AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260108

1. Entropy-Adaptive Fine-Tuning: Resolving Confident Conflicts to Mitigate Forgetting
🔑 Keywords: Entropy-Adaptive Fine-Tuning, catastrophic forgetting, token-level entropy, epistemic uncertainty, knowledge conflict
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address catastrophic forgetting in supervised fine-tuning by distinguishing uncertainty from knowledge conflict using Entropy-Adaptive Fine-Tuning (EAFT).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– EAFT employs token-level entropy as a gating mechanism to differentiate between epistemic uncertainty and knowledge conflict, allowing selective learning and gradient suppression.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments confirm that EAFT matches the downstream performance of standard supervised fine-tuning while effectively preserving general capabilities and reducing degradation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02151

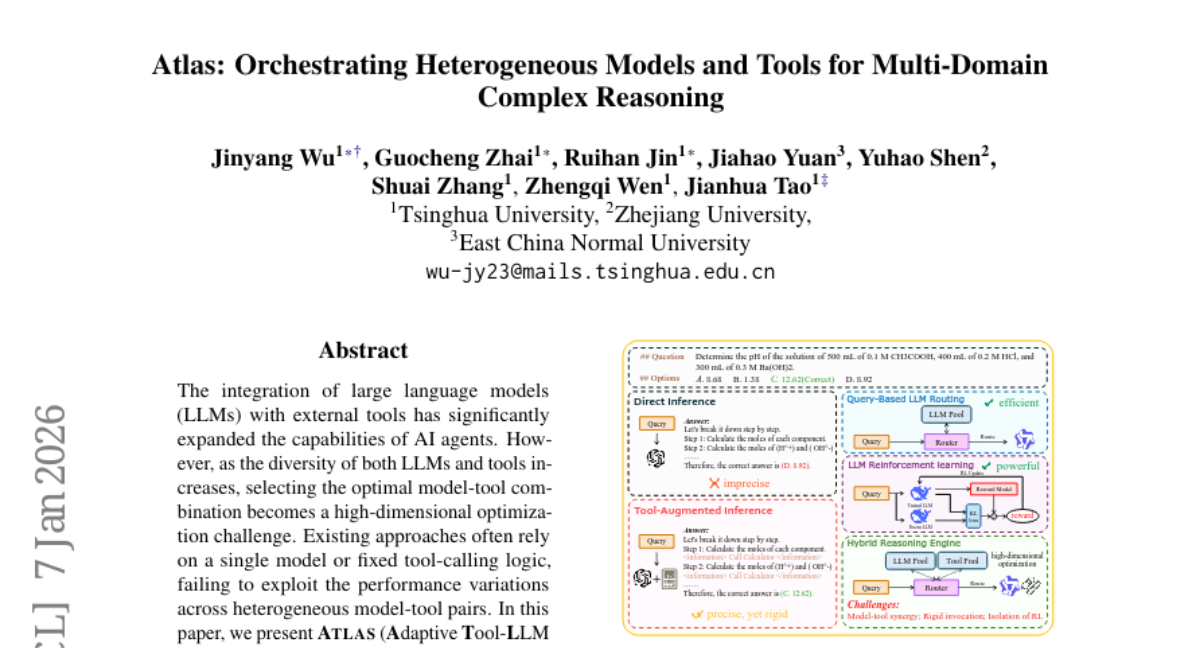
2. Atlas: Orchestrating Heterogeneous Models and Tools for Multi-Domain Complex Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: ATLAS, dual-path framework, model-tool combination, cross-domain reasoning, reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a dual-path framework called ATLAS for dynamically selecting optimal model-tool combinations to enhance cross-domain complex reasoning performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of training-free cluster-based routing and RL-based multi-step routing for dynamic tool usage and autonomous trajectory exploration.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ATLAS demonstrates superior performance over closed-source models like GPT-4, achieving significant improvements on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution reasoning tasks, including visual reasoning using specialized multi-modal tools.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03872
3. Klear: Unified Multi-Task Audio-Video Joint Generation
🔑 Keywords: Audio-video joint generation, Unified model architecture, Progressive multitask training, Dense-caption data
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address significant challenges in audio-video joint generation, particularly focusing on improving audio-visual asynchrony and alignment.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces Klear, utilizing a unified model architecture featuring DiT blocks and Omni-Full Attention mechanism.
– It employs a progressive multitask training regime and a multistage curriculum to enhance generalization and prevent unimodal collapse.
– A novel automated data-construction pipeline is presented to create a large-scale audio-video dataset with dense captions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Klear delivers notable improvements over previous methods in terms of audio-visual alignment and scalability.
– It achieves high-fidelity, semantically and temporally aligned audio-video synthesis and robustly generalizes to out-of-distribution scenarios.
– The model outperforms existing frameworks by significant margins and offers a unified, scalable approach for future audio-video synthesis projects.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04151

4. Agentic Rubrics as Contextual Verifiers for SWE Agents
🔑 Keywords: Agentic Rubrics, Reinforcement Learning, Test-Time Scaling, Scalable Verification, Codebase Context
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study investigates Agentic Rubrics for providing efficient and scalable verification for software engineering agents, creating context-aware checklists that outperform traditional methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Expert agents interact with repositories to create rubrics, allowing evaluation of candidate patches without test execution, validated through parallel TTS evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Agentic Rubrics achieve higher scores than baselines in SWE agent settings, offering consistent and unambiguous criteria for verification that align with ground-truth tests.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04171

5. E-GRPO: High Entropy Steps Drive Effective Reinforcement Learning for Flow Models
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Flow Matching Models, Stochastic Sampling, Entropy, SDE Sampling
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce E-GRPO, an Entropy-aware Group Relative Policy Optimization method to enhance exploration in flow matching models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of SDE and ODE sampling strategies to improve exploration efficiency, specifically by merging low entropy steps into high entropy ones.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results show that the proposed methods effectively deal with sparse and ambiguous reward signals, enhancing the exploration process.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.00423

6. RedBench: A Universal Dataset for Comprehensive Red Teaming of Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: LLM vulnerabilities, adversarial prompts, standardized taxonomy, domain coverage, red teaming datasets
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to introduce RedBench, a unified dataset designed to evaluate LLM vulnerabilities across multiple domains and attack types using a standardized risk categorization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Aggregating data from 37 benchmark datasets comprising 29,362 samples with a focus on attack and refusal prompts. Employing a standardized taxonomy with 22 risk categories and 19 domains.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RedBench enables consistent and comprehensive evaluations of LLM vulnerabilities, facilitates robust comparisons, supports future research, and aids in developing secure and reliable LLMs for real-world deployment. The dataset and evaluation code are available open-source.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03699

7. MAGMA: A Multi-Graph based Agentic Memory Architecture for AI Agents
🔑 Keywords: MAGMA, multi-graph memory architecture, long-context reasoning, external memory, semantic similarity
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose MAGMA, a novel multi-graph memory architecture that separates memory representation from retrieval logic across different dimensions to improve long-context reasoning in language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MAGMA employs a unique approach by representing each memory item using orthogonal semantic, temporal, causal, and entity graphs, facilitating policy-guided traversal for structured context construction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments with benchmarks such as LoCoMo and LongMemEval reveal that MAGMA surpasses existing state-of-the-art agentic memory systems, providing better accuracy in long-horizon reasoning tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03236
8. Pearmut: Human Evaluation of Translation Made Trivial
🔑 Keywords: Human evaluation, Multilingual NLP, Machine translation, Evaluation protocols, Active learning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Pearmut, a platform designed to simplify and streamline human evaluation in multilingual NLP, enabling seamless integration with standard automatic evaluation metrics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of standard evaluation protocols such as DA, ESA, and MQM, with features like document-level context and attention checks, allowing flexibility for prototyping new protocols and utilizing active learning strategies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Pearmut effectively lowers the barrier for conducting human evaluations, making it a routine component in the development and diagnosis of multilingual tasks and models, thereby enhancing the reliability of human-centered evaluations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02933
9. ThinkRL-Edit: Thinking in Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning-Centric Image Editing
🔑 Keywords: ThinkRL-Edit, Reinforcement Learning, Image Editing, Visual Reasoning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim is to enhance reasoning-centric image editing through a novel RL framework that expands visual reasoning exploration beyond traditional confines.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a reasoning-centric RL framework employing Chain-of-Thought-based reasoning sampling and unbiased reward strategies, including a binary checklist for precise evaluations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ThinkRL-Edit significantly outperforms previous methods, offering instruction-faithful edits that are visually coherent and semantically accurate in reasoning-centric image editing tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03467

10. RGS-SLAM: Robust Gaussian Splatting SLAM with One-Shot Dense Initialization
🔑 Keywords: RGS-SLAM, Gaussian-splatting, DINOv3 descriptors, rendering fidelity, real-time mapping
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces RGS-SLAM, a robust Gaussian-splatting SLAM framework focused on improving mapping stability and rendering fidelity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– RGS-SLAM replaces the residual-driven densification in GS-SLAM with a training-free correspondence-to-Gaussian initialization, using dense multi-view correspondences and DINOv3 descriptors refined by a confidence-aware inlier classifier.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RGS-SLAM shows superior localization and reconstruction accuracy on datasets like TUM RGB-D and Replica while maintaining real-time performance at up to 925 FPS, proving competitive compared to existing Gaussian and point-based SLAM systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.00705

11.

12. Gen3R: 3D Scene Generation Meets Feed-Forward Reconstruction
🔑 Keywords: Gen3R, video diffusion models, 3D scene generation, geometric latents, foundational reconstruction models
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To create a method, Gen3R, that integrates foundational reconstruction models and video diffusion models for effective 3D scene generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of VGGT reconstruction model to produce geometric latents by training an adapter on its tokens, aligning with video diffusion models’ appearance latents.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Gen3R achieves state-of-the-art results in single- and multi-image conditioned 3D scene generation and enhances reconstruction robustness by coupling reconstruction and generative models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04090

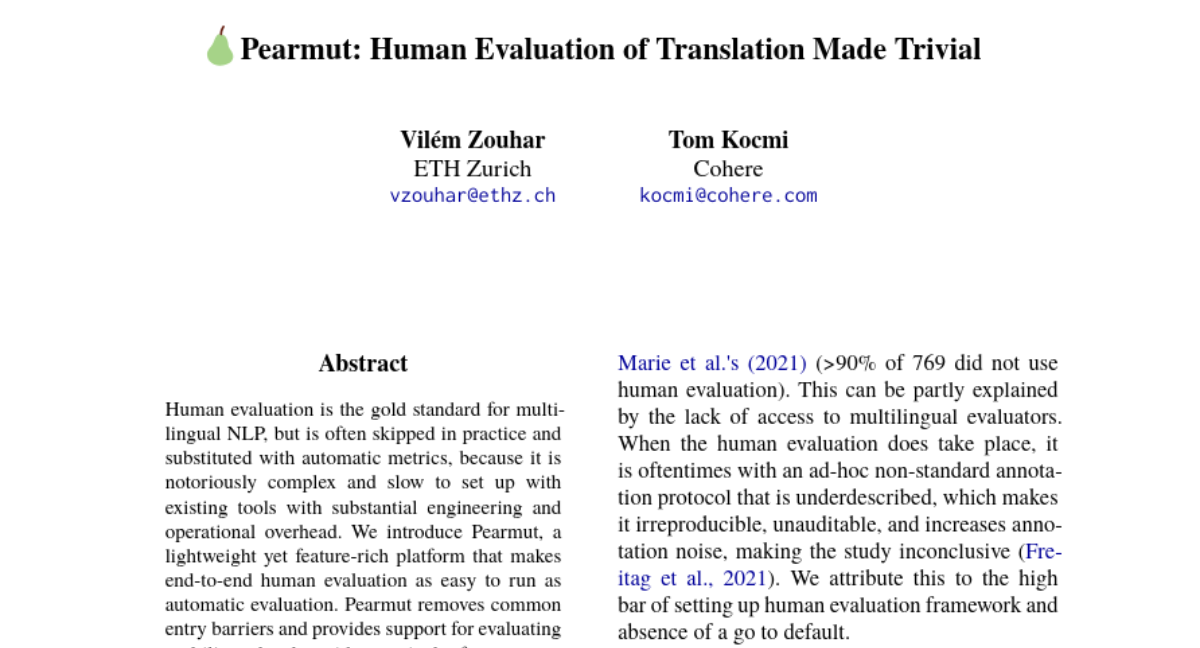
13. ResTok: Learning Hierarchical Residuals in 1D Visual Tokenizers for Autoregressive Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: Residual Tokenizer, Hierarchical Residuals, Autoregressive Image Generation, Visual Tokenizer, Hierarchical AR Generator
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the Residual Tokenizer, a 1D visual tokenizer that integrates hierarchical residuals to enhance autoregressive (AR) image generation by incorporating vision-specific design principles.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop hierarchical representations through progressively merging image and latent tokens, enabling cross-level feature fusion and reducing the number of AR generation sampling steps with a hierarchical AR generator.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Residual Tokenizer significantly improves AR image generation, achieving a gFID of 2.34 on ImageNet-256 with only 9 sampling steps, highlighting the effectiveness of reinstating hierarchical residual priors in visual tokenization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03955
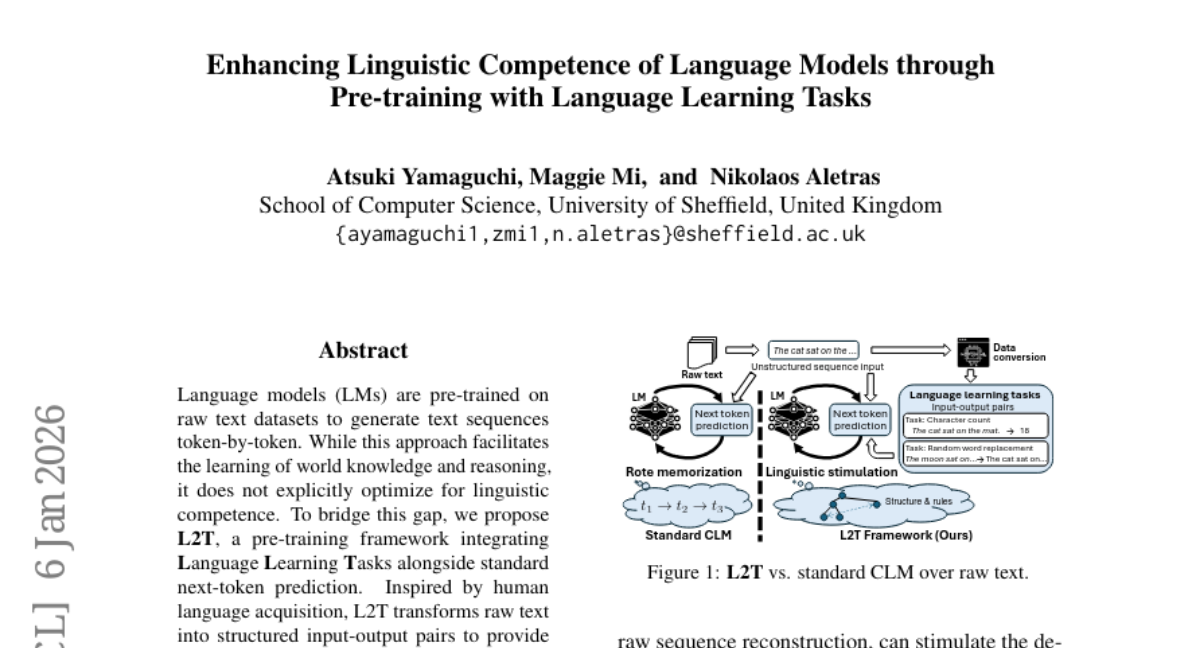
14. Enhancing Linguistic Competence of Language Models through Pre-training with Language Learning Tasks
🔑 Keywords: Language models, pre-training framework, next-token prediction, linguistic competence, general reasoning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose a pre-training framework, L2T, that integrates language learning tasks with standard next-token prediction to enhance linguistic competence in language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing a mixture of raw text and L2T structured input-output pairs for pre-training language models, mimicking human language acquisition.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The L2T framework improves performance on linguistic competence benchmarks and accelerates linguistic acquisition while maintaining competitive performance in general reasoning tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03448
15. Why LLMs Aren’t Scientists Yet: Lessons from Four Autonomous Research Attempts
🔑 Keywords: LLM agents, AI-scientist systems, autonomous scientific discovery, failure modes, Agents4Science 2025
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to explore the feasibility and challenges in autonomously generating ML research papers through a system of LLM agents mapped to a scientific workflow.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted a case study involving four attempts using a pipeline with six LLM agents aligned to stages of the scientific workflow, assessing their performance in generating an ML research paper.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Three of the four attempts failed, documenting recurring failure modes such as bias, implementation drift, and insufficient domain intelligence. One successful attempt resulted in a paper accepted by Agents4Science 2025. The study proposes design principles to enhance robustness in AI-scientist systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03315

16. EpiQAL: Benchmarking Large Language Models in Epidemiological Question Answering for Enhanced Alignment and Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Epidemiological reasoning, AI-generated overview, diagnostic benchmark, multi-step inference, Chain-of-Thought prompting
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce EpiQAL, a novel benchmark designed for evaluating the capability of language models in epidemiological reasoning, focusing on factual recall, multi-step inference, and conclusion reconstruction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized expert-designed taxonomy guidance, multi-model verification, and retrieval-based difficulty control to construct three distinct subsets from open-access literature, each measuring different aspects of epidemiological question answering.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current large language models display limited performance in epidemiological reasoning, with multi-step inference being particularly challenging. Chain-of-Thought prompting aids in multi-step inference but effectiveness varies; model success does not solely depend on scale.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03471
17. MDAgent2: Large Language Model for Code Generation and Knowledge Q&A in Molecular Dynamics
🔑 Keywords: MDAgent2, Molecular dynamics, Code generation, Reinforcement learning, Domain-specific question answering
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The development of MDAgent2 to automate molecular dynamics code generation and question answering using domain-adapted language models and a multi-agent runtime system.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Construction of a domain-specific data pipeline resulting in datasets for molecular dynamics knowledge, question answering, and code generation.
– Implementation of a three-stage post-training strategy: continued pre-training, supervised fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning to train domain-adapted models (MD-Instruct and MD-Code).
– Introduction of MD-GRPO, a closed-loop reinforcement learning method utilizing simulation outcomes for performance refinement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MDAgent2 and its associated systems outperform several baselines in LAMMPS code generation and question answering.
– Demonstrates the adaptability and generalization of large language models in industrial simulation tasks, setting a methodological foundation for automatic code generation in AI for science and industrial-scale simulations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02075

18. Choreographing a World of Dynamic Objects
🔑 Keywords: CHORD, Lagrangian motion, Eulerian representations, video generative models, robotics manipulation policies
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces CHORD, a universal generative framework designed to synthesize 4D dynamic scenes by extracting Lagrangian motion information from Eulerian video representations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– CHORD employs a distillation-based pipeline that leverages universal video generative models, avoiding reliance on category-specific heuristics or large datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method is versatile and category-agnostic, showing effectiveness in generating a variety of multi-body 4D dynamics and robotic manipulation policies, thereby outperforming existing methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04194
19. Benchmark^2: Systematic Evaluation of LLM Benchmarks
🔑 Keywords: Benchmark^2, large language models, benchmark quality, Cross-Benchmark Ranking Consistency, Discriminability Score
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address the urgent need for systematic methods to assess the quality of benchmarks for large language models (LLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper introduces Benchmark^2, a framework with three complementary metrics for evaluating benchmark quality: Cross-Benchmark Ranking Consistency, Discriminability Score, and Capability Alignment Deviation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study reveals significant variations in quality among existing benchmarks, demonstrating that selective benchmark construction guided by their metrics can achieve similar evaluation performance with much smaller test sets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03986

20. Evolving Programmatic Skill Networks
🔑 Keywords: Programmatic Skill Network, executable symbolic programs, skill acquisition, reflection, generalization
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study focuses on continual skill acquisition in open-ended embodied environments using a compositional network of executable skills.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces Programmatic Skill Network (PSN) which evolves through reflection, progressive optimization, and structural refactoring.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments demonstrate robust skill reuse, rapid adaptation, and generalization across diverse task distributions using the PSN framework.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03509
