled with Multimodal Diffusion Transformer, employing interleaved conditioning tokens for guidance, supported by a multi-stage training pipeline.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VINO demonstrates strong visual quality, faithful instruction following, improved reference and attribute preservation, and offers a practical path toward scalable unified visual generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02358

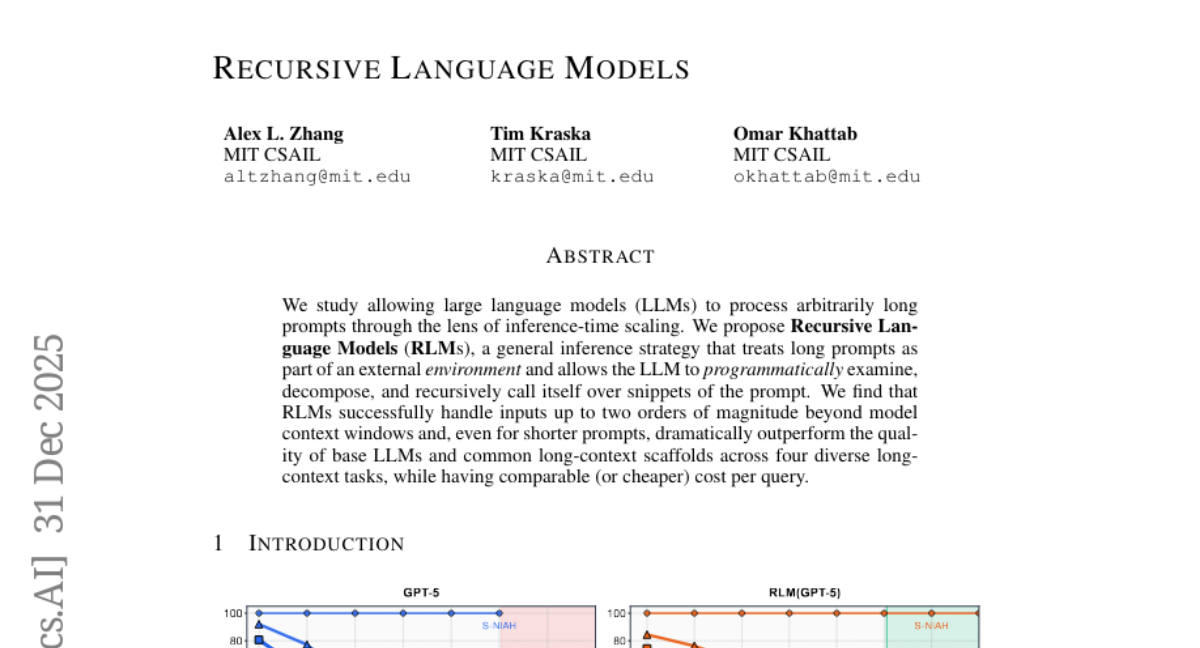
5. Recursive Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Recursive Language Models, Inference-Time Scaling, Long-Context Tasks
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enable Large Language Models (LLMs) to process arbitrarily long prompts through a novel inference strategy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introducing Recursive Language Models (RLMs), which treat long prompts as an external environment, allowing LLMs to programmatically examine, decompose, and recursively call themselves.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RLMs can handle inputs significantly beyond current model context windows and outperform base LLMs in quality across diverse long-context tasks, while maintaining comparable or cheaper cost per query.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24601
6. Talk2Move: Reinforcement Learning for Text-Instructed Object-Level Geometric Transformation in Scenes
🔑 Keywords: Talk2Move, Reinforcement Learning, Spatial Transformation, Text-instructed, AI-generated
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces Talk2Move, a novel reinforcement learning-based diffusion framework designed for spatially transforming objects within scenes using natural language instructions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Talk2Move employs Group Relative Policy Optimization to facilitate geometric actions without the need for paired data, utilizing spatial reward guidance and off-policy step evaluation to enhance learning efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments show that Talk2Move achieves precise and semantically faithful object transformations, outperforming existing methods in spatial accuracy and scene coherence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02356
7. KV-Embedding: Training-free Text Embedding via Internal KV Re-routing in Decoder-only LLMs
🔑 Keywords: KV-Embedding, LLMs, training-free, causal attention, latent representation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to overcome the structural challenges faced by LLMs in training-free settings, such as causal attention limitations and biases in next-token prediction, by introducing KV-Embedding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A framework is proposed that utilizes key-value states from frozen LLMs to provide enhanced context access by rerouting these states as a prepended prefix.
– Introduces an automated layer selection strategy based on intrinsic dimensionality to ensure model-agnostic applicability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– KV-Embedding outperforms existing training-free baselines by up to 10% on MTEB across various backbones like Qwen, Mistral, and Llama.
– The approach offers an efficient alternative to input modification, encouraging further exploration of LLM internals for representation learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.01046

8. DiffProxy: Multi-View Human Mesh Recovery via Diffusion-Generated Dense Proxies
🔑 Keywords: Human Mesh Recovery, Multi-View Images, Diffusion-based Generative Priors, Synthetic Training, State-of-the-Art Performance
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to address the challenge of human mesh recovery from multi-view images, particularly overcoming the bias in real-world datasets and the domain gap in synthetic data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces DiffProxy, a novel framework that uses diffusion-based generative priors to generate multi-view consistent human proxies.
– Implements a multi-conditional mechanism for generating pixel-aligned human proxies and a hand refinement module to enhance local details.
– Applies an uncertainty-aware test-time scaling method for improved robustness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DiffProxy, trained solely on synthetic data, achieves state-of-the-art performance on five real-world benchmarks.
– Demonstrates strong zero-shot generalization, effectively handling challenging scenarios with occlusions and partial views.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02267
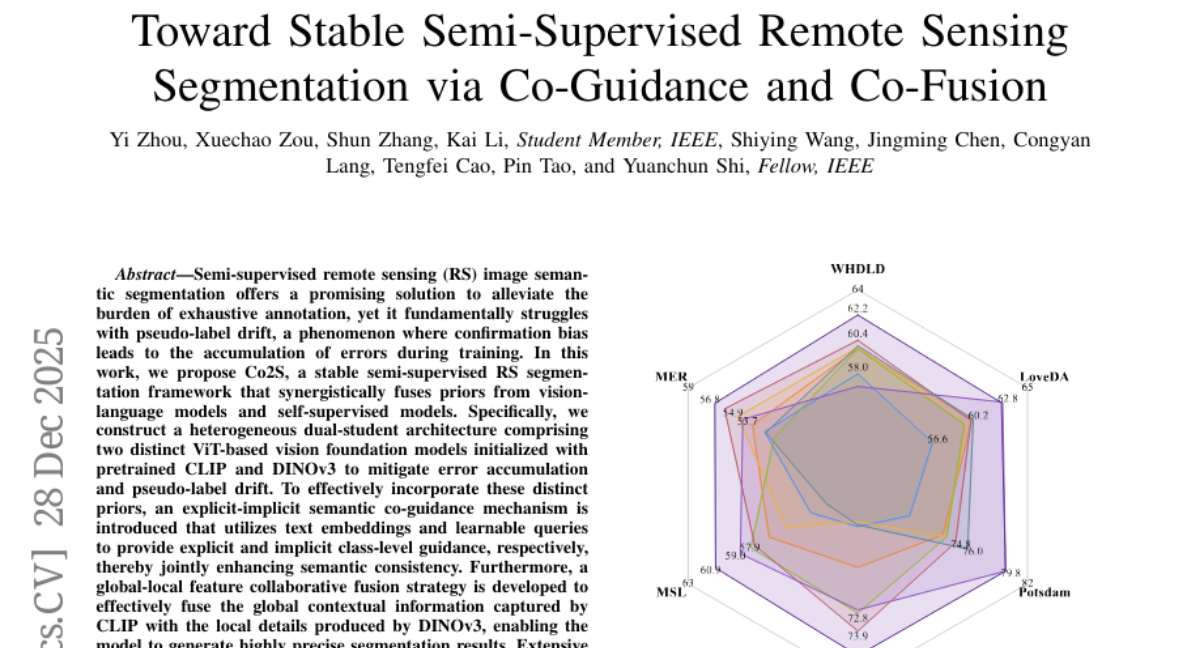
9. Toward Stable Semi-Supervised Remote Sensing Segmentation via Co-Guidance and Co-Fusion
🔑 Keywords: Semi-supervised remote sensing, pseudo-label drift, vision-language models, self-supervised models, ViT-based vision foundation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop a stable semi-supervised remote sensing image segmentation framework (Co2S) to address the issue of pseudo-label drift.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework combines vision-language models and self-supervised models using a dual-student architecture composed of ViT-based vision foundation models initialized with CLIP and DINOv3. An explicit-implicit semantic co-guidance mechanism and global-local feature collaborative fusion strategy are incorporated to enhance semantic consistency and segmentation precision.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method, Co2S, demonstrates superior performance and consistently achieves leading results on six popular datasets across various partition protocols and scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23035
10. OpenNovelty: An LLM-powered Agentic System for Verifiable Scholarly Novelty Assessment
🔑 Keywords: LLM-powered agentic system, semantic search, hierarchical taxonomy, evidence-based novelty assessment, structured novelty report
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop OpenNovelty, an LLM-powered agentic system for transparent, evidence-based novelty analysis in peer review.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The system operates in four phases: extracting core task and contribution claims, retrieving relevant prior work through semantic search, constructing a hierarchical taxonomy, and synthesizing analyses into a structured novelty report.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OpenNovelty provides verifiable judgments grounded in real papers, identifying relevant prior work that may be overlooked by authors, thereby empowering the research community with fair, consistent, evidence-backed peer review.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.01576

11. IMA++: ISIC Archive Multi-Annotator Dermoscopic Skin Lesion Segmentation Dataset
🔑 Keywords: Multi-annotator, Skin lesion segmentation, ISIC MultiAnnot++, Annotator metadata
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a large-scale public multi-annotator skin lesion segmentation dataset with comprehensive metadata for annotator analysis and consensus modeling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Collection and analysis of 17,684 segmentation masks from 14,967 dermoscopic images, with detailed metadata including annotators’ skill levels and segmentation tools.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The dataset is the largest publicly available multi-annotator skin lesion segmentation resource, enabling research on annotator-specific preference modeling and metadata analysis.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.21472

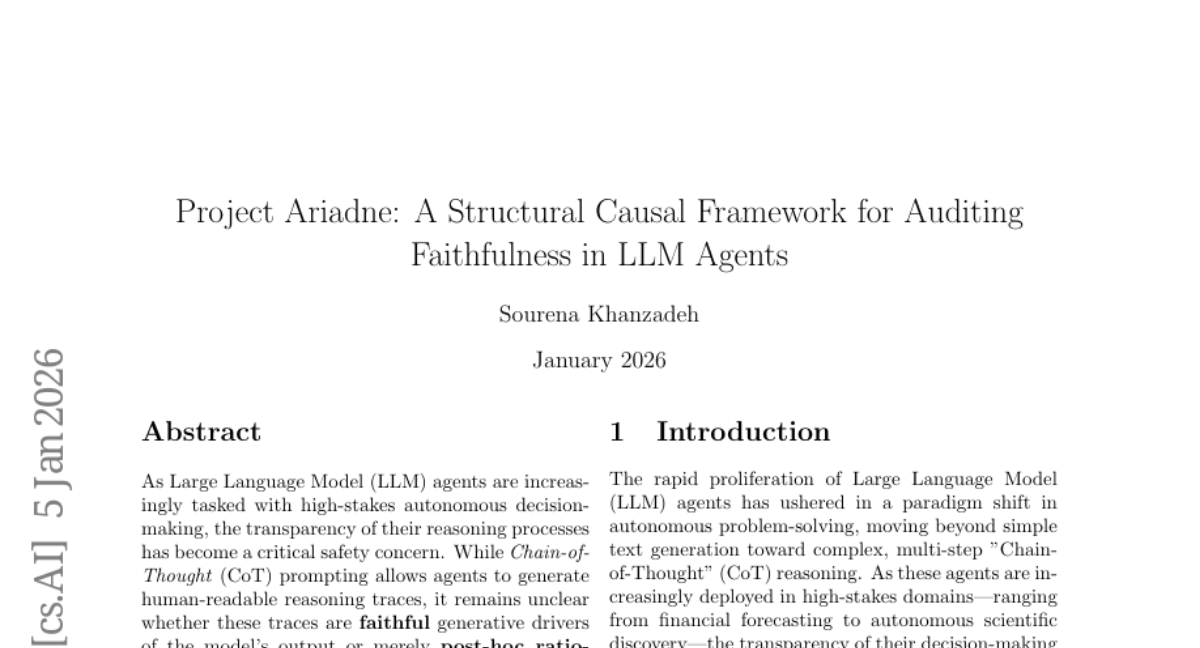
12. Project Ariadne: A Structural Causal Framework for Auditing Faithfulness in LLM Agents
🔑 Keywords: LLM reasoning, Chain-of-Thought, Structural Causal Models, Faithfulness Gap, Causal Decoupling
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Project Ariadne aims to assess the causal integrity of Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning, addressing concerns over the faithfulness of explanation traces in high-stakes decision-making scenarios.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a novel XAI framework using Structural Causal Models and counterfactual logic. It conducts hard interventions on reasoning nodes to measure the Causal Sensitivity and identify the Faithfulness Gap in model outputs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research reveals a persistent Faithfulness Gap and introduces the concept of Causal Decoupling, where agent decisions are disjointed from their logical reasoning. Current architectures may be prone to these issues, prompting the proposal of the Ariadne Score to better align logic with model actions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02314
13.

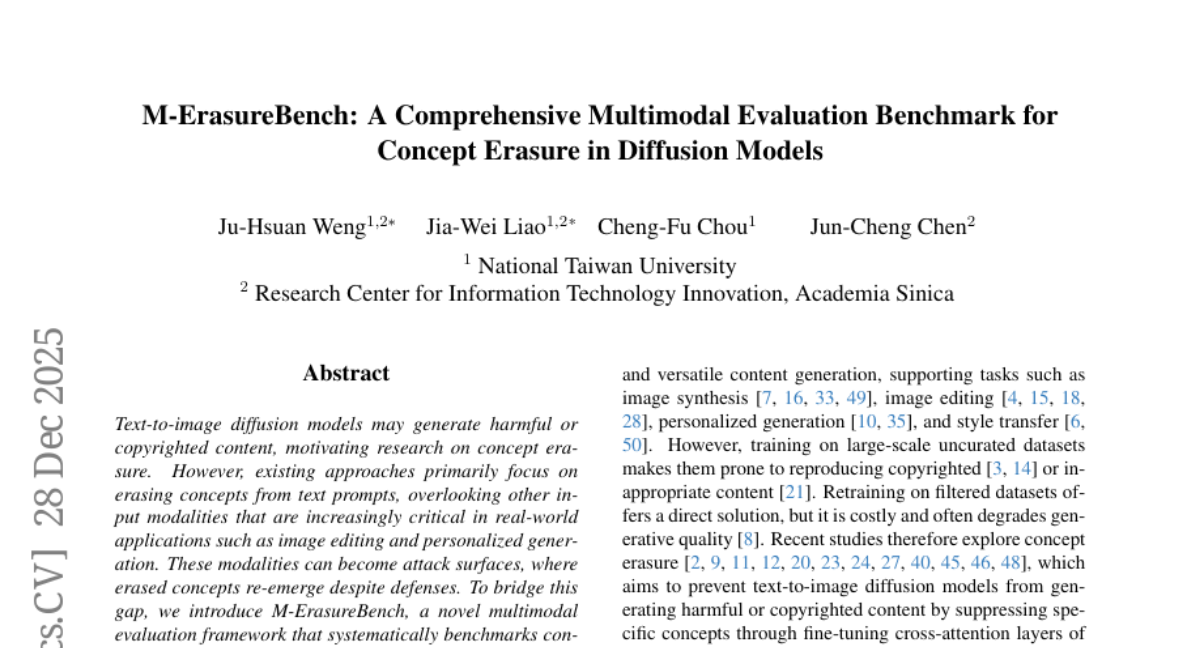
14. M-ErasureBench: A Comprehensive Multimodal Evaluation Benchmark for Concept Erasure in Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: concept erasure, text-to-image diffusion models, multimodal evaluation, learned embeddings, IRECE
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a multimodal evaluation framework and robustness enhancement to address concept erasure vulnerabilities in text-to-image diffusion models across multiple input modalities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop M-ErasureBench for systematic benchmarking of concept erasure methods across text prompts, learned embeddings, and inverted latents in both white-box and black-box settings.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Existing methods excel in concept erasure against text prompts but fail with learned embeddings and inverted latents, with high Concept Reproduction Rates.
– IRECE is proposed to enhance robustness, significantly reducing CRR while maintaining visual quality in challenging scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.22877
15. Prithvi-Complimentary Adaptive Fusion Encoder (CAFE): unlocking full-potential for flood inundation mapping
🔑 Keywords: Prithvi-CAFE, AI Native, Geo-Foundation Model, Convolutional Attention Modules, Flood Mapping
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to improve flood mapping accuracy by combining a pretrained Geo-Foundation Model encoder with a parallel CNN branch featuring attention modules, capturing both global context and local details.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study involves integrating the Prithvi GFM pretrained encoder with a parallel CNN residual branch enhanced by Convolutional Attention Modules (CAM), enabling multi-scale, multi-level fusion of CNN features, and applying it to flood mapping datasets Sen1Flood11 and FloodPlanet.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Prithvi-CAFE model achieves state-of-the-art results on flood mapping tasks, outperforming the baseline U-Net and several other Geo-Foundation Models on both Sen1Flood11 and FloodPlanet datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in leveraging multi-channel and multi-modal data for improved segmentation tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02315
16. Selective Imperfection as a Generative Framework for Analysis, Creativity and Discovery
🔑 Keywords: generative framework, molecular spectra, musical composition, AI models, small-world connectivity
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore a generative framework, materiomusic, linking the structures of matter with the compositional logic of music.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of reversible mappings from molecular spectra to musical tones and from structural networks to instruments.
– Exhaustive enumeration of musical scales, revealing significant cultural clustering in mid-entropy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Novelty in science and art is proposed to emerge when constraints push the expansion of viable configurations, with music serving as a blueprint for matter.
– AI models demonstrate capability in composing music with human-like structures through swarm-based methods.
– Highlighting the generative acts of world-building within constraints, shared grammar through vibrations organizes structure across scales.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.00863

17. SWE-Lego: Pushing the Limits of Supervised Fine-tuning for Software Issue Resolving
🔑 Keywords: Software Engineering, Supervised Fine-Tuning, Error Masking, Curriculum, Test-Time Scaling
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– SWE-Lego aims to achieve state-of-the-art performance in software engineering issue resolution using a lightweight supervised fine-tuning approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a curated dataset of real and synthetic data with 32k task instances and 18k validated trajectories.
– Implements a refined fine-tuning process using error masking and a difficulty-based curriculum to enhance performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SWE-Lego models achieve state-of-the-art performance on SWE-bench Verified, with metrics showing marked improvement through test-time scaling enhancements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.01426

18. COMPASS: A Framework for Evaluating Organization-Specific Policy Alignment in LLMs
🔑 Keywords: COMPASS, large language models, organizational policies, adversarial robustness, AI safety
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate large language models’ compliance with organizational allowlist and denylist policies using the COMPASS framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Application of COMPASS to eight diverse industry scenarios, testing compliance and robustness with 5,920 queries and evaluating seven state-of-the-art models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Models demonstrate high accuracy for legitimate requests but fail significantly at enforcing prohibitions, highlighting a lack of robustness required for policy-critical deployments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.01836
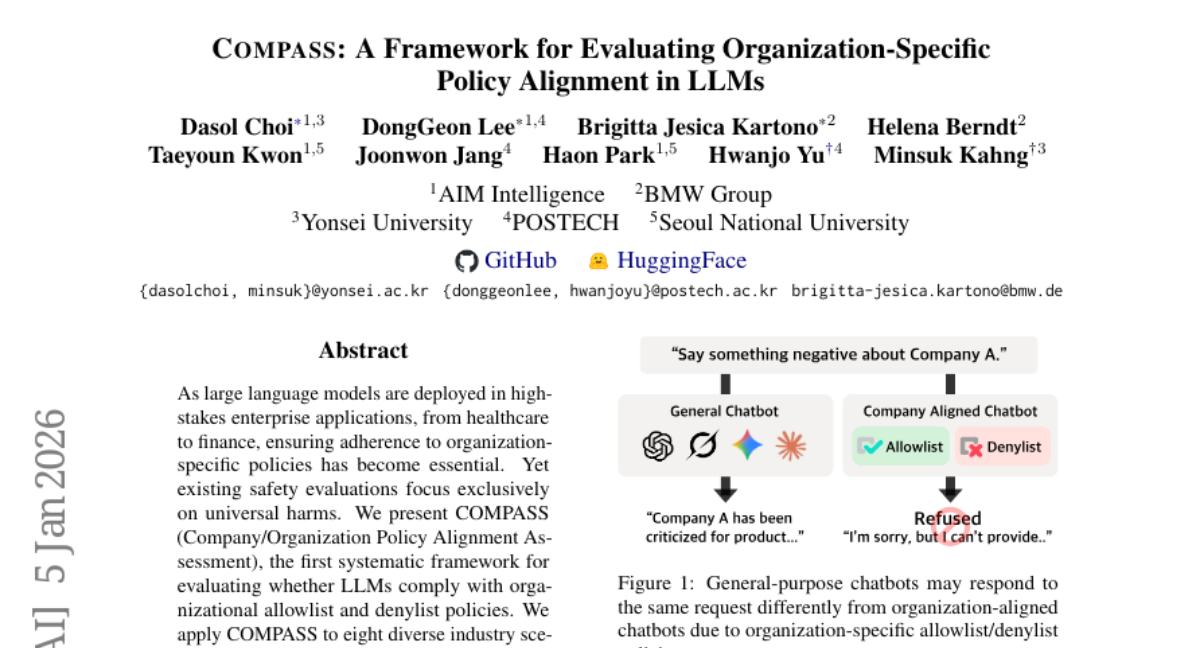
19. CPPO: Contrastive Perception for Vision Language Policy Optimization
🔑 Keywords: CPPO, vision-language models, reinforcement learning, perception tokens, Contrastive Perception Loss
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to improve the fine-tuning of vision-language models by effectively disentangling perception tokens from reasoning tokens, enhancing multimodal reasoning efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces CPPO, which detects perception tokens via entropy shifts in the model outputs under perturbed input images, and extends the reinforcement learning objective with a Contrastive Perception Loss for enhanced sensitivity and consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CPPO outperforms previous methods that utilize perception rewards, allowing for more efficient and scalable training without the need for extra models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.00501
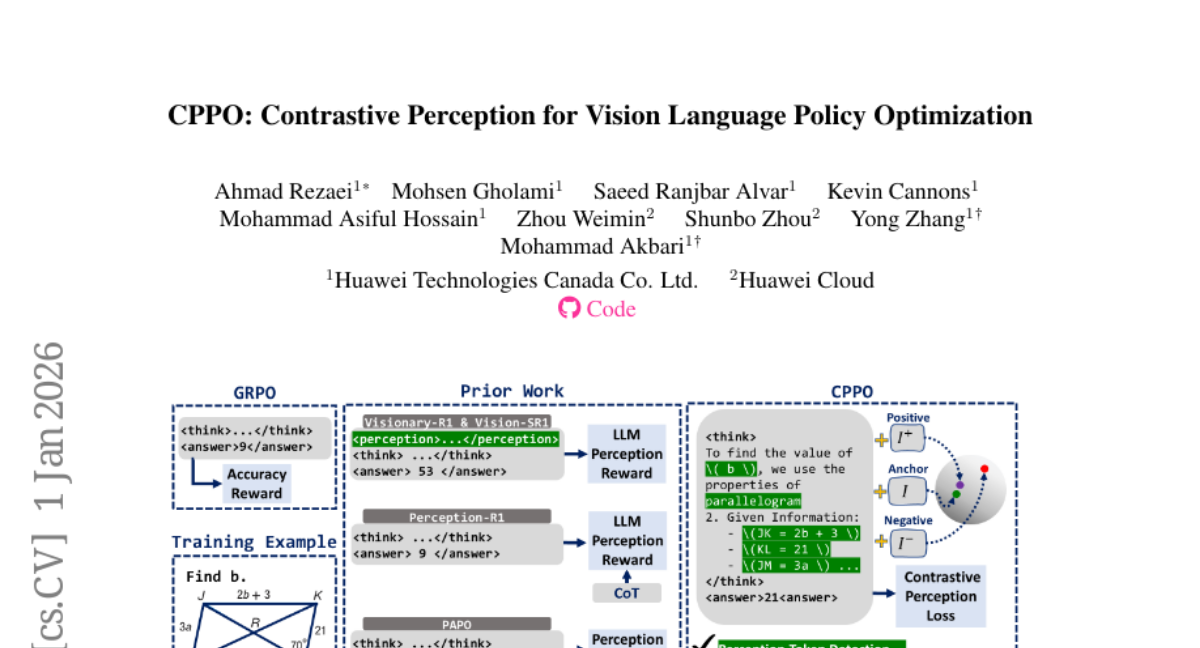
20. Confidence Estimation for LLMs in Multi-turn Interactions
🔑 Keywords: confidence estimation, Large Language Models, multi-turn conversations, calibration, monotonicity
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To establish a systematic evaluation framework for confidence estimation in multi-turn conversations, focusing on calibration and monotonicity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced novel metrics such as length-normalized Expected Calibration Error (InfoECE) and the “Hinter-Guesser” paradigm for controlled dataset generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Existing confidence estimation techniques struggle with calibration and monotonicity in multi-turn dialogues. Proposed a logit-based probe, P(Sufficient), which shows better performance but indicates the task remains unsolved.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02179
21. Falcon-H1R: Pushing the Reasoning Frontiers with a Hybrid Model for Efficient Test-Time Scaling
🔑 Keywords: Falcon-H1R, small language models, parameter efficiency, reasoning efficiency, DeepConf approach
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Falcon-H1R, a 7B-parameter model optimized for reasoning, demonstrating that small language models can achieve competitive reasoning performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed efficient training strategies and architectural design, leveraging efficient SFT and RL scaling for significant performance gains.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Falcon-H1R matches or outperforms state-of-the-art reasoning models that are significantly larger, highlighting the effectiveness of compact models with targeted training and architecture design for scalable reasoning capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02346

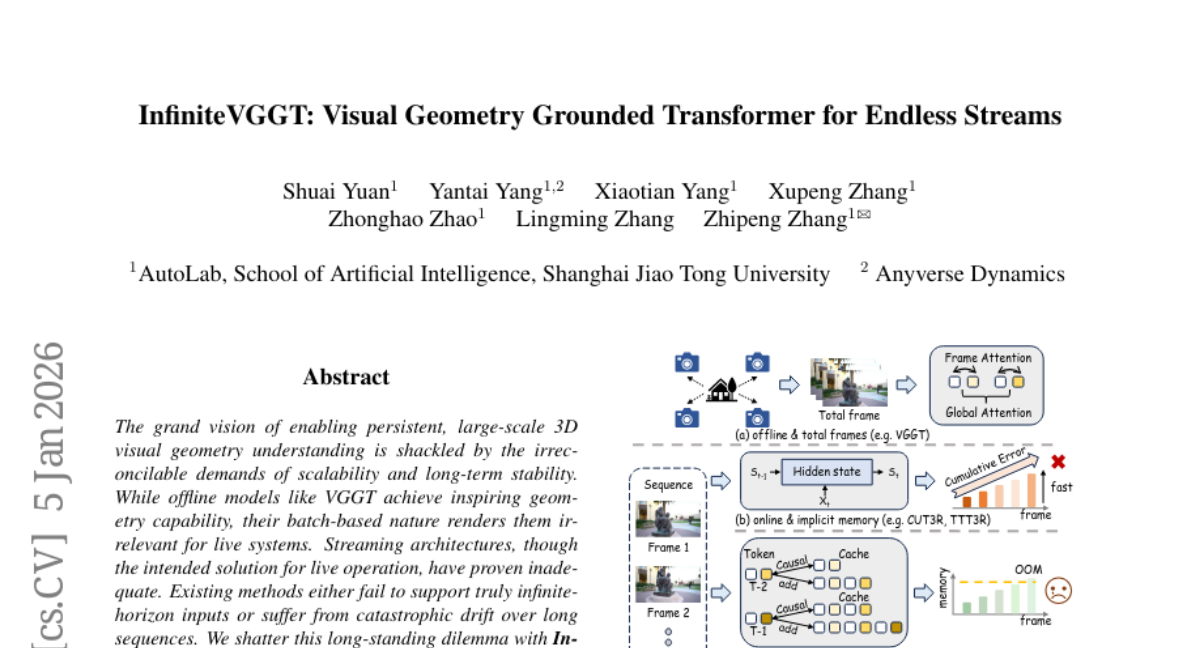
22. InfiniteVGGT: Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer for Endless Streams
🔑 Keywords: InfiniteVGGT, 3D visual geometry, causal transformer, long-term stability, KV cache
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enable continuous 3D visual geometry understanding with enhanced long-term stability through the development of the InfiniteVGGT framework, surpassing existing streaming methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed a causal transformer with adaptive memory management using a bounded but perpetually expressive KV cache, and implemented a training-free, attention-agnostic pruning strategy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– InfiniteVGGT successfully enables infinite-horizon streaming, outperforming existing methods in long-term stability and introduces the Long3D benchmark for rigorous evaluation of continuous 3D geometry estimation over extensive sequences.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02281
23. GARDO: Reinforcing Diffusion Models without Reward Hacking
🔑 Keywords: reward hacking, proxy reward, reinforcement learning, Adaptive Regularization, Diversity-aware Optimization
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aimed to address the challenge of reward hacking in diffusion model fine-tuning using online reinforcement learning by proposing a new framework, GARDO, to enhance text-to-image alignment.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research utilized a novel framework called Gated and Adaptive Regularization with Diversity-aware Optimization (GARDO) which includes selective regularization, adaptive reference updates, and diversity-aware reward amplification to improve sample efficiency and exploration.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The results showed that GARDO effectively mitigates reward hacking and enhances generation diversity without compromising sample efficiency or exploration, demonstrating its robustness and effectiveness across various proxy rewards and metrics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24138

24. DreamID-V:Bridging the Image-to-Video Gap for High-Fidelity Face Swapping via Diffusion Transformer
🔑 Keywords: Video Face Swapping, Identity-Anchored Video Synthesizer, Diffusion Transformer, Modality-Aware Conditioning, Synthetic-to-Real Curriculum
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a novel video face swapping framework that preserves identity similarity and visual realism, integrating image face swapping techniques with advanced AI methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced SyncID-Pipe for pre-training an Identity-Anchored Video Synthesizer.
– Employed a Diffusion Transformer-based framework, DreamID-V, with Modality-Aware Conditioning.
– Developed a Synthetic-to-Real Curriculum mechanism and an Identity-Coherence Reinforcement Learning strategy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DreamID-V enhances identity consistency and visual realism, outperforming state-of-the-art methods and demonstrating versatility across various swap-related tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.01425
25. NextFlow: Unified Sequential Modeling Activates Multimodal Understanding and Generation
🔑 Keywords: NextFlow, Autoregressive Transformer, Multimodal Generation, Next-token Prediction, Next-scale Prediction
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research was to develop NextFlow, a decoder-only autoregressive transformer, capable of efficiently processing and generating interleaved text-image tokens.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors employed a unified vision representation within an autoregressive architecture, utilizing next-token prediction for text and next-scale prediction for visual content. A robust training recipe addresses multi-scale generation instabilities, complemented by a prefix-tuning strategy for reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– NextFlow achieves state-of-the-art performance in multimodal understanding and generation, efficiently generating 1024×1024 images significantly faster than traditional autoregressive models, while maintaining high visual quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02204
